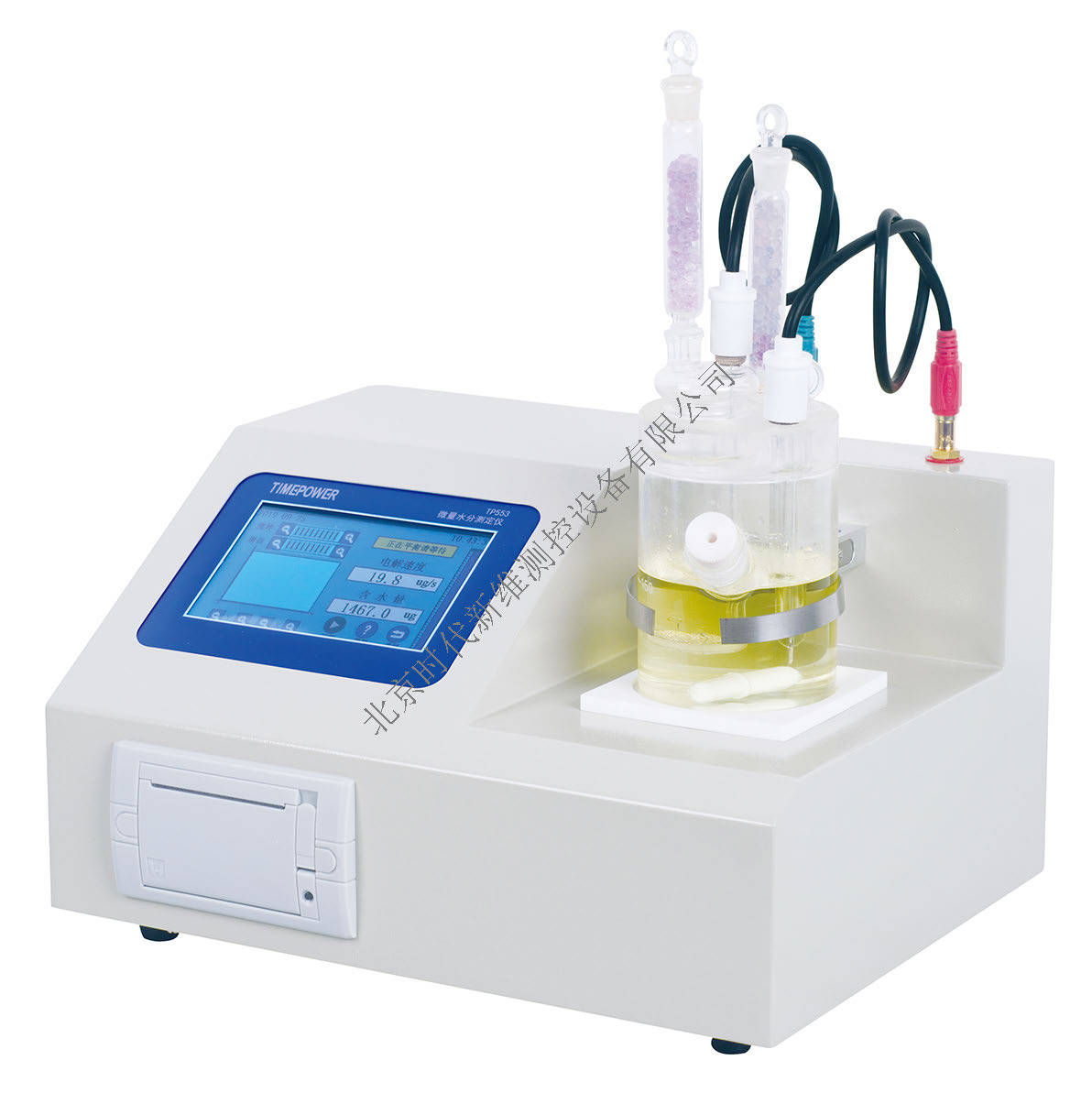
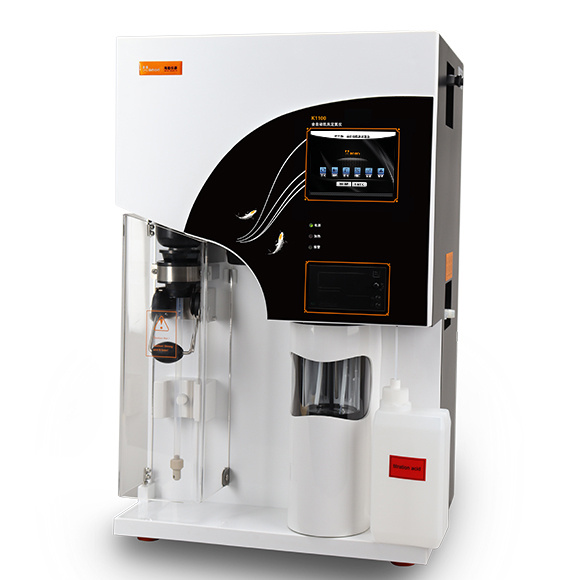
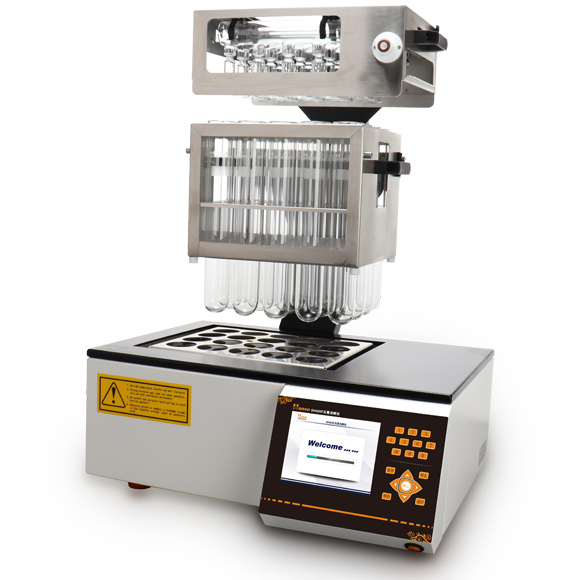
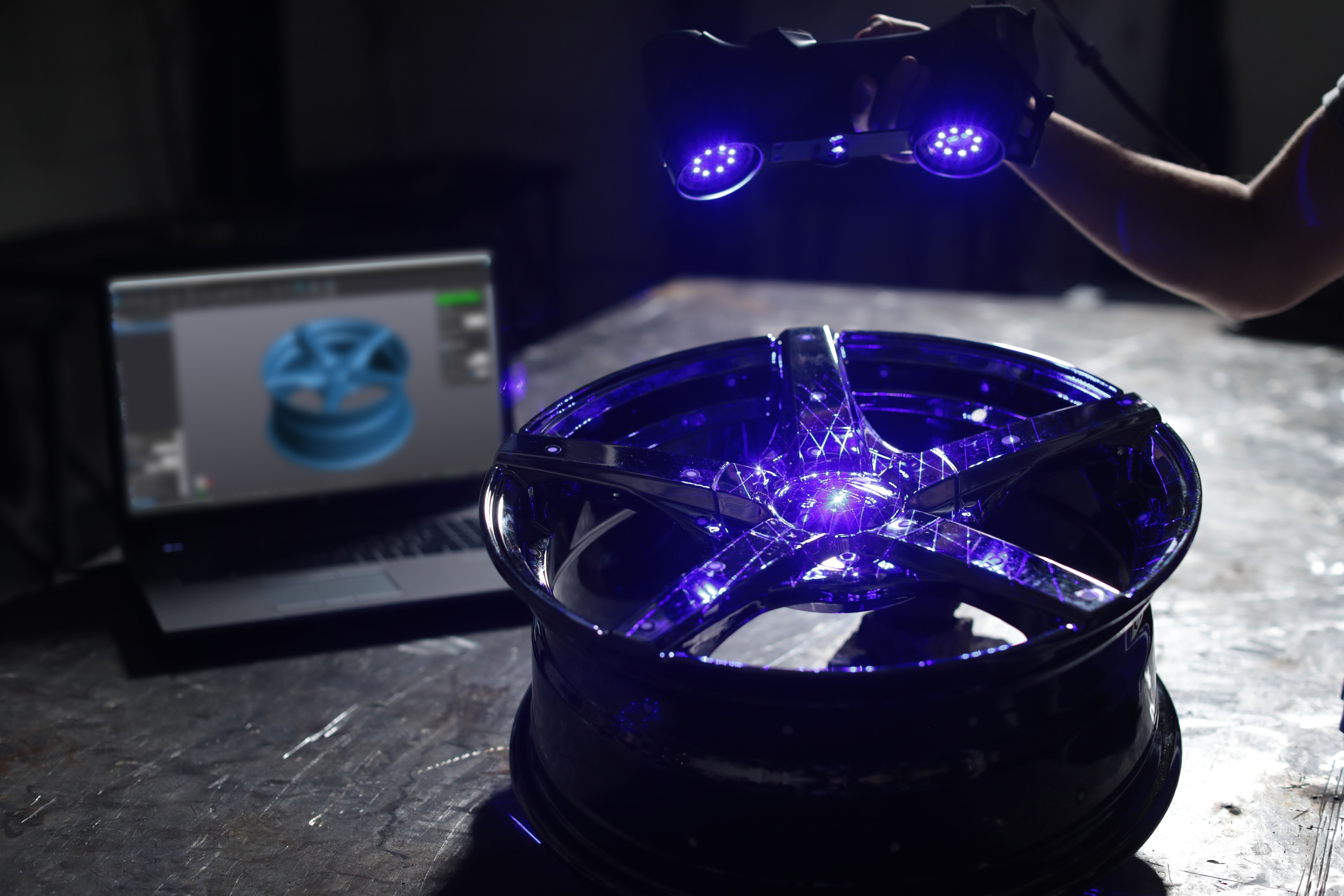
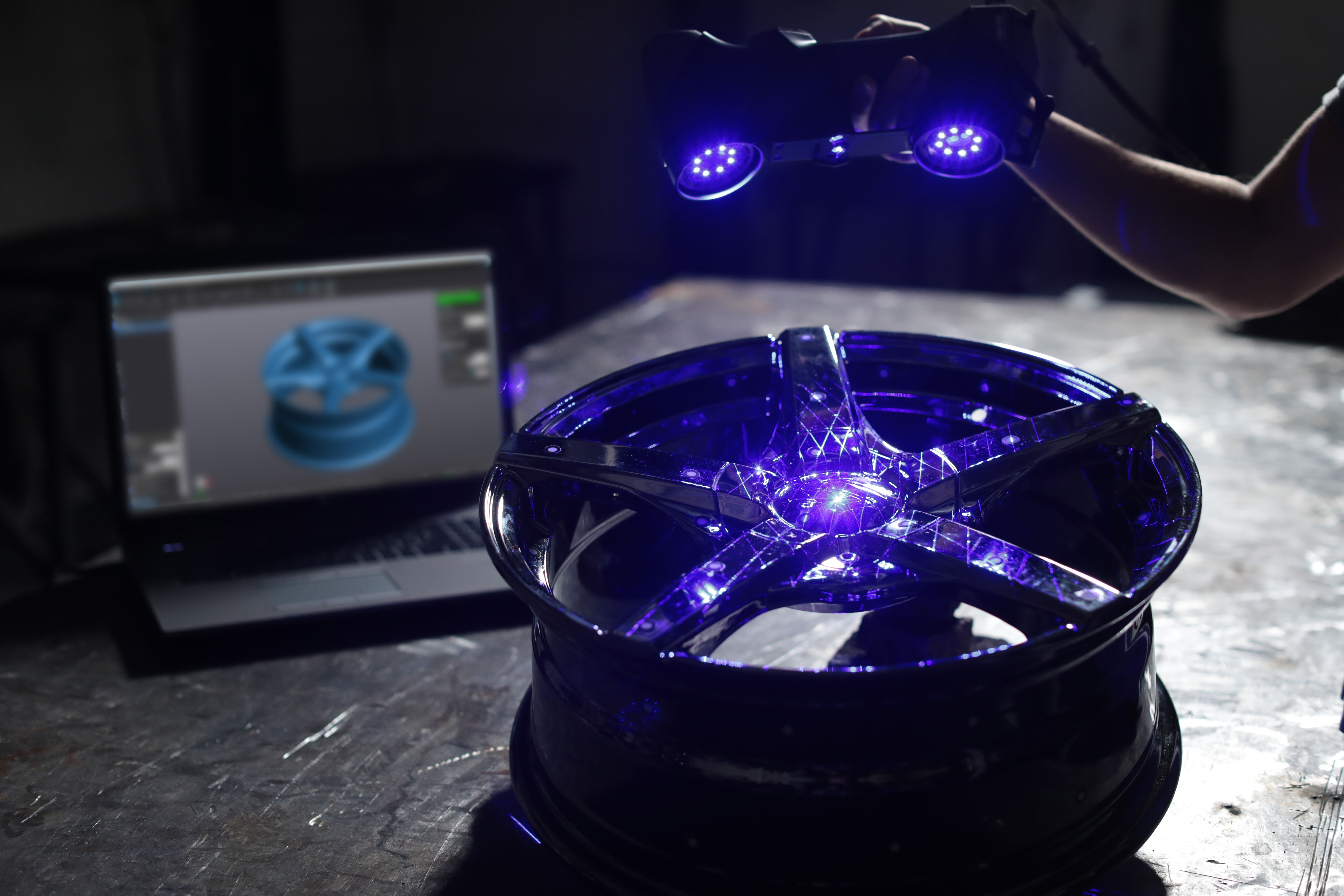
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Plasma actuators have been identified as having great
promise for flow control applications. A single dielectric
barrier discharge (SDBD) plasma actuator consists of two
staggered electrodes separated by a dielectric layer (Fig.
1). When an AC voltage of sufficient amplitude (a few kV)
is supplied to the exposed electrode, it causes the air over
the covered electrode to weakly ionize, resulting in a cold
plasma. An electro-mechanical coupling with the ambient
air is provided by the interaction between the ionized air
and the electric field between the two electrodes, generating
a body force.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流场中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Complex applications in fluid dynamics
research often require more highly resolved velocity data
than direct measurements or simulations provide. The
advent of stereo PIV and PCMR techniques has advanced
the state-of-the-art in flow velocity measurement, but 3D
spatial resolution remains limited. Here a new technique is
proposed for velocity data interpolation to address this
problem. The new method performs with higher quality
than competing solutions from the literature in terms of
accurately interpolating velocities, maintaining fluid
structure and domain boundaries, and preserving coherent
structures.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中PIV,粒子成像测速,流体图像,小波分析检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Flow past a cylinder in an unbound medium gives rise to
self-sustained, limit cycle oscillations involving formation
of a regular, periodically alternating Karman vortex street.
However, little attention has been paid to the effect of an
adjacent free surface on the development of the Karman
vortices and possible generation of new classes of the nearwake
structure[1], see Figure 1. The technique of Particle
Image Velocimetry (PIV) is a useful tool to this flow,
considering that it is unsteady and multi-scale in nature.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
PIV,粒子成像测速,流体图像,小波分析
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In particle image velocimetry (PIV) a temporally separated
image pair of a gas or liquid seeded with small particles is recorded
and analysed in order to measure fluid flows therein. We investigate a
variational approach to cross-correlation, a robust and well-established
method to determine displacement vectors from the image data. A “soft”
Gaussian window function replaces the usual rectangular correlation
frame. We propose a criterion to adapt the window size and shape that
directly formulates the goal to minimise the displacement estimation error.
In order to measure motion and adapt the window shapes at the
same time we combine both sub-problems into a bi-level optimisation
problem and solve it via continuous multiscale methods. Experiments
with synthetic and real PIV data demonstrate the ability of our approach
to solve the formulated problem. Moreover window adaptation
yields significantly improved results.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
油表面流动中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The prolific application of digital imaging and image processing for studying flows is
extended to surface oil flow visualization. The use of colored, fluorescent mixtures enable
bright, high-contrast images to be obtained which facilitate image processing. Examples
were provided in visualizing the surface flow past micro vortex generators. Image processing
of video sequences revealed minute features that are critical in understanding the flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
封闭湍动流体,表面活性剂中减阻,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Many surfactants and polymers are considered as excellent drag reducing agents. This phenomenon induces
a significant head loss reduction compared to the pure solvent. In this study an aqueous solution of CTAC/NaSal
(CetylTrimethyl Ammonium Chloride and Sodium Salicylate) is used in turbulent pipe flow system. Drag
reduction experiments were carried out for different experimental conditions using pressure drop measurements.
At the same time the spatial velocity distribution was measured and analysed using particle image velocimetry
(PIV).
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
减阻,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
溶液,流体中速度场,速度矢量场,显微速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Increasingly smaller electronics requires improvement in performance of cooling systems to keep it operating
reliably. We present herein a novel experimental study of convective heat transfer in serpentine
microchannels with segmented liquid–liquid emulsions. It is demonstrated that this concept yields significant
Nusselt number enhancement in microchannel heat sinks compared to that obtained using single
phase liquid cooling. Laser Induced Fluorescence (LIF) is employed to measure temperature of the coolant
with and without droplets, and micro-PIV is used to determine velocity field. For the segmented flow, up
to four-fold increase of the Nusselt number was observed compared to pure water flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场,显微速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
空气流体中速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Flow and far-field noise measurements are taken on a conical Convergent-
Divergent nozzle similar to the nozzles employed on high-performance
tactical jets. Matching flow and far-field computations are presented,
produced by Large Eddy Simulation and the Kirchhoff integral method.
The conditions examined are those in which the nozzle is operated at its
design Mach number of 1.56 while forward flight is simulated at Mach
numbers of 0.1, 0.3 and 0.8. Both measurement and LES show that
increasing forward flight Mach number to the high subsonic range
shortens the initial shock cell size, and weakens the shock cells induced by
the nozzle throat relative to the shock cells induced by the nozzle lip. LES
shows that high forward flight speed substantially reduces the noise
radiated into the forward quadrant where shock noise is dominant. It also
removes the screech tone entirely.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场,时空相关性检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Dual particle image velocimetry (dual PIV) measurements have been performed to investigate the space–time
correlations in two subsonic isothermal round jets at Mach numbers of 0.6 and 0.9. The correlation scales are
analyzed along the centerline and in the shear-layer center over the first 11 jet diameters from the nozzle exit. To
provide robust results over a wide range of flow conditions, these correlation scales are given in terms of their
appropriate quantities, namely, the mean or rms velocity in reference to velocity and the momentum thickness or the
half-velocity diameter in reference to length in the shear layer and on the jet axis, respectively. From these results, a
discussion on the modeling of turbulence in jets is addressed. The self-similarity of some space correlation functions
in the shear layer and on the jet axis is shown. Furthermore, far enough downstream in the shear layer, some of the
ratios between the space and time scales are relatively close to the values expected in homogeneous and isotropic
turbulence. It is also found that the ratio between the integral length and the time scales in the fixed frame is of the
order of the local mean flow velocity. In the convected frame, the appropriate scaling factor is the rms velocity.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,时空相关性
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
This article treats of the flow motion over the so-called vortex ripples which
are generated by water oscillations above a sand bed. We focus mainly our experimental
works on the morphology and the dynamics of transient flow patterns above real vortex
ripples. With the help of flow visualizations and Particle Image Velocimetry measurements
with a high-speed video CCD camera, we test numerical simulations, which predict the
existence of a secondary vortex with a streamlines representation. However, our
experimental findings show only one vortical structure and validate the observations of
Bagnold in 1946 (using real ripples but with no visualization and measurement) and Sand
Andersen & al. in 2004 (using model ripples) with respect to the existence of a transient jet.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The aim of this work was to understand the physical requirements as well as to develop
methodology required to employ Time Resolved Digital Particle Image Velocimetry
(TRDPIV) for measuring high speed, high magnification, near wall flow fields. Previous
attempts to perform measurements such as this have been unsuccessful because of
both limitations in equipment as well as proper methodology for processing of the data.
This work addresses those issues and successfully demonstrates a test inside of a
transonic turbine cascade as well as a high speed high magnification wall jet.
From previous studies it was established that flow tracer delivery is not a trivial task in a
high speed high back pressure environment. Any TRDPIV measurement requires
uniform spatial seeding density, but time-resolved measurements require uniform
temporal seeding density as well. To this end, a high pressure particle generator was
developed. This advancement enhanced current capability beyond what was previously
attainable. Unfortunately, this was not sufficient to resolve the issue of seeding all
together, and an advanced data reconstruction methodology was developed to
reconstruct areas of the flow field that where lost do to inhomogeneous seeding. This
reconstruction methodology, based on Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD), has
been shown to produce errors in corrected velocities below tradition spatial techniques
alone. The combination of both particle generator and reconstruction methodology was
instrumental for successfully acquiring TRDPIV measurements in a high speed high
pressure environment such as a transonic wind tunnel facility.
This work also investigates the development of a turbulent wall jet.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A stereoscopic PIV system was build to study laminar turbulent transition in pipe flow. The PIV system is based on an angular displacement of the two cameras and a 3D calibration based reconstruction method. In order to measure the cross flow over the entire cross section of the pipe, the light sheet is perpendicular to the main flow direction. Measurements have shown that the PIV system is capable of detecting the laminar and turbulent flow fields over a large portion of the pipe cross section (fig.1), with increasing errors in the near wall region.
In the error analysis, estimations and measurements of the registration error are shown (fig.2). The registration error is due to a small misalignment of the light sheet and the calibration plane. It is shown to make an important contribution to the total error. The transition measurements presented at the end of the paper are the result of brief test runs and are a good example of the kind of experiments planed for the near future.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
老化,屈服应力,流体,球形沉降物中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We have studied the flow induced by a macroscopic spherical particle settling in a Laponite
suspension that exhibits a yield stress, thixotropy, and shear thinning. We show that the fluid
thixotropy or aging induces an increase with time of both the apparent yield stress and
shear-thinning properties but also a breaking of the flow fore-aft symmetry predicted in
Hershel-Bulkley fluids yield-stress, shear-thinning fluids with no thixotropy. We have also varied
the stress exerted by the particles on the fluid by using particles of different densities. Although the
stresses exerted by the particles are of the same order of magnitude, the velocity field presents
utterly different features: whereas the flow around the lighter particle shows a confinement similar
to the one observed in shear-thinning fluids, the wake of the heavier particle is characterized by an
upward motion of the fluid “negative wake”, whatever the fluid’s age. We compare the features of
this negative wake to the one observed in viscoelastic shear-thinning fluids polymeric or micelle
solutions. Although the flows around the two particles strongly differ, their settling behaviors
display no apparent difference which constitutes an intriguing result and evidences the complexity
of the dependence of the drag factor on flow field.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
制冷器,热声制冷器中速度,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Thermoacoustic refrigeration systems generate cooling power from a high-amplitude acoustic
standing wave. There has recently been a growing interest in this technology because of its simple and
robust architecture and its use of environmentally safe gases. With the prospect of commercialization,
it is necessary to enhance the efficiency of thermoacoustic cooling systems and more particularly of
some of their components such as the heat exchangers. The characterization of the flow field at the
end of the stack plates is a crucial step for the understanding and optimization of heat transfer between
the stack and the heat exchangers. In this study, a specific Particle Image Velocimetry measurement(PIV) is
performed inside a thermoacoustic refrigerator. Acoustic velocity is measured using synchronization
and phase-averaging. The measurement method is validated inside a void resonator by successfully
comparing experimental data with an acoustic plane wave model. Velocity is measured inside the
oscillating boundary layers, between the plates of the stack, and compared to a linear model. The
flow behind the stack is characterized, and it shows the generation of symmetric pairs of counterrotating
vortices at the end of the stack plates at low acoustic pressure level. As the acoustic pressure
level increases, detachment of the vortices and symmetry breaking are observed.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流场中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We present in this paper a novel collaborative scheme
dedicated to the measurement of velocity in fluid experimental
flows through image sequences. The proposed technique
combine the robustness of correlation techniques with
the high density of global variational methods. It can be considered
either as a reenforcement of fluid dedicated opticalflow
methods towards robustness, or as an enhancement of
correlation approachs towards dense information. This results
in a technique that is robust under noise and outliers,
while providing a dense motion field. The method was applied
on synthetic images and on real experiments in turbulent
flows carried out to allow a thorough comparison with a
state of the art optical-flow and PIV methods.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
This paper presents flow field measurements of hydrogen/methane mixtures under near blowout
conditions. Previous high speed visualizations by our group of these flames shows that the blow off
phenomenology varies with percentage of hydrogen [1]. This paper further characterizes the flow field of these
flames using particle image velocimetry (PIV). A variety of highly dynamic flame and flow features are observed,
which vary substantially with the H2 levels in the fuel. This variation is apparently due to the enhanced strain
resistance of hydrogen augmented flames and flow dilatation ratio effects upon flow dynamics, particularly vortex
breakdown.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In order to avoid model support interference, the flow over cylinders of varying fineness ratio (length
/diameter) aligned with the free stream were examined using a magnetic suspension and balance system. The
drag coefficient variation of a right circular cylinder was obtained for a wide range of fineness ratios. Particle
Imaging Velocimetry (PIV) was used to examine the flow field, particularly the behavior of the leading-edge
separation shear layer and its effect on the wake. Reynolds numbers based on the cylinder diameter ranged
from 5x104 to 1.1x105, while the major portion of the experiment was conducted at the ReD= 1.0x105. For the
moderately large fineness ratio, the shear layer reattaches with subsequent growth of the boundary layer,
whereas over shorter cylinders, the shear layer remains detached. Differences in the wake recirculation region
and the immediate wake patterns are clarified in terms of both the mean velocity and turbulent flow fields,
including longitudinal vortical structures in the cross-flow plane of the wake. The minimum drag
corresponded to the fineness ratio where the separated shear layer reattached at the trailing edge of the
cylinder. The base pressure was obtained with a telemetry technique. Pressure fields and aerodynamic force
fluctuations are also discussed.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Gene expression studies are important for understanding gene
regulation, deducing cell signal cascades, etc. More broadly, these
studies are often used to understand disease development, as specific
genes are commonly up regulated in clinical pathologies. These
studies can be paired with the application of a mechanical stimulus as well; for example, endothelial cells can be exposed to a defined fluid flow (physiological or pathological) in order to understand the possible mechanisms for atherosclerosis development.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Lifting surfaces are used both for propulsion and control of sea vessels and must meet performance criteria such as lift, drag, and (in some military applications)hydroacoustic noise limits. Design tools suitable to predict such criteria must handle complex flow phenomena and manage the wide range of flow scales inherent in marine
applications (Reynolds numbers ~108). To date, the development of such tools has been limited by the lack of controlled experimental data in this high Reynolds numbers range.
Lifting surface flow is the focus of current high Reynolds number experiments involving a two-dimensional hydrofoil in the world’s largest water tunnel, the US Navy’s William B. Morgan Large Cavitation Channel (LCC). The goal of these experiments is
to provide a unique high Reynolds number experimental dataset at chord-based Reynolds numbers (Re) approaching those of full-scale propulsors (~108). This data will be used for validation of scaling laws and computational models, with particular emphasis given
to the unsteady, separated, turbulent flow at the trailing edge. In addition, these experiments will provide fundamental insight into the fluid mechanics of trailing-edge noise generation in marine propulsion systems.
This paper describes the experimental equipment and methods employed in the test program. Described herein is the use of the LCC’s Laser Doppler Velocimetry (LDV) capability to acquire flow velocity mean and turbulence quantities, as well as estimates of boundary layer transition. Also presented is a Particle Imaging Velocimetry
(PIV) system developed for these experiments and employing seed injection upstream of the channel’s flow straightener. Finally, a description is given of instrumentation mounted in the foil for measurement of vibration and surface static and dynamic pressures.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
漩涡,空穴中漩涡间相互作用,空穴生成机理,速度场,速度矢量场,流场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Multiple concentrated vortices are often produced in the wake of lifting surfaces and downstream of pumps, turbines, and propulsors. The roll-up of multiple vortex strands is a common feature of these flows. In this study, we are examining the interaction of two vortices of variable strength and relative rotation (e.g. co-rotating or counter-rotating). A pair of equal-strength co-rotating vortices will merge to form a single vortex. However, as the relative strength of the vortices is decreased, the weaker vortex can wrap around the stronger vortex, causing the weaker vortex to be stretched. This stretching process can lead to cavitation inception. In the present work, we will examine this inception process.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
漩涡间相互作用,空穴生成机理,速度场,速度矢量场,流场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体,喷射中速度场, 夹带行为检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Although turbulent jets have been studied extensively, one configuration that has not received much attention is the viscosity-stratified jet, wherein a turbulent jet of lower viscosity issues into a densitymatched host liquid of higher viscosity. We present
experimental data for scalar dispersion and two-dimensional velocity measurements in the axial plane of a turbulent axisymmetric jet with a Reynolds number (Re) of 2,000 issuing into a viscous host liquid at viscosity ratios (m) ranging from 1 to 55. The presence of a
strong viscosity discontinuity across the jet edge results in a significant decrease in the scalar spread rate. We attribute this to the rapid reduction in turbulence intensity and the suppression of large engulfing eddies at the jet edge. The velocity profile, on the other hand, indicates that the velocity width and mass flux reduce
with increasing m up to about 20, but then increase for higher values of m. This non-monotonic variation is explained by the growing influence of viscous stress for m>20. The scalar spread rate, the velocity spread rate, the centerline velocity decay rate, and the jet mass flux are all minimized for m20 for Re=2,000.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场, 夹带行为
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中时间分辨3D3C速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A survey is conducted to quantitatively visualise the wake flow behind a circular cylinder at Reynolds numbers of 180 to 2500. A time-resolved tomographic PIV method is used to measure the
sequence of three-dimensional vector fields evolving in time. The attention is focused upon the unsteady 3D wake organization with the interaction of primary rollers (Karman-Benard) and the secondary vortices resulting from 3D instability of the vortex wake.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
时间分辨3D3C速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2245篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等