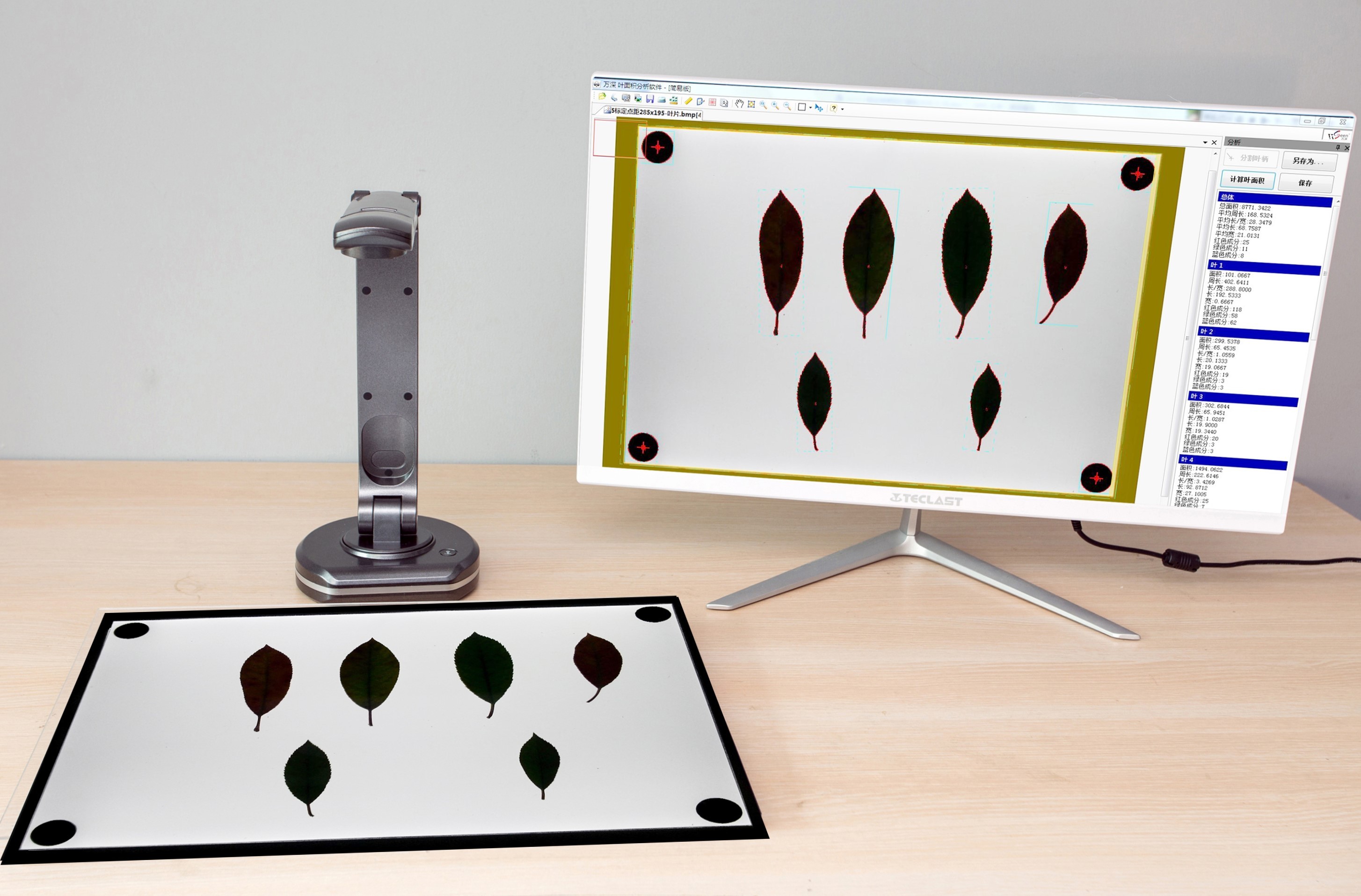
Phenom飞纳台式扫描电镜-生命科学应用案例-海藻
DIATOMS TELL THE TRUTH ABOUT OUR ENVIRONMENT
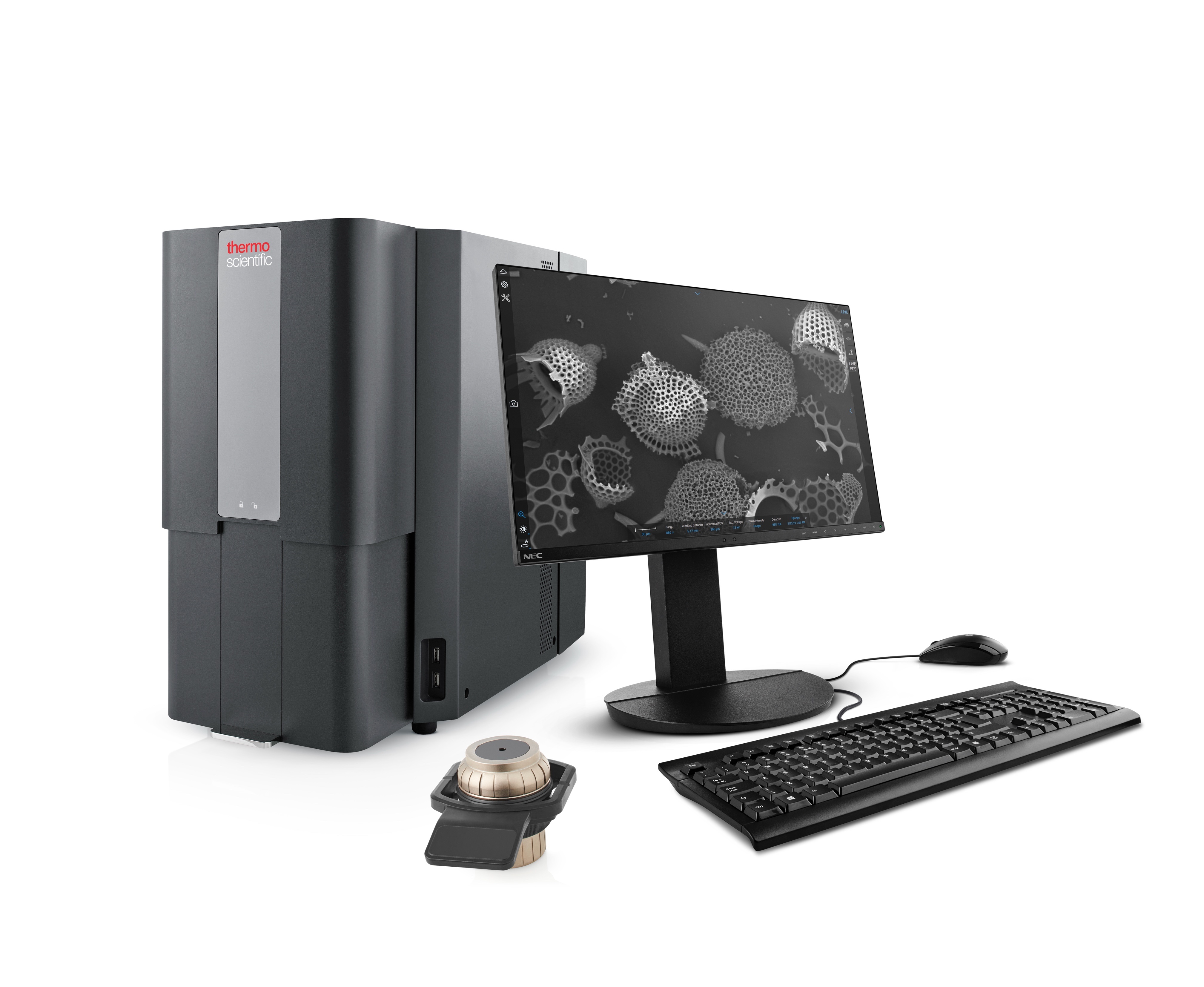
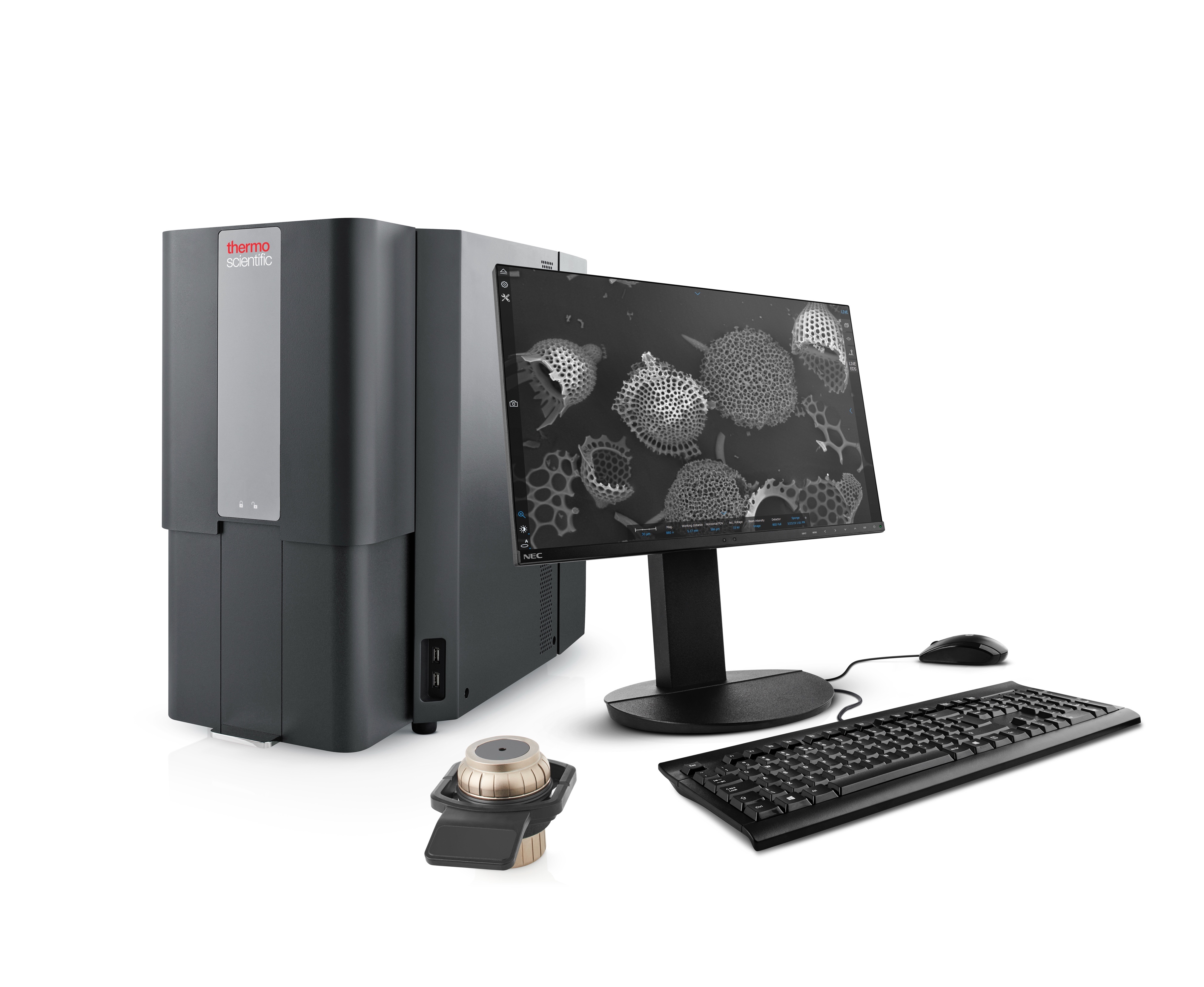
Diatoms provide information on both the biological integrity of the ecosystem and those factors likely to be causing any observed changes. Researchers are rapidly developing new techniques for using diatoms to provide even more quantitative and accurate inferences of ecosystem condition, and diatoms are being included in a growing number of local and regional-scale monitoring programs. FEI Company’s Phenom™, a new type of microscope, proves to be a valuable and cost-effective instrument for imaging and classification of diatoms at the Dutch Water Treatment & Control Laboratories.
检测样品:
生物环保
检测项:
复纳科学仪器(上海)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
海藻中EEM,PARAFAC检测方案(分子荧光光谱)
The conclusions of this study center on the flow chart in Figure 8 which explains how the CLS and PARAFAC methods in Solo can be compared as a basis for establishing rapid, reliable analysis methods for differentiating different algal types. The PARAFAC method, when calibrated with pure culture spectra, affords the capacity to rapidly and effectively separate and identify major algal orders (Cyanophyta, Chrysophyta and Chlorophyta). PARAFAC can also possibly identify different types of cyanobacteria more specifically based on evaluation component scores and score ratios. PARAFAC calibration may not yield unique spectral loadings for each algal culture nor necessarily allow unambiguous assignments of spectral components to identifiable physical components in the calibration data set. CLS on the other hand requires calibration with pure culture samples and exhibits the capacity to generate unique, culture-specific spectral component libraries. Further, based on independent cell density and biovolume calculations it was clear the CLS method can potentially provide rapid, reliable estimates of these parameters with high-precision. In conclusion, it is clear that the Aqualog EEM and Solo model analyses show potential for rapid evaluation of algal types and could prove useful in rapid field and laboratory level cyano harmful algal bloom identification, especially when carefully calibrated with pure algal culture samples. Due caution is noted in terms of dealing with the morphological and physiological properties of the samples in terms of spectroscopy and the requirement for due diligence in terms of establishing detection concentration limits in the ranges needed for positive identification. Importantly, it is well known that algal spectral properties are significantly affected by the light-environment, temperature and nutrient conditions among other factors so algal culture methods used for calibration would ideally take these factors into consideration and independent
检测样品:
生物环保
检测项:
EEM,PARAFAC
HORIBA(中国)
查看联系电话
前往展位
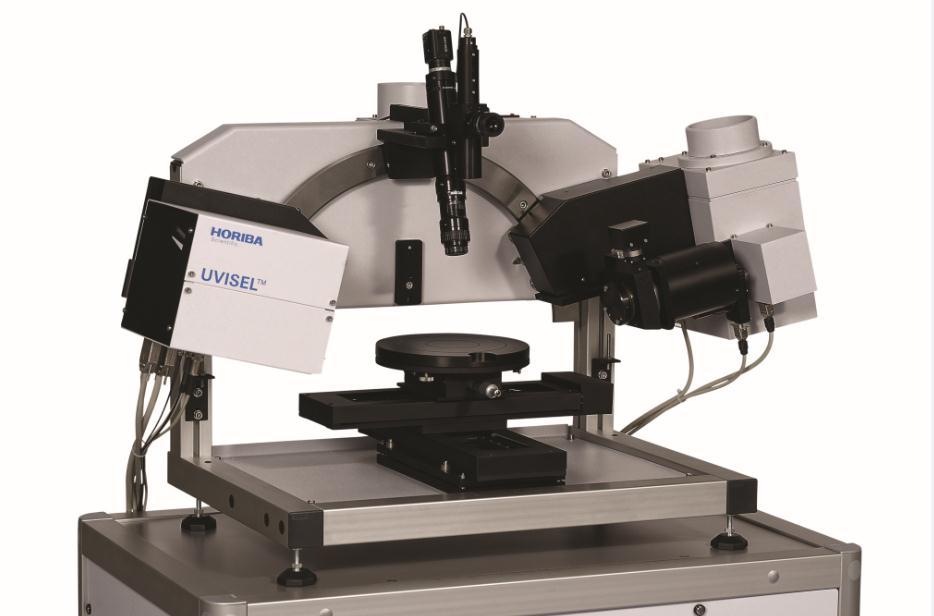
流动液体池环境中的生物芯片中生物芯片结构检测方案(椭偏仪)
Interpretation of this behaviour is not fully understood, but it is likely to be due to the ionic interaction between the DNA and the buffer solution. A natural negative charge on the DNA fragments means that in a neutral environment, such as water, their preferred orientation would be for the molecules to lay on the gold layer with no preferred orientation. When the buffer solution is added there is an interaction with the positive ions in the solution, and the DNA fragments stand up leading to an increase in layer thickness.
检测样品:
生物环保
检测项:
生物芯片结构
HORIBA(中国)
查看联系电话
前往展位
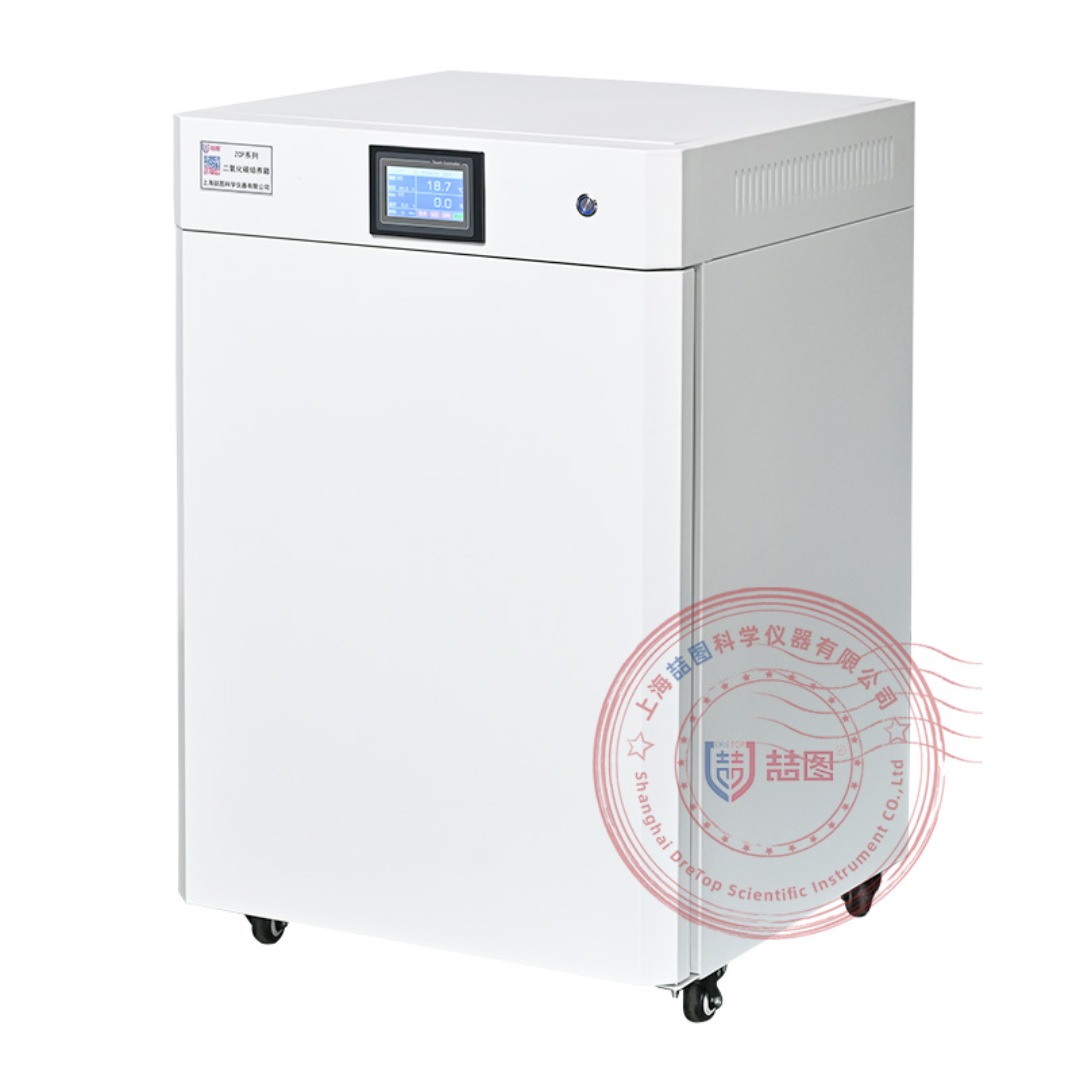
二氧化碳培养箱做细胞培养实验准备
二氧化碳培养箱,又称细胞培养箱,喆图ZCQ、ZCW系列二氧化碳培养箱是通过在培养箱箱体内模拟形成类似细胞/组织在生物体内的生长环境,要求稳定的温度37℃、稳定的CO2水平5%、较高的相对饱和湿度(95%)来对细胞/组织进行体外培养的一种仪器。二氧化碳培养箱是开展免疫学、肿瘤学、遗传学及生物工程所必需的关键设备,广泛应用于细胞、组织培养和某些特殊微生物的培养,常见于细胞动力学研究、哺乳动物细胞分泌物的收集、各种物理、化学因素的致癌或毒理效应、抗原的研究和生产、培养杂交瘤细胞生产抗体、体外授精(IVF)、干细胞、组织工程、药物筛选等研究领域。
检测样品:
生物环保
检测项:
细胞培养
上海喆图科学仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
环境和生态中同位素技术检测方案(同位素质谱仪)
由robert Michener 和 Kate Lajtha编辑 自从第一版之后,同位素的领域又已经非常扩大了。从开始的应用,地理学家和海洋学家已经更深入的发展了同位素在的理论和实际应用,过去的水土状况,热系统,追踪岩石来源等。相似的,植物生物学家,地理学家,和环境化学家也已经发展了新的理论框架,经验数据库,为了研究植物和动物的同位素应用。自然丰度的同位素记号可以被用来发现单个有机体的类型和机理就像追踪食物的网络一样, 理解营养,和追踪整个生态的营养循环不论是陆地生物还是海洋系统。因此,同位素分析已经越来越作为生物学家,生态学家和所有研究元素和物质一个标准化的手段。 从历史视角的方法 每一个不同的元素,制备样品的方法都不一样。稳定同位素分析的目标是使得样品定量的转变成合适的纯气体(比如CO2,N2或者H2等)使得质谱能够分析。硫可以以SO2或者SF6的方法分析。通常,有机样品首先被干燥(或者在60℃的烘箱中或者冷冻干燥),并且被碾压成粉末。样品可以被保存在一个密闭容器中,使得他们保持干燥。如果对样品的碳元素感兴趣,但是样品中含有无机碳的话,样品需要首先被酸化(通常使用1NHCL,即便有很多用户使用稀释的磷酸) 有机样品中的C和N 早起的同位素测定中,大多数研究者使用氧化反应要不就是“离线”或者“在线”,将有机样品燃烧成气体。 现在均转变成在线的方式,通过元素分析仪连接同位素质谱的装置。1-20mg(或者更多)的样品被称量后,用锡纸包好,放在样品盘上。样品会在氧气流中,在高温下燃烧,然后燃烧的气体被氦气流带到吸附阱上进行分离成H2O,N2,CO2等。感兴趣的气体然后被导入到质谱中进行分析。这就是目前所知的连续流分析模式。 碳酸盐和溶解无机碳 无机碳样品与100%磷酸反应在真空下反应,使其完全转化为纯CO2。这使得可以同时分析C13和O18,条件是磷酸是纯的,并且不能有水。 水样中的溶解无机碳,通过酸化水样并且搅拌水样,在部分真空下产生CO2样品,然后分离纯化该气体。该样品制备原则可以被用来制备血液中的生物碳酸盐。 关于上诉样品的最新方法使用了自动的连续流系统。不需要估计瓶子中的碳酸盐,氦气在酸化之前已经代替了瓶子中的所有气体。在一个反应时间之后,CO2气体被转移到样品环中,然后使用氦气做载气导入到质谱中。一个相似的方法使用在水中DIC的测定中。 氨和水中的硝酸盐δ15N 早期的溶解无机氮分析中,水样中的氨被分离,使用各种蒸汽蒸馏技术或者使用扩散技术等。所有的步骤使得水中的pH变化,然后将氨气被一个酸trap捕获。蒸馏技术比较适合于大量水中含有痕量氨气的情况,可以使用盐水溶液,大概每个样品需要30分钟。一旦氨气被收集在酸阱中,沸石将会用来从溶液中转移出氨气。在所有的方法中,需要小心NH3在每个阶段的收集也纺织分馏。硝态-N可以使用同样的技术蒸馏在使用还原剂将水中的硝酸根还原为氨气。 水中氧 水中氧的分析主要有两种:水平衡法和元素分析仪-同位素质谱法。 水平衡法: 氘: 水平衡法和EA-IRMS方法。 硫: 测定硫的办法,取决于样品的初始状态,核心是将硫转变成SO2还是SF6。 SF6的优势是F只有一个同位素原子,但是技术上转化有点复杂,所以大部分的实验室使用SO2气体。 大部分的方法都是将硫分离出来然后采用氧化硫成溶液中的硫酸盐。硫酸盐可以使用10%的氯化钡转变成BaSO4沉淀。在这里,样品可以氧化为SO2气体并且导入到质谱中进行检测。 连续流的方法:在元素分析仪中,高温下燃烧S,然后进入柱子分离。之后SO2被导入到质谱中进行分析。
检测样品:
生物环保
检测项:
理化分析
束蕴仪器(上海)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
使用球磨机对污水中细菌的细胞壁进行破碎——德国Fritsch公司P 6 单罐行星式高能球磨机
污水中的淤泥是城市生活废弃物的一种,常常被人视为是无用的废品。但是某些从事无机材料研究的学者发现,在这些污水淤泥中存在着细菌,而细菌包含着蛋白质。随着可持续环境发展的需要,这种物质日益成为重要的研究课题。
德国某些科学家通过系列的实验,对比了不用实验室仪器对细菌细胞破壁率的影响,并分别检测了使用德国Fritsch公司的 “pulverisette 6” 单罐行星式高能球磨机时,增加研磨时间和干性样品浓度对破壁率的影响。实验证明,使用Fritsch公司的 “pulverisette 6” 单罐行星式高能球磨机进行细胞破壁,比之使用其他的机器进行细胞破壁,破壁率更加高。而细胞破壁率的大小是衡量一种分析方法最重要的标准。
具体的研磨粉碎实验方法及相关实验数据,欢迎您来电话与北京飞驰科学仪器有限公司取得联系。
检测样品:
生物环保
检测项:
细胞壁破碎
北京飞驰科学仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
赤潮的危害与赤潮毒素—麻痹性贝毒(PSP)
近年来,随着海洋环境的恶化,有害赤潮发生的频率大大增加, 对海水养殖业造成了巨大的损害,甚至威胁到人类的健康。
根据有害赤潮的危害形式,可将其大致分为三类。第一类赤潮一般是无害的,只是由于赤潮藻的数量过高,当它们死亡分解时造成海水缺氧,可能致使鱼类和无脊椎动物的死亡;第二类赤潮虽然对人无害,但藻体本身的特殊结构或化学物质能够使鱼类及其它无脊椎动物的鳃发生堵塞、机械损伤或中毒,部分微藻如米氏裸甲藻产生的溶血性毒素,可造成鱼类大量死亡,即属于此类;第三类形成赤潮的生物能产生毒素,这些赤潮毒素通过食物链的积累和传递可对高营养级生物和人类造成危害,具体有:麻痹性贝毒(Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning, PSP)、腹泻性贝毒(Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning, DSP)、记忆缺失性贝毒(Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning, ASP)、神经性贝毒(Neurotoxic Shellfish Poisoning, NSP)和西加鱼毒(Ciguatera Fish Poisoning, CFP),其中麻痹性贝毒是目前已知的赤潮生物毒素中,发生次数最频繁,对人类影响最严重的一种。
检测样品:
生物环保
检测项:
深圳市朗诚科技股份有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供22篇生物环保检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等