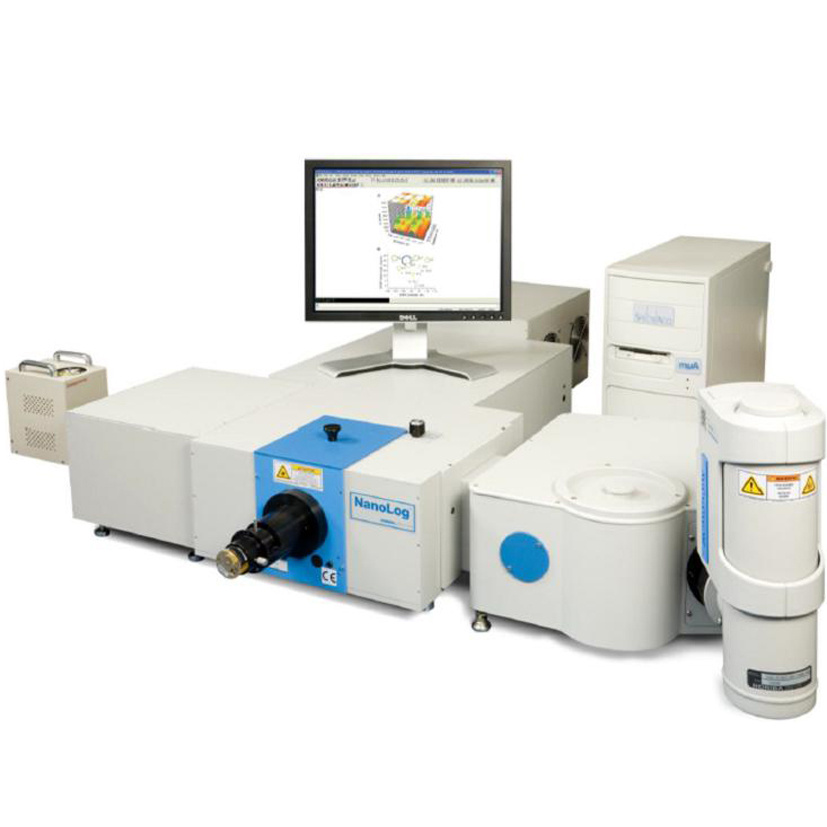
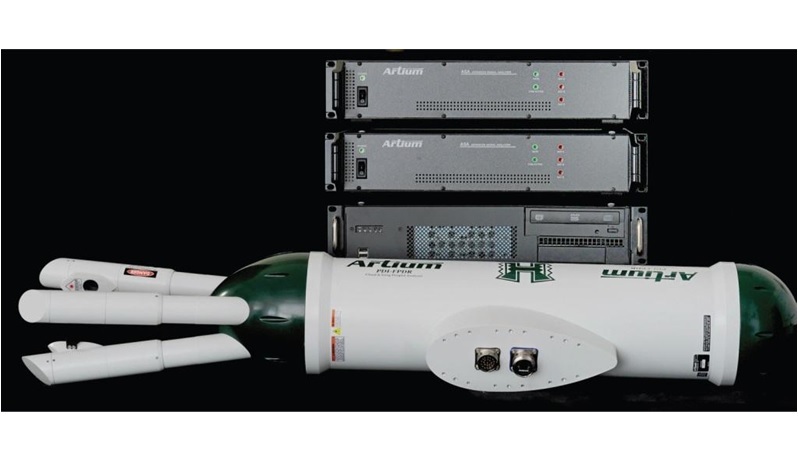
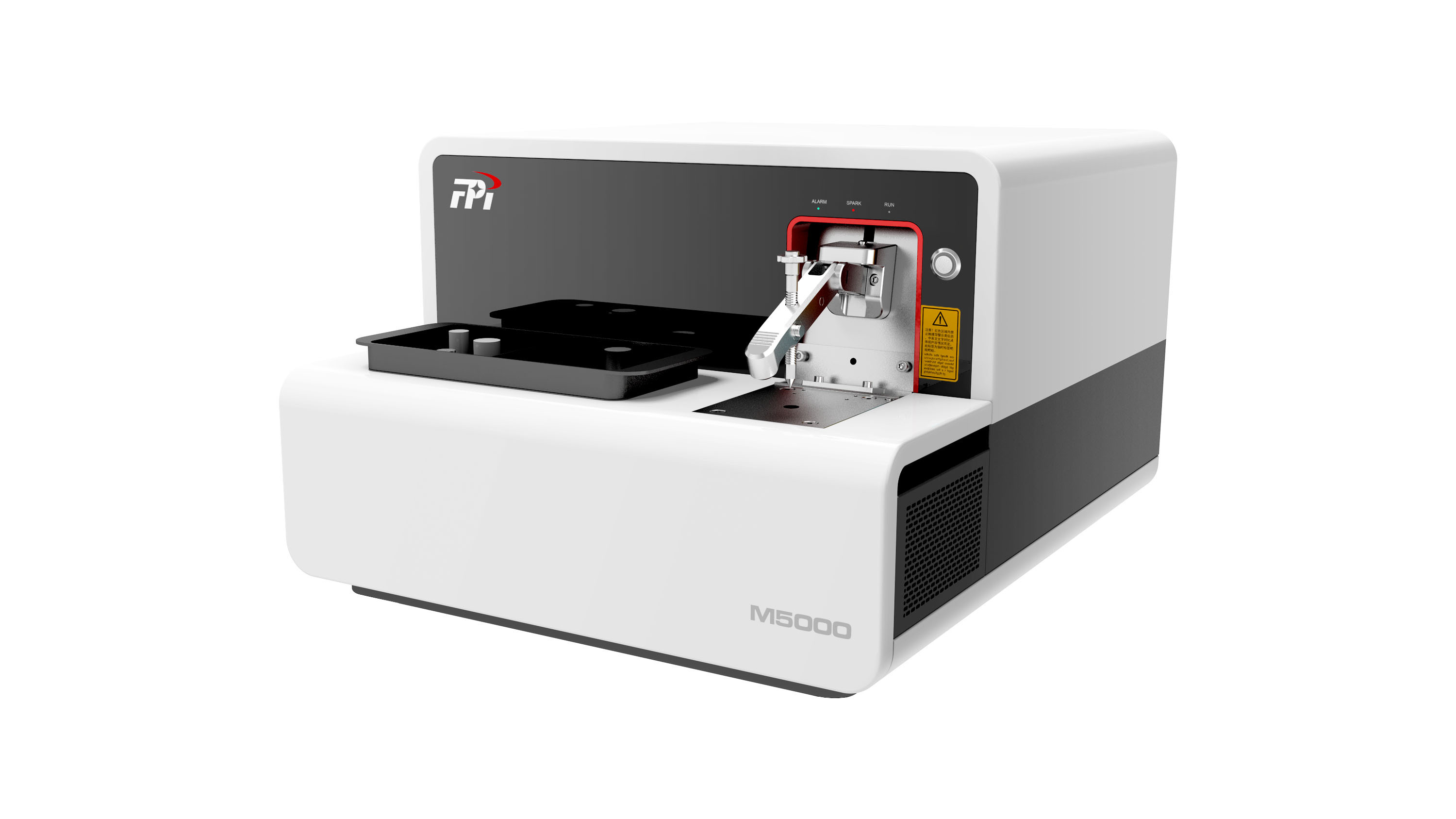
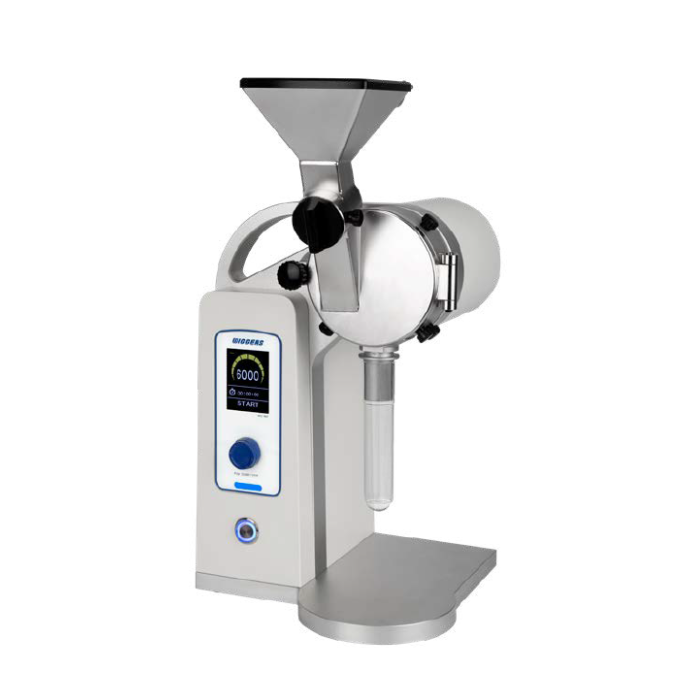
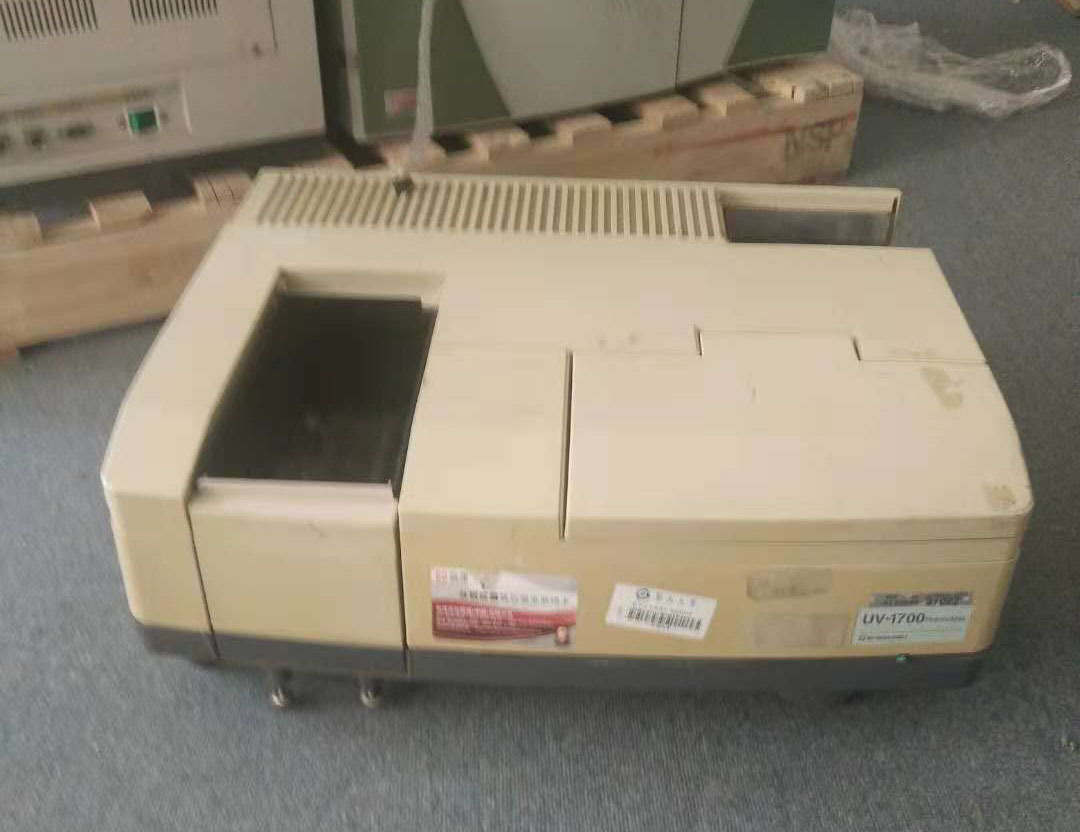
液滴中速度,粒径,惯性聚簇效应检测方案(干涉仪)
Water droplets are introduced via four spray nozzles,
with the resulting size distribution being quite broad
( ¯ d = 22 μm, ¾d = 13 μm). Downstream, a Phase Doppler
Interferometer (PDI) (15) simultaneously measures the
diameter (di), downstream speed (vi), and arrival time
(ti) of any droplets that traverse its view volume (which
has a linear dimension of roughly 150 μm). The PDI system
was built and calibrated by Artium Technologies, Inc.
and is designed for in situ measurement, such that the instrument
does not disturb the flow through the measurement
volume when aligned parallel to the mean flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度,粒径,惯性聚簇效应
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
隔热材料,保温材料,真空绝热板中导热系数,热阻,热导率检测方案(导热仪)
为了彻底深入了解防护热板法导热系数测试过程中国际标准方法ISO 8302和A-S-T-M C177对热稳定测试间隔时间的界定,本文从热时间常数的定义着手,进行了详细的推导,揭示出热时间常数的物理意义以及防护热板法热稳定性判断的整个详细过程,通过此详细过程的结果指出国际标准ISO 8302和国家标准中存GB/T 10294在的错误,并对国际标准中的热时间常数经验公式进行了修正,最后采用MapleSim仿真模拟计算结果验证了修正公式的正确性。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
导热系数,热阻,热导率
上海依阳实业有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
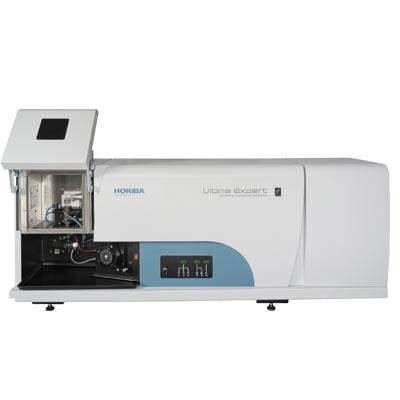
渗析液中主要成分分析检测方案(ICP-AES)
Dialysis is a method of removing toxic substances (impuritities or wastes) from the blood when the kidneys are unable to do so. ICP-OES
is particularly suitable to measure the dialysis solutions for the high accuracy analysis of Na, K,Ca, Mg and Cl. This Application Note presents the preparation and analysis results of two dialysis
samples.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
主要成分分析
HORIBA(中国)
查看联系电话
前往展位
单缸,发动机,进气歧管,倾角,进气门中流动特性,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Abstract—In-cylinder flow field structure in an internal
combustion (I.C) engine has a major influence on the combustion,
emission and performance characteristics. Fluid enters the
combustion chamber of an I.C engine through the intake manifold
with high velocity. Then the kinetic energy of the fluid resulting in
turbulence causes rapid mixing of fuel and air, if the fuel is injected
directly into the cylinder. With optimal turbulence, better mixing of
fuel and air is possible which leads to effective combustion. A good
knowledge of the flow field inside the cylinder of an I.C
engine is very much essential for optimization of the design
of the combustion chamber for better performance especially
in modern I.C engines like gasoline direct injection (GDI),
homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI)
engines.The main objective of this work is to study the incylinder
fluid flow field characteristics of a single-cylinder
engine to see the effect of intake manifold inclination at
equivalent rated engine speed using Particle Image
Velocimetry (PIV) under various static intake valve lift
conditions. To facilitate the PIV experiments, the metal cylinder of
the engine was replaced by a transparent one. For every operating
test condition, 50 image pairs were captured and processed using
DAVIS software. From the results, it is seen that the in-cylinder
flow structure is greatly influenced by the intake manifold
inclinations irrespective of intake valve lift. Maximum Turbulent
Kinetic Energy (TKE) was highest at full intake valve lift
irrespective of the inclination. Also, the maximum TKE was
the highest for 600 intake manifold inclination compared to
other inclinations irrespective of the intake valve lift at
equivalent rated engine speed. Finally, it is concluding that
the analysis carried in this work is useful in predicting the
flow and inturn optimizing combustion chamber of modern
I.C engines.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流动特性,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
老化,屈服应力,流体,球形沉降物中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We have studied the flow induced by a macroscopic spherical particle settling in a Laponite
suspension that exhibits a yield stress, thixotropy, and shear thinning. We show that the fluid
thixotropy or aging induces an increase with time of both the apparent yield stress and
shear-thinning properties but also a breaking of the flow fore-aft symmetry predicted in
Hershel-Bulkley fluids yield-stress, shear-thinning fluids with no thixotropy. We have also varied
the stress exerted by the particles on the fluid by using particles of different densities. Although the
stresses exerted by the particles are of the same order of magnitude, the velocity field presents
utterly different features: whereas the flow around the lighter particle shows a confinement similar
to the one observed in shear-thinning fluids, the wake of the heavier particle is characterized by an
upward motion of the fluid “negative wake”, whatever the fluid’s age. We compare the features of
this negative wake to the one observed in viscoelastic shear-thinning fluids polymeric or micelle
solutions. Although the flows around the two particles strongly differ, their settling behaviors
display no apparent difference which constitutes an intriguing result and evidences the complexity
of the dependence of the drag factor on flow field.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Tomographic particle image velocimetry is a 3D PIV technique based
on the illumination, recording, reconstruction and analysis of tracer-particle motion
within a three-dimensional measurement volume. The recently developed technique
makes use of several simultaneous views of the illuminated particles, typically 4, and
their three-dimensional reconstruction as a light-intensity distribution by means of
optical tomography. The reconstruction is performed with the MART algorithm
(multiplicative algebraic reconstruction technique), yielding a 3D distribution of
light intensity discretized over an array of voxels. The reconstructed tomogram
pair is then analyzed by means of 3D crosscorrelation with an iterative multigrid
volume-deformation technique, returning the three-component velocity vector distribution
over the measurement volume. The implementation of the tomographic
technique in time-resolved mode by means of high repetition rate PIV hardware
has the capability to yield 4D velocity information. The first part of the chapter describes
the operation principles and gives a detailed assessment of the tomographic
reconstruction algorithm performance based upon a computer-simulated experiment.
The second part of the chapter proposes four applications on two flow cases:
1. the transitional wake behind a circular cylinder; 2. the turbulent boundary layer
developing over a flat plate. For the first case, experiments in air at ReD = 2700
are described together with the experimental assessment of the tomographic reconstruction
accuracy.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
溶液,流体中速度场,速度矢量场,显微速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Increasingly smaller electronics requires improvement in performance of cooling systems to keep it operating
reliably. We present herein a novel experimental study of convective heat transfer in serpentine
microchannels with segmented liquid–liquid emulsions. It is demonstrated that this concept yields significant
Nusselt number enhancement in microchannel heat sinks compared to that obtained using single
phase liquid cooling. Laser Induced Fluorescence (LIF) is employed to measure temperature of the coolant
with and without droplets, and micro-PIV is used to determine velocity field. For the segmented flow, up
to four-fold increase of the Nusselt number was observed compared to pure water flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场,显微速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
液体中三维贯穿度和速度分布检测方案(粒子图像测速)
An experimental study has been conducted to study the effect of a swirling crossflow on transversely injected liquid jets. In-house designed axial swirlers with vane exit angles of 30°, 45° and 60° were used to generate the swirling crossflow. Laser Doppler Velocimetry (LDV) results indicate that the axial (Ux) and the tangential (Uθ) components of the crossflow velocity decrease with increasing radial distance from the center. Also, flow angle (ψ) of the crossflow is lesser than the swirler vane exit angle indicating that the swirlers did not impart sufficient tangential momentum for the flow to be parallel to the vanes at swirler exit. The deficit in flow angle increased with swirler angle. Water jets were injected from a 0.5 mm diameter orifice located on a cylindrical centerbody that protruded through the hub of the swirler. Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) was used to study the behavior of the jets. PIV measurements were conducted in multiple cross-sectional and streamwise planes. Mie-Scattering images were col-lated to create three-dimensional representation of the jet plume, which was used to study penetration. In cylindrical coordinate system, the penetration can be described in terms of radial and “circumferential” penetration, where cir-cumferential penetration is defined as the difference in the circumferential displacement of the jet and the crossflow over the same streamwise displacement. Increasing the momentum flux ratio (q) resulted in a higher radial penetra-tion. Increasing the swirl angle reduced radial penetration and increased circumferential penetration. PIV results of the cross-sectional and streamwise planes each yielded two velocity components which were merged to obtain three-dimensional droplet velocity distribution. The three-dimensional velocity distribution yielded further insight into the evolution of the jet plume
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
三维贯穿度和速度分布
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
热卷流中高普朗特数薄层热卷流发展的剖析检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We present an experimental study of the
dynamics of a plume generated from a small heat source in
a high Prandtl number fluid with a strongly temperaturedependent
viscosity. The velocity field was determined
with particle image velocimetry, while the temperature
field was measured using differential interferometry and
thermochromic liquid crystals. The combination of these
different techniques run simultaneously allows us to identify
the different stages of plume development, and to
compare the positions of key-features of the velocity field
(centers of rotation, maximum vorticity locations, stagnation
points) respective to the plume thermal anomaly, for
Prandtl numbers greater than 103. We further show that the
thermal structure of the plume stem is well predicted by the
constant viscosity model of Batchelor (Q J R Met Soc 80:
339–358, 1954) for viscosity ratios up to 50.
1 Introduction
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
高普朗特数薄层热卷流发展的剖析
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度矢量,速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The unsteady lift generated by the flow of turbulence over the trailing edge of an airfoil can be an
effective source of dipole sound. The objective of the present research was to experimentally measure
the velocity field behind an asymmetric 45 degree beveled trailing edge in order to develop an understanding
of the flow mechanisms responsible for the generation of trailing edge noise. Particle Image
Velocimetry (PIV) data were acquired in the near wake region of the trailing edge at a chord Reynolds
number of 1.9x106. The time averaged velocity statistics are indicative of a wake flow containing
semi-periodic vortex shedding. These large scale shedding motions are commonly responsible for the
tonal noise produced by the trailing edge. A phase average decomposition of the velocity field with
respect to this shedding process was utilized to separate the small scale turbulent motions responsible
for broadband sound production. This analysis has shown that the characteristics of the small scale
turbulence are dependent on the phase of the vortex shedding process.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The analysis of the flow field inside hydraulic valves has become in the last few years a very important issue to be
addressed in order to optimize the spool shapes and to obtain the desired flow metering characteristics.
The Fluid-Power research unit of the Polytechnic of Bari realized many works dealing with the Computational Fluid
Dynamics (CFD) analysis of directional control valves.
Experimental measurements concerning discharged flow rate and needed driving force values have been performed
in order to validate the numerical results, but the validation of CFD results has been limited, in the past, only to the
global fluid dynamic response of the valve and not to the local flow conditions.
In order to provide the flow field inside the valve through PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) measurements, a valve
model, equipped with a great optical access, has been realized. The scaled model has been realized according to the fluid
dynamic similarity laws in order to use a fluid different from the oil (water) and to increase the dimensions of the valve.
In particular, the realized model has a circumferential development useful to acquire important data about the
circumferential flows and their effects on the global flow rate crossing the valve. The experimental results show that the
velocity profiles in the metering sections are strongly influenced by the three-dimensional effects of the flow, confirming
the results obtained numerically in previous works.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
等离子体制动器,高速高雷诺数喷射,流动,噪声中流动和噪声控制,噪声,速度场,矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The idea of manipulating flow to change its characteristics is over a century old. Manipulating instabilities of a jet to increase its mixing and to reduce its radiated noise started in the 1970s. While the effort has been successful in low-speed and low Reynolds number jets, available actuators’ capabilities in terms of their amplitude, bandwidth, and phasing have fallen short in control of high-speed and high Reynolds number jets of practical interest. Localized arc filament plasma actuators have recently been
developed and extensively used at Gas Dynamics and Turbulence Laboratory (GDTL) for control of highspeed and high Reynolds number jets. While the technique has been quite successful and is very
promising, all the work up to this point had been carried out using small high subsonic and low supersonic jets from a 2.54 cm diameter nozzle exit with a Reynolds number of about a million. The
preliminary work reported in this paper is a first attempt to evaluate the scalability of the technique.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流动和噪声控制,噪声,速度场,矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体,光学发动机中速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Within the framework of an investigation into valve operating strategies for homogeneous charge
direct injection spark ignition engines under part load conditions this paper discusses the in-cylinder flow
fields developed by running an optical engine with an early inlet valve closing strategy with a lift of 3.9 mm
that produces 3bar IMEP at 3500 rpm under firing conditions. The experimental facilities are similar to
previous work but measurement technique has been optimized with the significant aspect of this work being
that the flow fields were determined in three vertical planes and one horizontal plane to highlight the three
dimensional and the highly cyclic nature of the flow. These characteristics have significant impact on
the application of the PIV technique and data processing to ensure a high degree of confidence in
the flow fields generated. The time varying nature of this three dimensional flow field is discussed and
how it impacts on the PIV measurement technique particularly as regards data acquisition and data
processing. The true extent of the complex three dimensional flow field is readily seen and that, even though
the combustion chamber geometry is symmetrical, the swirl flow field is not. The main features of the
vertical flow structure are described over a crankangle period from 90oCA to 120oCA which
highlight the dominant feature as being a wall jet flow which interacts with the piston crown to
generate a strong reverse tumble flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
液体流体中流速检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Two-phase annular flow is commonly used in both commercial and industrial heat transfer; however, we do not yet possess a thorough understanding of the nature of the fluid. Most analytical annular two-phase models are based on a relationship between the
liquid film thickness, liquid film mass flux, and the axial pressure gradient or interfacial
shear stress. The film thickness calculated from these models can then be utilized to
determine the heat transfer coefficient of the flow. Although they are specific to certain
flow regimes and fluids, empirical models remain more accurate than these analytical
models. The key to understanding these flows lies with the liquid film. Therefore, to
better understand the pressure drop and heat transfer of annular two-phase flow, this
study involves the development of local, liquid velocity measurement techniques and
their application to horizontal, wavy-annular two-phase flow.
Two techniques, Bubble Streak Tracking (BST) and Thin Film Particle Image
Velocimetry (TFPIV), have been developed in this study. Utilizing naturally occurring
bubbles within the liquid film, the BST technique determines the liquid velocity by
measuring reflected light streaks from the bubbles. A three-colored LED array creates
directionally unambiguous streaks, while a strobe illuminates interfacial features that
affect the liquid velocity. The TFPIV technique applies a typical micro-PIV system to a
macroscopic flow with the addition of a non-trivial image processing algorithm. This
algorithm successfully overcomes the image noise that occurs when applying PIV to a
two-phase, thin film. Although difficulties arise when processing the BST data, the
results of the BST and TFPIV methods are comparable, making BST an economical
alternative to TFPIV for calculating liquid film velocities.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流速
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
微流动装置中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Along with the rapid growth of research of microfluidics, monitoring and understanding micro flow
behavior is a challenge for researchers. Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV), a powerful tool that
makes flow visible, was extended to microscale by Santiago et al. 1998. In this paper, we presented
the micro Particle Image Velocimetry (μPIV) system at Nanyang Technological University (NTU),
its calibration and characterizations of microfluidic devices using μPIV. Since the fully developed
microchannel flow has been well investigated, it is suitable to calibrate the measurements of μPIV.
In our experiment, an in-channel microdispenser fabricated on printed circuit board is used to form a
microchannel. A syringe pump forces water that contains fluorescent particles. The flow field is obtained
by μPIV. At the same time, a three-dimensional model with ANSYS/FLOTRAN was used.
The comparison between the two results demonstrates that our μPIV system works well. Furthermore
we use this system to characterize a Tesla valve - a non-moving part valve. The valve consists
of a fluid channel structure that has rectification property, which favors forward flow while hampers
reverse flow. The velocity fields are also validated by ANSYS/FLOTRAN.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
冷却反应器中INL在棱镜气体冷却反应器下腔室比例模型上获得流动现象基准数据来验证CFD模拟的有效性的项目计划检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The experimental program that is being conducted at the Matched Index-of-Refraction (MIR) Flow
Facility at Idaho National Laboratory (INL) to obtain benchmark data on measurements of flow
phenomena in a scaled model of the lower plenum of a typical prismatic gas-cooled reactor (GCR) using
3-D Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) is presented. A detailed description of the model, scaling, the
experimental facility, 3-D PIV system, measurement uncertainties, experimental procedures and samples
of the data sets that have been obtained are included. Samples of the data set that are presented include
mean-velocity-field and turbulence data in an approximately 1:7 scale model of a region of the lower
plenum. This experiment has been selected as the first Standard Problem endorsed by the Generation IV
International Forum.
Results concentrate on the region of the lower plenum near its far reflector wall (away from the outlet
duct). Inlet jet Reynolds numbers (based on the jet diameter and the time-mean flow rate) are
approximately 4,300 and 12,400. The measurements reveal undeveloped, non-uniform flow in the inlet jet
ducts and complicated flow patterns in the modeled lower plenum. Data include three-dimensional vector
plots, data displays along the coordinate planes (slices) and charts that describe the component flows at
specific regions in the model. Information on inlet flow is also presented.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
INL在棱镜气体冷却反应器下腔室比例模型上获得流动现象基准数据来验证CFD模拟的有效性的项目计划
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
食品安全实验室中无机金属元素的ICP-MS常规检测的实际问题探讨
本文采用图文并茂的方式介绍本室采用PE DRC-e型ICP-MS分析食品中重点关心的14种金属元素(Hg、Cd、Cr、Mn、Cu、Fe、Mn、Zn、Sr、I、Pb、Se、P和As等)方法,,该法为本室常规检测方法,每年大约有5000-10000件食品样品被检测;重点讨论了实验室用酸选择、检测过程中酸效应、盐效应、记忆效应,以及部分元素的光谱干扰等常见问题。有待完善中,请大家补充!
一、装备
1.1 实验用酸
ICP-MS分析常用酸主要有HNO3, H2O2 和HF; 杂质较少的进口高纯酸由于其价格比较昂贵,亚沸蒸馏器产酸率较小,长期使用性价比较高。我们比较了国内电子级BV-3型(图1. 北京化学试剂研究所)和常见的优级纯(GR)硝酸、双氧水和氢氟酸中的杂质,见图2。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
北京诚驿恒仪科技有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2243篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等