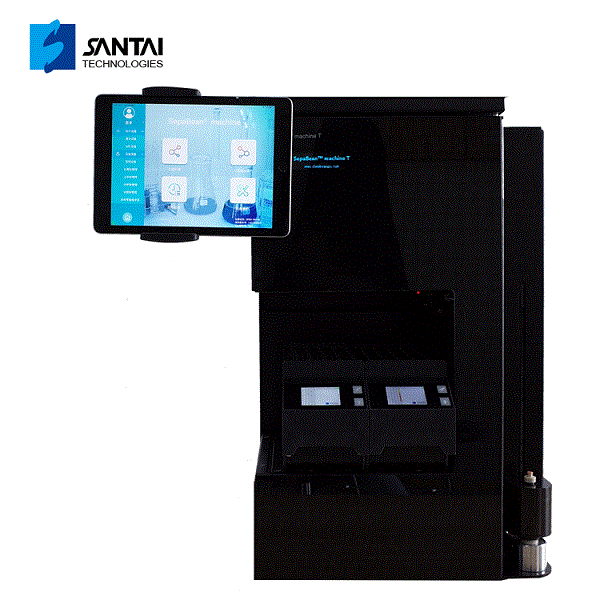
ACQUITY UPLC H-Class PLUS中BSM二元系统检测方案(液相色谱仪)
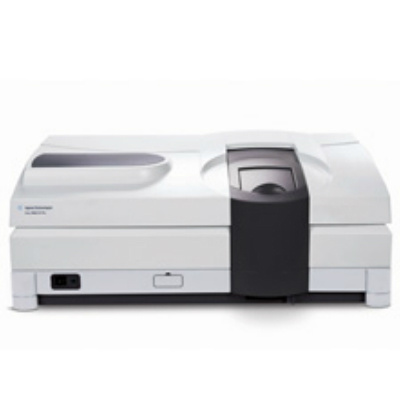
采用全新二元配置的Waters ACQUITY UPLC H-Class PLUS二元系统是对现有ACQUITY UPLC H-Class PLUS四元系统的补充。 该系统具有二元溶剂管理功能,拥有与四元系统相同的低扩散性和稳定性,采用0.005 in/0.127 mm管路,最高可支持15,000 psi的工 作背压。系统由二元溶剂管理器、流通针式样品管理器以及带主动预加热功能的色谱柱管理选件组成,用户可选配单色谱柱柱温箱或 最多可加热/冷却6根色谱柱的色谱柱管理器。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
BSM二元系统
沃特世科技(上海)有限公司(Waters)
查看联系电话
前往展位
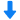
多孔介质中双尺度瞬态流动行为的显微PIV研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
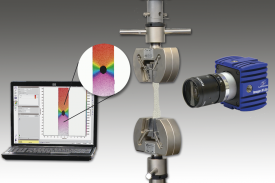
Injection processing of composite materials most often includes infiltration of a
thermoset resin into a multi-scale porous fabric. Controlling the fluid flow within the multiscale
fabric is essential for the quality of the final composite material, since the transport of
fluid between regions with different scales plays an important role in phenomena such as void
formation and filtration of particle doped resins.
In this work, the transient flow behaviour in dual scale porous media is investigated
with Micro Particle Image Velocimetry in order to enhance the knowledge and control of the
processing of multi-scale composites so that their quality can be improved. Experiments show
that the fluid transport between the two scales can be controlled by the injection velocity.
Validation of the measured velocity fields furthermore shows excellent agreement with
theory.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
双尺度瞬态流动行为的显微PIV研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
燃烧,火焰,空气流体中浓度场,温度场检测方案(流量计)
Two novel techniques based on Laser-Induced Fluorescence (LIF) were applied to measure gas-phase temperature distributions in boundary layers close to wall surfaces. Single line toluene-LIF thermometry was used to image temperature in a nitrogen gas flow above a heated wall. The nitrogen gas flow was doped with evaporated toluene. When excited at 266 nm, the toluene LIF-signal shows an exponential dependence on temperature. This behavior was used to calculate absolute temperatures from LIF images after calibration at known conditions. The second technique, multi-line NO-LIF thermometry was applied to image temperature in the quenching boundary layer close to a metal wall located on a flat flame burner. A small amount of nitric oxide was mixed into the air/methane mixture. NO molecules were excited in the A-X (0,0)-band at 225 nm. NO-LIF excitation spectra were acquired by tuning the excimer laser wavelength and recording the NO LIF-signal with an ICCD camera. Absolute temperatures were calculated for every pixel by fitting simulated
excitation spectra to the experimental data. Temperature distributions close to the wall surface were measured at two different flow-rate conditions. A high nominal spatial resolution of
0.016 mm/pixel in direction perpendicular to the wall was reached. Wall surface temperatures were recorded simultaneously by embedded thermocouples and compared with gas-phase temperature near the wall surface.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
浓度场,温度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度矢量场检测方案
A numerical implementation of the advection
equation is proposed to increase the temporal resolution of
PIV time series. The method is based on the principle that
velocity fluctuations are transported passively, similar to
Taylor’s hypothesis of frozen turbulence. In the present
work, the advection model is extended to unsteady threedimensional
flows. The main objective of the method is that
of lowering the requirement on the PIV repetition rate from
the Eulerian frequency toward the Lagrangian one.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
自由游动鲨鱼中水动力学推进机理,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Two-dimensional velocity fields around a freely swimming freshwater black shark fish in longitudinal (XZ) plane and
transverse (YZ) plane are measured using digital particle image velocimetry (DPIV). By transferring momentum to
the fluid, fishes generate thrust. Thrust is generated not only by its caudal fin, but also using pectoral and anal fins,
the contribution of which depends on the fish’s morphology and swimming movements. These fins also act as roll
and pitch stabilizers for the swimming fish. In this paper, studies are performed on the flow induced by fins of freely
swimming undulatory carangiform swimming fish (freshwater black shark, L = 26 cm) by an experimental hydrodynamic
approach based on quantitative flow visualization technique. We used 2D PIV to visualize water flow pattern
in the wake of the caudal, pectoral and anal fins of swimming fish at a speed of 0.5–1.5 times of body length per
second. The kinematic analysis and pressure distribution of carangiform fish are presented here. The fish body and fin
undulations create circular flow patterns (vortices) that travel along with the body waves and change the flow around
its tail to increase the swimming efficiency. The wake of different fins of the swimming fish consists of two counterrotating
vortices about the mean path of fish motion. These wakes resemble like reverse von Karman vortex street
which is nothing but a thrust-producing wake. The velocity vectors around a C-start (a straight swimming fish bends
into C-shape) maneuvering fish are also discussed in this paper. Studying flows around flapping fins will contribute to
design of bioinspired propulsors for marine vehicles.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
水动力学推进机理,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
柴油喷嘴中近场速度空化效应研究检测方案(CCD相机)
The entire process of atomization of the fuel in an internal combustion engine plays a very important role in determining the overall efficiency of these engines. A good atomization process could help the fuel to mix with the air properly leading to its efficient combustion, thereby reducing the emitted pollutants as well. The recent trend followed by the engineers focused on designing fuel injectors for more efficient atomization is to increase the atomization pressure while decreasing the nozzle orifice diameter. A consequence of this is the development of cavitation (formation of vapor cavities or bubbles in the liquid) inside the injector close to the nozzle. The main reason behind this is the sudden changes in the pressure inside the injector and these cavities or bubbles are usually formed where the pressure is relatively low.
This work mainly focuses on studying the formation of cavitation and its effect on the velocity of the spray in the near nozzle region using asymmetrical transparent nozzle equipped with a needle lift sensor with nozzle diameter of 0.35 mm at 300 bar of injection pressure.
The experiment consists in recording of several image-pairs, which are separated by about 300 ns, capturing the dynamics of the spray, a few millimeters from the nozzle in the direction of the flow. These image-pairs are then used to compute the velocity from the displacement of the liquid structures and ligaments by correlating the first image with the second. About 200 of such velocity graphs are then averaged to obtain a velocity map and is compared with the similar average velocity maps obtained at different times from the start of the injection. The angular spread of the spray from each of these images is calculated as well. The images showing cavitation in-side the injector are also recorded at these same instants of time so as to understand the effects of cavitation on the velocity and angular spread of the spray close to the nozzle.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
近场速度空化效应研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
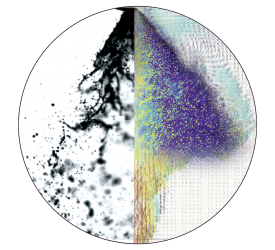
微通道气泡中堵塞现象检测方案(流量计)
This paper highlights the influence of contact line (pinning) forces on the mobility of dry bubbles
in microchannels. Bubbles moving at velocities less than the dewetting velocity of liquid on the
surface are essentially dry, meaning that there is no thin liquid film around the bubbles. For these
“dry” bubbles, contact line forces and a possible capillary pressure gradient induced by pinning
act on the bubbles and resist motion. Without sufficient driving force (e.g. external pressure) a
dry bubble is brought to stagnation. For the first time, a bipartite theoretical model that estimates
the required pressure difference across the length of stagnant bubbles with concave and convex
back interfaces to overcome the contact line forces and stimulate motion is proposed. To validate
our theory, the pressure required to move a single dry bubble in square microchannels exhibiting
contact angle hysteresis has been measured. The working fluid was deionized water. The
experiments have been conducted on coated glass channels with different surface
hydrophilicities that resulted in concave and convex back interfaces for the bubbles. The
experimental results were in agreement with the model’s predictions for square channels. The
predictions of the concave and convex back models were within 19% and 27% of the
experimental measurements, respectively.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
堵塞现象
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
非线性内波中通过参量亚谐波不稳定性的穿透检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We present the results of a laboratory experimental study of an internal wave
field generated by harmonic, spatially periodic boundary forcing from above of a
density stratification comprising a strongly stratified, thin upper layer sitting atop
a weakly stratified, deep lower layer. In linear regimes, the energy flux associated
with relatively high frequency internal waves excited in the upper layer is prevented
from entering the lower layer by virtue of evanescent decay of the wave field. In
the experiments, however, we find that the development of parametric subharmonic
instability in the upper layer transfers energy from the forced primary wave into a pair
of subharmonic daughter waves, each capable of penetrating the weakly stratified
lower layer. We find that around 10% of the primary wave energy flux penetrates
into the lower layer via this nonlinear wave-wave interaction for the regime we
study.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
通过参量亚谐波不稳定性的穿透
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
复合板中爆炸力对复合板造成的变形检测方案(其它无损检测仪器/设备)
Recent advances in composite manufacturing have occurred
predominantly in the aerospace, marine, automotive and related
industries. Whilst, formerly, naval vessels were constructed from
steel, composites provide a significant weight reduction and
increase in stealth properties whilst maintaining high strength
properties. However composite sandwich materials have yet to be
widely adopted in the construction of naval vessels despite their
excellent strength to weight ratio and low radar return. One barrier
to their wider use is our limited understanding of their performance
when subject to air blast.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
爆炸力对复合板造成的变形
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
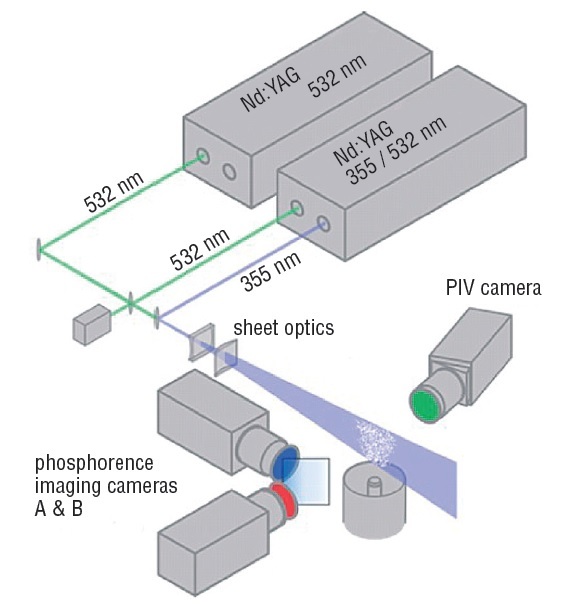
激光诱导水动力学和气泡中PIV和PDA实验研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Research on laser-liquid interaction and its induced fluid flows, as well as microbubbles, is important in many
applications, such as laser ophthalmic microsurgery, manufacturing and repairing of micro-electronic-mechanical
devices, laser deposition of thin liquid film to a specific location in micro system, etc. This work was focused on the
interaction mechanisms of a laser pulse with distilled/degassed water as well as the characteristics of the microbubbles.
Microbubbles and optohydrodynamic flows induced by a Nd:YAG pulse laser (New Wave Research) were studied. A
recently improved PIV and PDA system were used to analyze the bubble dynamics and fluid flow quantitatively. Two
CCD cameras were used to capture the images of microbubbles and visualize the laser induced Optohydrodynamic flows.
The experimental results show that a bright fluid beam (density flow) with duration less than 127μs is produced by a
focused laser pulse while an explosive cavitation just around the focus point is also occurred. Immediately following the
fluid beam and the explosive cavitation, two new fluid regions which may be formed with the superheated dense fluid
were found. One of them is just under the fluid beam due to the optical pressure while the other one is around the
explosion area due to the force caused by the explosive cavitation. As shown in Figure 1, Single and multi microbubbles
were generated immediately after the cavitation explosion when the nucleation conditions were satisfied. In addition, the
characteristics, such as bubble velocities and diameters, were measured by a recently improved phase-Doppler
anemometry (PDA). These results will help to have a better understanding of the mechanisms of laser-induced
optohydrodynamic flows and bubbles related phenomena, which is crucial to numerical modeling.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
PIV和PDA实验研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
T型混合器中三维流动,速度场,速度矢量场,2D3C显微速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A stereo-μ-PIV system for the measurement of all three components of the velocity vector in a
measurement plane (2D-3C) in a closed microchannel has been developed and first test measurements have been
performed on the three-dimensional laminar flow in a T-shaped micromixer. Stereo-μ-PIV measurements in closed
microchannels require a calibration based on the self-calibration of the tracer particle images. In order to include the
effects of different refractive indices of the water in the microchannel, the glass of the entrance window, and the
surrounding air a three-media-model is included in the triangulation procedure of the self calibration. A preliminary
test case shows that the stereo-μ-PIV results deviate less than 5% from theoretical values. First measurements in the
mixing zone of a T-shaped micromixer show that three-dimensional flow in a microchannel can be resolved,
however, the accuracy of the measurements needs to be improved.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
三维流动,速度场,速度矢量场,2D3C显微速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
盘芯喷嘴质量平衡中体积有效性判定检测方案(气溶胶)
The mass balance of orchard air-blast sprayers has historically been assessed using an array of samplers
to capture airborne particles. However, these methods only provide an idea of flux with no other information
which is pertinent to understand the movement of droplets and their potential to drift. While
droplet analysis for agricultural sprayers has always been conducted in a laboratory setting with the use
of laser devices, a new phase Doppler approach is being explored to assess droplet spectra, velocity, and
flux in outdoor field conditions. Therefore it is the objective of this study to develop a methodology and
the potential limitations for using a phase Doppler system while in a laboratory setting. Due to the
expected variability of field conditions as well as the turbulence of orchard sprayers, a computational
approach was sought to assess flux from a single scan of a conical spray plume's diameter. Using a
constant scanning speed of 0.0079 m/s, a disc core (D1/DC33) hollow cone nozzle was examined at 310,
410, and 520 kPa pressure at five different heights (10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 cm). Computational flux was
then compared to the actual flow rate, finding a 3.3% average error with a range of 16.9% and 4.7%
illustrating a small underestimation of mass with the phase Doppler which was related to distance and
droplet frequency. Further, comparisons were also assessed including pattern/symmetry, droplet spectra,
velocity, and the overall number of samples. The proposed methodology indicates potential for the use of
phase Doppler technology for in situ measurements of spray equipment using a conical-type spray
nozzle, such as that of the orchard air-blast sprayer.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
体积有效性判定
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
水洗喷嘴中液滴粒径,液滴速度,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(干涉仪)
Crude Unit Column Overhead – Corrosion
Water is usually injected in the
overhead piping to:
• Help quench and scrub the
overhead vapors
• Dilute acids formed
• Prevent any salts or acids from
forming in the system
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
液滴粒径,液滴速度,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2245篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等