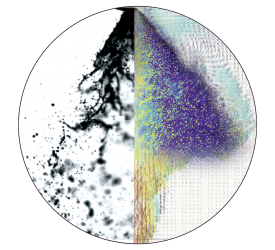
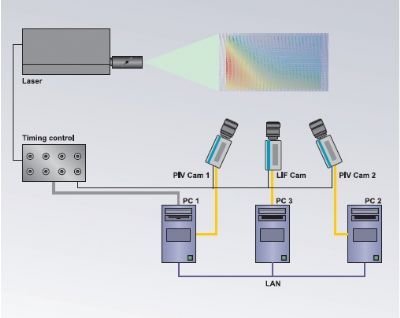
电致颗粒悬浮,可燃尘埃混合体中流场,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The Electric Particulate Suspension (EPS) is a combustion ignition system being developed at Iowa State University for evaluating quenching effects of powders in microgravity (quenching distance, ignition energy, flammability limits). Because of the high cloud uniformity possible and its simplicity, the EPS method has potential for ‘benchmark’ design of quenching flames that would provide NASA and the scientific community with a new fire standard.
Microgravity is expected to increase suspension uniformity even further and extend combustion testing to higher concentrations (rich fuel limit) than is possible at normal gravity. Two new combustion parameters are being investigated with this new method: (1) the particle velocity distribution and (2) particle-oxidant slip velocity. Both walls and (inert) particles can be tested
as quenching media. The EPS method supports combustion modeling by providing accurate measurement of flame-quenching distance as a parameter in laminar flame theory as it closely relates to characteristic flame thickness and flame structure. Because of its design simplicity, EPS is suitable for testing on the International Space Station (ISS). Laser scans showing stratification effects at 1-g have been studied for different materials, aluminum, glass, and
copper. PTV/PIV and a leak hole sampling rig give particle velocity distribution with particle slip velocity evaluated using LDA. Sample quenching and ignition energy curves are given for aluminum powder. Testing is planned for the KC-135 and NASA’s two second drop tower.
Only 1-g ground-based data have been reported to date.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流场,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
混浊介质中混浊介质角域成像(ADI)实验中光传播时间门控和偏振优选效应检测方案(CCD相机)
Angular Domain Imaging (ADI) employs an angular filter array to accept photons within a small acceptance angle
along the axis of an aligned laser light source and preferentially reject scattered light. Simulations show that the
accepted photons travel the shortest paths between source and detector and are therefore the earliest to arrive. We
fabricated angular filter arrays using silicon bulk micromachining and found that an array of 60 μm square shape microtunnels
1 cm in length accepted photons within 0.48 degree of axis of the micro-tunnels. This small acceptance angle
rejected most of the scattered light and sub-millimeter resolution targets could be resolved in a few centimeters of turbid
medium with at least six times reduced mean free path. ADI through media with higher scattering coefficients was not
achievable due to unwanted acceptance of late arriving scattered photons. To reject the late arriving photons, we added
time-domain filtration and linear polarization to ADI. The implementation of a time-gated camera, a 780 nm femtosecond
pulsed laser, and linear polarization to our ADI system resulted in improved image contrast. The use of ADI
with time-gating (gate width 250 ps) and linear polarization enabled visualization of sub-millimeter absorbing objects
with approximately eight times higher image contrast compared to ADI in a scattering medium equivalent to six times
reduced mean free path.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
混浊介质角域成像(ADI)实验中光传播时间门控和偏振优选效应
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Recent years have seen an increasing interest in micro aerial vehicles
(MAVs) and flapping flight in connection to that. The Delft University of
Technology has developed a flapping wing MAV, “DelFly II”, which relies on a
flapping bi-plane wing configuration for thrust and lift. The ultimate aim of the
present research is to improve the flight performance of the DelFly II from both an
aerodynamic and constructional perspective. This is pursued by a parametric wing
geometry study in combination with a detailed aerodynamic and aeroelastic
investigation. In the geometry study an improved wing geometry was found,
where stiffeners are placed more outboard for a more rigid in-flight wing shape.
The improved wing shows a 10% increase in the thrust-to-power ratio.
Investigations into the swirling strength around the DelFly wing in hovering flight
show a leading edge vortex (LEV) during the in- and out-stroke. The LEV appears
to be less stable than in insect flight, since some shedding of LEV is present.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
氢气和甲烷中相对喷嘴结构氢气和甲烷边界和扩散火焰:结构和稳定性检测方案(流量计)
Hydrogen/air and methane/air flames in axi-symmetric opposed jet burners were investigated
experimentally for different flow velocities, burner geometries and fuel dilutions.
Above critical strain rate values there is the local extinction of the planar diffusion flame,
and the edge flame forms, which propagates and stabilizes further away from the axis
of symmetry, assuming a toroidal shape. The ranges of air and fuel flow velocities over
which the diffusion or the edge flame are stable were determined. There is a substantial
range over which both flames can be stabilized, and the transition between the two flame
types exhibits a strong hysteresis.
Raman spectroscopy was used for the determination of the spatial distribution of
temperature and major species concentrations, while the OH radical distribution was
obtained with Planar Laser Induced Fluorescence (LIF). Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV)
was employed to characterize the flow fields both in cold and reactive conditions.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
相对喷嘴结构氢气和甲烷边界和扩散火焰:结构和稳定性
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
水流中湍流中进行拉格朗日加速度测量检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Acceleration is of primal relevance in fluid mechanics, as it shows the effect of the combination of all the forces acting on a fluid flow; the Navier-Stokes equations highlight this fact and the importance of its knowledge in the description of a fluid motion:
Moreover, only in few particular cases (as for example, in parallel fluxes such as Couette one) it is possible to analytically solve them: for the other cases it would be important to measure their single components. Unfortunately, despite the acceleration is at
the very base of fluid motion (see, for instance, Tsinober 2001), only few measurement of the acceleration in the Lagrangian frame can be found in literature. Even if, on one hand, a certain number of authors have studied acceleration properties via numerical simulations, for instance Vedula and Yeung (1999), Tsinober et al. (2001), Biferale et al. (2004), Goto et al. (2005), Osborne et al. (2005), Chen et al. (2006), on the other very few examples of its experimental measure are available up to now. Moreover,among them not all the measurements are taken in the Lagrangian frame: among the
Eulerian measurements, Christensen and Adrian (2002), Dong et al. (2001) and Lowe and Simpson (2005) can be pointed out, among the Lagrangian ones, Virant and Dracos (1997), Ott and Mann (2000), La Porta et al. (2001), Voth et al. (2002) and Luthi et al.(2005) can be found.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
湍流中进行拉格朗日加速度测量
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
三乙基铝-乙酰基丙酮金属配合物-水配合体系引发对二氧环己酮 PDO 开环聚合的研究
1 实验部分
1. 1 试剂 对二氧环己酮, 自制, 纯度99. 8%; 三乙基铝, 南京通联化学有限公司, 含量> 95%;M (A cA c) n和A lEt32M (A cA c) n2H2O 参照参考文献[10 ]方法制备.
1. 2 PDO 的聚合 将干燥的聚合瓶反复加热, 抽真空, 通氮气3~ 4 次, 在高纯氮气的保护下, 用注射器依次加入纯化后的PDO 及计量的A lEt32M (A cA c) n2H2O 引发剂, 于设定温度的恒温油浴中聚合一定时间.
1. 3 表征 用瑞士万通KFC2831 微量水分测定仪测定单体含水量. 将聚合产物在甲苯溶液中抽提48 h后, 在50 ℃下真空干燥至恒重, 通过称量干燥产物的质量确定单体的转化率, 重复实验验证单体转化率的最大误差小于±2%.
……
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
上海纳锘实业有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
铁电液晶波导中相位匹配二次谐波的产生检测方案(椭偏仪)
True phase-matched second-harmonic generation in a waveguide of crosslinkable ferroelectric liquid crystals is demonstrated. These materials allow the formation of macroscopically polar
structures whose order can be frozen by photopolymerization. Homeotropic alignment was chosen which offers decisive advantages compared to other geometries. All parameters contributing to the
conversion efficiency are maximized by deliberately controlling the supramolecular arrangement.The system has the potential to achieve practical level of performances as a frequency doubler for low power laser-diodes.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
相位匹配二次谐波的产生
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
碳烟,火焰,流体中速度场,浓度场,碳烟体积分数,碳烟初级粒径检测方案(粒子图像测速)
An experimental study of the interaction of a planar diffusion flame with a line vortex is presented. A planar
diffusion flame is established between two coflowing, equal velocity streams of acetylene diluted with nitrogen
and air. A line vortex is generated on demand by momentarily pulsing one of the flow streams by way of electromagnetic
actuation of a piston in the flow apparatus. The flame–vortex interactions are diagnosed by planar
laser-induced incandescence for soot yield and by particle image velocimetry for vortex flow characterization. The
results show that soot formation and distribution are influenced by the reactant streams from which vortices are
initiated. The vortices interacting with the flame from the air side produce more soot and soot is distributed in and
around the vortex core in diffuse layers. In contrast, topography of soot in vortices interacting from the fuel side
is such that soot is confined to thinner layers around the vortex core which does not contain any soot. The flame
curvature is found to influence the local soot production with the flame regions convex to the fuel side containing
more soot locally. It is also found that the overall soot yield is less sensitive to the vortex strength and is of lower
magnitude when vortex is spun from the fuel side. The knowledge of this type of asymmetry in soot yield in
flame–vortex interactions is useful for combustion engineering and design of practical devices.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,浓度场,碳烟体积分数,碳烟初级粒径
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
喷雾,液滴,喷嘴,流体中速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Pulsed jets have found a wide variety of applications in the area of flow control during
the recent years. The goal of the current study is to identify the flow field and mixing
characteristics associated with an incompressible circular jet through a flexible nozzle. The
flow was self-excited over a range of conditions and produced a pulsatile flow. The frequency
of excitation was found to be between 150-175Hz. Phase-locked and time averaged 2D
Particle image Velocimetry (PIV) was used to study the dynamic characteristics of the flow.
The flow field shows that two different modes could be excited depending on nozzle
characteristic. The flapping mode was associated with alternate shedding of vortices. This
introduces strong steering of the jet to one side or the other. Turbulence, Jet spread and
entrainment characteristics were far more superior to the non-flapping or a pulsed jet. The
second mode which was a non-flapping mode is associated with the formation of a counter
rotating vortex pair. The turbulence associated with both these modes was convected along
with the vortical structure in the flow. The jet vortices formed by the self-excited flow were
not just convected by the flow, but these determined the flow field and mixing characteristics
of the jet.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
纳米颗粒中多种元素检测方案(等离子体质谱)
单颗粒 ICP-MS (spICP-MS) 是一种功能强大的工具,适用于表征分散或悬浮在液体样品中的纳米颗粒 (NP)。尽管 spICP-MS 是一项相对较新的技术,但已越来越多地应用于制成品以及环境和生物样品中 NP 的分析。借助适当的样品前处理和稀释,spICP-MS 能够从单个颗粒通过等离子体时所产生的元素信号中检测 NP。另外,只有该技术能够同时测定颗粒数量和粒径分布以及目标元素的颗粒和溶解态物质的浓度。
已证明 spICP-MS 对预先知道 NP 组成的测定非常有价值,支持待测元素的选择。然而,分析 NP 混合物组成未知或多变的天然样品也受到了一定关注。此外,某些 NP 含多种金属,例如核-壳颗粒,其中一种金属组成的核被另一种金属组成的壳包围。这些多元素和双金属颗粒测量为所有传统 ICP-MS 仪器带来了新的分析挑战,因为这类仪器使用单个检测器执行连续测量。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
多种元素
安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场,湍流检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Turbulent dispersed two-phase flows are abundant in both industry and nature. The ability to
predict the behaviour of this type of flow - either using numerical or theoretical models - will
be benificial to a wide range of disciplines. However, a lack of consistent experimental data
currently makes validation of both numerical and theoretical results difficult. The main aim
of this thesis is to generate experimental data that could fill this void. In order to do so, a
facility is built to generate isotropic, homogeneous turbulence. This is done using a grid in a
vertical water channel. This new facility is validated and documented for the particle-free case
using Laser Doppler Anemometry (LDA) and Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV). The results
of both measurement techniques are in good quantitative agreement, and the flow is a close
approximation of decaying homogeneous, isotropic turbulence.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,湍流
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
在线露点仪应用解析
在线露点仪是一个紧凑的、简单易用的在线仪表,可以在-100℃~+20℃的范围内快速准确地测量干燥空气或其它气体的湿度。也可以说它是在低露点且需要控制干点的工业环境中的理想选择。它具有化学物质清除功能,这使得在高浓度化学物质和清洁剂的环境中能进行精确稳定的测量,从而保证了每次校验间隔之间的准确测量。这项功能既能通过控制系统在线执行,也能按预先设定的时间间隔定期执行。同时,在线露点仪的数字技术的先进性是显而易见的,数字信号处理和传输保证了产品高精度、可靠,传输线缆的信号衰减和干扰不会影响测量精度。
在线露点仪直接在线安装用于手套箱等用途,在此应用下不适用旁路。该装置通过1/2"MNPT或G1/2可调插入式压力配件,易于安装。应用范围包括手套箱、环境室和高空试验。在线露点仪主要用于工业湿度测量。高品质与智能化电子部件的完美结合,使得该传感器成功应用于各种极端恶劣的工业环境中。该仪器传感器采用高分子薄膜电容式原理在全量程测量精确可靠,并具有卓越的长期稳定性,它不受灰尘粒子和大多数化学物污染的影响,极适合工业环境的使用。
在线露点仪的现场校准氢气专用探头Humicap.j 抗油/抗污染符合本质安全型仪表的要求采用最新技术符合国际上的高标准适应几乎所有的测量要求 ,在干燥环境下是最理想的产品,另外,探头是抗结露、油气且适合大多数化学环境。它带有自动校准软件,软件可校正干点漂移。湿度稳定,使用再捕获过程来维护。这些智能自动校准和捕获过程使TPGSM-5100露点仪成为一个高等级设备且维护量达到最小。
在线露点仪*应用领域
在线露点仪应用领域包括石化,天然气,干燥气和压缩气,发电机冷却氢气,变压器和高压开关绝缘气,焊接气以及船舶和航空用的氧气。广泛用于电厂、冶金、科研、卫生检疫、粮食仓储、医疗器械、环境实验、比对校准、造纸和纺织、电子工业和其它工业气体水分的测量等领域。
在线露点仪*原理与结构
原理与结构:内芯为一高纯铝棒,表面氧化成氧化铝薄膜,其外涂一层多空的金膜,该金膜与内芯之间形成电容,由于氧化铝薄膜的吸水特性,当水蒸汽分子被吸入其中时,导致电容值发生变化,检测并放大该电容信号即可得到湿度大小。
在线露点仪*功能特点
● 零点自动校准
● 独有的数据自动存储及自动调出
● 首创的电量显示
● 操作简单、携带方便
● 重复性好、响应速度快
● 全量程单点法露点校准
● 斜率自动校准
● 独特的大屏数据曲线实时显示
● 先进的湿度探头保护功能
●抗油、 抗污染、抗干扰
● 灵敏度高、稳定性好、年漂移小
●简单、4-20mA双线连接
●无故障户内或户外安装
●精确的温度、湿度、露点测量
● 传感器与表体分体设计
● 多种互换性探头可供选择,适合不同场合的湿度测量
● 高精度:±0.8%RH,±0.1℃,±2℃DP(at-40℃Td)
● 可以换算露点和PPm
● 传感器自动诊断和自动修正
● 自动校准:无须任何其它设备,可定期对仪器自动校准
● 多参数显示:可显示温度,湿度,包括:露点,PPMv,克/升,LBS等
在线露点仪*技术指标
露点传感器单元:
原 理:超薄的氧化铝电容原理
量 程:-100℃~+20℃
准 确 度:±3℃
重 复 性:±0.5℃
响应时间:达到63%时用时90秒
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
北京方石亚盛科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
工业双频电容耦合射频放电,等离子体中空间和相位分辨等离子体参数检测方案(CCD相机)
The dynamics of high energetic electrons (11.7 eV) in a modified industrial
confined dual-frequency capacitively coupled RF discharge (Exelan, Lam
Research Inc.), operated at 1.937MHz and 27.118 MHz, is investigated by
means of phase resolved optical emission spectroscopy. Operating in a He–O2
plasma with small rare gas admixtures the emission is measured, with
one-dimensional spatial resolution along the discharge axis. Both the low and
high frequency RF cycle are resolved. The diagnostic is based on time
dependent measurements of the population densities of specifically chosen
excited rare gas states. A time dependent model, based on rate equations,
describes the dynamics of the population densities of these levels. Based on
this model and the comparison of the excitation of various rare gas states, with
different excitation thresholds, time and space resolved electron temperature,
propagation velocity and qualitative electron density as well as electron energy
distribution functions are determined. This information leads to a better
understanding of the dual-frequency sheath dynamics and shows, that separate
control of ion energy and electron density is limited.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
空间和相位分辨等离子体参数
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
封闭湍动流体,表面活性剂中减阻,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Many surfactants and polymers are considered as excellent drag reducing agents. This phenomenon induces
a significant head loss reduction compared to the pure solvent. In this study an aqueous solution of CTAC/NaSal
(CetylTrimethyl Ammonium Chloride and Sodium Salicylate) is used in turbulent pipe flow system. Drag
reduction experiments were carried out for different experimental conditions using pressure drop measurements.
At the same time the spatial velocity distribution was measured and analysed using particle image velocimetry
(PIV).
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
减阻,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中粒子成像测速,PIV,流场,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Memorial University purchased a Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) system in January 2004. So far it has been used to study flow around a small propeller and a tug hull. Studies have also been made to determine the best seeding particles and the best method of introducing the seeding particles into the flow. This report describes the major components of the PIV system, and the analysis software. Some studies on the selection of seeding particles were made and they are described in this report. The PIV system was used to measure the flow field around a small model propeller and a model of a tug. The results of these experiments are also described. Finally, some recommendations are made for improving the experiment procedures and analysis techniques for future experiments.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
粒子成像测速,PIV,流场,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
粒子图像强度和图像预处理中对显微PIV的影响检测方案
The depth of correlation (DOC) is an experimental parameter, introduced to quantify the thickness of the measurement volume and thus the depth resolution in microscopic particle image velocimetry (μPIV). The theory developed to estimate the value of the DOC relies on some approximations that are not always verified in actual experiments, such as the use of a Gaussian function to describe the particle image intensity distribution. In addition, the application of image pre-processing, widely used in μPIV evaluations, significantly contributes to modify the actual size of the DOC. In the presented paper, the effect of real particle image intensity distribution and image pre-processing on the thickness of the measurement volume is investigated. Furthermore, the bias error induced by the DOC in μPIV measurements is qualified on a Poiseuille flow in a microchannel. Results and guidelines to appropriately reduce the bias error due to DOC are discussed.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
对显微PIV的影响
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A stereoscopic PIV system was build to study laminar turbulent transition in pipe flow. The PIV system is based on an angular displacement of the two cameras and a 3D calibration based reconstruction method. In order to measure the cross flow over the entire cross section of the pipe, the light sheet is perpendicular to the main flow direction. Measurements have shown that the PIV system is capable of detecting the laminar and turbulent flow fields over a large portion of the pipe cross section (fig.1), with increasing errors in the near wall region.
In the error analysis, estimations and measurements of the registration error are shown (fig.2). The registration error is due to a small misalignment of the light sheet and the calibration plane. It is shown to make an important contribution to the total error. The transition measurements presented at the end of the paper are the result of brief test runs and are a good example of the kind of experiments planed for the near future.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
旋转沙床底,水流,涟漪,瞬态漩涡中漩涡动态演化机制,PIV,粒子成像测速,速度矢量场,速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
This study deals with the flow motion over the so-called rolling-grain ripples which are generated by water oscillations above a sand bed. We focus our efforts on quantifying by means of laboratory
experiments and numerical calculations the morphology and the dynamics of transient flow patterns. We report, for the first time, on the formation of an unsteady pattern with closed streamlines ~we call it ‘‘eddy’’! above rolling-grain ripples using flow visualizations and particle image velocimetry(PIV) measurements. This structure appears in the ripple trough during flow reversal and scales with the ripple wavelength. The experimental results are in qualitative agreement with the perturbative flow solution calculated by Vittori in 1989. Even if the relative ripple amplitude is not small in the experiment the perturbative expansion at the first order gives an accurate description of the flow dynamics.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
漩涡动态演化机制,PIV,粒子成像测速,速度矢量场,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
喷嘴,喷雾中流量,速度场检测方案(激光粒度仪)
Detailed atomization measurements in actual sprinklers are needed for proper
spray specification in suppression modeling and analysis. In basic pendant
sprinkler configurations, the spray originates from two streams corresponding to
flow deflected along the tines of the pendant and flow passing through the void
spaces between the tines. In this study, measurements of flow splits (between
space and tine streams), sheet breakup distances, drop size, and drop velocity
measurements were performed over a range of sprinkler geometries and injection
pressures to characterize the near-field sprinkler spray. These detailed
measurements were used to support the development of scaling laws describing
the effects of injector geometry and injection conditions on sprinkler discharge
characteristics.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流量,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2243篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等