
乙氧基脂肪醇是常用的非离子型表面活性剂。CMC随乙氧基增加而增加因此可用于描述乙氧基化程度。表征表面活性剂乙氧基含量。
方案详情

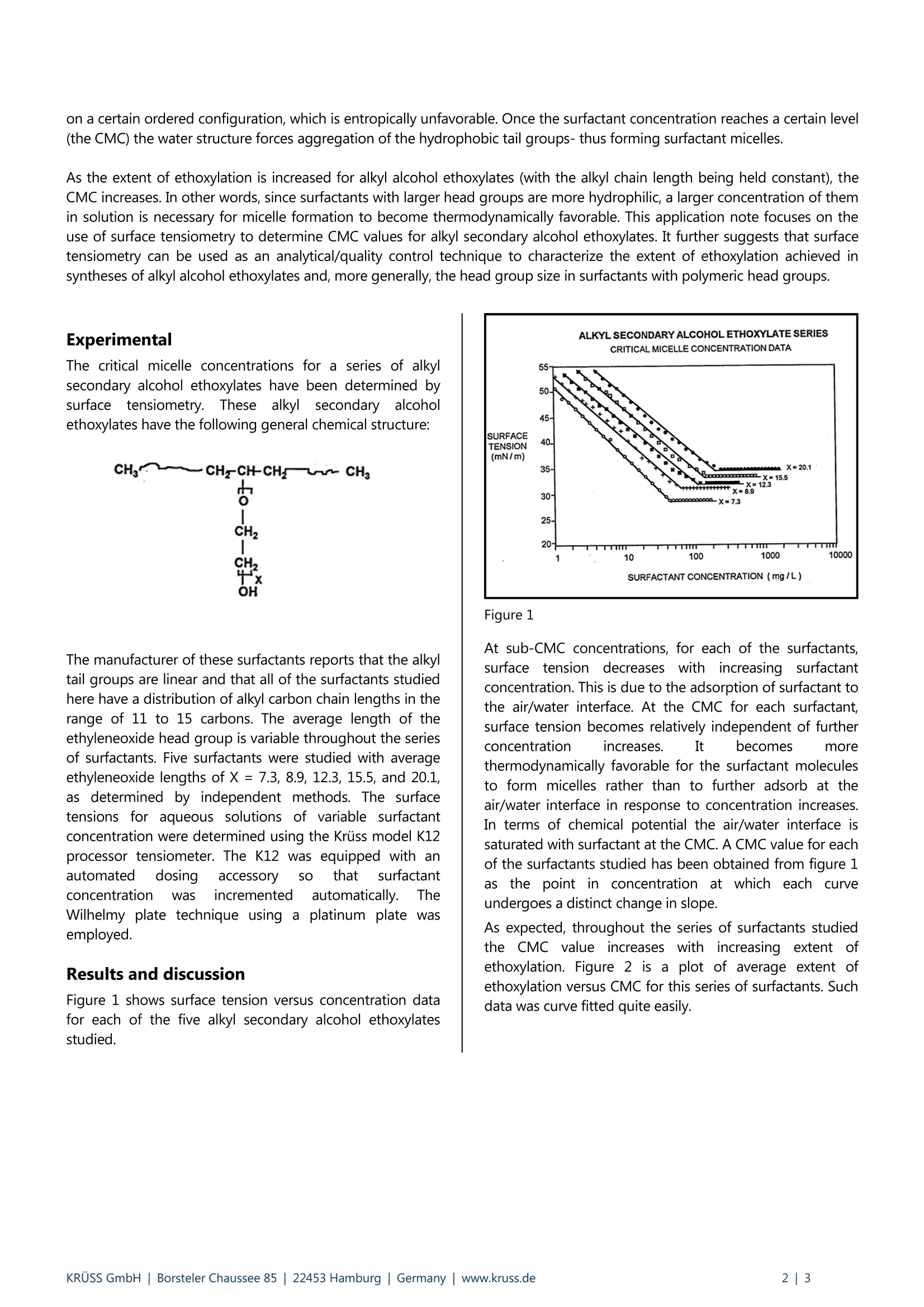
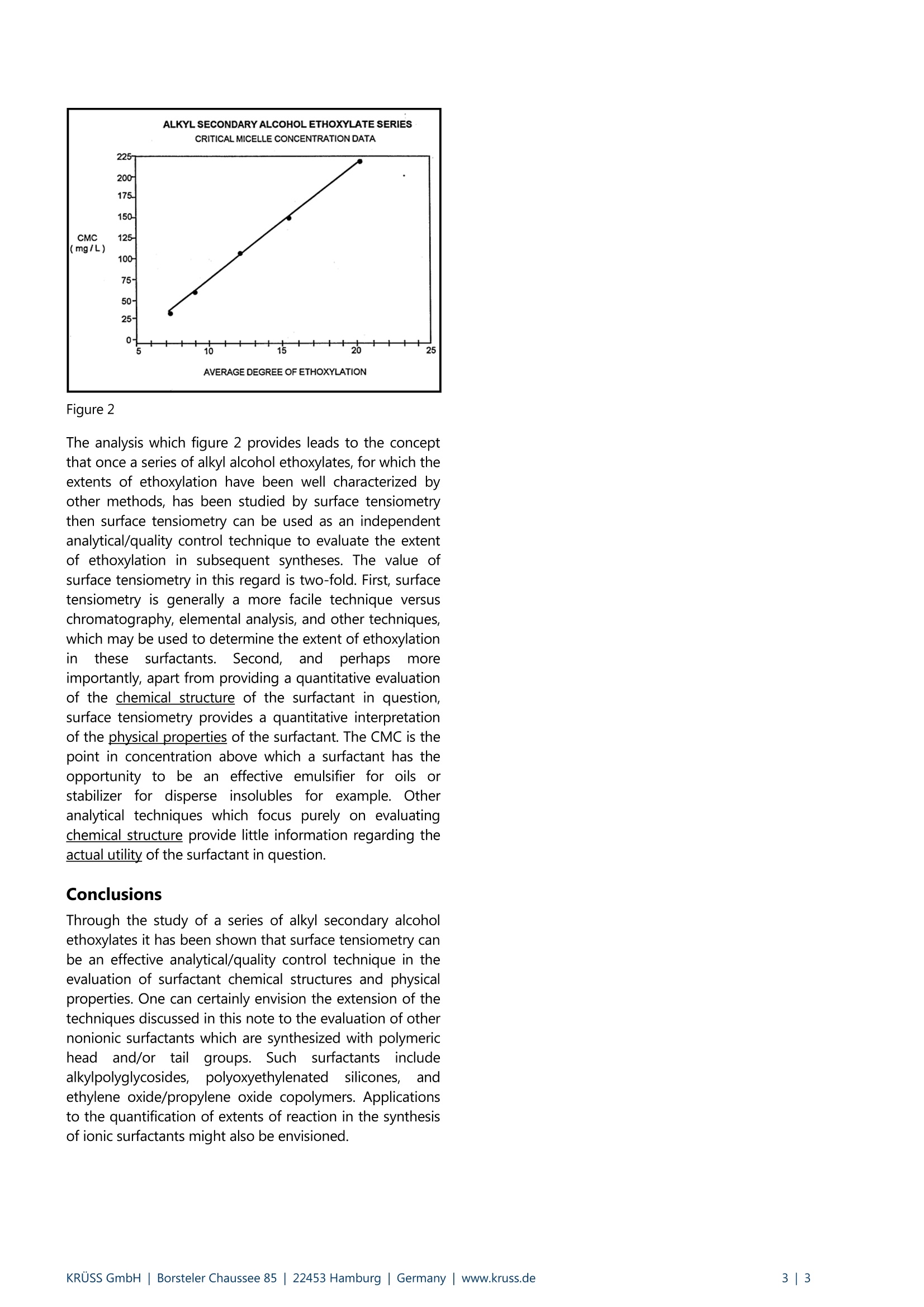
KRUSS Application Report Characterization of surfactants Application report: AR201e Industry section: Chemical Author: Christopher Rulison, Ph.D. Date: 09/1995 Method: C Force Tensiometer-K12 Keywords: Surfactant, critical micelle concentration CMC, hydrophilic-lipophilic balance HLB, surface tension Critical micelle concentration as a function of head group size for alkylalcohol ethoxylates Background Nonionic surfactants are of utmost importance in many commercial and industrial products. These compounds act as cleaners,dispersants, emulsifiers, and defoamers just to name a few applications. One of the largest advantages of nonionic surfactantsin product formulations is that, since they are non-electrolytic, their properties are largely resistant to changes in system pHand electrolyte content. In addition nonionic surfactants are generally compatible with ionic surfactants, neutral polymers, andpolyelectrolytes. Alkyl alcohol ethoxylates are among the most commonly used nonionic surfactants. These compounds are synthesized via thereaction of an alkyl alcohol with ethylene oxide to form a surfactant with an alkyl tail (hydrophobic) group and apolyethyleneoxide head (hydrophilic) group. The physical/chemical properties of alkyl alcohol ethoxylates are largelydependent on the specific and relative lengths of their head groups and their tail groups. For example alkyl alcoholethoxylates with low degrees of ethoxylation (2 to 5 ethylene oxide units in the head group) are generally only oil soluble.They are commonly used as degreasers and fiber lubricants in a variety of industries. On the other hand, alkyl alcoholethoxylates with high degrees of ethoxylation (7 to 20 ethylene oxide units in the head group for example) are generally watersoluble. These surfactants are often used as oil-in-water emulsion stabilizers and wetting agents. One of the great challenges in the synthesis of alkyl alcohol ethoxylates is to precisely control the extent and distribution ofethoxylation to produce surfactants with the desired physical/chemical properties. A number of catalysts and processingtechniques have been developed for this purpose. A strongly related analytical/quality control problem is to identify a facilephysical technique which can be used to quantify the extent of ethoxylation obtained from a given synthesis with respect tosome benchmark of surfactant performance. One of the most commonly cited benchmarks of a surfactant's physical/chemical properties is the surfactant's critical micelleconcentration. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) is the point in concentration at which it becomes thermodynamicallyfavorable for surfactant molecules in solution to form aggregates (micelles) in order to minimize the interaction of either theirhead groups or their tail groups with the solvent. For alkyl alcohol ethoxylates in aqueous solution micellization is due toentropic considerations. Water molecules in close proximity to the hydrophobic tail groups of the surfactant molecules take on a certain ordered configuration, which is entropically unfavorable.Once the surfactant concentration reaches a certain level(the CMC) the water structure forces aggregation of the hydrophobic tail groups- thus forming surfactant micelles. As the extent of ethoxylation is increased for alkyl alcohol ethoxylates (with the alkyl chain length being held constant), theCMC increases. In other words, since surfactants with larger head groups are more hydrophilic, a larger concentration of themin solution is necessary for micelle formation to become thermodynamically favorable. This application note focuses on theuse of surface tensiometry to determine CMC values for alkyl secondary alcohol ethoxylates. It further suggests that surfacetensiometry can be used as an analytical/quality control technique to characterize the extent of ethoxylation achieved insyntheses of alkyl alcohol ethoxylates and, more generally, the head group size in surfactants with polymeric head groups. Experimental The critical micelle concentrations for a series of alkylsecondary alcohol ethoxylates have been determined bysurfacee tensiometry. These alkyl/lSsecondary alcoholethoxylates have the following general chemical structure: The manufacturer of these surfactants reports that the alkyltail groups are linear and that all of the surfactants studiedhere have a distribution of alkyl carbon chain lengths in therange of 11 to 15 carbons. The average length of theethyleneoxide head group is variable throughout the seriesof surfactants. Five surfactants were studied with averageethyleneoxide lengths of X= 7.3, 8.9, 12.3, 15.5, and 20.1,as determined by independent methods.s. The surfacetensions for aqueous solutions of variable surfactantconcentration were determined using the Kruss model K12processor tensiometer. The K12 was equipped with anautomatedddosing accessorv SO thatt ssurfactantconcentration was incremented automatically. TheWilhelmy plate technique using a platinum plate wasemployed. Results and discussion Figure 1 shows surface tension versus concentration datafor each of the five alkyl secondary alcohol ethoxylatesstudied. Figure 1 At sub-CMC concentrations, for each of the surfactants,surface tension decreaseswithincreasing surfactantconcentration. This is due to the adsorption of surfactant tothe air/water interface. At the CMC for each surfactant,surface tension becomes relatively independent of furtherconcentration increases. It becomes morethermodynamically favorable for the surfactant moleculesto form micelles rather than to further adsorb at theair/water interface in response to concentration increases.In terms of chemical potential the air/water interface issaturated with surfactant at the CMC. A CMC value for eachof the surfactants studied has been obtained from figure 1as;tthe point in concentration at which each curveundergoes a distinct change in slope. As expected, throughout the series of surfactants studiedthe CMC value increaseswithincreasing extent oofethoxylation. Figure 2 is a plot of average extent ofethoxylation versus CMC for this series of surfactants. Suchdata was curve fitted quite easily. Figure2 The analysis which figure 2 provides leads to the conceptthat once a series of alkyl alcohol ethoxylates, for which theextents of ethoxylation have been well characterized byother methods, has been studied by surface tensiometrythen surface tensiometry can be used as an independentanalytical/quality control technique to evaluate the extentof ethoxylation in subsequent syntheses. The value ofsurface tensiometry in this regard is two-fold. First, surfacetensiometry is generally a more facile technique versuschromatography, elemental analysis, and other techniques,which may be used to determine the extent of ethoxylationnthesesurfactants.5.Second,andperhapssmoreimportantly, apart from providing a quantitative evaluationof the chemical structure of the surfactant in question,surface tensiometry provides a quantitative interpretationof the physical properties of the surfactant. The CMC is thepoint in concentration above which a surfactant has theopportunity to be an effective emulsifier for oils orstabilizer for disperse insolubles for example. Otheranalytical techniques which focus purely on evaluatingchemical structure provide little information regarding theactual utility of the surfactant in question. Conclusions Through the study of a series of alkyl secondary alcoholethoxylates it has been shown that surface tensiometry canbe an effective analytical/quality control technique in theevaluation of surfactant chemical structures and physicalproperties. One can certainly envision the extension of thetechniques discussed in this note to the evaluation of othernonionic surfactants which are synthesized with polymericheadand/or tail groups. Suchsurfactantsincludealkylpolyglycosides,polyoxyethylenateddssilicones,,aandethylene oxide/propylene oxide copolymers. Applicationsto the quantification of extents of reaction in the synthesisof ionic surfactants might also be envisioned. KRUSS GmbH |Borsteler Chaussee Hamburg| Germany|www.kruss.dei
确定

还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
克吕士科学仪器(上海)有限公司为您提供《表面活性剂中CMC检测方案(表面张力仪)》,该方案主要用于其他中CMC检测,参考标准--,《表面活性剂中CMC检测方案(表面张力仪)》用到的仪器有
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多








