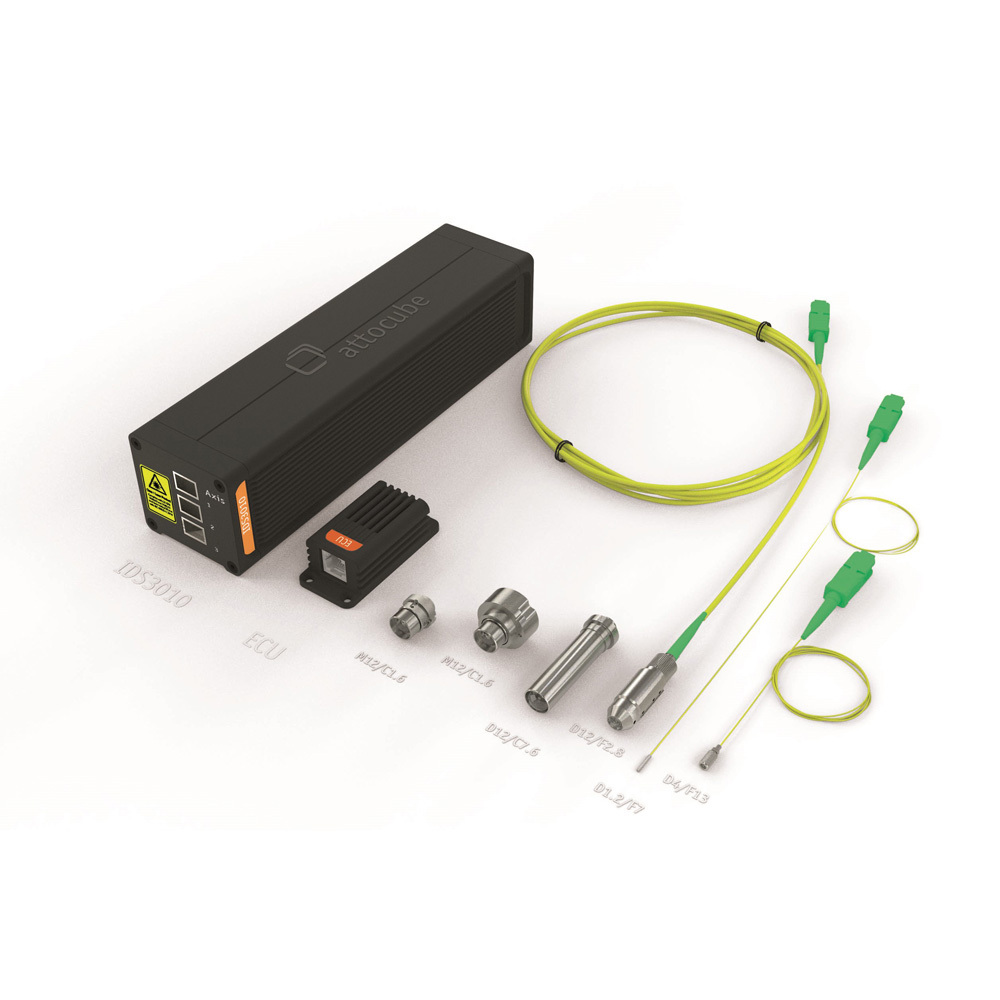
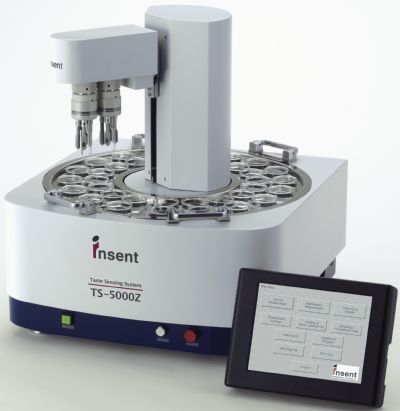
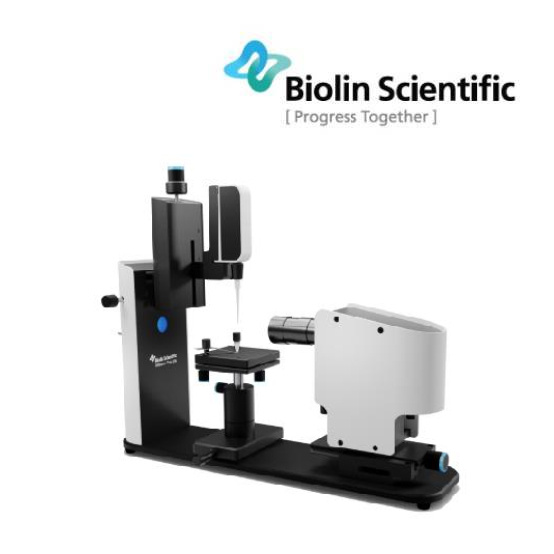
扫描荧光X射线显微镜中激光干涉仪检测方案(激光干涉仪)
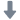
在搭建具有纳米分辨率的X射线显微镜时,对于系统稳定性的要求提出了更高的要求。在整个过程中实验过程中,必须确保各个组件以及组件之间的热稳定性和机械稳定性。德国attocube的IDS3010激光干涉仪具有优异的稳定性和测量亚纳米位移的能力,表现出优异的性能。IDS3010在40小时内具有优于1.25nm的稳定性,并且在100赫兹带宽的受控环境中具有优于300pm的分辨率。因此,IDS3010是对所述X射线显微镜装置中使用的所有部件进行机械控制的不二选择,使得整个X射线显微镜实现了40nm的分辨率,而在数据收集所需的整个时间内系统稳定性优于45nm。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
激光干涉仪
QUANTUM量子科学仪器贸易(北京)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
盘芯喷嘴质量平衡中体积有效性判定检测方案(气溶胶)
The mass balance of orchard air-blast sprayers has historically been assessed using an array of samplers
to capture airborne particles. However, these methods only provide an idea of flux with no other information
which is pertinent to understand the movement of droplets and their potential to drift. While
droplet analysis for agricultural sprayers has always been conducted in a laboratory setting with the use
of laser devices, a new phase Doppler approach is being explored to assess droplet spectra, velocity, and
flux in outdoor field conditions. Therefore it is the objective of this study to develop a methodology and
the potential limitations for using a phase Doppler system while in a laboratory setting. Due to the
expected variability of field conditions as well as the turbulence of orchard sprayers, a computational
approach was sought to assess flux from a single scan of a conical spray plume's diameter. Using a
constant scanning speed of 0.0079 m/s, a disc core (D1/DC33) hollow cone nozzle was examined at 310,
410, and 520 kPa pressure at five different heights (10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 cm). Computational flux was
then compared to the actual flow rate, finding a 3.3% average error with a range of 16.9% and 4.7%
illustrating a small underestimation of mass with the phase Doppler which was related to distance and
droplet frequency. Further, comparisons were also assessed including pattern/symmetry, droplet spectra,
velocity, and the overall number of samples. The proposed methodology indicates potential for the use of
phase Doppler technology for in situ measurements of spray equipment using a conical-type spray
nozzle, such as that of the orchard air-blast sprayer.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
体积有效性判定
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
不导电样品中样品喷镀及不喷镀扫描电镜成像对比检测方案(扫描电镜)
对导电性不好的样品进行喷镀处理,一是可避免材料荷电。所谓荷电是入射电子的量大于产生的二次电子或者背散射电子的数量,从而导致在材料表面形成电子的富集(产生负电位)。由于负负相斥的原理,使得后面的入射电子不能在材料表面会聚,产生一系列的后果,例如聚焦不太容易聚清楚,表面形成一道一道白色的二次电子突然放电的现象。因此要得到满意的形貌,应该在材料表面形成一个有效的电子通路,即在样品台和材料表面有导电通路。最佳的办法就是在表面镀膜,这就是为什么扫描电镜要镀膜的原因。另一个原因是增加二次电子发射率,使图像信噪比增强,使图片看上去更漂亮。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
样品喷镀及不喷镀扫描电镜成像对比
复纳科学仪器(上海)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
电子鼻用于脂质高分子膜甜味传感器的响应物质
A sweetness sensor with lipid/polymer membranes has been developed for evaluatingthe sweetness of sugars and sugar alcohols. Among the constituents of lipid/polymermembranes, gallic acid has been used as the main substance involved in sucrose responsein our group. In this study, as a step toward understanding the response mechanism ofthe sweetness sensor, functional groups of gallic acid, namely, carboxyl and hydroxylgroups, were focused on. Theresultsdemonstrated that the carboxyl group is essentialfor the sweetness sensor, whereas the hydroxyl group is not always necessary for thesucrose response. It was also revealed that the phosphate group may be a substitutefor the carboxyl group. Then, for one of the sensors with the highest response to a 300mM sucrose solution, named the sweetness sensor GL1, the basic characteristics suchas selectivity and correlation with sweetness were investigated. The behavior of GL1sensor outputs was relatively similar to the sweetness perception in humans.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
北京盈盛恒泰科技有限责任公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
镀膜材料中定性和厚度分析检测方案(红外光谱仪)
FTIR 检测技术一直用于涂布工艺,但过去主要是 用于研究和开发应用,因为传统的 FITR 仪器必须 在实验室环境中使用,必须将小型样品或大型样品的小片送往实验室进行分析,而不能在关键时刻或生产过程中进行测量。安捷伦的手持式 FTIR 系统采用创新的采样技术,使得 FTIR 分析仪不仅限于实验室分析,还能用于生产车间或者需要对样品进行分析的任何地点。此性能对于需要在现 场进行测量,或者由于样品体积过大而无法在实 验室条件下进行测量的情况意义重大,因为并非所有样品都可以在出现问题时取一小片带回实验室进行测量。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
定性和厚度分析
安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
盐酸盐中超声波纳米结晶利用度检测方案(超声波萃取仪)
水杨酸盐是被称为水杨酸盐的一类天然化学物质的一部分,是最古老的处方药,抗炎药 [1]。最常见的水杨酸盐是乙酰水杨酸(ASA)(拜耳公司于1899年由阿司匹林生产的阿司匹林),其主要生化功能是通过抑制环氧合酶(COX)减轻炎症和发烧[2]。在上个世纪,有人提出水杨酸酯可能具有其他医学益处,特别是在轻度糖尿病患者中[3,4,7]。阿司匹林已被施用于糖尿病前期/肥胖症患者,以阻止疾病的发展。不幸的是,阿司匹林抑制COX会导致出血,血小板聚集和胃调节异常[8,9]。 盐酸盐具有与阿司匹林相似的抗炎特性,但已证明对肠道的损害明显较小[10]。为了使药物的生物利用度最大化并促进有效的治疗,必须对盐酸盐簇进行纳米结晶,以将其中值粒径减小到一微米以下[12]。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
超声波纳米结晶利用度
图拉扬科技有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
量子点中光致发光谱检测方案(分子荧光光谱)
Particle size and composition can control quantum confinement. QDs may assist deep-tissue molecular imaging in living systems, because of their near-IR and far-red fluorescence away from aqueous absorption. QDs also provide absorption coefficients much larger than typical organic dyes. The ultrasensitive FluoroMax spectrofluorometer is useful for research related to nanostructures and materials science.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
光致发光谱
HORIBA(中国)
查看联系电话
前往展位
螺栓中氢气预热器连接螺栓失效分析及解决对策检测方案(电镜部件)
从断口宏观特征、材质、断口电镜形貌以及微观组织等方面对发生断裂的氢气预热器连接螺栓进行了分析 ,结果表明 ,螺栓断口腐蚀产物为单纯的 FeS晶粒。根据高温硫腐蚀机理分析 ,确定该连接螺栓的断裂是一起典型的高温硫环境下的应力腐蚀开裂失效案例 ,主要是由于工作介质中含有硫化氢或者硫蒸汽所致。建议提高材料等级 ,采用 0Cr18N i10Ti不锈钢螺栓 ,以解决腐蚀问题。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
氢气预热器连接螺栓失效分析及解决对策
参考标准:
HJ 766-2015 固体废物 金属元素的测定 电感耦合等离子体质谱法
北京欧波同光学技术有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
颗粒中粒度分布检测方案(激光粒度仪)
颗粒测量技术可分为高分辨(分离)技术和Ensemble粒度分析技术《1》。高分辨率技术的特点是因为在颗粒测量分析的过程中,粒子可以根据大小或者质量的不同而进行分离。Ensemble粒度分析技术在没有物理分离的情况下对所有粒子同时进行测量。高分辨的粒度分析技术包括毛细管流体分离(CHDF)、场流分离、单颗粒计数和圆盘离心组成。Ensemble粒度分析技术包括激光衍射、数字相关技术(PCS)、声衰减光谱和浊度测定方法等。电镜也属于高分辨粒径测量的技术,但是其并不能在分析的过程中将颗粒进行分离。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
粒度分布
上海胤煌科技有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
各种类型样品中纳米颗粒表征与定量检测方案(等离子体质谱)
工程制造的纳米颗粒在提高半导体材料到食品、药品、化妆品以及消费品等各类产品的性能或性质方面的使用正在迅速增加。由于这些材料的理化性质较为新颖,它们的许多环境归宿和毒理学性质仍然不为人知。因此,人们对一种能够快速、准确而灵敏地完成各种类型样品中纳米颗粒表征与定量的技术的需求也日益增长。通过近期实现的一些针对特定应用的硬件和软件增强功能,ICP-MS 已证明能够满足这些要求。
• 高灵敏度 ― 小颗粒的信号强度随直径的立方而降低
• 低背景可改善小粒径的检测
• 时间分辨模式中的快速扫描,扫描间的稳定时间降至最短
• 即使在快速扫描模式下也可有效去除多原子干扰
• 管理复杂计算和超大数据集的专用软件
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
纳米颗粒表征与定量
安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
云微观物理特性中液滴粒径,液滴速度,液态水含量检测方案(气溶胶)
High-level Nitrogen oxides (NOx) released to the atmosphere cause health and environmental hazards. Conventional power plants are required to have NOx emission control systems to abide by local environmental regulations. Com-mon post-combustion techniques include selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) or selective catalytic reduction (SCR) techniques. SNCR is a proven technology that can be implemented virtually without affecting existing indus-trial operations with low capital cost. SNCR is a method involving either aqueous ammonia or urea as the reagent injected into flue gas in the boiler/furnace within specific temperature range. This method commonly reduces the emission of NOx by 30-50%. However, high reductions can be achieved by system optimization. Placement within the proper temperature window, distribution within the cross section and residence time of reagent significantly in-fluence performance of an SNCR system. Therefore, spray lance and nozzle design is crucial for assurance of oper-ating efficiency and ammonia utilization.
In this paper, an SNCR system in a circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boiler was studied with using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations, as it relates to spray technology. The simulation solves Navier-Stokes equa-tions with heat and mass transfer using ANSYS Fluent SNCR model with Lagrangian multiphase models and spe-cies transport model. CFD was used to diagnose the gas phase behavior and thermal distribution, to determine opti-mal spray placement and maximum penetration. The focus of this work was the parameters of the injection, which were determined based on test data acquired through in-house laboratory equipment. Temperature profile, pollutant reduction, ammonia slippage and wall impingement were used from the CFD results to assist determining the best spray design to achieve the greatest efficiency.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
液滴粒径,液滴速度,液态水含量
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2256篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有《HJ 766-2015 固体废物 金属元素的测定 电感耦合等离子体质谱法》、《无水葡萄糖-2015年版药典标准》等