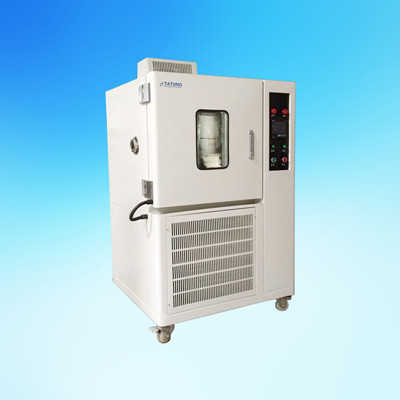
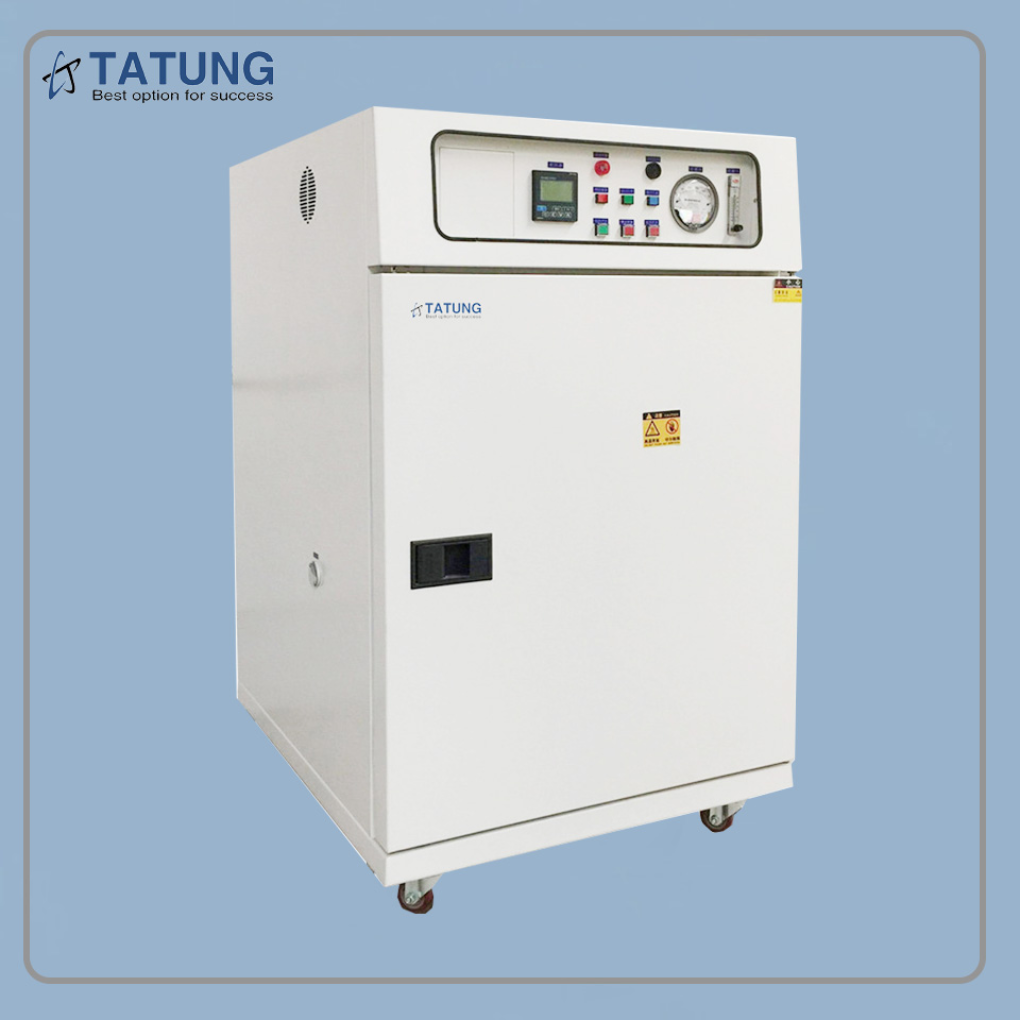
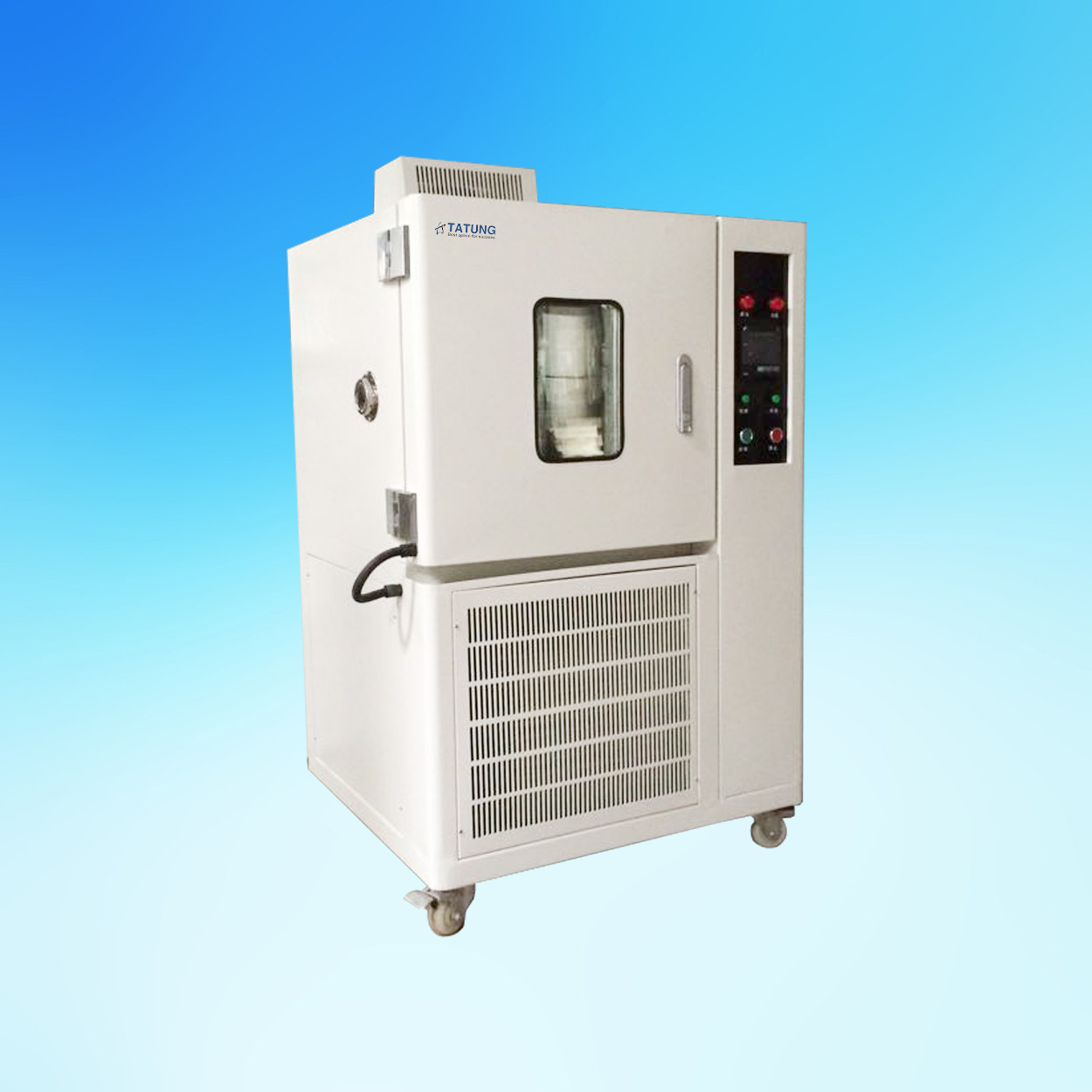
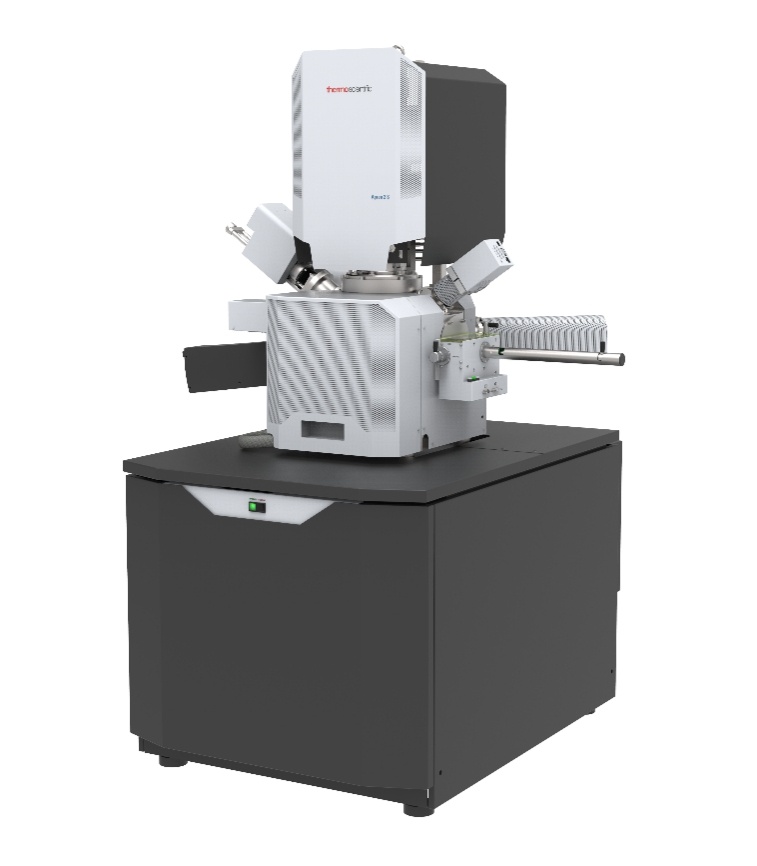
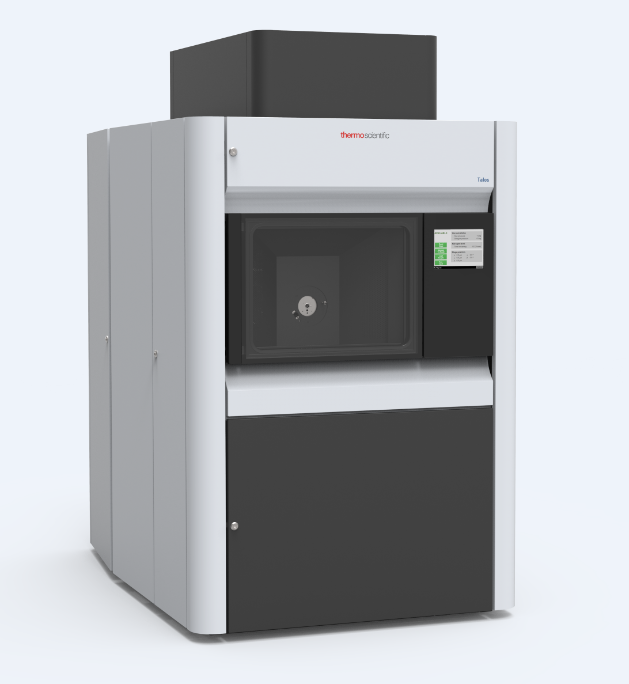
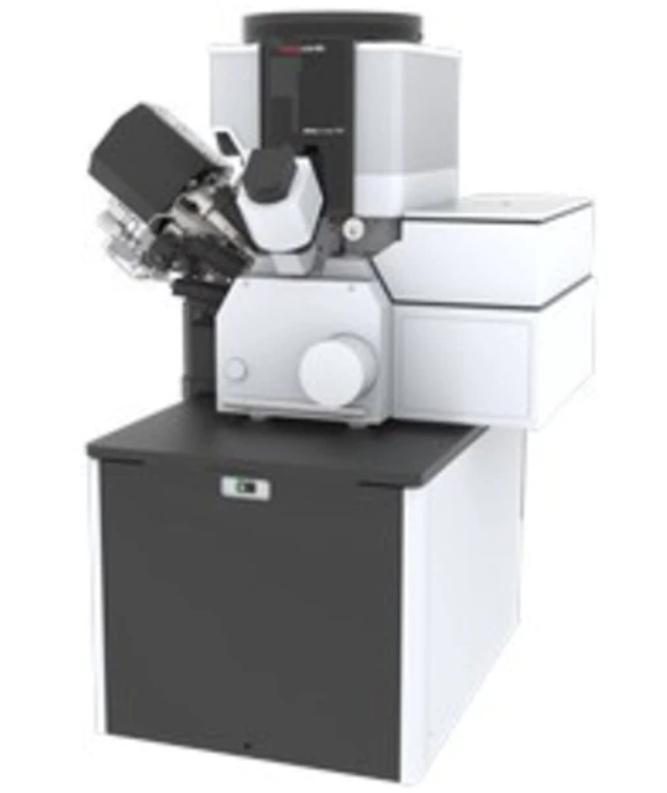
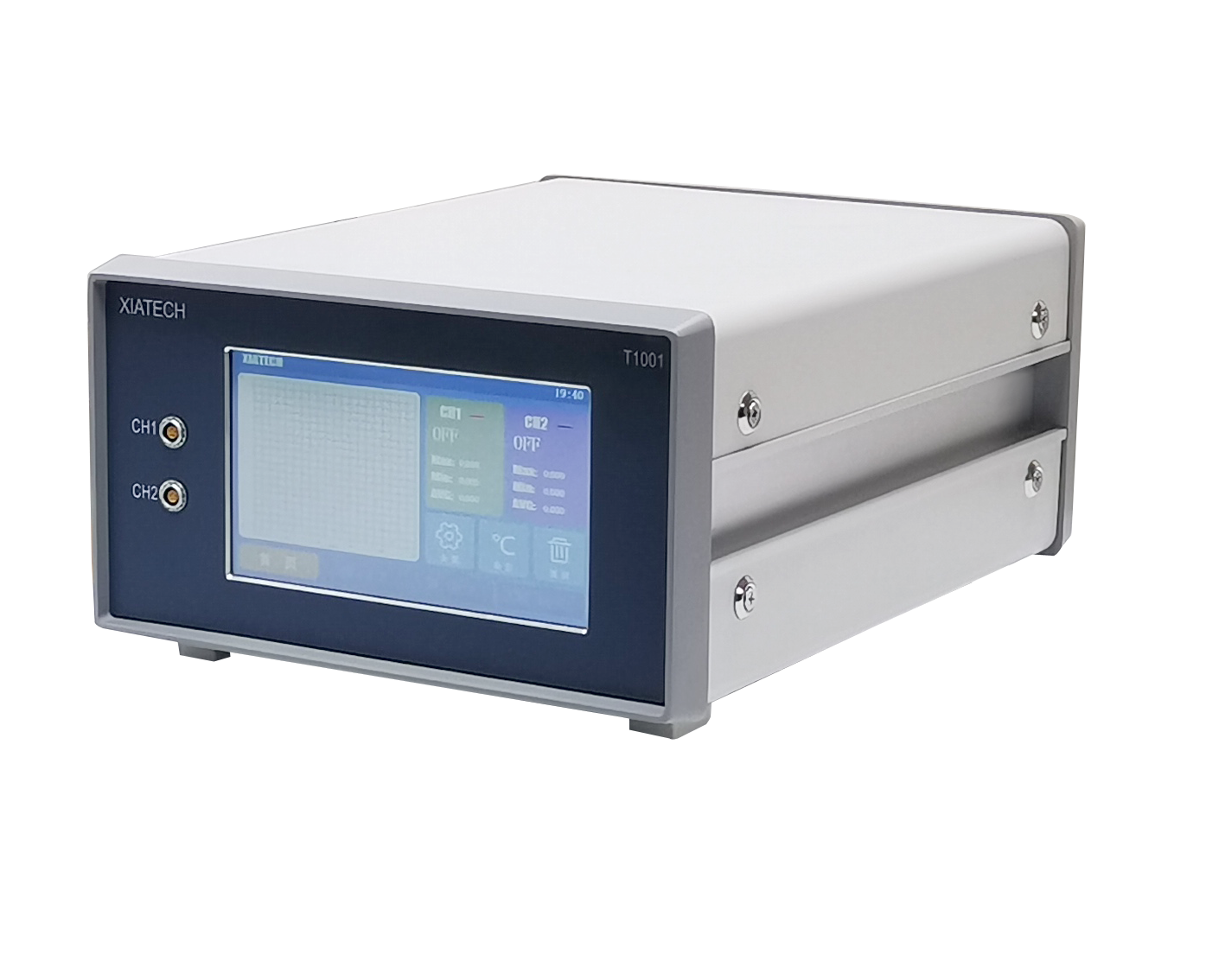
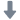
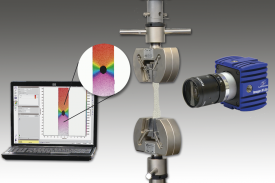
隔热材料中高温比热检测方案
本文介绍了采用下落式量热计方法开发的一种温度范围为100~1000℃的材料比热容测量装置。由于绝热材料一般密度低、气孔率高、低导热系数和热容较小,所以绝热材料的比热容很难准确测量。通过此开发的测试设备,采用将被加热试样落入水中的下落法,可以很容易的进行绝热材料比热容测量,所得到的测量结果是从下落前试样温度与试样下落后水平衡温度之间的平均比热容。采用此测试设备对标准参考材料SRM 720人造蓝宝石进行了测试,测试结果与标准数据偏差小于±10%。对碳化硅耐火材料、岩棉、硅铝矾土硅石纤维、硅铝矾土硅石板、硅酸钙和二氧化硅玻璃等材料进行了测试。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
高温比热
上海依阳实业有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
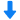
流场中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We present in this paper a novel collaborative scheme
dedicated to the measurement of velocity in fluid experimental
flows through image sequences. The proposed technique
combine the robustness of correlation techniques with
the high density of global variational methods. It can be considered
either as a reenforcement of fluid dedicated opticalflow
methods towards robustness, or as an enhancement of
correlation approachs towards dense information. This results
in a technique that is robust under noise and outliers,
while providing a dense motion field. The method was applied
on synthetic images and on real experiments in turbulent
flows carried out to allow a thorough comparison with a
state of the art optical-flow and PIV methods.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
高低温试验箱的收货注意事项
高低温试验箱,高低温湿热试验箱,交变湿热试验箱,恒温恒湿箱等环境试验设备的安全运输方式
这些仪器设备因为都安装了制冷压缩机装置,因此我们包装上注明:精密仪器,不可倾斜.物流运输时,一定要使用专用的升降机或者叉车置放于车上或卸货,对于物流运输人员不按规定卸货造成的设备损坏,要按照相关的承运合同,物流公司要给予该设备的损坏程度的一定经济赔偿,同时我们还要与用户协商沟通,并及时补发货物给用户,尽量减少因货物损坏造成的时间耽搁.
用户签收货物时注意的事项:
1.对于送货上门的物流公司,买家收货人员首先要监督一下卸货情况,卸车后并检查一下外包装有无损坏,如发现外包装破损,请跟物流公司协商能否打开包装查看设备有无损坏,如果设备没有损坏的情况下,方可签收物流运单,如果发现运输损坏,请不要签收物流运单,及时致电给卖家,让卖家处理.
2.对于货到自提的用户,需要去物流站点去提货,提货前验收货物与送货上门的一致.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
上海实贝仪器设备厂
查看联系电话
前往展位
浅水池模型中两维浅水池模型中设置麦仙翁栖息地模型:应用于浅水湾检测方案(粒子图像测速)
This paper presents a methodology to evaluate the stability of cockles in shallow estuaries for different hydrodynamic
conditions. Two methodologies are proposed in order to determine the suitability of the different regions of the estuary
for cockles. Considering the complexity of all the processes which determine the movement of cockles, the
methodology proposed here is intended to be a first approach to the problem taking into account only hydrodynamic
variables, although the inclusion of biological variables is being studied at the present time. The aim of this work is to
stablish an objective criteria for comparing the stability of cockles in different parts of an estuary under different
hydrodynamic conditions. In order to perform this analysis we have developed a cockle habitat model model which
considers the hydraulic characteristics of cockles and the flow patterns in the estuary.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
两维浅水池模型中设置麦仙翁栖息地模型:应用于浅水湾
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
碳烟中碳烟体积分数,碳烟初级粒径检测方案(烟气分析仪)
Laser-Induced Incandescence (LII) occurs when a high-energy pulsed laser beam
encounters graphitic particulate matter particles like soot or carbon black. The
particles absorb laser energy from the beam and see an increase in their internal
energy, resulting in an increase of temperature. At the same time, the particles loose
energy through heat transfer mechanisms. If the energy absorption rate is sufficiently
high, particle temperature will rise to levels where significant incandescence
(blackbody emission) can occur .Typically, Laser-Induced Incandescence produces
50ns to 1μs long light pulses at atmospheric pressure.
So far, LII measurements had been restrained to conduction-dominated conditions,
whereby signals are short-lived (less than one microsecond) and require sensitive
nanosecond resolution instrumentation. This thesis introduces a novel LII – based
measurement method performed under high vacuum conditions. The novelty of LII
under vacuum resided in the fact that heat conduction away from the soot particle
becomes negligible below 10-2 mbar and this constituted a step away from the typical
situation, whereby laser absorption is followed by heat conduction from the particles
to the surrounding medium. Instead, sublimation and radiative heat transfer would
follow laser absorption. The consequence was the obtention of long-lived LII signals
(up to 100 microseconds) and a large gain of photons (ranging between 50 to 300)
emitted per primary soot particle during LII temperature decays. Furthermore, the
refractive index function E(m) value could be determined directly from measured
radiative temperature decays, with potentially an uncertainty of circa 7%, which
outperformed current soot extinction measurements. In addition, for laser fluences
below 0.06 J/cm2, a regime where only laser energy absorption and radiative heat
transfer apply would be reached and LII signals became independent of particle size.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
碳烟体积分数,碳烟初级粒径
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
飞机模型中襟翼喷射飞机模型的漩涡分析检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The wake behind a simpli¯ed model of a generic aircraft (the SWIM model) is measured
in the Low Speed Low turbulence wind tunnel (LSL) at Delft University of Technology.
Two measurement techniques have been used in order to qualitatively and quantitatively
measure the wake, i.e. stereoscopic particle image velocimetry (Stereo PIV) and a 5 hole
probe (5HP). Furthermore balance measurements have been carried out over a range of
con¯gurations for later comparison purposes. The goal of the wake measurements is to
give a comparison between the two measurement techniques.
The 5HP measurements are processed using a windows based program called Pressure
Field Visualisation. This program calculates vector ¯elds from the input pressure data
and has several exporting options. The Stereo PIV measurements are correlated using
DaVis 7.3 using a window size of 16 x 16 pixels with 50% overlap.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
襟翼喷射飞机模型的漩涡分析
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场,时空相关性检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Dual particle image velocimetry (dual PIV) measurements have been performed to investigate the space–time
correlations in two subsonic isothermal round jets at Mach numbers of 0.6 and 0.9. The correlation scales are
analyzed along the centerline and in the shear-layer center over the first 11 jet diameters from the nozzle exit. To
provide robust results over a wide range of flow conditions, these correlation scales are given in terms of their
appropriate quantities, namely, the mean or rms velocity in reference to velocity and the momentum thickness or the
half-velocity diameter in reference to length in the shear layer and on the jet axis, respectively. From these results, a
discussion on the modeling of turbulence in jets is addressed. The self-similarity of some space correlation functions
in the shear layer and on the jet axis is shown. Furthermore, far enough downstream in the shear layer, some of the
ratios between the space and time scales are relatively close to the values expected in homogeneous and isotropic
turbulence. It is also found that the ratio between the integral length and the time scales in the fixed frame is of the
order of the local mean flow velocity. In the convected frame, the appropriate scaling factor is the rms velocity.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,时空相关性
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
火焰,氢燃料中组分,温度,自由基,羟基检测方案
We report on spatially resolved simultaneous measurements of temperature and majority species
concentrations along a line segment in a premixed laminar H2-air flame. The results are obtained from
Raman and Rayleigh scattering by using a narrow-band KrF excimer laser and a spectrally and spatially
resolving detector system that consists of a high-throughput spectrometer and a gated, intensified,
two-dimensional CCD camera. The data presented here are integrated over 100 laser shots. Absolute
density profiles of N2, 02, H20, and H2, as well as temperature profiles at various heights through the
flame, are presented. A discussion of the required calibration procedures and a summary of the
necessary spectroscopic background are also included in this paper.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
组分,温度,自由基,羟基
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
气相聚合反应器中水动力学研究,流场,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Polyolefins are polymers produced from olefins such as ethylene and/or
propylene. Although polyolefins can be produced via different production
methods, the gas-phase polymerization process based on fluidized
bed reactor technology is the most important method for the production
of polyethylene since the 1980’s and also polypropylene is increasingly
produced via the gas-phase polymerization process. Although fluidized
bed reactors have been employed for several decades in the chemical
industry, quantitative information on solids motion and macroscopic
circulation patterns is still incomplete.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
水动力学研究,流场,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
液滴中粒径,速度检测方案(激光粒度仪)
This paper discusses the measurement of transparent particles and droplets from a few microns to mm in diameter with the Droplet Imaging Velocimeter and Sizer (DIVAS), a two-dimensional technique to measure particle size and velocity. Unlike Interferometric Laser Imaging for Droplet Sizing (ILIDS), DIVAS can measure sprays with realistic concentrations, size distributions from microns to millimeters, and non-spherical spray features. The measurement of particles with a broad range of diameters is discussed to illustrate the capability of DIVAS and signal analysis strategies are suggested to expand the measurement envelop and accuracy of the technique. DIVAS uses a Particle Imaging Velocimetry (PIV) configuration; that is, pulsed lasers illuminate the droplets in the measurement plane and CCD cameras collect the off-axis scattered light, thus yielding a small measurement volume and correspondingly a high number density measurement capability. Particle sizing is based on measuring the separation of cross-polarized glare points captured by two separate cameras.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
粒径,速度
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
葡萄糖中加入二氧化硅分散剂后粒径检测方案(激光粒度仪)
摘 要:
葡萄糖(Dextrose),又称右旋糖,遇水易发生结晶,微溶于乙醛,不溶于乙醚和芳香烃。葡萄糖是生物代谢中的关键中间物质,食品工业用作甜味料(甜度约为蔗糖74%)。葡萄糖的粒径大小和形状可直接影响到食品添加剂的口感和保质期,由于其物质密度很低,通常的粒径分析方法不易得到准确的结果,在葡萄糖粉末中,加入气相二氧化硅作为分散剂,用RETSCH TECHNOLOGY公司的CAMSIZER粒径及形态分析仪进行粒径大小和形态的分析,可以得到准确而直观的结果。
Glucose(Dextrose)is easy to be crystallized and dissolve in the acetaldehyde while it is not to be dissolved in ether and arene. The glucose is a key intermediate relating to metabolism. it is used to be sweet flavor in food industry. The particle size and shape of glucose can influence the tasting of food and quality period. Because of its low density, it is very difficult to analysis it with sieve and laser instruments. Mixed with the gas-silicon and using CAMSIZER can help to get the correct results and images.
关键词:葡萄糖、气相二氧化硅、粒径、形态、CAMSIZER
Key words:Dextrose, Gas phase silicon, particle size, shape, CAMSIZER
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
加入二氧化硅分散剂后粒径
弗尔德(上海)仪器设备有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
湍动,稳定环形分层火焰中速度场,自由基,羟基,浓度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A burner for investigating lean stratified premixed flames propagating in intense
isotropic turbulence has been developed. Lean pre-mixtures of methane at different
equivalence ratios are divided between two concentric co-flows to obtain annular
stratification. Turbulence generators are used to control the level of turbulence intensity
in the oncoming flow. A third annular weakly swirling air flow provides the flame
stabilization mechanism. A fundamental characteristic is that flame stabilization does
not rely on flow recirculation. The flames are maintained at a position where the local
mass flux balances the burning rate, the result is a freely propagating turbulent flame
front. The absence of physical surfaces in the vicinity of the flame provides free access
for laser diagnostics.
Stereoscopic Planar Image Velocimetry (SPIV) has been applied to obtain the three
components of the instantaneous velocity vectors on a vertical plane above the burner
outlet where the flames propagate. The instantaneous temperature fields have been
determined through Laser Induced Rayleigh (LIRay) scattering. Planar Laser Induced
Fluorescence (PLIF) on acetone has been used to calculate the average equivalence ratio
distributions. Instantaneous turbulent burning velocities have been extracted from SPIV
results, while flame curvature and flame thermal thickness values have been calculated
using the instantaneous temperature fields. The probability distributions of these
quantities have been compared considering the separate influence of equivalence ratio
stratification and turbulence.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,自由基,羟基,浓度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体轨迹相关方法中提高时间分辨PIV测量的速度动态范围和精度检测方案
A novel method is introduced for increasing the accuracy and extending the dynamic range of
time-resolved PIV. The approach extends the well-known concept of multiframe particle tracking
velocimetry (PTV) to cross-correlation analysis employed by PIV. The working principle is based on the
determination of fluid element trajectories by tracking their position across an image sequence. The fluid
trajectory correlation (FTC) algorithm deals with the effect of trajectory curvature and non-uniform velocity
during the considered time interval by allowing the motion within the trajectory to be nonlinear. In addition,
the local image deformation accounts for the spatial velocity gradient and its change along the trajectory.
The principle for reduction of the measurement error is threefold: by enlarging the temporal
measurement interval, the relative error becomes smaller; secondly, the random error is reduced with the use
of a least-squares polynomial fitting approach to the individual trajectory; and finally, the use of nonlinear
fitting functions allows for a reduction in truncation errors. The evaluation of velocity proceeds then directly
from the analytical derivatives of the least-squares functions. The principal features of this algorithm are
compared with a single-pair iterative image deformation method through the use of synthetic image
sequences depicting steady flows (solid body rotation and uniform motion), and with an application to an
experimental data set of a submerged circular jet.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
提高时间分辨PIV测量的速度动态范围和精度
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
电容中不同压力下电容耦合射频放电鞘层区域的电场反转检测方案(CCD相机)
Electric field reversals in single and dual-frequency capacitively coupled radio frequency
discharges are investigated in the collisionless (1 Pa) and the collisonal (65 Pa) regimes.
Phase resolved optical emission spectroscopy is used to measure the excitation of the neutral
background gas caused by the field reversal during sheath collapse. The collisionless regime is
investigated experimentally in asymmetric neon and hydrogen single frequency discharges
operated at 13.56MHz in a GEC reference cell. The collisional regime is investigated
experimentally in a symmetric industrial dual-frequency discharge operated at 1.937 and
27.118 MHz. The resulting spatio-temporal excitation profiles are compared with the results of
a fluid sheath model in the single frequency case and a particle-in-cell/Monte Carlo simulation
in the dual-frequency case. The results show that field reversals occur in both regimes. An
analytical model gives an insight into the mechanisms causing the reversal of the electric field.
In the dual-frequency case a qualitative comparison between the electric fields resulting from
the PIC simulation and from the analytical model is performed. The field reversal seems to be
caused by different mechanisms in the respective regimes. In the collisionless case it is caused
by electron inertia, whereas in the collisional regime it is caused by a combination of the low
mobility of electrons due to collisions and electron inertia. Finally, the field reversal during the
sheath collapse seems to be a general source for energy gain of electrons in both single and
dual-frequency discharges.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
不同压力下电容耦合射频放电鞘层区域的电场反转
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中2D3C速度矢量场,时间分辨速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In the last years, several techniques have been developed and improved in such a way that it is
possible to measure the three velocity components in a flow. Some techniques as Stereoscopic PIV or
holographic PIV are well known. Others, like tomographic PIV started to develop more recently.
Stereoscopic Particle Image Velocimetry (SPIV) or Tomographic PIV need a complex set-up, involving flow
visualization with several cameras, and present important restrictions when applied to confined liquid flows.
Others like Holographic PIV cannot be applied in flows with a high particle density. Here a new technique,
called High Speed Digital Image Plane Holography has been developed for the measurement of the three
velocity components in a complex geometry brain aneurysm model using a configuration similar to regular
PIV. This was done by using a two cavity high speed laser, one double frame high speed camera and normal
visualization. The two in-plane velocity components were obtained from the holograms reconstructed
intensity distribution using a PIV analysis. The out-of plane component was obtained from the reconstructed
phase differences using an interferometric method. Due to the laser short coherence length, a portable and
compact system has been built in order to be able to the measure larger fluid areas.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
2D3C速度矢量场,时间分辨速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中圆形冲击射流混合过程的LIF研究-边界条件效应检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We consider the effects of the mixing conditions at the nozzle, on the mixing
in a circular impinging jet. Two situations are considered: the completely premixed tracer
or a locally injected tracer. The local instantaneous concentration field is determined by
using Planar Laser-Induced Fluorescence (PLIF) technique. The premixed injection
variant reveals the mixing effects of the outer shear layer, while the local mixing approach
helps in understanding how to utilize the local injection for controlling the mixing of a
scalar in an impinging jet. The concentration statistics and the mixing properties indicated
by concentration probability density function (PDF) with the two injection methods are
presented. The results show the well-known structural features in the turbulent impinging
jet, the nature of mixing varies significantly in different regions of the jet. In the jet core
region and the impingement region, the mixing is dominated mainly by the large-scale
coherent structure, while in the mixing layer and wall jet region, both the large-scale
structure and small scale turbulence control the mixing.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
圆形冲击射流混合过程的LIF研究-边界条件效应
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场,流动方向检测方案(粒子图像测速)
If exposed to bulk water flow, fish lateral line afferents respond only to flow fluctuations (AC) and not to the steady (DC) component of the
flow. Consequently, a single lateral line afferent can encode neither bulk flow direction nor velocity. It is possible, however, for a fish to
obtain bulk flow information using multiple afferents that respond only to flow fluctuations. We show by means of particle image
velocimetry that, if a flow contains fluctuations, these fluctuations propagate with the flow.Across-correlation of water motion measured
at an upstream point with that at a downstream point can then provide information about flow velocity and flow direction. In this study,
we recorded from pairs of primary lateral line afferents while a fish was exposed to either bulk water flow, or to the water motion caused
by a moving object.Weconfirm that lateral line afferents responded to the flow fluctuations and not to theDCcomponent of the flow, and
that responses of many fiber pairs were highly correlated, if they were time-shifted to correct for gross flow velocity and gross flow
direction. To prove that a cross-correlation mechanism can be used to retrieve the information about gross flow velocity and direction, we
measured the flow-induced bending motions of two flexible micropillars separated in a downstream direction. A cross-correlation of the
bending motions of these micropillars did indeed produce an accurate estimate of the velocity vector along the direction of the
micropillars.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,流动方向
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
燃烧,火焰中浓度,羟基,OH,温度,痕量成分,富含成分检测方案(流量计)
Three-dimensional gradients of the hydroxyl radical (OH) concentration were measured in a premixed, lean natural
gas / air flame by simultaneous laser induced fluorescence imaging (LIF) in a crossed-light-sheet confguration and
one-dimensionally resolved Raman scattering. The technique is applied to measurements in a turbulent bluff-body
flame with the aim to investigate correlations between species concentration gradients and local concentrations.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
浓度,羟基,OH,温度,痕量成分,富含成分
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2243篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等