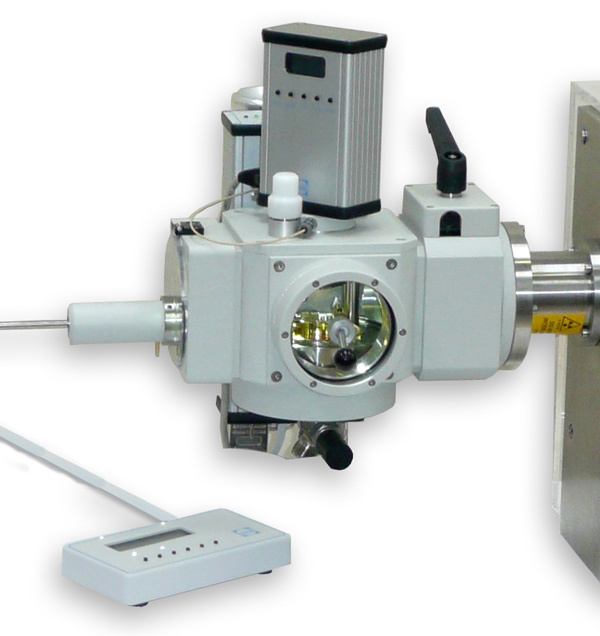
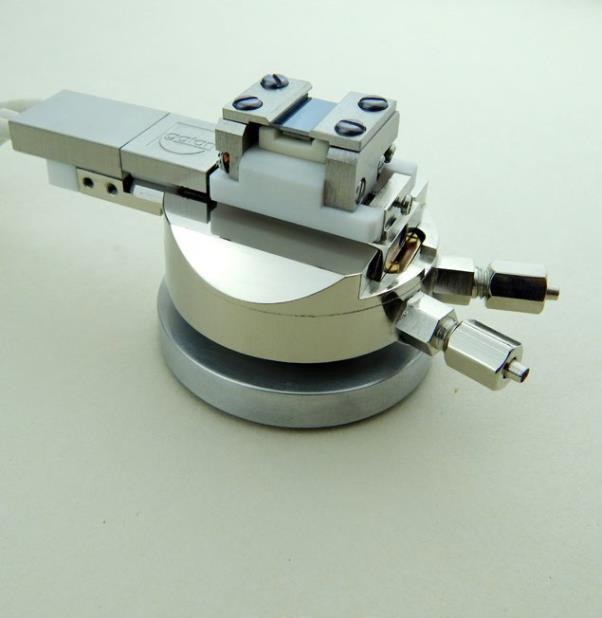
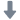
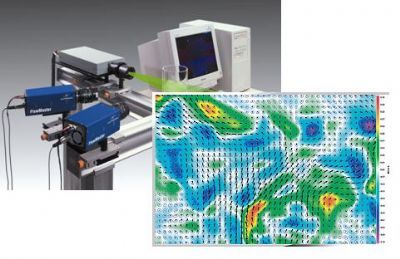
孤立型透镜中对博格(Burger)数和初始几何条件的依赖关系检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Geostrophic adjustment of an isolated axisymmetric lens was examined to better understand the
dependence of radial displacements and the adjusted velocity on Burger number and the geometry
of initial conditions. The behavior of the adjustment was examined using laboratory experiments
and numerical simulations, which were in turn compared to published analytical solutions. Three
defining length scales of the initial conditions were used to distinguish between various asymptotic
behaviors for large and small Burger number: the Rossby radius of deformation, the horizontal
length scale of the initial density defect, and the horizontal length scale of the initial pressure
gradient. Numerical simulations for the fully nonlinear time dependent adjustment agreed both
qualitatively and quantitatively with analogous analytical solutions. For large Burger number,
similar agreement was found in laboratory experiments. Results show that a broad range of final
states can result from different initial geometries, depending on the values of the relevant length
scales, and the Burger number computed from initial conditions. For Burger number much larger
or smaller than unity, differences between different initial geometries can readily exceed an order of
magnitude for both displacement and velocity.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
对博格(Burger)数和初始几何条件的依赖关系
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
层流,界面混合中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Stratified exchange flows driven by a density difference are found in many natural water bodies and in the atmosphere. A typical case in nature is the strait of Gibraltar, where the water of the Mediterranean Sea flows under the less saline water of the Atlantic Ocean. At the interface between the layers shear is responsible for instabilities (Kelvin-Helmholtz), which results in turbulent mixing and entrainment. Gaining deeper understanding of these processes is the main motivation for this thesis. An experimental study into the development of a mixing layer of a two layer stratified exchange flow is performed and an LIF measurement system was used to obtain the concentration fields. The main objectives of this study were to calibrate and understand the experimental set-up and to investigate the influence of four different parameters on the development of
the mixing layer. The calibration of the experimental set-up has led to a simple calibration procedure, which was applied with success.
To study the development of the mixing layer the influence of four different parameters was analyzed namely: the buoyant acceleration, the bottom friction, the water depth and the sill slope. After careful analysis of the experimental results it was observed that fluid from the upper layer was entrained into the lower layer in all the experiments. Analysis of the dye visualization showed that the large-scale structures, the Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities, are mainly responsible for the mixing and entrainment. The overall conclusion was that the variation of geometric condition on the
development of the mixing layer has a much stronger influence than the variation of the hydraulic conditions. An enhanced bottom friction affected the Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities but the mechanism is not completely understood by the author.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
等离子体中高水平等离子体能量耦合预混火焰中氮氧化物生成检测方案(流量计)
This paper presents quantitative planar laserinduced
fluorescence (PLIF) imaging of nitric oxide (NO) in a
transient-arc direct-current plasmatron igniter using premixed
air/fuel mixtures. Quantitative measurements of NO are reported
as a function of gas flow rate (20–50 standard cubic feet per
hour), plasma power (100–900 mA, 150–750 W), and equivalence
ratio (0.7–1.3). Images were corrected for temperature effects by
using 2-D temperature field measurements obtained with infrared
thermometry and calibrated by a more accurate multiline fitting
technique. The signals were then quantified using an NO addition
method and spectroscopic laser-induced fluorescence modeling
of NO. NO PLIF images and single-point NO concentrations
are presented for both plasma-discharge-only and methane/air
plasma-enhanced combustion cases. NO formation occurs predominantly
through N2(v) + O → NO + N for the plasmadischarge-
only case without combustion. The NO concentration
for the plasma-enhanced combustion case (500–3500 ppm) was
an order of magnitude less than the plasma-discharge-only case
(8000–15 000 ppm) due to the reduction of plasma reactions by the
methane. Experiments show the linear decay of NO from equivalence
ratio 0.8–1.2 under the same flow condition and discharge
current.
Index Terms—Nitric oxide (NO), plasma torch, plasma-assisted
combustion.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
高水平等离子体能量耦合预混火焰中氮氧化物生成
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
离心机在化学实验中的应用——无机定性分析实验
基本的概念及操作须知
· 离心机高速运转,产生离心力,使密度不同的物质沉淀.
· 离心沉淀过程中,需要部分的少量试剂会在离心力的作用下很容易的在试管中沉降.
· 运转过程中,应该小心操作,避免试管、离心管等的损坏.
· 液体不能超过试管的一半位置,防止液体在运转过程中溢出.
· 试管放入前应擦去外部残余液体,放置离心管极其内部转子等部件腐蚀.
· 离心管插入转子的数量必须成对,并且相对放置,已保证运转过程中的稳定性
· 两个离心管中,所放置物质的重量必须相同.
· 打开盖子时,如果转子还未停止旋转,不要视图取出试管,一定要等转子停止后才能去取出实验物.
· 不用的试管一定要记得从离心管中取出,余留的试管极易造成离心机事故的发生.
· 保护管中的试管在离心机运转过程中破碎时,应立即停止离心机工作,将破碎的试管碎片和液体从机器内清理干净.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
济南禾普仪器设备有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
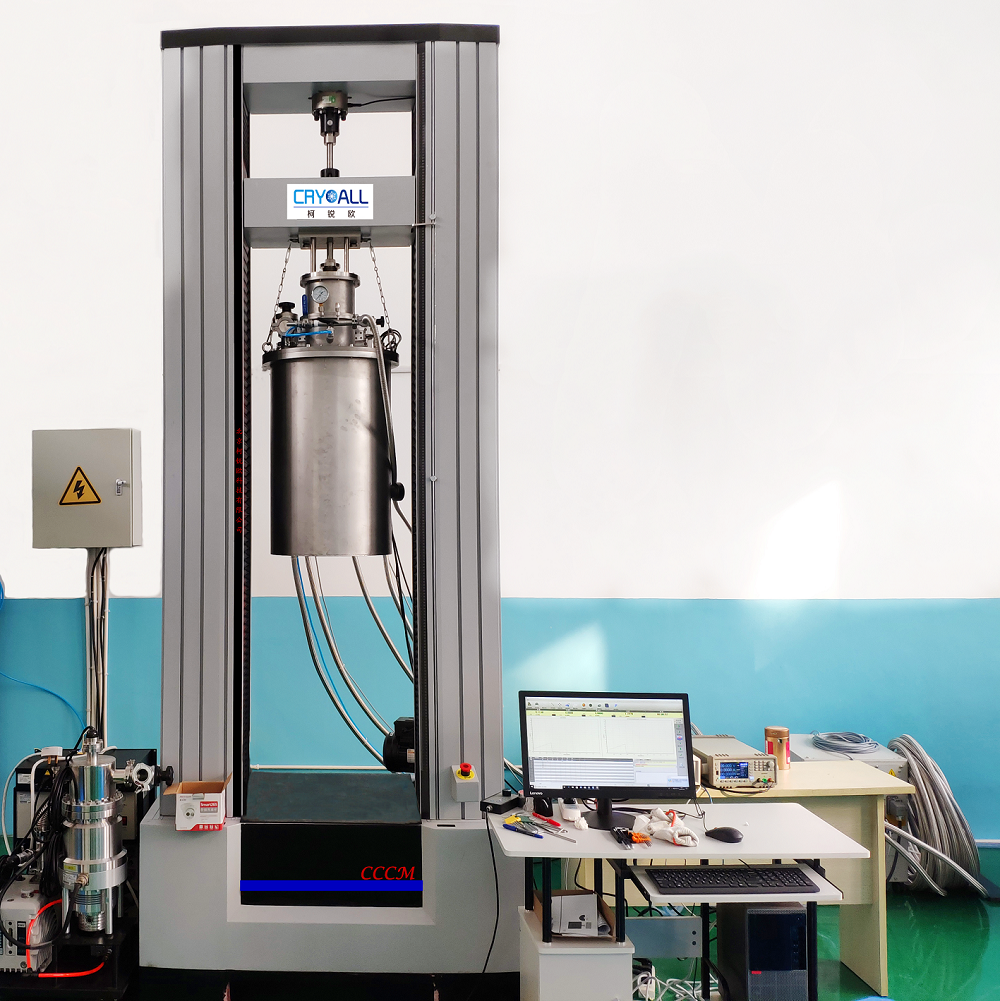
A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications
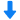
材料在低温下常常表现出“奇异”的力学行为。获得材料在低温区各温度点的力学性能数据才能认识材料随温度变化的力学行为,进而更深入地揭示材料力学行为中的规律。精确测量材料在低温环境中的力学性能,对材料、力学和物理等基础研究和高精技术应用发展具有重要的意义。要进行低温下的材料力学行为研究,材料低温力学性能测试系统是必不可少的重要装备之一。如2014年9月,Science 杂志报道了 CrMnFeCoNi 高熵合金优异的低温力学性能(A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications,Science 2014: Vol. 345 no. 6201 pp. 1153-1158 DOI: 10.1126/science.1254581),此项成果的取得,离不开美国劳伦斯-伯克利国家实验室低温力学性能测试装备的支持。
中国科学院理化技术研究所经过二十多年的研制和积累,开发出低温综合力学测试系统,此系统能进行材料低温环境(4.2K—300K(-269℃—室温)温区内任意温度)的力学性能测试,包括:拉伸、压缩、弯曲、剪切、扭转、断裂韧度等静态力学性能;疲劳裂纹扩展速率;拉拉疲劳、拉压疲劳、压压疲劳、扭转疲劳、拉(压)扭复合疲劳等疲劳性能测试。同时,还包括超导材料(低温超导线材、高温超导带材)加载电流时的力学性能、电学性能测试;非标试样和零部件的低温力学性能测试。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
北京柯锐欧科技有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
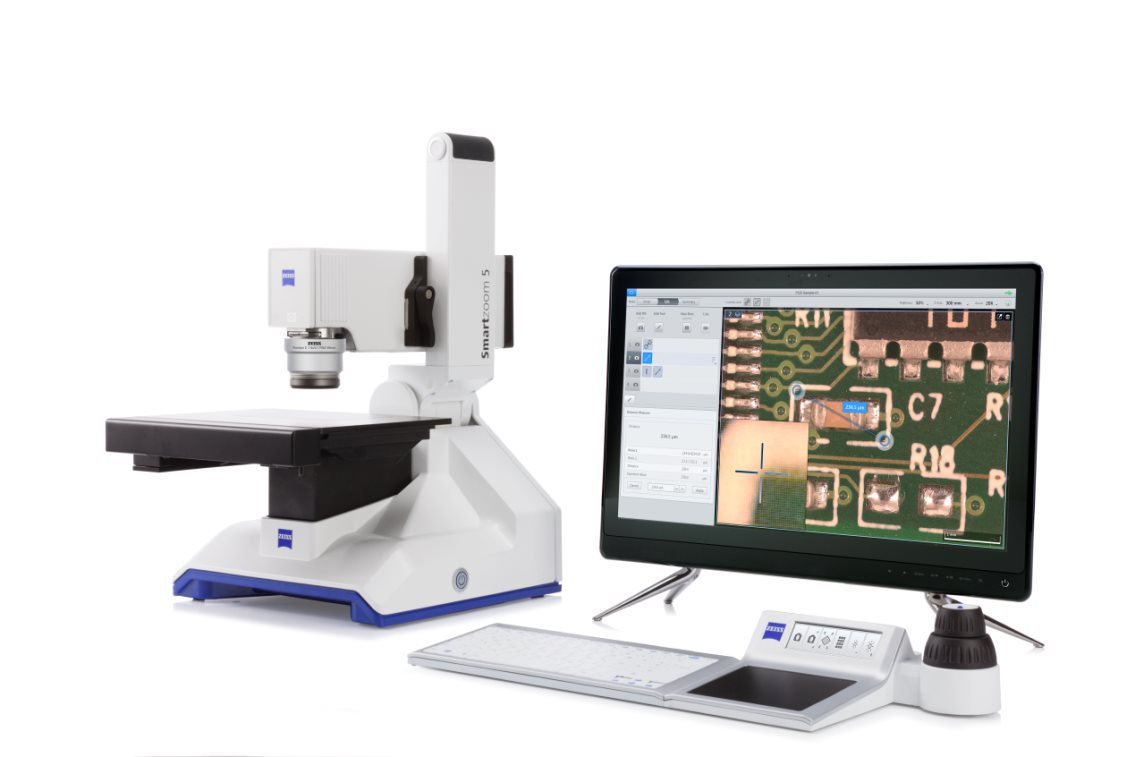
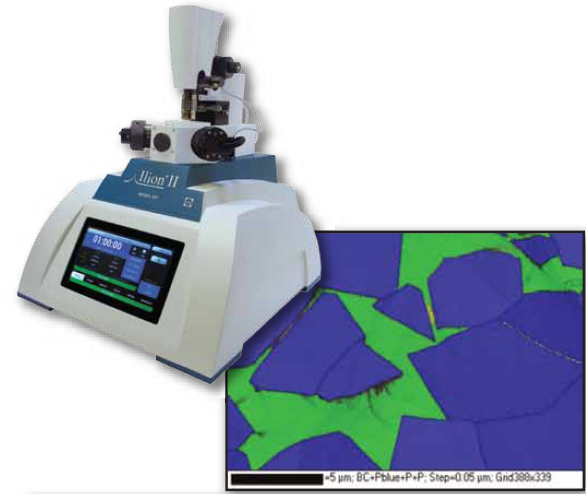
蔡司3D数码显微镜 Smartzoom5 解决方案
蔡司最新推出的Smartzoom 5智能3D数码显微镜是一款为工业质量控制领域的客户提供的一项全新解决方案的显微镜。可对样品进行三维成像,数码变倍及光学变焦,让数码显微镜实现了无极连续变倍,并可快速便捷地对样品进行二维、三维的观察和测量,适用于日常检测与失效分析。
蔡司3D数码显微镜特点:
1.全自动无极变焦,可连续变倍,用户可在任意倍数下准确测量
2.全触摸屏操作,无论是调焦、变倍、移动样品都可通过触摸屏实现,方便快捷。
3.镜头可倾斜观察,贴近客户应用。
4.集成式LED光源,光源集成到物镜中,可同时使用环形光和同轴光,极大的扩展各种应用。
5.大载物台设计,可放置大和重的样品,行程达130X100mm。
6.智能化设计与操作,特别设计的管理员模式与操作者模式,操作者只需根据管理员设计的程序操作即可,避免出错并提高工作效率,应用报告也自动生成。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
北京普瑞赛司仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
铝阳极氧化层中硬度、模量等机械性能检测方案(纳米压痕仪)
在当今轻量化需求的汽车工业里,铝合金材料得到广泛的应用。然而,为提高铝合金的机械性能和耐磨性,硬质氧化层的使用变的越来越普遍。
硬质氧化层一般有30-80μm厚,有的甚至只有几微米。对于这类涂层,传统的依赖于用光学方式查看压痕大小从而测算硬度的方法(如显微维氏硬度)已达到其测量极限。仪器化压痕法是替代传统测量方式的最佳方法,不仅能够去衡量其塑性变形性能(HV),还能够测量一系列决定涂层质量优劣的其它机械性能。用仪器化压痕法,即便是非常薄的阳极氧化层,也不用担心基材对测量氧化层性能时的影响。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
硬度、模量等机械性能
菲希尔测试仪器(中国)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
离子体中制动器控制高升力翼型下弯襟翼的流动分离检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In current wing design, multiple flaps are incorporated into the trailing edge to allow mixing of
high and low pressure sides to reduce flow separation. These flaps reduce the efficiency by
adding weight and complexity to the aircraft. A single hinged flap would reduce these
inefficiencies but is more susceptible to flow separation. Active flow control is a means by
which the fluid flow over a body is deliberately altered and can be altered such that it becomes
less likely to separate from the object. By energizing the flow, the degree of separation of the
flow can be controlled, and this inherently controls lift. Dielectric barrier discharge (DBD)
plasma actuators are a form of active flow control. These actuators are created by
asymmetrically aligning two electrodes and adding a dielectric layer between the electrodes.
When the electrodes are electrically connected, ionized air (plasma) travels from the exposed
electrode towards the covered electrode. Collisions occur between the plasma and neutral air
over the body, and momentum is transferred to the neutral air, effectively energizing it. The
purpose of this study is to examine the lift enhancement and flow control authority that multiple
DBD plasma actuators have on a high-lift airfoil when compared to the flow exhibited by noncontrolled
and single DBD plasma actuator controlled cases. Electrodes were mounted onto a
simplified NASA Energy Efficient Transport airfoil near the flap. The airfoil was tested in a
closed, recirculating wind tunnel operating at a Reynolds number of 240,000, 20° flap deflection
angle and 0° degree angle of incidence. The actuators were independently powered in order to
determine the most effective input parameters. Using multiple actuators operated in-phase has
increased the lift and has delayed flow separation on the trailing edge flap when compared to
baseline and single actuation cases.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
制动器控制高升力翼型下弯襟翼的流动分离
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案
Turbulence of the round jet has been assessed using invariants
of the velocity gradient tensor. Experimental data, obtained
using Tomographic Particle Image Velocimetry (Tomo-PIV),
using four PCO-4000 cameras with 11 megapixel resolution,
is presented for a seeded free air jet, operating in the turbulent
regime and the Re number based on the diameter of the nozzle
is 10000. Using the acquired 3-D velocity fields, the local
statistical and geometrical structure of three-dimensional
turbulent flow can be described by properties of the velocity
gradient tensor. The invariants of the velocity gradient (R and
Q), rate-of-strain ( Rs andQs ), and rate-of-rotation (Qw )
tensors are analyzed across the turbulent expanding regions at
different distances from the nozzle outlet. More specifically,
the JPDF of invariants is computed, which allows a detailed
statistical characterization of the dynamics, geometry and
topology of the flow during the entrainment process. It should
be noted that the results obtained are indicative of the
preliminary work in this area.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
固体、液体物质中比热容检测方案(其它表面测试)
比热容,是物质的一项基本物理特性,DSC法因为具有操作简便,测试快速等特点,已经成为比热容测试的一个常用方法。但同时,比热容的测试也一直是DSC的难点之一。与相变热、反应热等热量相比,物质的比热产生的DSC信号通常是很微弱的,在DSC图曲线上一般反映为“基线漂移”。
卡尔维式三维热流传感器中,热电偶阵列呈三维排列,完全包围样品空间,全方位探测样品与环境间的热交换。
-高灵敏度,比DSC的灵敏度高一至两个数量级。
-高效率,完全搜集样品的吸放热,效率高达95%以上
-电标定,一劳永逸:标定结果适用于任何样品的任何反应,包括比热容测试
-样品适应性,适用于固体,粉末,液体及多相混合物等各种形态的样品测试。
各种样品的比热容测试准确度优于98%。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
比热容
凯璞科技(上海)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中3D3C速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Over the past twelve years, two-dimensional and stereoscopic particle image velocimetry (PIV)
techniques have been used to obtain detailed measurements of the thermal and transport properties
of the microparticle component of dusty plasma systems. This letter reports on an extension of these
techniques to obtain a volumetric, three-dimensional velocity vector measurement using
tomographic PIV. Initial measurements using the tomographic PIV diagnostic are presented.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
3D3C速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
肝静脉中三支汇合血流动力学的粒子成像测量检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Despite rapid advancements in the patient-specific
hemodynamic analysis of systemic arterial anatomies, limited
attention has been given to the characterization of major
venous flow components, such as the hepatic venous confluence.
A detailed investigation of hepatic flow structures is
essential to better understand the origin of characteristic
abnormal venous flow patterns observed in patients with
cardiovascular venous disease. The present study incorporates
transparent rapid-prototype replicas of two pediatric
hepatic venous confluence anatomies and two-component
particle image velocimetry to investigate the primary flow
structures influencing the inferior vena cava outflow. Novel
jet flow regimes are reported at physiologically relevant mean
venous conditions. The sensitivity of fluid unsteadiness and
hydraulic resistance to multiple-inlet flow regimes is documented.
Pressure drop measurements, jet flow characterization,
and blood damage assessments are also performed.
Results indicate that the orientation of the inlets significantly
influences the major unsteady flow structures and power loss
characteristics of this complex venous flow junction. Compared
to out-of-plane arranged inlet vessel configuration, the
internal flow field observed in planar inlet configurations was
less sensitive to the venous inlet flow split. Under pathological
flow conditions, the effective pressure drop increased as
much as 77% compared to the healthy flow state. Experimental
flow field results presented here can serve as a
benchmark case for the surgical optimization of complex
anatomical confluences including visceral hemodynamics as
well as for the experimental validation of high-resolution
computational fluid dynamics solvers applied to anatomical
confluences with multiple inlets and outlets.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
三支汇合血流动力学的粒子成像测量
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
钝后缘刨面物体中近涡结构雷诺数相关性检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The three dimensional near wake flow topology behind a blunt trailing edge flat plate is
investigated for a Reynolds number range varying from 500 to 4.6x104 using a combination of
flow visualization, numerical simulations and experiments. The secondary wake instabilities are
identified using vorticity maps from CFD and performing Proper Orthogonal Decomposition
(POD) on PIV data from experiments to identify the underlying dominant coherent structures.
These structures are found to appear at a spanwise spacing ranging from 2.2 to 4.8. At higher
Reynolds numbers the secondary wake instabilities appear to be unsteady in space and time.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
近涡结构雷诺数相关性
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
转动环中PIV,粒子成像测速,速度矢量场,速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
PIV- and LDV- measurements of baroclinic wave interactions
in a thermally driven rotating annulus
U. Harlander, Th.v. Larcher, K. Alexandrov, and C. Egbers
Department of Aerodynamics and Fluid Mechanics, BTU Cottbus
October 7, 2008
EULAG
1 Experimental setup
2 Equations and boundary conditions
3 Regime Transitions
4 Data processing
5 Recent results
Frame co-rotating with cylinder
Frame co-rotating with wave
LDA observations
6 Numerical simulations with EULAG
7 Outlook
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
PIV,粒子成像测速,速度矢量场,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
微通道气泡中堵塞现象检测方案(流量计)
This paper highlights the influence of contact line (pinning) forces on the mobility of dry bubbles
in microchannels. Bubbles moving at velocities less than the dewetting velocity of liquid on the
surface are essentially dry, meaning that there is no thin liquid film around the bubbles. For these
“dry” bubbles, contact line forces and a possible capillary pressure gradient induced by pinning
act on the bubbles and resist motion. Without sufficient driving force (e.g. external pressure) a
dry bubble is brought to stagnation. For the first time, a bipartite theoretical model that estimates
the required pressure difference across the length of stagnant bubbles with concave and convex
back interfaces to overcome the contact line forces and stimulate motion is proposed. To validate
our theory, the pressure required to move a single dry bubble in square microchannels exhibiting
contact angle hysteresis has been measured. The working fluid was deionized water. The
experiments have been conducted on coated glass channels with different surface
hydrophilicities that resulted in concave and convex back interfaces for the bubbles. The
experimental results were in agreement with the model’s predictions for square channels. The
predictions of the concave and convex back models were within 19% and 27% of the
experimental measurements, respectively.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
堵塞现象
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
粒子成像测速系统的数据分析中粒子成像测速系统的数据分析检测方案
The emission of oxides of nitrogen, or NOx, by aircraft is an international concern. NOxcontributes to smog in the lower atmosphere and destroys ozone in the stratosphere. To reduce NOxand other harmful emissions, NASA has developed Multipoint Lean-Direct Injection (MP-LDI). To determine the effectiveness of MP-LDI and its potential for future commercial use, particle image velocimetry (PIV) obtains velocity data which is important for setting the inlet and boundary conditions needed for validating computational fluid dynamics codes such as the National Combustor Code (NCC).
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
粒子成像测速系统的数据分析
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
检测物质中待测物质检测方案(工作站及软件)
Thermo ScientificTM DionexTM ChromeleonTM 7 色谱数据系统 (CDS) 软件采用CobraTM 峰检测算
法、SmartPeaksTM 积分助手和动态交互数据处理,可节省您的宝贵时间。Cobra 检测算法可准确地检测峰起始和终止的时间,并正确地确定峰基线,无需输入一系列检测参数。独一无二的SmartPeaks 积分助手帮助用户快速、直观地确定基线。Chromeleon 7 CDS 帮助用户快速完成从样品到结果的过程,从而全面提高实验室的工作效率。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
待测物质
赛默飞色谱与质谱
查看联系电话
前往展位
旋转流体中惯性波束的黏滞扩散检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We report experimental measurements of inertial waves generated by an oscillating cylinder in a
rotating fluid. The two-dimensional wave takes place in a stationary cross-shaped wavepacket.
Velocity and vorticity fields in a vertical plane normal to the wavemaker are measured by a
corotating particle image velocimetry system. The viscous spreading of the wave beam and the
associated decay of the velocity and vorticity envelopes are characterized. They are found in good
agreement with the similarity solution of a linear viscous theory, derived under a quasiparallel
assumption similar to the classical analysis of Thomas and Stevenson “A similarity solution for
viscous internal waves,”
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
惯性波束的黏滞扩散
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中评价比较分析手段的方法检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In this report we present the methodology we are using in the AMI group to
compare optic flow estimation methods in the context of the FLUID Specific
Targeted Research Project - Contract No 513633 founded by the CEE. The main
goal of this report is to try to unify comparison criteria between the different
parnerts in order to share information and conclusions. We think that it is one
of the topics we have to address in Las Palmas Meeting December next. In
order to describe the methodology we use, we divide it in five steps:
1. We choose a number of optic flow estimation methods
2. We choose an image sequence dataset to apply the methods.
3. We apply the methods and we store the results in a ASCII file using an
standard format
4. We define a number of statistics to compare the methods (we use the
ASCII files as basic information to compare).
5. We compute the statistics for each pair of methods and we generate tables
with the information. To help result interpretation we use arrow images
and in the case we know the optic flow groundtruth we generate image to
provide the information about what method perform better in the different
areas of the image.
To illustrate this approach and to fit ideas we present the results of this
approach in a particular image sequence provided by LaVision in sections from
1.1 to 1.4. Then, in section 2 we remark some of the difficulties we have found
in our work, which should be discussed in order to be able to compare results
provided by all the partners of the FLUID project.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
评价比较分析手段的方法
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2243篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等