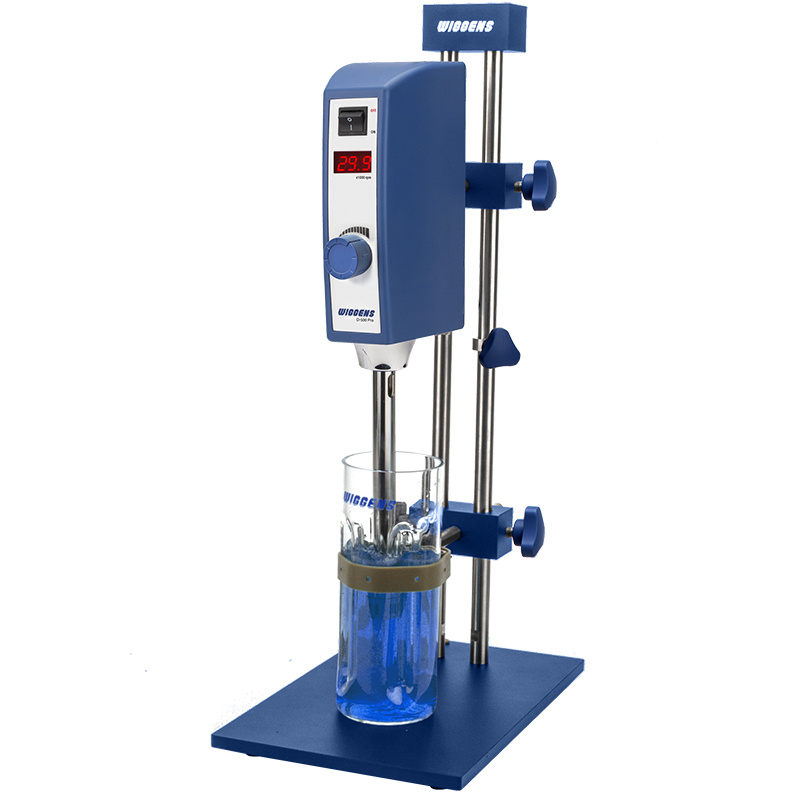
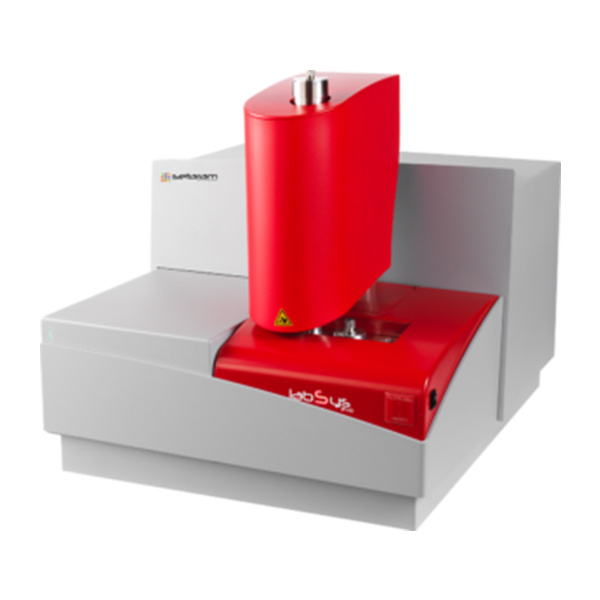
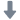
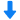
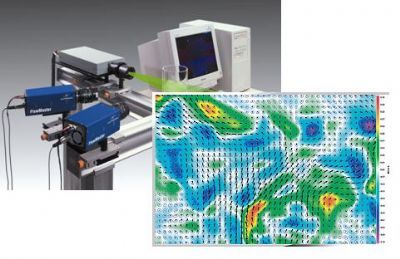
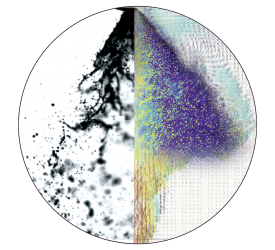
燃料,喷雾,液滴中粒径,速度,形状检测方案(激光粒度仪)
In the present work the process of a transient fuel injection in a constant high-pressure atmosphere is investigated experimentally. As fuel, dimethyl ether (DME) is used. The goal is to receive new information about the charac-teristics referring to the droplet size, the droplet velocity and the droplet shape in the jet. The high-pressure chamber has a constant pressure of 2 MPa and the fuel spray is injected with a pressure of 6 MPa, 7 MPa and 8 MPa. The spray is analysed by a Shadow-Sizing-technique and digital image analysis with temporal and spatial resolution, which even allows investigating non-spherical droplets. The correlations of d
velocity and droplet shape are presented as Joint Probability Density Functions (JPDF). The conclusion of the investigation shows that little increase of the injection pressure has a remarkable effect on the droplet size. Furthermore, the centricity is widely influenced by the injection pressure. With lower injection pressure the droplet velocity decreases. Moreover, the droplets mean diameter shows a significant decrease with increasing time after the injection
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
粒径,速度,形状
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
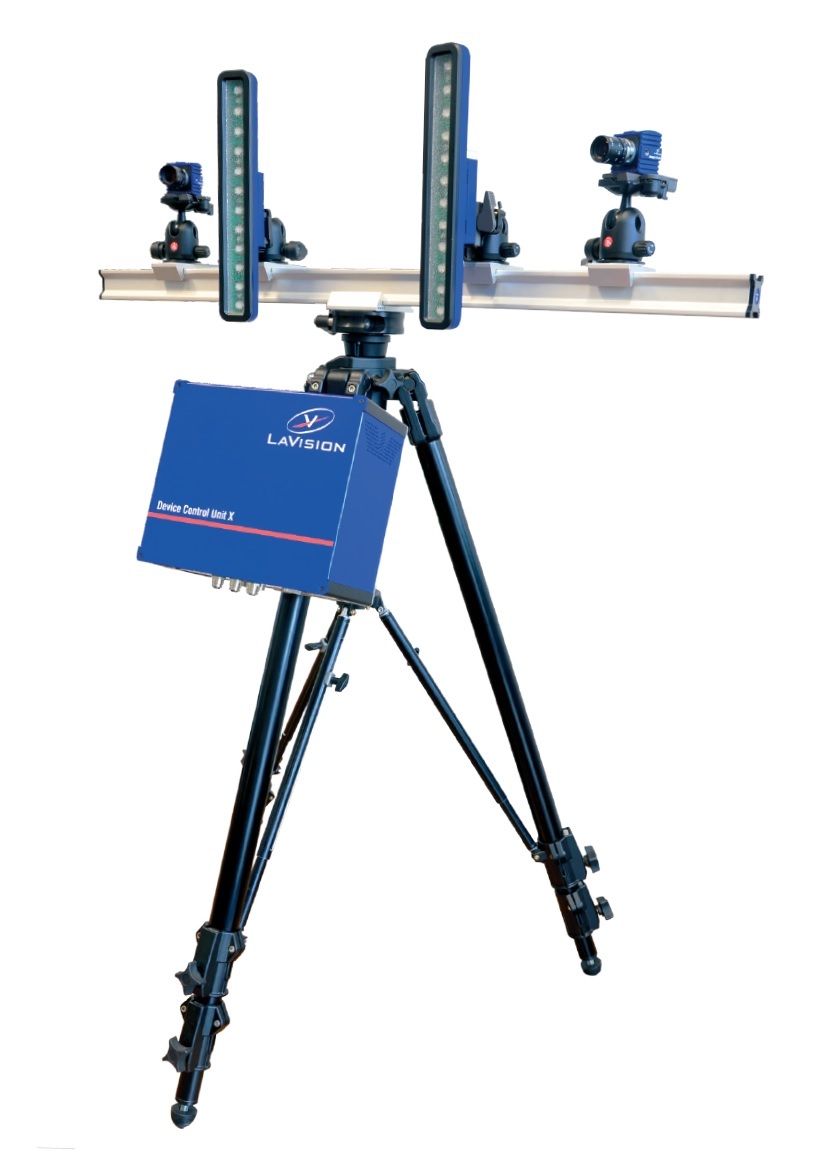
流体中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In particle image velocimetry (PIV) a temporally separated
image pair of a gas or liquid seeded with small particles is recorded
and analysed in order to measure fluid flows therein. We investigate a
variational approach to cross-correlation, a robust and well-established
method to determine displacement vectors from the image data. A “soft”
Gaussian window function replaces the usual rectangular correlation
frame. We propose a criterion to adapt the window size and shape that
directly formulates the goal to minimise the displacement estimation error.
In order to measure motion and adapt the window shapes at the
same time we combine both sub-problems into a bi-level optimisation
problem and solve it via continuous multiscale methods. Experiments
with synthetic and real PIV data demonstrate the ability of our approach
to solve the formulated problem. Moreover window adaptation
yields significantly improved results.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
湍动槽中采用层析粒子成像测速技术来测量耗散元素检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A new method to describe small scale statistical information from passive scalar fields has been
proposed by Wang and Peters (2006). They used direct numerical simulations (DNS) of homogeneous shear
flow to introduce the innovative concept. This novel method determines the local minimum and maximum
points of a fluctuating scalar field via gradient trajectories starting from every grid point in the direction of
the steepest ascending and descending scalar gradients. Relying on gradient trajectories, a dissipation element
is defined as the region of all the grid points the trajectories of which share the same pair of maximum
and minimum points. The procedure has also been successfully applied to various DNS fields of homogeneous
shear turbulence using the three velocity components and the kinetic energy as scalar fields. To validate
statistical properties of these elements derived from DNS (Wang and Peters 2006, 2008), dissipation elements
are for the first time determined based on experimental data of a fully developed turbulent channel
flow. The dissipation elements are deduced from the gradients of the instantaneous fluctuation of the three
velocity components u5, v5, and w5 and the instantaneous kinetic energy k5, respectively. The required 3D velocity
data is obtained investigating a 17.82 × 17.82 × 2.7 mm3 (0.356 × 0.356 × 0.054 ) test volume
using tomographic particle-image velocimetry (Tomo-PIV). The measurements are conducted at a Reynolds
number of 1.7× 104 based on the channel half-height and the bulk velocity U. Detection and analysis of
dissipation elements from the experimental velocity data are presented. The statistical results are compared
to the DNS data from Wang and Peters (2006, 2008).
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
采用层析粒子成像测速技术来测量耗散元素
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
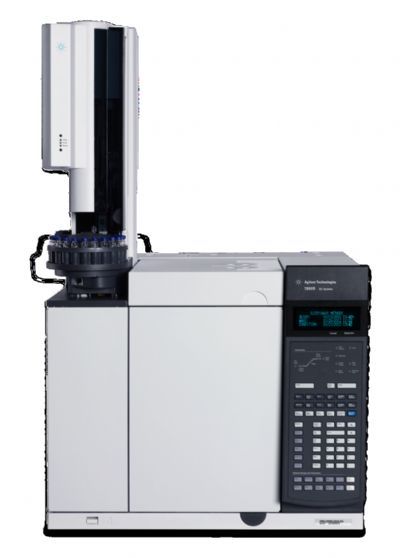
GC/MS 离子源中清洁和调节检测方案(气相色谱仪)
GC/MS 维护是在样品分析过程中保留分析目标的普遍要求。快速柱内反吹是 GC/MS 维护过程中的一次重要改进,能够改善离子源并延长 GC 使用寿命,并在不放真空的情况下快速完成气相色谱柱和进样口维护。另外,消除污染离子源的后洗脱组分已成为压力控制三通配置的突出特点。通过这些改进,离子源清洁频率显著降低,但是仍然需要进行清洁。冷却仪器、从分析 仪中取出离子源、机械清洁离子源、更换离子源、重新抽真空以及对分析仪 进行重新调谐和调节以改善系统灵敏度,整个过程可能需要操作人员花费大量的时间。Agilent JetClean 智氢洁离子源能够将冷却、取出、手动清洁、更换和抽真空等步骤替换为原位过程,从而节省了时间,减轻了操作人员的负担。为除去积聚的物质并恢复离子源性能,智氢洁离子源处理中形成的氢类 物质改变了离子源内部的条件。本应用简报介绍了智氢洁离子源的两种操作方法。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
清洁和调节
安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
上海伯东普发涡轮分子泵组脉冲激光沉积系统应用
脉冲激光沉积(Pulsed Laser Deposition, PLD),是一种利用激光对物体进行轰击,然后将轰击出来的物质沉淀在不同的衬底上, 得到沉淀或者薄膜的一种手段. PLD 系统由多个真空腔体组成,整个系统需要超高真空且不能引入任何杂质,对环境的清洁度要求较高,必须配备无油干泵和分子泵抽真空。由于各个辅助腔体体积较小, 因此特别适合使用 pfeiffer Hicube 系列分子泵组. 伯东公司销售维修的 Pfeiffer 分子泵组因其结构紧凑体积小,清洁无油(前级泵配备干泵)、抽速快、极限真空度高达10-11mbar等优点一经上市好评如潮。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
伯东公司德国普发真空pfeiffer
查看联系电话
前往展位
喷雾,燃料中浓度场检测方案(尾气检测)
To understand and optimize the combustion processes in new types of internal
combustion engines, like gasoline direct-injection engines, non-intrusive laser-based
diagnostics methods have proven to be versatile and important tools to measure
combustion characteristics. Most engine developers already rely on optical methods in
the development of new engines. To guarantee accurate and reliable results of optical
measurements it is necessary to carefully evaluate and characterize these techniques
under realistic conditions.
In this work a variety of laser-based diagnostics techniques, mostly based on the tracer-
LIF principle, have been evaluated for their applicability and limitations and have been
applied to different spray systems – reaching from single droplets, over model sprays to
fuel sprays in a firing test engine.
The tracer-laser-induced-fluorescence (LIF) method is based on doping the fuel with a
fluorescent substance whose fluorescence characteristics are used to measure various
physical properties of the spray, such as temperature, droplet size, or droplet velocity.
From these properties information about heat and mass-transfer mechanisms in the
spray can be gained. However, the characteristics of the used tracers must be known in
detail in order to guarantee useful and comparable results. Therefore, in this work
various tracers were characterized in terms of their evaporation and temperaturedependent
properties. The tracers Atto 680, Rhodamine 800 and Rhodamine B have
further been tested for their applicability to realistic fuels.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
浓度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
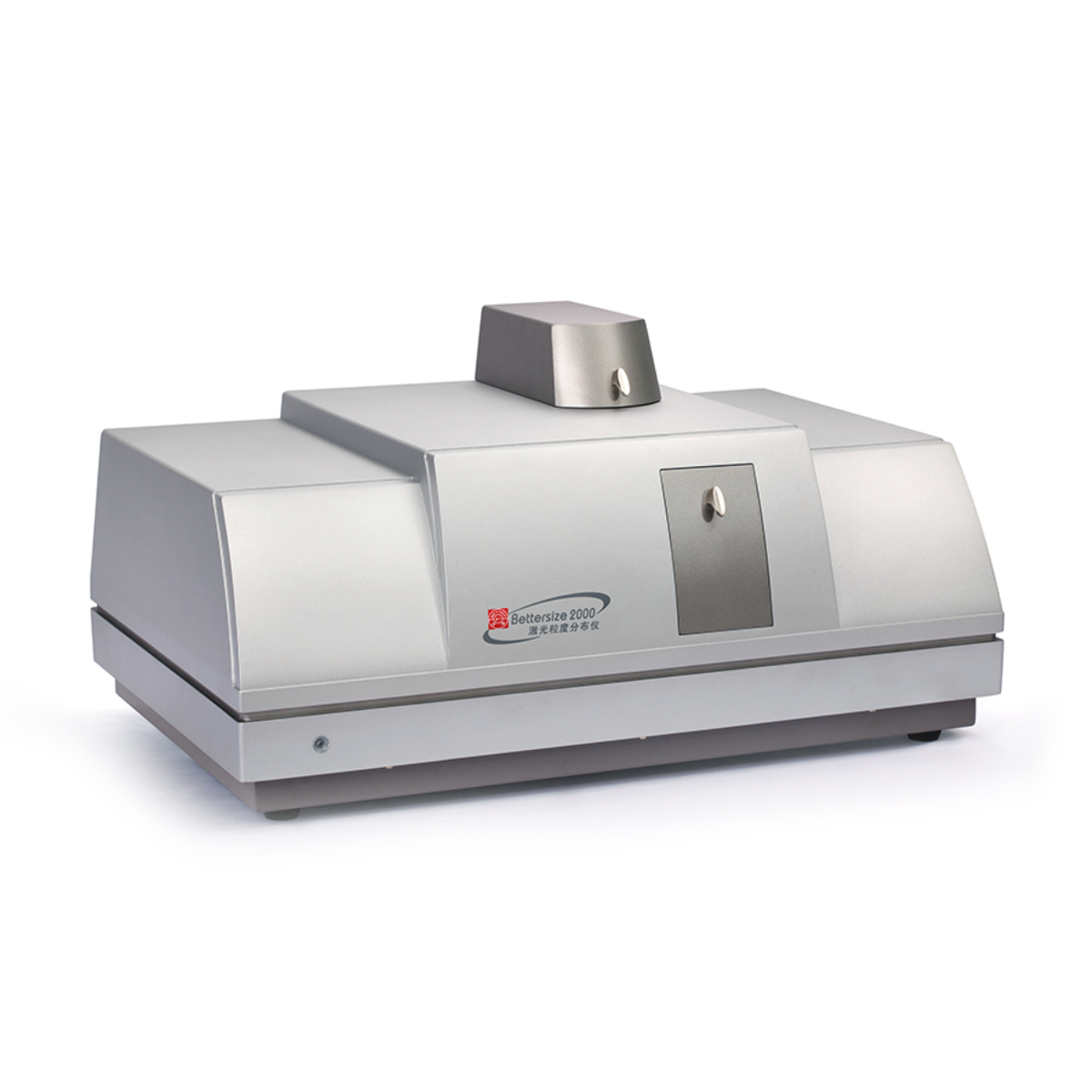
露点温度中处理和预防方法检测方案(激光粒度仪)
样品池结露对粒度测试有这么大的危害,如果我们在发现测试过程或测试结果异常才去处理,将可能出现错误的结果,提供错误的信息,带来重大的损失。为此百特在激光粒度仪中安装了露点温度监测系统,这在国内外激光粒度仪中首次采用此项技术。该系统实时监测仪器运行环境的温度、湿度以及用介质温度,并将温湿度数据实时传输到电脑中用来监测露点温度,一是用来指导用户通过控制介质温度来使样品池远离露点温度,使测试结果准确有效。二是当发生样品池结露现象时,电脑系统会自动报警提示,以方便用户提高介质温度,消除结露现象
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
处理和预防方法
丹东百特仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
光子中双色,双光子检测方案(CCD相机)
Over centuries, the classical optical microscope was the only tool that provided researchers
images behind the limits defined by their eyes. During the last century light microscopy went
through a tremendous development. But the basic idea of a lens or a set of lenses enlarging a
reflective or transmitive image and making it visible to the eye of the viewer remained.
Today, light microscopy shows a vast variety of different techniques. On the one hand, the
classical light microscopy has been refined by additional contrast enhancing techniques. On
the other hand, a complete new field of light microscopy has been established: the
fluorescence microscopy. Here, the sample is excited to emit fluorescence light. Manipulating
the excitation light and analyzing the emission light offers new ways of obtaining information
about the often specifically prepared sample. This thesis deals mainly with a new way of
excitation in fluorescence microscopy: the two-color two-photon (2c2p) excitation. For the
first time femtosecond laser pulses are used to excite fluorescence by simultaneous absorption
of two photons of different wavelengths.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
双色,双光子
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
采用激光干涉法测试量块的热膨胀系数
本文介绍了一种在室温附近测试各种量块和其它相似形状材料的高精度热膨胀系数测试仪器的研究开发。量块热膨胀所引起的长度变形通过一个差分平面镜干涉仪进行测量,采用特殊的干涉相位检测技术来补偿极化混合带来的非线性误差,再结合电子相位计可以实现纳米量级的精度。由于是在真空中进行量块热膨胀测量,从而无需进行空气折射率补偿。对于导热系数较高的被测试样,缓慢的辐射热交换使得试样上的温度梯度很小并具有很好的热平衡稳定性。在所获得典型的10~30℃温度之间热膨胀测试曲线,其线性和二次方热膨胀系数都等于在20℃参考温度时的热膨胀系数。本文对此激光干涉法热膨胀仪的测量不确定进行了详细分析,而且此测量不确定度也通过国际比对得到了验证。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
上海依阳实业有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
鱼道中2D非稳定流动实验研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Vertical slot fish passes have been applied as a solution to mitigate fish migration problems in running waters, for over
two decades. They are commonly used to enable target fish to ascend through obstacles in rivers. However, small
species are rarely considered in such fishways, of which the performance for small fish still remains unknown. This
experiment was to study the turbulence structure in a vertical slot fish pass concerning two different pool length/width
ratios of 9 and 6.67 as well as the effect of installing a cylinder behind the slot in affecting the characteristics of
instationary flow. Cylinders are considered an effective solution to modify the flow structure and to reduce velocity and
turbulent energy in order to adapt the flow for the passage of small fish species. Flow visualization and particle image
velocimetry were used to study the characteristics of mean flow and turbulence and particular emphasis on the unsteady
flow. The results show that flow patterns consist of a water jet and one or two recirculation zones depending on the
length/width ratio of the pool. The direction of the jet was strongly affected by the vertical cylinders. The frequencies
and spatio-temporal evolutions of the main jet beats were analyzed. Combining with the previous studies of fish
migration experiments, the results provide hydraulic evidence on the biological performance.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
2D非稳定流动实验研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
环形喷嘴中利用声激发主动控制大直径比初始区域环形不稳定性检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (P.O.D.) is a technique used for analysis of vortex structures in a turbulent flow. In this study, complex shear flows are observed by P.I.V. measurements (Particle Image Velocimetry) of a large diameter ratio annular jet. The annular jet is an example of complex shear flow situations. Two axisymmetric shear layers, originating at the jet exit, one at the nozzle lip and the other at the centre body, eventually meet downstream or interact with each other. The main aim of this study is to observe and analyze the effects of active control using acoustic waves on an annular jet with a great diameter ratio (r= 0.91), in order to find a new way to reduce jet instabilities. This contribution discusses the application of Proper Orthogonal Decomposition to the P.I.V. (Particle Image Velocimetry) velocity fields of an annular jet and on a statistic of time resolved tomographic images of the initial zone of the annular jet. Acoustic waves are then applied on the annular jet with different frequencies (fundamental, first harmonic̷). Measurements are conducted with a Reynolds number ReDo=107800. The fluctuation frequency of the stagnation point is known for this Reynolds number. The Strouhal number corresponding to this frequency is StDo = 0.27. The P.O.D. analysis applied on a natural annular jet and an excited annular jet enables us to see the importance of the triggering of the acoustic wave with the stagnation point motion. An active control is therefore necessary to use acoustic excitation to reduce instabilities in the initial zone of these turbulent jets. Active control has already been used with round jets and has given promising results, but only a few studies have been conducted on annular jets in this field. This work will permit us essentially to have a better knowledge of annular jets and to meet manufacturers' needs.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
利用声激发主动控制大直径比初始区域环形不稳定性
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
碳气化反应中机理及热分析动力学研究检测方案
采用热分析 (TG、DTG、DSC)技术,进行不同升温速率(10℃/min ,,20℃/min ,30℃/min)下碳气化反热分析研究。结果表明:在线性升温条件下,碳气化反应分为反应放热的缓慢阶段和吸热的快速阶段。慢速气化阶段呈现放热的原因是CO2 在固体碳表面发生吸附作用热大于气化反应热。通过Coats-Redffen 法求解动力学参数,得出慢速和快速气化阶段的活化能分别为65.68~33.38 kJ·mol和159.26 ~105.58kJ·mol,并随升温速率的提高而降低。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
机理及热分析动力学研究
凯璞科技(上海)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中PIV,粒子成像测速,流体图像,小波分析检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Flow past a cylinder in an unbound medium gives rise to
self-sustained, limit cycle oscillations involving formation
of a regular, periodically alternating Karman vortex street.
However, little attention has been paid to the effect of an
adjacent free surface on the development of the Karman
vortices and possible generation of new classes of the nearwake
structure[1], see Figure 1. The technique of Particle
Image Velocimetry (PIV) is a useful tool to this flow,
considering that it is unsteady and multi-scale in nature.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
PIV,粒子成像测速,流体图像,小波分析
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
granular matter,颗粒流,粒子流,颗粒体中流动场,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The paper presents results of strain measurements in cohesionless sand in two different
boundary value problems, namely quasi-static pull-out test of a steel wall and
confined granular flow in a rectangular model silo using a non-destructive method
called Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) which is a technique for measuring surface
displacements from digital images. Advantages and disadvantages of the method are
outlined.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流动场,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
PIV测量技术中性能优势检测方案
Active flow control earns growing interest for manufacturers of large transport aircraft
because of the constant need to improve these aircraft in terms of less fuel consumption,
higher efficiency, steep approaches and departures and less weight. Flow control devices
that are based on fluidic actuators, e.g. vortex generator jets (VGJs), have shown a promising
potential to influence separating boundary layers and keep them attached (e.g. Godard &
Stanislas (2006a‐c); Johari. & Rixon (2003); Johnston & Nishi (1990); Mc Manus et al. (1996);
Ortmanns et al. (2008a); Pauley & Eaton (1988); Scholz et al. (2006)). For an efficient operation
such devices need to be optimized regarding their ability to influence the flow. However,
optimization turns out to be very challenging because of the vast parameter space and the
lack of an adequate “figure of merit”. The proposed contribution will discuss the possibility
to assess and optimize such devices by analyzing the velocity fields from stereoscopic PIV
measurements.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
性能优势
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
气流中垂直通道的对流研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The flow generated by heat convection in a long, vertical channel is
studied by means of particle imagery velocimetry techniques, with the help of the
thermal measurements from a previous paper (Gibert et al 2009 Phys. Fluids 21
035109). We analyse the mean velocity profiles and the Reynolds stresses, and
compare the present results with the previous ones obtained in a larger cell and
at a larger Reynolds number.We calculate the horizontal temperature profile and
the related horizontal heat flux. The pertinence of effective turbulent diffusivity
and viscosity is confirmed by the low value of the associated mixing length.
We study the one-point and two-point statistics of both velocity components.
We show how the concept of turbulent viscosity explains the relations between
the local probability density functions (pdf) of fluctuations for temperature,
vertical and horizontal velocity components. Despite the low Reynolds number
values explored, some conclusions can be drawn about the small scale velocity
differences and the related energy cascade.
4 Author
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
垂直通道的对流研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
离子源中传输时间,速度场,速度矢量场,速度检测方案(粒子图像测速)
At atmospheric pressure (AP)ions are subject to a high frequency of collisions with bulk gas particles and other species present.Due to the high number of collisions,even relatively slow chemical reactions may become relevant in an AP ion source.The length of the ion migration path is directly correlated with the absolute number of collisions, therefore it may serve as a figure of merit to estimate the relevance of individual chemical interactions. In addition the experimental investigation of ion transfer times allows the verification of complex numerical models, which consider transport due to electrical fields and viscous gas flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
传输时间,速度场,速度矢量场,速度
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流场中3D3C速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The Tomographic-PIV measurement system performances are experimentally assessed within the present
study. The technique is applied to the turbulent air flow past circular cylinders in two configurations, namely the
thin light sheet and the thick light sheet. In the first case the Tomo-PIV measurements are compared with
stereoscopic PIV, which is assumed as a reference result. Image signal conditioning by pre-processing seems to be
essential in order to achieve an accurate particle field reconstruction in presence of background light and electronic
noise. The comparison shows that the two techniques are basically equivalent in the thin light sheet configuration.
The 3D measurements are performed with the thick light sheet technique where the instantaneous velocity vector
distribution is measured over a domain of 31x26x10 mm3 yielding 28x24x5 velocity vectors. The vortex wake past a
circular section cylinder is visualized within the volume snapshots and the time-averaged flow representation shows
a consistent flow pattern with respect to the geometric boundary conditions with the separated shear layers aligned
along the cylinder axis.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
3D3C速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
新型波中新型波的产生检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We present the results of a combined experimental and numerical study of the
generation of internal waves using the novel internal wave generator design of
Gostiaux et al. (Exp. Fluids, vol. 42, 2007, pp. 123–130). This mechanism, which
involves a tunable source composed of oscillating plates, has so far been used for a
few fundamental studies of internal waves, but its full potential is yet to be realized.
Our study reveals that this approach is capable of producing a wide variety of twodimensional
wave fields, including plane waves, wave beams and discrete vertical
modes in finite-depth stratifications. The effects of discretization by a finite number
of plates, forcing amplitude and angle of propagation are investigated, and it is found
that the method is remarkably efficient at generating a complete wave field despite
forcing only one velocity component in a controllable manner. We furthermore find
that the nature of the radiated wave field is well predicted using Fourier transforms
of the spatial structure of the wave generator.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
新型波的产生
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
激波中湍动边界层相互作用失稳特性的双平面PIV研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The unsteady organization and temporal dynamics of the interaction between a planar
shock wave impinging on a turbulent boundary layer at a free stream Mach number of
M∞=1.69 is investigated experimentally by means of dual-plane Particle Image Velocimetry
(dual-PIV). Two independent PIV systems were combined in two component mode to obtain
instantaneous velocity fields separated by a prescribed small time delay. This enables to
obtain, in addition to mean and statistical flow properties, also instantaneously time resolved
data to characterize the temporal dynamics of the flow phenomenon in terms of time scales,
temporal correlations and convective velocities. The characteristic time scales for the
incoming boundary layer, the separation region and the reflected shock are evaluated by
means of measuring the temporal auto-correlation coefficient in the complete flow field for a
range of time delays from 5 ms to 2000 ms. These auto-correlation fields are used to quantify
the time scales in selected regions of the flow. This permits resolving the dominant time
scales within the boundary layer and the interaction region.
I. Introduction
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
湍动边界层相互作用失稳特性的双平面PIV研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2243篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等