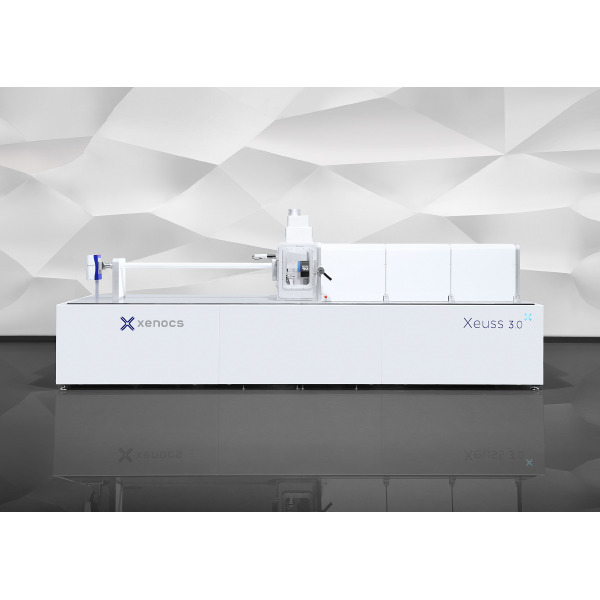
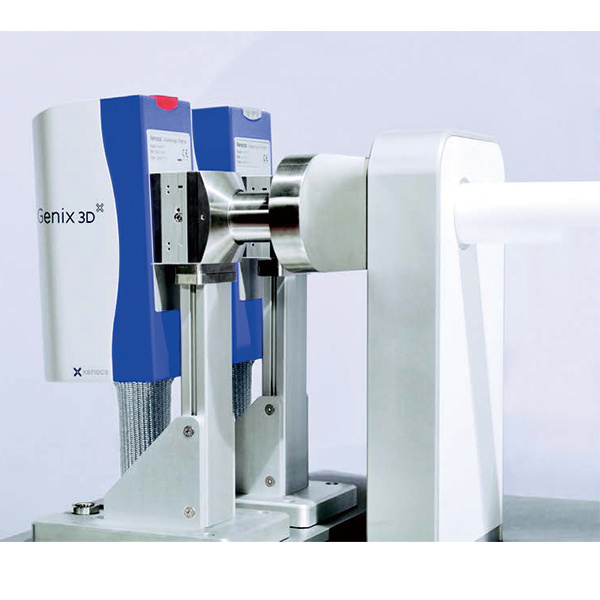
流体中速度矢量,速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The unsteady lift generated by the flow of turbulence over the trailing edge of an airfoil can be an
effective source of dipole sound. The objective of the present research was to experimentally measure
the velocity field behind an asymmetric 45 degree beveled trailing edge in order to develop an understanding
of the flow mechanisms responsible for the generation of trailing edge noise. Particle Image
Velocimetry (PIV) data were acquired in the near wake region of the trailing edge at a chord Reynolds
number of 1.9x106. The time averaged velocity statistics are indicative of a wake flow containing
semi-periodic vortex shedding. These large scale shedding motions are commonly responsible for the
tonal noise produced by the trailing edge. A phase average decomposition of the velocity field with
respect to this shedding process was utilized to separate the small scale turbulent motions responsible
for broadband sound production. This analysis has shown that the characteristics of the small scale
turbulence are dependent on the phase of the vortex shedding process.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
合成冲击射流,电子冷却机理中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The efficiency and mechanisms of cooling a constant heat flux surface by impinging synthetic jets were investigated experimentally and compared to cooling with continuous jets. Effects of jet formation frequency and Reynolds number at different nozzle-to-surface distances (H/d) were investigated. High formation frequency (f = 1200 Hz) synthetic jets were found to remove heat better than low frequency (f = 420 Hz) jets for small H/d, while low frequency jets are more effective at larger H/d. Moreover, synthetic jets are about three times more effective in cooling than continuous jets at the same Reynolds number. Using PIV, it was shown that the higher formation frequency jets are associated with breakdown and merging of vortices before they impinge on the surface. For the lower frequency jets, the wavelength between coherent structures is larger such that vortex rings impinge on the surface separately.
KEYWORDS:
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
层流,界面混合中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Stratified exchange flows driven by a density difference are found in many natural water bodies and in the atmosphere. A typical case in nature is the strait of Gibraltar, where the water of the Mediterranean Sea flows under the less saline water of the Atlantic Ocean. At the interface between the layers shear is responsible for instabilities (Kelvin-Helmholtz), which results in turbulent mixing and entrainment. Gaining deeper understanding of these processes is the main motivation for this thesis. An experimental study into the development of a mixing layer of a two layer stratified exchange flow is performed and an LIF measurement system was used to obtain the concentration fields. The main objectives of this study were to calibrate and understand the experimental set-up and to investigate the influence of four different parameters on the development of
the mixing layer. The calibration of the experimental set-up has led to a simple calibration procedure, which was applied with success.
To study the development of the mixing layer the influence of four different parameters was analyzed namely: the buoyant acceleration, the bottom friction, the water depth and the sill slope. After careful analysis of the experimental results it was observed that fluid from the upper layer was entrained into the lower layer in all the experiments. Analysis of the dye visualization showed that the large-scale structures, the Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities, are mainly responsible for the mixing and entrainment. The overall conclusion was that the variation of geometric condition on the
development of the mixing layer has a much stronger influence than the variation of the hydraulic conditions. An enhanced bottom friction affected the Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities but the mechanism is not completely understood by the author.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
旋转沙床底,水流,涟漪,瞬态漩涡中漩涡动态演化机制,PIV,粒子成像测速,速度矢量场,速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
This study deals with the flow motion over the so-called rolling-grain ripples which are generated by water oscillations above a sand bed. We focus our efforts on quantifying by means of laboratory
experiments and numerical calculations the morphology and the dynamics of transient flow patterns. We report, for the first time, on the formation of an unsteady pattern with closed streamlines ~we call it ‘‘eddy’’! above rolling-grain ripples using flow visualizations and particle image velocimetry(PIV) measurements. This structure appears in the ripple trough during flow reversal and scales with the ripple wavelength. The experimental results are in qualitative agreement with the perturbative flow solution calculated by Vittori in 1989. Even if the relative ripple amplitude is not small in the experiment the perturbative expansion at the first order gives an accurate description of the flow dynamics.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
漩涡动态演化机制,PIV,粒子成像测速,速度矢量场,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
横流扇,空气流,内部流场结构中速度矢量场,速度场,内部流场,流场结构检测方案(粒子图像测速)
室内机的流场结构会因为不同的压损值以及搭配的不同转速时会有所不同,主要分成兩种形式。当压损较小时,通过横流扇而被提供动能的流体,大多能沿著背板的几何形狀朝下游移动。若当压损逐渐提高,在低转速下的流场结构会产生明显的差異,在葉輪侧靠近出口处区域与舌部下方的之间,回流区范围有显著的扩大趋势,在靠近葉輪部分流体的运动方向可被观测出有被卷吸回葉輪的情形,大多是受到高速旋转的葉輪在通过舌部後,产生的低压结构所引致的现象。此时若提高葉輪的转速,将有助於提供流体更多的动量,可使舌部附近的回流区结构缩小,同时在横流扇入口上方的回流区结构也明显受到抑制。
然而,当压损值提高时,不同转速下的流场结构相当類似,葉輪上方的入风口处,都有明显的回流结构,部分情形下甚至可达近一半的入口面积。另外,出风口处的回流区结构相当大,速度较大的区域皆集中在弧形背板处,并且造成出口处的气流速度产生骤降的现象。当压损在特定范围以上时,本研究之横流扇的出风特性有明显的变化,即便再提高转速,仍无法提供流体产生足够的动量,以形成有效的气流流动,风扇运转已偏離有效操作点。
经由上述的实验结果中得知,此横流扇结构在低压损或是高转速下的出风流场结构多能沿著背板进而流至出风口。倘若压损提高或转速降低时,出口风速锐减,室内机的送风性能明显降低。因此,此室内机的几何形狀应针对不同的压损下的送风性能讨論,进行改良设计,本文以PIV进行量测,提供一种快速有效的研究方法。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场,速度场,内部流场,流场结构
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
LG触摸屏中接触角检测方案(接触角测量仪)
等离子清洗机德国电路技术:采用德国高压激励电源电路技术,产生高密度等离子体,确保出众的清洗效果。
全面安全防护:温度过高,过载,气压失常,短路断路,误操作,等全面的报警保护功能。
军工级密封腔体:军工级的高真空度密封腔体材质及制造工艺。
灵活的气体配方选择:可选择两路、三路、四路气体配方方案,满足不同工艺要求。
优质产品部件:全部部件采用国内外顶尖优质部件,运行稳定寿命更长。
低温清洗:满足不同场合温度要求,不对清洗产品造成温度影响。
环保简易:极低的运行成本,操作简单,过程无化学污染物排放,符合环保规范。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
接触角
东莞市晟鼎精密仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2245篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等