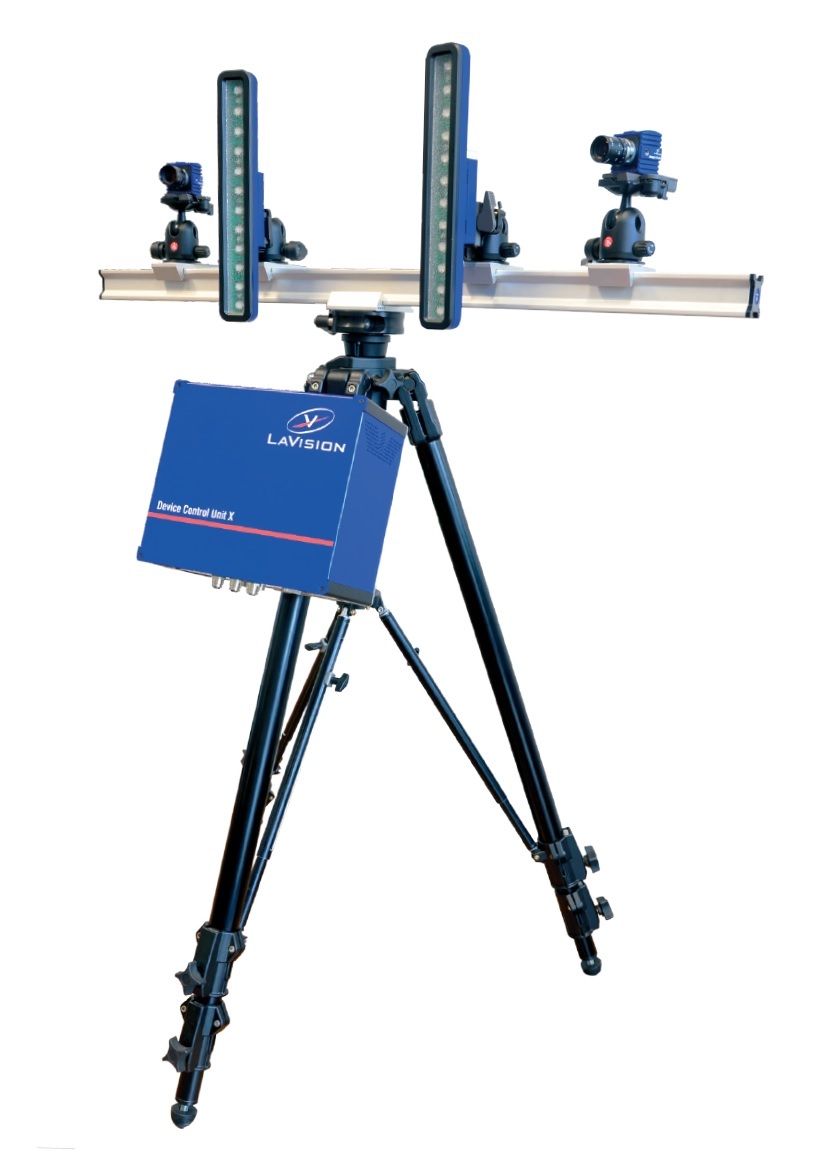
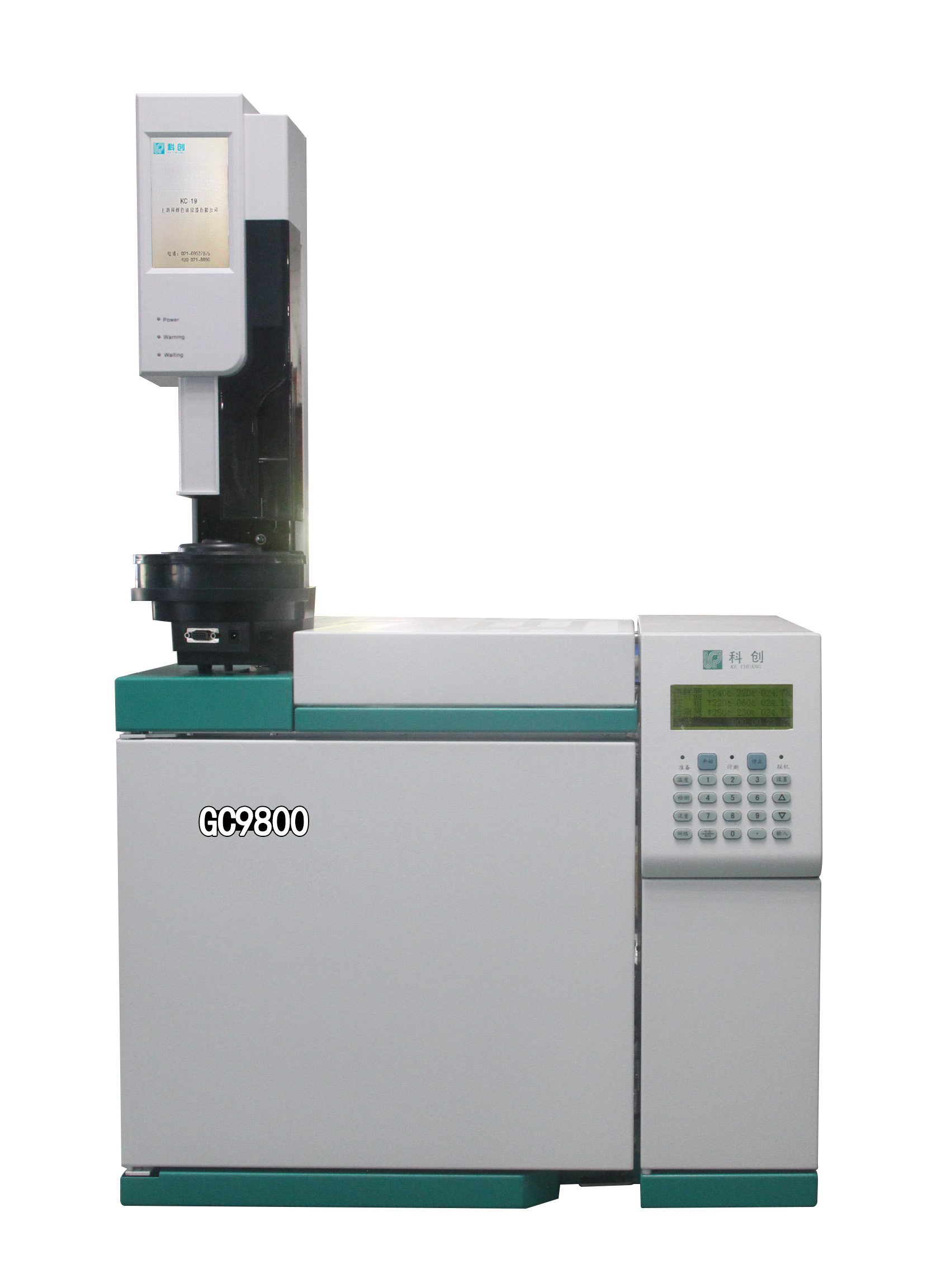
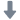
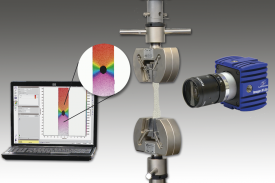
冷却反应器中INL在棱镜气体冷却反应器下腔室比例模型上获得流动现象基准数据来验证CFD模拟的有效性的项目计划检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The experimental program that is being conducted at the Matched Index-of-Refraction (MIR) Flow
Facility at Idaho National Laboratory (INL) to obtain benchmark data on measurements of flow
phenomena in a scaled model of the lower plenum of a typical prismatic gas-cooled reactor (GCR) using
3-D Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) is presented. A detailed description of the model, scaling, the
experimental facility, 3-D PIV system, measurement uncertainties, experimental procedures and samples
of the data sets that have been obtained are included. Samples of the data set that are presented include
mean-velocity-field and turbulence data in an approximately 1:7 scale model of a region of the lower
plenum. This experiment has been selected as the first Standard Problem endorsed by the Generation IV
International Forum.
Results concentrate on the region of the lower plenum near its far reflector wall (away from the outlet
duct). Inlet jet Reynolds numbers (based on the jet diameter and the time-mean flow rate) are
approximately 4,300 and 12,400. The measurements reveal undeveloped, non-uniform flow in the inlet jet
ducts and complicated flow patterns in the modeled lower plenum. Data include three-dimensional vector
plots, data displays along the coordinate planes (slices) and charts that describe the component flows at
specific regions in the model. Information on inlet flow is also presented.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
INL在棱镜气体冷却反应器下腔室比例模型上获得流动现象基准数据来验证CFD模拟的有效性的项目计划
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The active control of laminar and turbulent flows with dynamic actuators is of
great scientific and technological interest in nearly all fields of fluid mechanics.
Today, most of the well established actuator concepts are based on pneumatic and
micro-mechanic bases. However, owing to their limited dynamic range, their potential
seems to be limited from the present point of view [1]. Recently it was successfully
demonstrated that a boundary layer flow can be efficiently controlled by
using an optical actuator concept, which allows non-intrusive excitation of the flow
with nearly any pulse-width and repetition-rate by heating the surface of a model
with a short-focused laser pulse [2]. The drawback of the proposed and examined
method was the gradual ablation of the model surface. To avoid this problem the
excitation was performed above the surface in this investigation [3]. By using the
phased locked stereoscopic PIV and Schlieren technique the dynamic effect of the
laser induced plasma on a boundary layer flow could be examined in detail. In this
contribution the main results will be summarized and the perspective of this actuation
method for fundamental and applied fluid mechanics will be outlined.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
液体流体中流速检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Two-phase annular flow is commonly used in both commercial and industrial heat transfer; however, we do not yet possess a thorough understanding of the nature of the fluid. Most analytical annular two-phase models are based on a relationship between the
liquid film thickness, liquid film mass flux, and the axial pressure gradient or interfacial
shear stress. The film thickness calculated from these models can then be utilized to
determine the heat transfer coefficient of the flow. Although they are specific to certain
flow regimes and fluids, empirical models remain more accurate than these analytical
models. The key to understanding these flows lies with the liquid film. Therefore, to
better understand the pressure drop and heat transfer of annular two-phase flow, this
study involves the development of local, liquid velocity measurement techniques and
their application to horizontal, wavy-annular two-phase flow.
Two techniques, Bubble Streak Tracking (BST) and Thin Film Particle Image
Velocimetry (TFPIV), have been developed in this study. Utilizing naturally occurring
bubbles within the liquid film, the BST technique determines the liquid velocity by
measuring reflected light streaks from the bubbles. A three-colored LED array creates
directionally unambiguous streaks, while a strobe illuminates interfacial features that
affect the liquid velocity. The TFPIV technique applies a typical micro-PIV system to a
macroscopic flow with the addition of a non-trivial image processing algorithm. This
algorithm successfully overcomes the image noise that occurs when applying PIV to a
two-phase, thin film. Although difficulties arise when processing the BST data, the
results of the BST and TFPIV methods are comparable, making BST an economical
alternative to TFPIV for calculating liquid film velocities.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流速
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中相关的几何学的剪切区模拟检测方案(其它无损检测仪器/设备)
The geometry of ductile strain localization phenomena is related to the rheology of the deformed rocks. Both qualitative and quantitative
rheological properties of natural rocks have been estimated from finite field structures such as folds and shear zones. We apply physical modelling
to investigate the relationship between rheology and the temporal evolution of the width and transversal strain distribution in shear zones,
both of which have been used previously as rheological proxies. Geologically relevant materials with well-characterized rheological properties
(Newtonian, strain hardening, strain softening, MohreCoulomb) are deformed in a shear box and observed with Particle Imaging Velocimetry
(PIV). It is shown that the width and strain distribution histories in model shear zones display characteristic finite responses related to material
properties as predicted by previous studies. Application of the results to natural shear zones in the field is discussed. An investigation of the
impact of 3D boundary conditions in the experiments demonstrates that quantitative methods for estimating rheology from finite natural structures
must take these into account carefully.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
相关的几何学的剪切区模拟
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
孤立型透镜中对博格(Burger)数和初始几何条件的依赖关系检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Geostrophic adjustment of an isolated axisymmetric lens was examined to better understand the
dependence of radial displacements and the adjusted velocity on Burger number and the geometry
of initial conditions. The behavior of the adjustment was examined using laboratory experiments
and numerical simulations, which were in turn compared to published analytical solutions. Three
defining length scales of the initial conditions were used to distinguish between various asymptotic
behaviors for large and small Burger number: the Rossby radius of deformation, the horizontal
length scale of the initial density defect, and the horizontal length scale of the initial pressure
gradient. Numerical simulations for the fully nonlinear time dependent adjustment agreed both
qualitatively and quantitatively with analogous analytical solutions. For large Burger number,
similar agreement was found in laboratory experiments. Results show that a broad range of final
states can result from different initial geometries, depending on the values of the relevant length
scales, and the Burger number computed from initial conditions. For Burger number much larger
or smaller than unity, differences between different initial geometries can readily exceed an order of
magnitude for both displacement and velocity.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
对博格(Burger)数和初始几何条件的依赖关系
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
英国和爱尔兰范围内的热流计装置比对试验
热流计(heat flow meter—HFM)技术在防隔热材料的表观导热系数快速和可靠测量中应用十分广泛,在英国和爱尔兰有着大量不同尺寸和形式的热流计,这些热流计多数归属于防隔热材料生产商的质量保证部门和研究实验室。随着欧洲法律要求生产厂商公布产品的热性能数值,英国国家物理实验室(NPL)为此在英国和爱尔兰范围内组织了一次比对试验以评估工业用热流计测量的可比性和准确性,目的是帮助建立测量的一致性。
在此次比对试验中,共评定了17个热流计装置,评定装置采用了保护热板法测量装置以提供导热系数数值基线。在10℃和23℃温度下,采用了发泡聚苯乙烯、挤塑聚苯乙烯和高密度岩石纤维板三种材料各两种厚度试样进行了评定测量。除了少数例外,大多数测量结果都在±5%偏差范围内。在总共154个数据点中,69%的数据点位于±3%偏差范围内,50%的数据点位于±2%偏差范围内。由于校准原因和平衡时间变化所带来的测量偏差本文进行了讨论,并对今后进一步降低测量不确定给出了建议。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
上海依阳实业有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
采用ICP方法分析与核潜艇运行有关的样品
Eight samples from the Nuclear Division of a company were analyzed. These samples have complex matrices such as salt, concentratedacid, etc. and required high dilution factors when flame AAS is used. This application note will demonstrate the feasibility and simplicity of the ICP technique for this type of analysis.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
HORIBA(中国)
查看联系电话
前往展位
饮用水、地表水、地下水、化妆品、石化中阴离子、阳离子、亚硝酸盐、硅酸盐、碳酸、硼酸盐检测方案(离子色谱仪)
对《标准检验方法》中离子色谱法检测饮 用水中常规阴阳离子及特殊被测组分的方法进行了简要综述,同时给出了戴安推荐的相应检测方法:对阳离子分析,推荐使用CSRS阳离子连续自动再生电解抑制器,IonPacCS16或IonPacCS A色谱柱等度淋洗;对常见阴离子、亚氯酸盐、氯酸盐、溴酸盐、卤代乙酸分析,推荐使用ASRS阴离子连续自动再生电解抑制器,IonPac AS19 色谱柱梯度淋洗、IonPacAS-HC或者IonPacAS23色谱柱等度淋洗。这些方法均得到美国EPA等组织的认证,完全可以满足相应部门对饮用水中各种离子的检测要求。
...
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
阴离子、阳离子、亚硝酸盐、硅酸盐、碳酸、硼酸盐
上海禹重实业有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中时间分辨3D3C速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A survey is conducted to quantitatively visualise the wake flow behind a circular cylinder at Reynolds numbers of 180 to 2500. A time-resolved tomographic PIV method is used to measure the
sequence of three-dimensional vector fields evolving in time. The attention is focused upon the unsteady 3D wake organization with the interaction of primary rollers (Karman-Benard) and the secondary vortices resulting from 3D instability of the vortex wake.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
时间分辨3D3C速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
燃料,喷嘴,喷射中速度场,浓度场,喷雾几何参量检测方案(流量计)
The transient behaviour of the fuel spray from an air-assisted fuel
injector in a constant volume chamber has been investigated
experimentally. The relative Sauter mean diameter (SMD) of the
spray droplets was determined using planar laser induced
fluorescence (PLIF) and planar Mie scattering. Planar images of
the ensemble averaged relative SMD with various injection
conditions were obtained by calculating the ratio between the two
laser light intensities at a given point. The penetration length and
the spray shape factor were also obtained. The ensemble
averaged results suggest the existence of vortices that are shed
from the injector tip, and which entrain the smaller droplets.
Results also show that the characteristics of the injector vary
weakly with several particular injection parameters, notably the
fuel injection pressure and the delay between fuel and air
injection.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,浓度场,喷雾几何参量
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
气泡中分离,速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Vortex generator jets (VGJs) have proven to be effective in minimizing the separation losses on low-pressure turbine blades at low Reynolds numbers. Experimental data collected using phase-locked particle image velocimetry and substantiated with a hot-film
anemometer were used to answer fundamental questions about the influence of VGJs on a separated boundary layer. The data were collected on the suction surface of the Pack B blade profile, which has a non-reattaching separation bubble beginning at 68% axial
chord. Two VGJ pulse histories were created with different frequencies, jet durations,and duty cycles. The mechanisms responsible for boundary layer separation control were
shown to be a combination of boundary layer transition and streamwise vortical structures. Jet duration and relaxation time were important VGJ characteristics in determining the extent of control. The unsteady environment characterisitic of the low-pressure turbine section in a gas turbine engine effectively reduces the time-averaged separation zone by as much as 35%. Upstream blade rows create unsteady flow disturbances (wakes) that transition the flow. This transitioned flow propagates downstream, re-attaching the separation bubbles on the subsequent blade row. Phase-locked PIV and hot-film measurements were used to document the characteristics of this separation zone when subjected to synchronized unsteady wakes and VGJs. The phase difference between VGJ actuation and the wake
passing, blowing ratio, and VGJ duration were optimized to achieve the greatest timeaveraged control of the separation zone. The experimental data were used to identify the important characteristics of the wake/jet interaction. Phase-locked PIV measurements were taken to isolate the wake event.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
分离,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
检测总酸度
Determination of acidic constituents in petroleum products and lubricants by potentiometric titration. The total acid number TAN is the quantity of base, expressed in milligrams of potassium hydroxide, that is required to neutralize all acidic constituents present in 1 g of sample.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
优莱博技术(北京)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
ICP-AES分析10g/L铑溶液时获得的各元素检出限
The analysis of impurities in Rhodium samples requires an instrument with high resolution to avoid inter-element correction and obtain low
detection limits. For this reason the JY ULTIMA was used. This Application Note reports the wavelengths that were used in this difficult matrix and the detection limits obtained.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
HORIBA(中国)
查看联系电话
前往展位
使用铝模块自动消化装置消解样本的操作步骤
使用铝模块自动消化装置进行样本消解是一个相对简单的过程,但仍需要谨慎操作。以下是一般的操作步骤,具体的步骤可能会因设备型号和厂商而有所不同。在进行操作之前,请务必仔细阅读设备的使用手册和操作指南。
1. 准备工作:
确保铝模块自动消化装置的电源连接正常,设备处于工作状态。
检查试剂、样品和其他实验器材的准备情况。
2. 打开设备:
启动铝模块自动消化装置,等待设备初始化。
3. 设置实验参数:
使用设备上的液晶触摸屏,进入实验参数设置界面。
选择或创建一个用户定义方案,设置升温阶段的温度、时间等参数。
4. 放置样品:
打开设备的样品仓,将待消解的样品放置在相应的位置。
确保样品数量不超过设备的承载能力,并避免样品之间的干扰。
5. 启动自动消解程序:
确认实验参数设置无误后,启动自动消解程序。
设备将按照设定的升温阶段,自动完成升温、搅拌、消解等程序,无需人工干预。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
消解样品
山东三体仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2272篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等