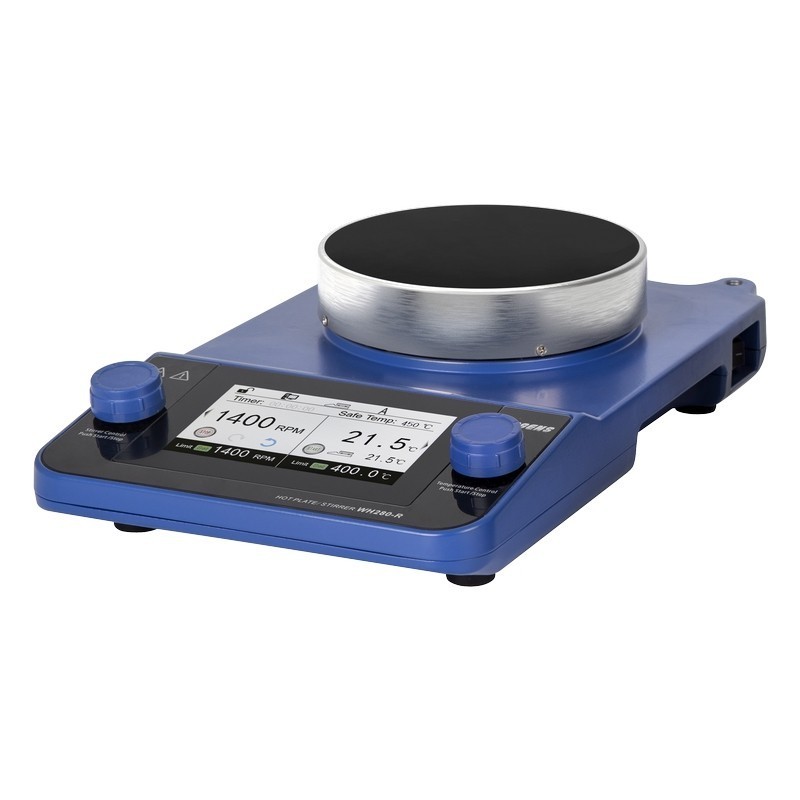
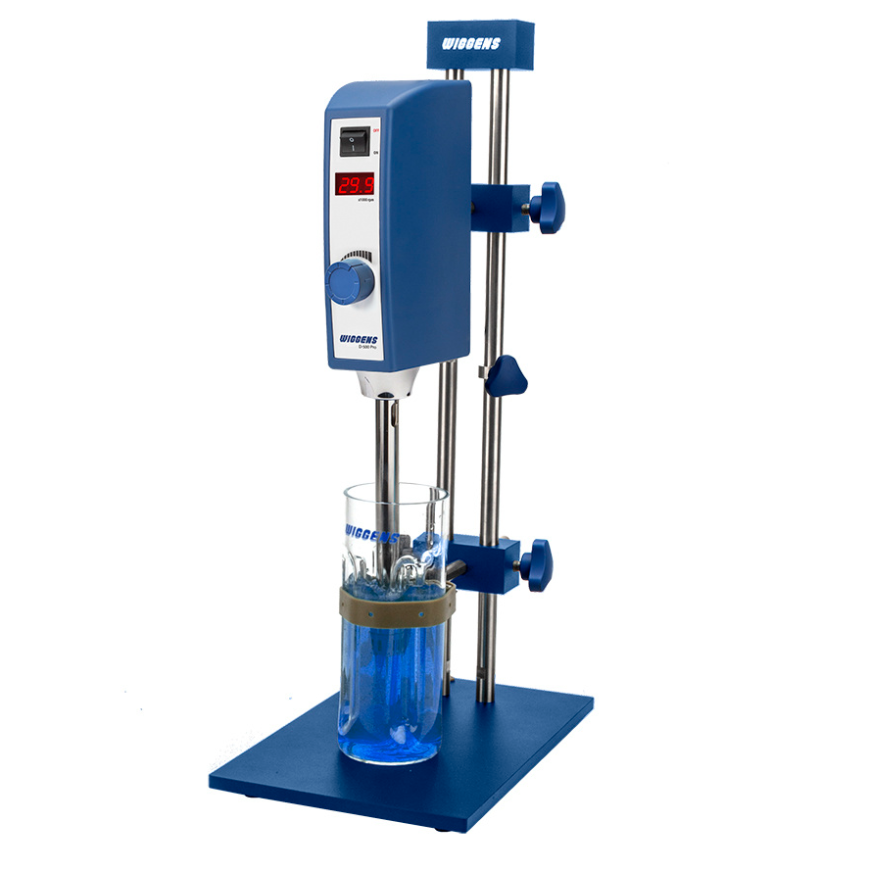
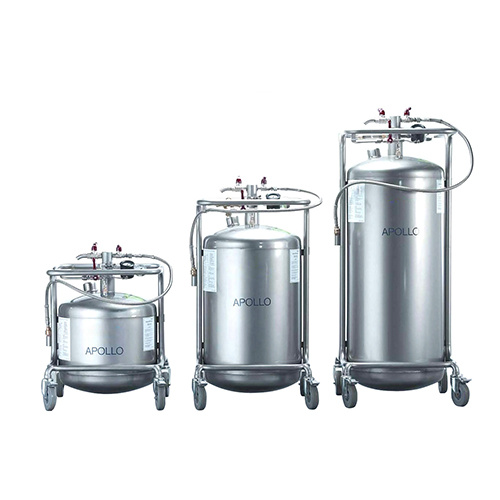
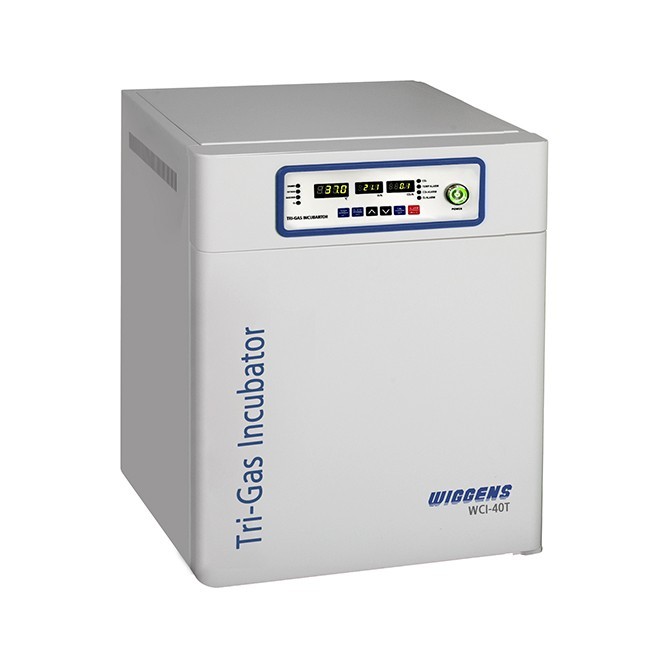
软骨肉瘤细胞系中13C-谷氨酰胺检测方案(自动进样器)
在缺少动态信息的情况下,代谢组学数据的解读通常十分复杂,这是因为在相应代谢物丰度未发生改变时,某个通路的代谢流可能已经发生显著变化。稳定同位素示踪(定性代谢流分析)的巨大潜力有助于解决这些状况,以便更深入地了解生物系统。在定性代谢流分析中,将稳定同位素示踪剂(通常含有 13C、15N 或 2H)引入生物系统, 导致下游代谢物的同位素模式(同位素异数体分布)发生改变。该方法尤其适用于易于 引入稳定同位素示踪剂的细胞模型,对产生的标记模式及示踪剂掺入动力学的分析将提供对酶功能、途径依赖、基因表达和蛋白功能变化效应的洞察。 Agilent MassHunter VistaFlux 软件旨在设计一套完整的工作流程,帮助科学家进行定性代谢流分析,助于高分辨率准确质量数 TOF 和 Q-TOF LC/MS 数据的处理和可视化。软件提供的工具可进行特征提取、同位素掺入分析、同位素异数体丰度分析、天然丰度校正、统计学分析以及数据在通路中的可视化。
检测样品:
癌细胞/肿瘤细胞
检测项:
13C-谷氨酰胺
安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
癌症肿瘤中真空技术的作用检测方案(真空泵)
MIT 的普发真空解决方案一览:
隔膜泵
在 MIT,隔膜泵用作涡轮分子泵的前级泵。由于其紧凑性,普发真空的隔膜泵是集成到系统中的最佳选择。该产品优势明显:
■ 绝对干燥的无油真空
■ 隔膜使用寿命长
■ 低振动和低噪音水平
■ 高操作可靠性
■ 易于维护,因为膜和阀门更换简单
■ 由于使用了双电压电机或直流驱动器,可在全球范围内使用
涡轮分子泵
普发真空的涡轮分子泵在 MIT 产生所需的超高真空条件。凭借其高性能和可靠性以及极好的经济性和效率,它们是满足离子束机器要求的最佳解决办法。其优势包括:
■ 经验证的轴承系统实现了高可靠性
■ 设计、技术组件和泵速度等级的差异实现了灵活性
■ 高度发达的泵设计实现了高压缩性能和高效率
■ 低能耗
■ 很长的保养间隔周期
质谱仪
在 MIT,普发真空的 PrismaPlus 质谱仪用于在真空系统中进行残余气体分析。高灵敏度、稳定性和智能处理的结合使 PrismaPlus成为最佳解决方案。优势一览:
■ 模块化设计实现了最佳适应性
■ 紧凑的尺寸和高性能
■ 通过各种接口实现了方便的系统集成
■ 通过以太网联网
■ 高测量速度、稳定性和分辨率
测量设备
MIT 使用普发真空的 ActiveLine 和 DigiLine 高精度真空计测量仪器。它们具有模拟和数字两种输出。它们非常适合离子束系统的要求,并具有许多优势:
■ 磁性杂散场最小
■ 轻松集成
■ 耐用且易于维护
检测样品:
癌细胞/肿瘤细胞
检测项:
真空技术的作用
普发真空技术(上海)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
卵巢癌细胞中对顺铂的摄入情况检测方案(等离子体质谱)
在西方国家,顺铂,卡铂和奥沙利铂是使用最广泛的铂类癌症化疗药物。卡铂的有效性是由于其可以与DNA结合从而导致DNA- 铂(Pt)加合物的形成,但这也会造成DNA 的弯曲。因此在化疗后细胞必须修复DNA损伤,否则DNA复制受阻会导致细胞死亡。许多癌症患者最初对基于铂类的治疗比较敏感,但一段时间后,患者通常对顺铂治疗表现出耐药性,导致了癌症的复发。顺铂耐药性归因于三种主要的分子机制:DNA 修复的加速,胞浆失活的加速和细胞摄取药物能力的变化。其中,细胞摄取药物能力的变化主要表现在细胞对顺铂的摄入能力降低或者顺铂转运
的加速。细胞内顺铂的摄入与肿瘤负荷相关,也就是说肿瘤对顺铂反应降低会导致细胞内顺铂的含量降低。所以,分析单个细胞水平对顺铂的摄入和分布对于评估治疗的有效性具有非常重要的意义。过多顺铂进入细胞内会增加DNA 损伤和细胞死亡的频率。了解细胞对顺铂的摄入将能为新疗法的开发提供参考,以提高肿瘤对顺铂的敏感性。传统方法的缺陷在于铂的浓度只反映整体细胞群内的浓度而不是个体细胞内的浓度。因此,顺铂摄入在个体细胞之间的分布和差异无法通过传统方法体现。实际上,细胞对顺铂的摄入最有可能根据个体有很大差异,但至今还没有有效的方法来评估。本文介绍了一种全新的技术,可对金属在单一细胞水平上进行定量:单细胞电感耦合等离子体质谱 (SCICP-MS)。SC-ICP-MS 是以单颗粒电感耦合等离子体质谱(SP-ICP-MS)技术为基础,后者能够在溶液中对纳米粒子进行评估与定量。两种技术都基于测量单个细胞(或单个纳米颗粒)在进入等离子体时产生的离散信号的原理。每个细胞中的金属成分离子化,产生离子流,检测器以每秒100000 数据点的速度快速对信号采集测量,从而使得单个细胞中的金属含量能被定量到阿克(ag)/ 每细胞的水平。相比测量细胞内顺铂摄入的传统方法,SC-ICP-MS 所得结果的信息量更加全面。
检测样品:
癌细胞/肿瘤细胞
检测项:
对顺铂的摄入情况
珀金埃尔默企业管理(上海)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
颅内侧壁动脉瘤中流动特性的计算和实验研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Pulsatile flow patterns in an intracranial side-wall aneurysm of a human carotid artery were investigated experimentally using microscopic particle image velocimetry on a flexible wall model. Numerical calculations were performed on a stiff-walled artery with the same geometry and flow conditions. Experimental results showed cyclical vortex formation and decay within the aneurysm. Numerical simulations agreed well with the experimental results and indicate that vortex position and magnitude are due to pulsatile flow conditions rather than wall elasticity. However, the present results suggest that wall compliance plays a role in sustaining the pressure gradients needed for vortex development.
检测样品:
癌细胞/肿瘤细胞
检测项:
流动特性的计算和实验研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
多形性成胶质细胞瘤中综合分析检测方案(液相色谱仪)
Agilent GeneSpring and Mass Profiler Professional (MPP) software was used to perform integrated multi-omics analysis of mRNA expression, miRNA expression, protein expression, and copy number aberration (CNA) associated with glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the most frequent and lethal of the central nervous system tumors. The genomic data was obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project. The molecular subtypes defined by TCGA for GBM were based on mRNA expression. We applied GeneSpring metadata analysis framework to explore the relationship between GBM subtypes and genomic CNA. A multi-omics correlation analysis was performed between mRNAs involved in neurogenesis and their validated miRNAs highlighting the molecular events in Proneural tumors that result in suppression of p53 signaling. Furthermore, a combined analysis of mRNA expression data from TCGA with an independent, label-free GBM proteomics study revealed core subset of 54 signature genes and proteins highlighting the integrated biology analysis power of GeneSpring/MPP software. The core genomics signature clearly differentiated the known tumor subtypes in TCGA cohort. Intriguingly, while TCGA categorization of the proteomics samples were not experimentally determined, the core proteomics signature separated this cohort in 2 or 3 groups, suggesting that different TCGA subtypes may be present.
检测样品:
癌细胞/肿瘤细胞
检测项:
综合分析
安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
肺癌细胞中血管生成--甲状腺转录因子-1(TTG-1)对影响肺癌细胞血管生成影响检测方案(实验器材)
美国的科研人员通过对TTF-1的调控发现,TTF-1能直接调节血管内皮生长因子(VEGF),并且发现VEGF启动子上有多处TTF-1响应序列。 比如,VEGF的主要受体,VRGFR2显示出收到TTF-1的直接正调节。本文中显示,低氧并没有促进 TTF-1+肺癌细胞中的VEGF的表达。而采用外泌体培养基或者是去外泌体的培养基(EDM)时,TTF-1都能促进VEGF表达。但在研究中意外的发现TTF-1+肺癌细胞的去外泌体培养基(EDM-TTF-1+)能够内皮细胞的血管形成。
检测样品:
癌细胞/肿瘤细胞
检测项:
血管生成--甲状腺转录因子-1(TTG-1)对影响肺癌细胞血管生成影响
上海净信实业发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
细胞中环形细胞侵袭实验检测方案(实验器材)
肿瘤细胞的侵袭能力是肿瘤转移的一个重要特征。为了研究肿瘤细胞侵袭过程的机制,一系列体外细胞实验建立起来,用于研究细胞侵袭基底膜和基质的过程。体外侵袭实验首先是采用人工重构基底膜材料Matrigel,可以在37℃逐渐凝固成胶,结构与天然基质膜结构极为相似。通常的实验是在孔径8μm的滤膜上铺上一层Matrigel,细胞不能自由穿过,必须分泌水解酶,并通过变形运动才能穿过。实验之后通过对穿过“基质膜”的细胞进行计数,来确定细胞的侵袭能力。这一方法非常仿真的模拟了细胞在生理状态下的侵袭过程,但是其也有一定的局限性。由于滤膜的不透光性,使得直接观察细胞伪足和骨架变化变得非常困难。
检测样品:
癌细胞/肿瘤细胞
检测项:
环形细胞侵袭实验
上海净信实业发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
脑动脉瘤中流体力学特性的影响研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Embolic coiling is the most popular endovascular treatment available for cerebral aneurysms. Nevertheless,
the embolic coiling of wide-neck aneurysms is challenging and, in many cases, ineffective. Use
of highly porous stents to support coiling of wide-neck aneurysms has become a common procedure in
recent years. Several studies have also demonstrated that high porosity stents alone can significantly
alter aneurysmal hemodynamics, but differences among different stent configurations have not been
fully characterized. As a result, it is usually unclear which stent configuration is optimal for treatment.
In this paper, we present a flow study that elucidates the influence of stent configuration on cerebral
aneurysm fluid dynamics in an idealized wide-neck basilar tip aneurysm model. Aneurysmal fluid
dynamics for three different stent configurations (half-Y, Y and, cross-bar) were first quantified using
particle image velocimetry and then compared. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations were
also conducted for selected stent configurations to facilitate validation and provide more detailed
characterizations of the fluid dynamics promoted by different stent configurations. In vitro results
showed that the Y stent configuration reduced cross-neck flow most significantly, while the cross-bar
configuration reduced velocity magnitudes within the aneurysmal sac most significantly. The half-Y
configuration led to increased velocity magnitudes within the aneurysmal sac at high parent-vessel
flow rates. Experimental results were in strong agreement with CFD simulations. Simulated results
indicated that differences in fluid dynamic performance among the different stent configurations can be
attributed primarily to protruding struts within the bifurcation region.
检测样品:
癌细胞/肿瘤细胞
检测项:
流体力学特性的影响研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供46篇癌细胞/肿瘤细胞检测方案,可分别用于生化检验检测、遗传检测,参考标准主要有等