方案详情
文
Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzofurans (PCDFs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are
classes of related environmental pollutants produced through diverse sources or industrial use and are known to
strongly bio-accumulate and produce multiple toxic endpoints in animals and humans 1,2 . The 2,3,7,8-
tetrachlorodibenzobenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) isomer has been classified as a group 1A human carcinogen by IARC 2 .
PCBs with dioxin-like properties are often measured with the PCDD/Fs. These three classes of chemicals are listed
as persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by the Stockholm convention designated for world-wide reduction in the
environment 1 .The primary route of non-occupational human exposure to PCDDs and PCDFs is foods and animal
feeds 3-5 . Monitoring programs established are aimed to aid efforts to control contamination in foods and animal
feeds 5 . Central to these efforts are confirmatory methods capable of measuring these chemicals at low
concentrations in foods. We investigated an orbital trapping mass spectrometer for the measurement of PCDD/Fs
and PCBs at low concentrations in whole cow’s milk.
方案详情

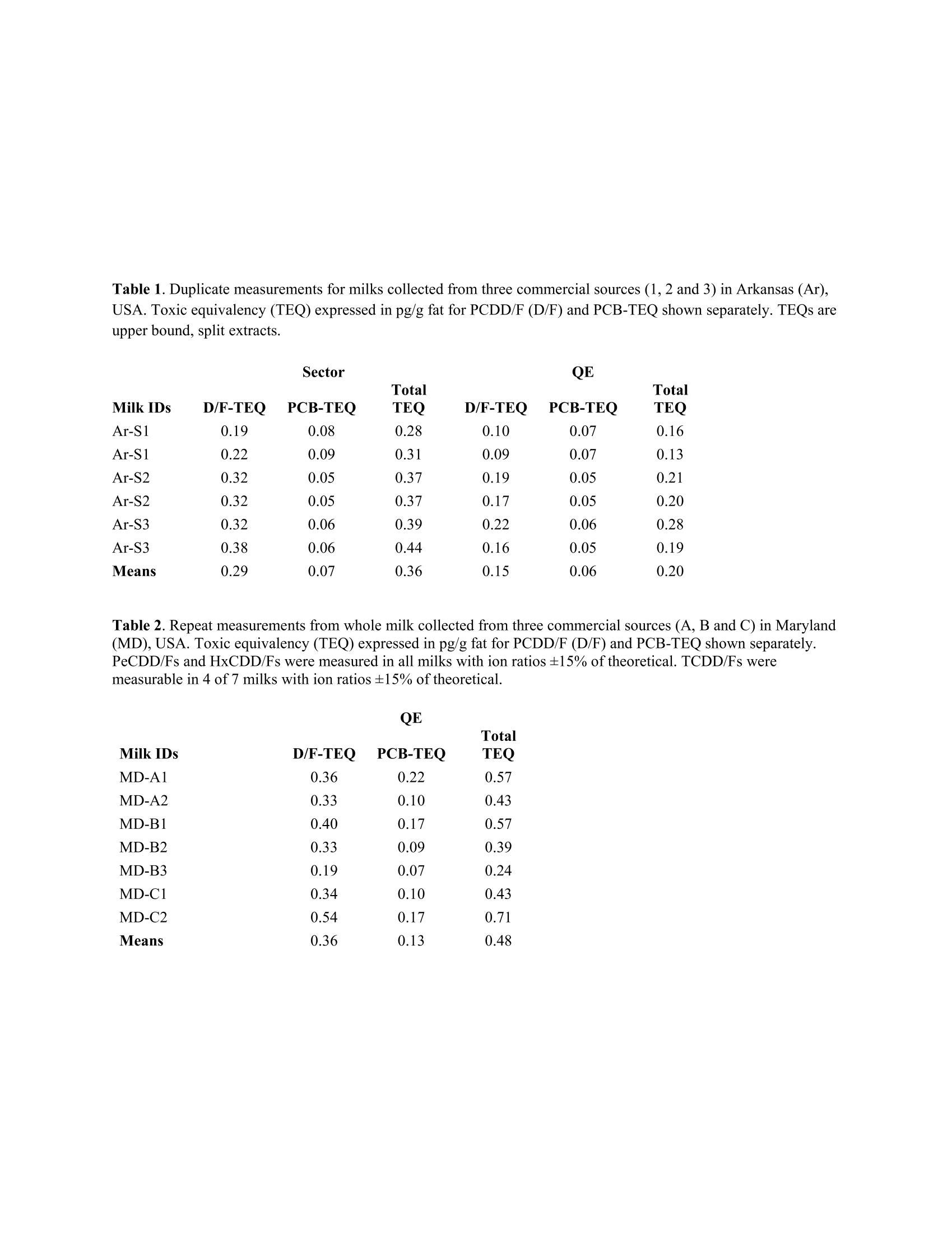
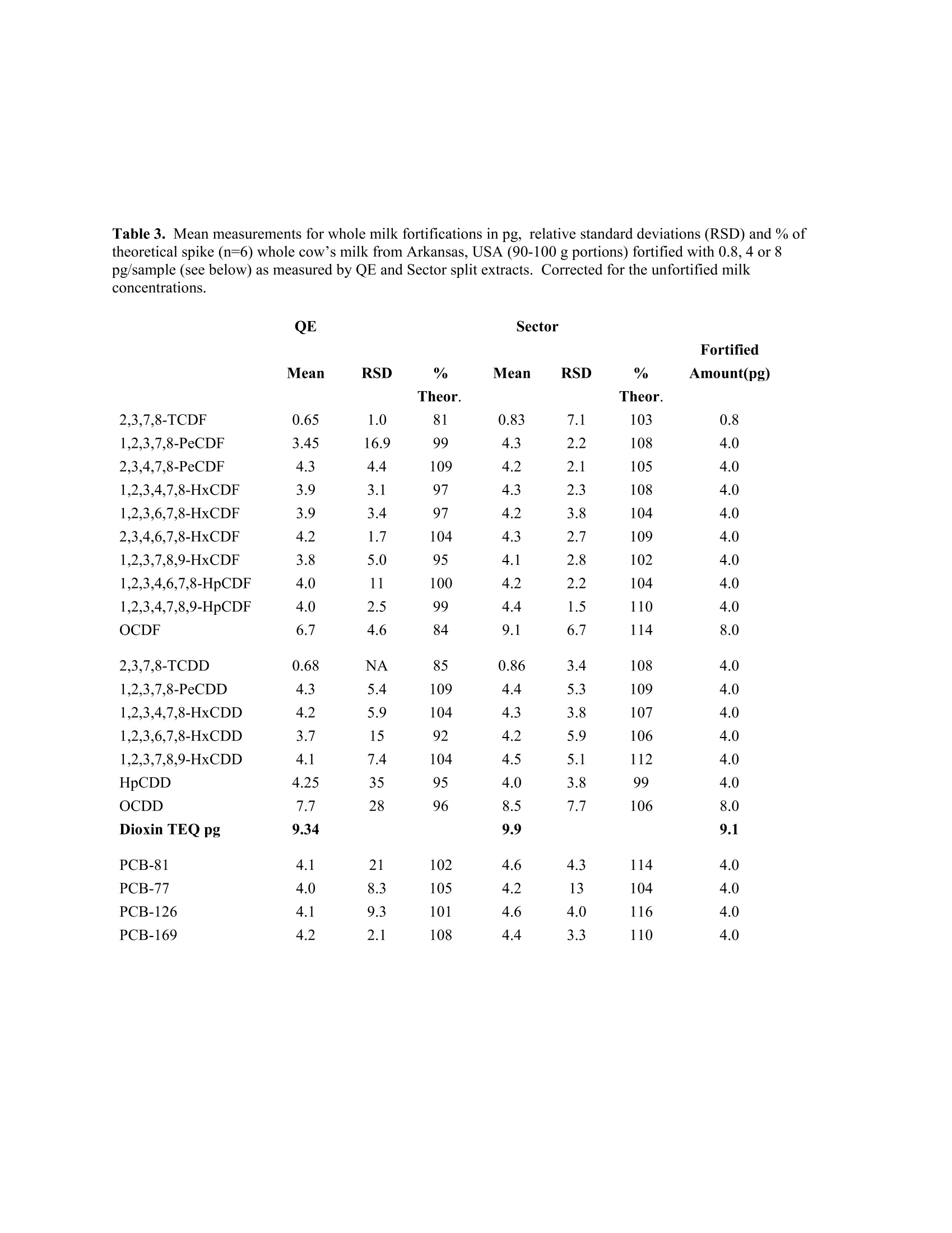
Accepted Organohalogen Compounds August 2017 HIGH RESOLUTION ORBITAL TRAPPING MASS SPECTROMETRYMEASUREMENT OF PERSISTENT ORGANIC POLLUTANTS IN COW’s MILK Hayward DG, Archer JC U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition, 5001 Campus Dr, College Park,MD 20740 USA "U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Office of Regulatory Affairs, 3900 NCTR Rd. Jefferson Ar. 72079 USA Introduction Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzofurans (PCDFs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are classes of related environmental pollutants produced through diverse sources or industrial use and are known tostrongly bio-accumulate and produce multiple toxic endpoints in animals and humans1.2. The 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzobenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) isomer has been classified as a group 1A human carcinogen by IARC.PCBs with dioxin-like properties are often measured with the PCDD/Fs. These three classes of chemicals are listedas persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by the Stockholm convention designated for world-wide reduction in theenvironment .The primary route of non-occupational human exposure to PCDDs and PCDFs is foods and animalfeeds3-5. Monitoring programs established are aimed to aid efforts to control contamination in foods and animalfeeds. Central to these efforts are confirmatory methods capable of measuring these chemicals at lowconcentrations in foods. We investigated an orbital trapping mass spectrometer for the measurement of PCDD/Fsand PCBs at low concentrations in whole cow’s milk. Materials and methods Two calibration curves were constructed. One curve was prepared using Wellington Laboratory mixtures of all 17native 2,3,7,8-substituted congeners and all 17 13Ci2 labeled standards at concentrations of 0.1, 0.2, 1, 5, 10, 20 and40 ng/mL for PCDD/F along with PCBs 77, 81, 126 and 169 at 1, 2,5,20,100,1000 ng/mL used only withMaryland milks. The second curve uses the Cambridge Isotope laboratories (CIL) mixtures, EDF-9999-1-5, dilutingthem 10 fold resulting in concentrations of 0.25, 1, 5,20 and 100 ng/mL. PCBs 77, 81, 126 and 169 were added at0.25,1, 5,20 and 100ng/mL. Whole cow’s milks from 3 commercial sources in Arkansas, USA were fortified 6times near the maximum level allowable by EU (2.5 pg PCDD/F TEQ/g fat) and 6 unfortified milk portions (90-100g each)2 each from the 3 sources were also analyzed. Whole milk samples from 3 commercial sources inMaryland USA, were collected and measured. The Arkansas whole milks were extracted using a GerhardtHydrotherm M/SoxthermMusing 90-100g milk, 20 mL ethanol and 0.5g sodium oxalate and processed with 2Msulfuric acid using a Hydrotherm M/Soxtherm Msystem. Fat obtained was removed by GPC followed by multi-layered silica columns. Final PCDD/F separation was performed with HPLC employing a 2-(1-pyrenyl)ethyl silica(PYE) column. The PCDD/Fs fraction was reconstituted in 10 pL of nonane. Whole milks from Maryland wereextracted using hexane/diethyl ether after addition of ethanol and sodium oxalate following a previously describedmethod4. Whole milk extracts from Arkansas milks were measured using a Micromass AutoSpec Premier highresolution mass spectrometer a double focusing instrument (sector) with an Agilent 7890A gas chromatograph(GC)equipped with a 4 mm ID split/splitless liner with 1uL injections onto a 60 M x 0.25 mm ID DB-5ms column. Allmilk extracts from Arkansas and Maryland, USA were measured using a TRACE 1300 GC coupled to a Q-Exactivemass spectrometer (QE) (ThermoFisher, San Jose, CA,USA). The GC column was a 40 Mx 0.18 mm DB-5ms with a split/splitless injector, 4mm ID Restek sky liner. Two uLs were injected splitless at 300° C. GC was programmedfrom a starting temperature of 120℃ which was held for 2 min prior to ramping at 20 ℃ /min. to 200 C. It was thenramped at 5C/min. to 240C and held for 12 min. before ramping at 10°/min. to 280°C with a final hold time of 10min. The QE was operated in full scan SIM mode with 6 quadrupole filters. Settings used were 285-340, 300-340,335-354, 335-380, 369-410, 435-480 m/z. An offset of -2V was set between the source and the C-Trap. Otherelectron ionization source parameters were default including 70 eV, 50 pamps emission current, 1E6 target, AGC.No lock masses were used. Transfer line and source temperatures were 250℃ and 300 ℃, respectively. Results and Discussion Table 1 provides the TEQs measured by the sector and QE for PCDD/Fs,PCB-81, 77, 126 and 169 in Arkansasmilks. The TEQs for the PCBs agree closely with a range of 0.05-0.08 pg/g fat for the HRMS-sector and 0.05-0.07pg/g fat for the QE. However, the PCDD/F TEQs were lower with the QE (0.06-0.22 pg/g fat upper bound) than thesector (0.19-0.38 pg/g fat). The sector identified PeCDD and 2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF in all milks, while QE found only 2of 6 milks extracts with these congeners identified (ion ratios within ±15% of theoretical). The QE did not detectany signals for TCDD, TCDF or 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDF in the unfortified milk unlike the sector which measured thesecongeners in nearly all milks (data not shown). Five of the six Arkansas milks by QE failed the upper bound/lowerbound criteria’ of±30% for the PCDD/F TEQ. For milks collected in Maryland, USA, PCDD/Fs and PCBs weremeasured using the QE only (Table 2). PCDD/F TEQs were 0.19-0.54 pg/g fat the QE (Table 2) in a similar rangeto Arkansas milks measured the by the sector (Table 1). All the PeCDD/Fs and HxCDD/Fs were measurable in allMaryland milk by the QE with isotope ratios ±15%, except 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDF (not detected). All these milkspassed the upper bound/lower bound criteria. All milk PCDD/F TEQs from the Arkansas or Maryland were 5-12times below the maximum limit set by the EU. The results from the two instruments were comparable for the milksfortified near the current EU maximum limit for PCDD/Fs (2.5 pg/g fat TEQ). Mean congener amounts werebetween 76-116% of theoretical with 1-28 relative standard deviations (RSDs)using the QE while the sector was99-112% and 1.5-13 RSDs. TCDD, TCDF 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDF amounts by the QE were lower due to evaporationlosses during and after multiple injections in the sector and APGC (Table 3). The mean amounts of PCDD/F TEQmeasured in the fortified milks were nearly the same using either instrument (9.3 and 9.9 pg) (Table 3). The milkcleanup aided QE measurements in the fortified milks by maintaining low noise and interference in the TIC.Nevertheless, HpCDD was observed co-eluting with an unknown compound that produced a 0.8 minute wideresponse in the TIC of most milk samples. The peak was 1000 times larger than the labeled standard with a fragmention at m/z 423.17 close to the native HpCDD mass of 423.7767. The presence of this compound may be responsiblefor a lower than expected result for one lower fortified HpCDD measurement increasing that congener's RSD. References: 1 http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/Overview/TextoftheConvention/tabid/2232/Default.aspx 2 Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and Polychlorinated dibenzofurans; IARC Mongraphs on the Evalutationof Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 1997 Vol 69 3 Travis CC, Hattemer-Frey HA (1991) Sci. Total Environ, 104 97-127. 4 Hayward DG (1997) Chemosphere, 34 929-939. 5Malisch R, Kotz A (2014) Sci. Tot. Environ, 49 2-10. 6Archer JC, Jenkins RG (2017) J. Chromatogr. B, 1041-1042 70-76. 7 Malisch R, Baumann B, Behmisch PA, Canady R, Fraisse D, Furst P, Hayward D, Hoogenboom R,Hoogerbrugge R, Liem D, Papke O, Wiesmuller T (2001) Organohalogen Compounds, 50 53-58. Table 1. Duplicate measurements for milks collected from three commercial sources (1, 2 and 3) in Arkansas (Ar),USA. Toxic equivalency (TEQ) expressed in pg/g fat for PCDD/F (D/F) and PCB-TEQ shown separately. TEQs areupper bound, split extracts. Milk IDs Total Total D/F-TEQ PCB-TEQ TEQ D/F-TEQ PCB-TEQ TEQ Ar-S1 0.19 0.08 0.28 0.10 0.07 0.16 Ar-S1 0.22 0.09 0.31 0.09 0.07 0.13 Ar-S2 0.32 0.05 0.37 0.19 0.05 0.21 Ar-S2 0.32 0.05 0.37 0.17 0.05 0.20 Ar-S3 0.32 0.06 0.39 0.22 0.06 0.28 Ar-S3 0.38 0.06 0.44 0.16 0.05 0.19 Means 0.29 0.07 0.36 0.15 0.06 0.20 Table 2. Repeat measurements from whole milk collected from three commercial sources (A, B and C) in Maryland(MD), USA. Toxic equivalency (TEQ) expressed in pg/g fat for PCDD/F (D/F) and PCB-TEQ shown separately.PeCDD/Fs and HxCDD/Fs were measured in all milks with ion ratios ±15% of theoretical. TCDD/Fs weremeasurable in 4 of 7 milks with ion ratios ±15% of theoretical. QE Milk IDs D/F-TEQ PCB-TEQ TEQ MD-A1 0.36 0.22 0.57 MD-A2 0.33 0.10 0.43 MD-B1 0.40 0.17 0.57 MD-B2 0.33 0.09 0.39 MD-B3 0.19 0.07 0.24 MD-C1 0.34 0.10 0.43 MD-C2 0.54 0.17 0.71 Means 0.36 0.13 0.48 Table 3. Mean measurements for whole milk fortifications in pg, relative standard deviations (RSD) and % oftheoretical spike (n=6) whole cow’s milk from Arkansas,USA (90-100 g portions) fortified with 0.8, 4 or 8pg/sample (see below) as measured by QE and Sector split extracts. Corrected for the unfortified milkconcentrations. Sector Mean RSD % Mean RSD % Amount(pg) Theor. Theor. 2,3,7,8-TCDF 0.65 1.0 81 0.83 103 0.8 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDF 3.45 16.9 99 4.3 108 4.0 2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF 4.4 109 4.2 105 4.0 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDF 3.1 97 4.3 108 4.0 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDF 3.4 97 4.2 104 4.0 2,3,4,6,7,8-HxCDF 1.7 104 4.3 109 4.0 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDF 5.0 95 4.1 102 4.0 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDF 4.0 11 100 4.2 2.2 104 4.0 1,2,3,4,7,8,9-HpCDF 2.5 99 4.4 1.5 110 88 OCDF 4.6 84 9.1 6.7 114 2,3,7,8-TCDD 0.68 NA 85 0.86 3.4 108 4.0 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDD 4.3 5.4 109 4.4 5.3 109 4.0 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDD 5.9 104 4.3 3.8 107 4. 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDD 15 92 4.2 5.9 106 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDD 7.4 104 4.5 5.1 112 4.0 HpCDD 4.25 35 95 4.0 3.8 99 0CDD 7.7 28 96 8.5 7.7 106 Dioxin TEQ pg 9.34 9.9 PCB-81 4.1 21 102 4.6 4.3 114 4.0 PCB-77 4.0 8.3 105 4.2 13 104 4.0 PCB-126 41 9.3 101 4.6 4.0 116 4.0 PCB-169 4.2 2.1 108 4.4 3.3 110 4.0 Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzofurans (PCDFs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are classes of related environmental pollutants produced through diverse sources or industrial use and are known to strongly bio-accumulate and produce multiple toxic endpoints in animals and humans 1,2 . The 2,3,7,8- tetrachlorodibenzobenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) isomer has been classified as a group 1A human carcinogen by IARC 2 . PCBs with dioxin-like properties are often measured with the PCDD/Fs. These three classes of chemicals are listed as persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by the Stockholm convention designated for world-wide reduction in the environment 1 .The primary route of non-occupational human exposure to PCDDs and PCDFs is foods and animal feeds 3-5 . Monitoring programs established are aimed to aid efforts to control contamination in foods and animal feeds 5 . Central to these efforts are confirmatory methods capable of measuring these chemicals at low concentrations in foods. We investigated an orbital trapping mass spectrometer for the measurement of PCDD/Fs and PCBs at low concentrations in whole cow’s milk.
确定


还剩2页未读,是否继续阅读?
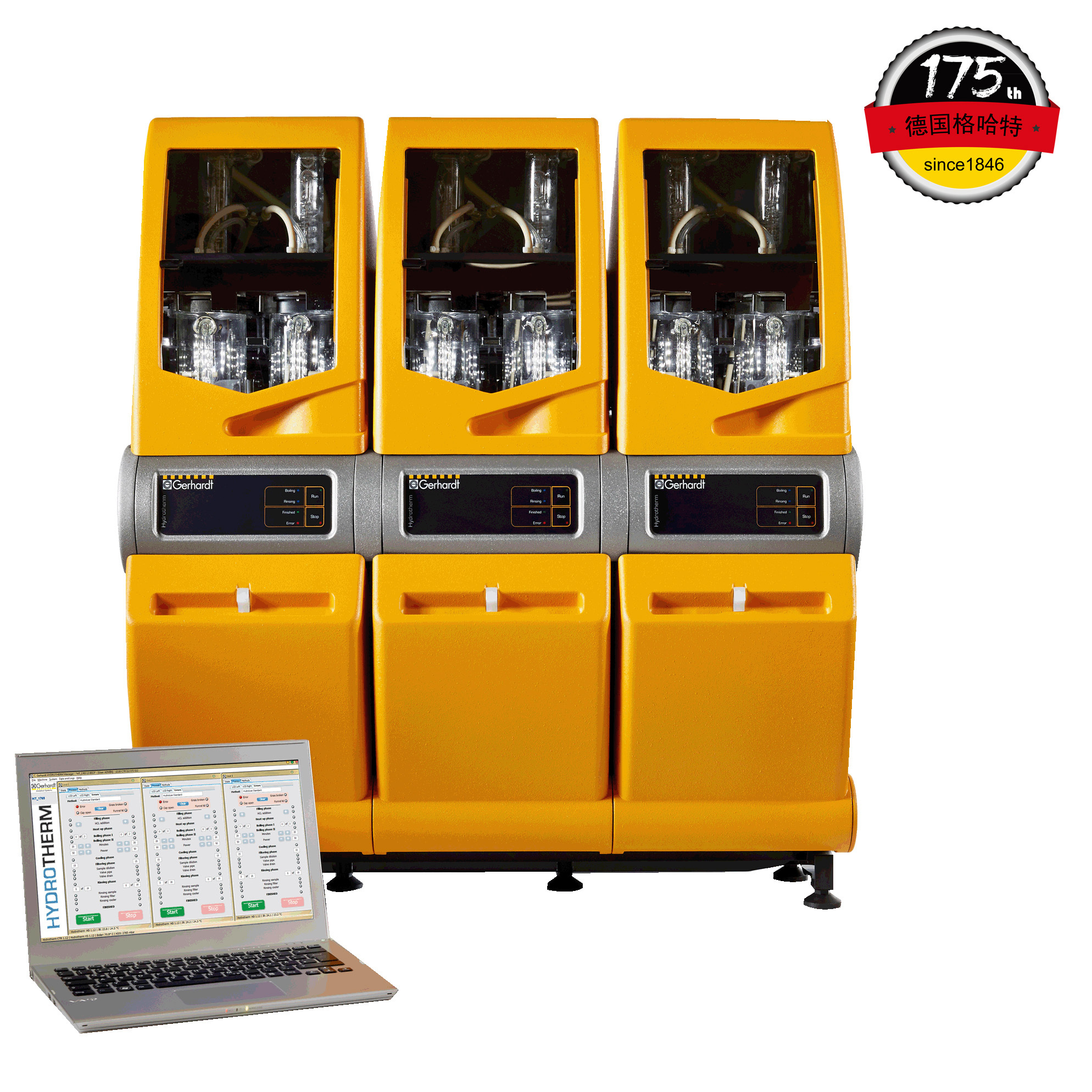
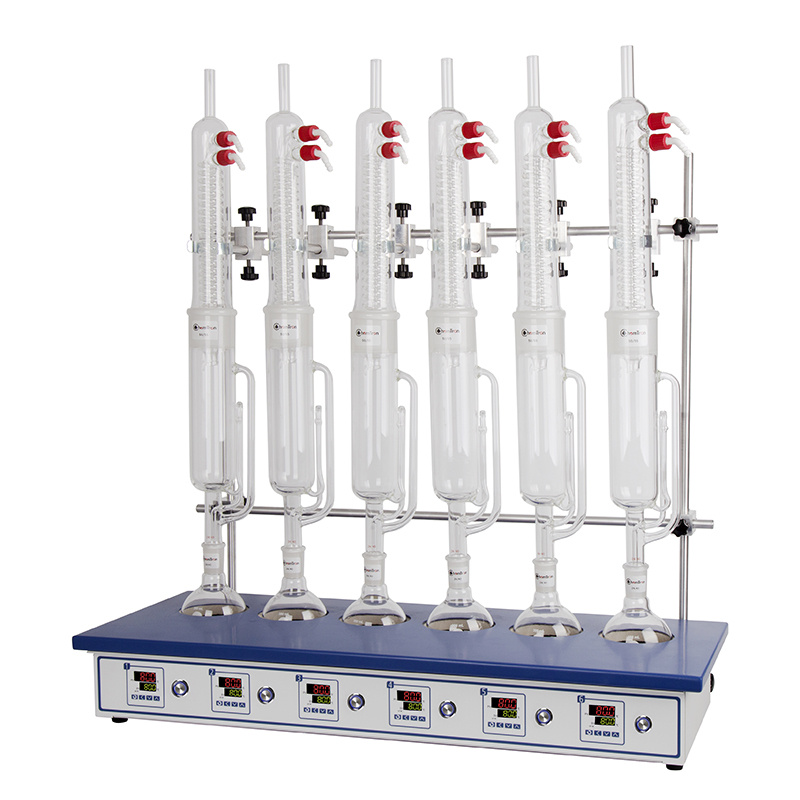
中国格哈特为您提供《牛奶中萃取前处理检测方案(抽提萃取)》,该方案主要用于液体乳中前处理检测,参考标准《GB 5009.205-2013 食品中二噁英及其类似物毒性当量的测定》,《牛奶中萃取前处理检测方案(抽提萃取)》用到的仪器有格哈特全自动超级水解脂肪测定系统HT6、格哈特全自动快速索氏提取SOXTHERM、德国加液器MM
推荐专场
该厂商其他方案
更多