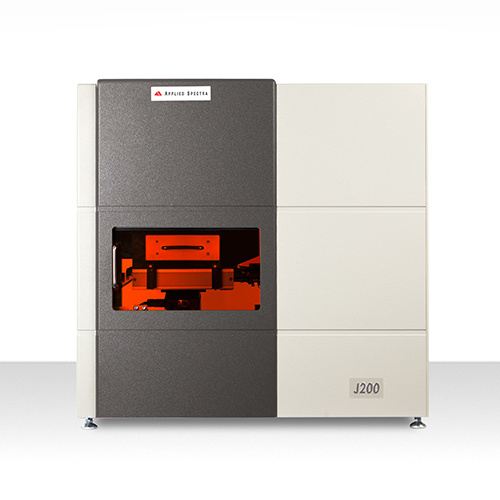
铸铁和毛坯铸件分析是具有挑战性的,例如,在铸铁中通常有2%到4%的碳以各种形式存在,从微小的石墨球(球墨铸铁)到大的薄片(灰铸铁)。常用的火花/电弧原子发射光谱技术需要预燃时间进行表面均匀化,但在预燃过程中一些游离碳优先蒸发,从而导致定量结果不准确。辉光放电光谱法(GDS, Glow Discharge Spectrometry, GDS)需要较长的预燃时间,才能获得亚铁材料中碳等元素的稳定信号。LIBS(激光诱导击穿光谱)仪器为对所有铸铁中的碳和其他元素进行定量分析提供了另一种方法。J200 LIBS采用短激光脉冲将高功率密度传输到样品表面,并直接激发像碳薄片这样的坚韧材料进行快速的原子发射光谱分析。对铸铁中所有材料相的有效激发使J200 LIBS仪器能够对铸铁样品进行准确、快速的碳和其他重要元素的定量分析,而不需要进行长时间的预燃。该仪器还可以提供深度剖析和关键元素的3D地图,所有这些都不需要额外的硬件。功能强大,易于使用的Clarity LIBS数据分析软件,使可视化的地图结果毫不费力。由于没有或极少量的氩气消耗,操作成本很低,LIBS是对生产中的原材料进行快速QC和对铸件进行分析以确定铸件成品的元素组成的理想选择。
方案详情

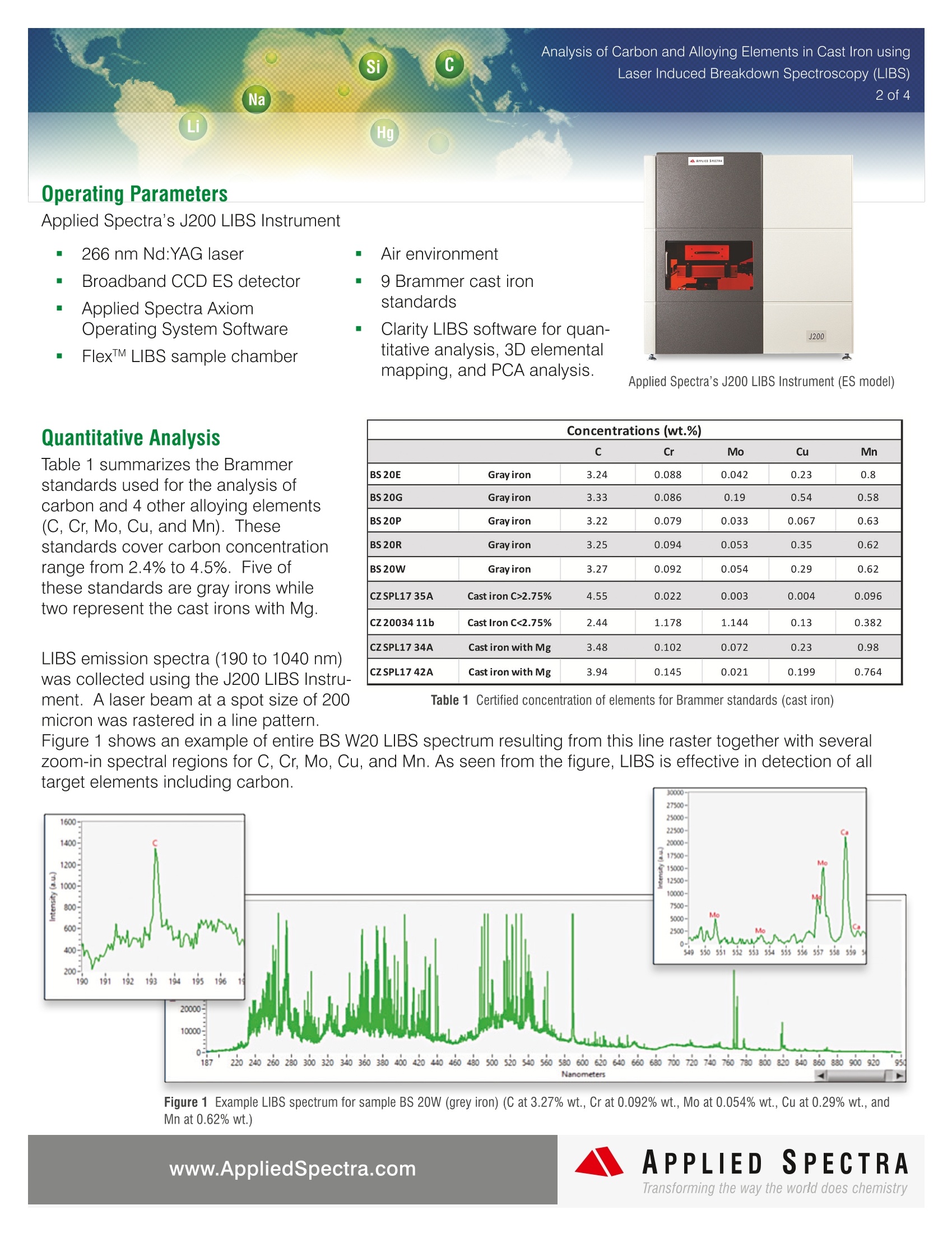
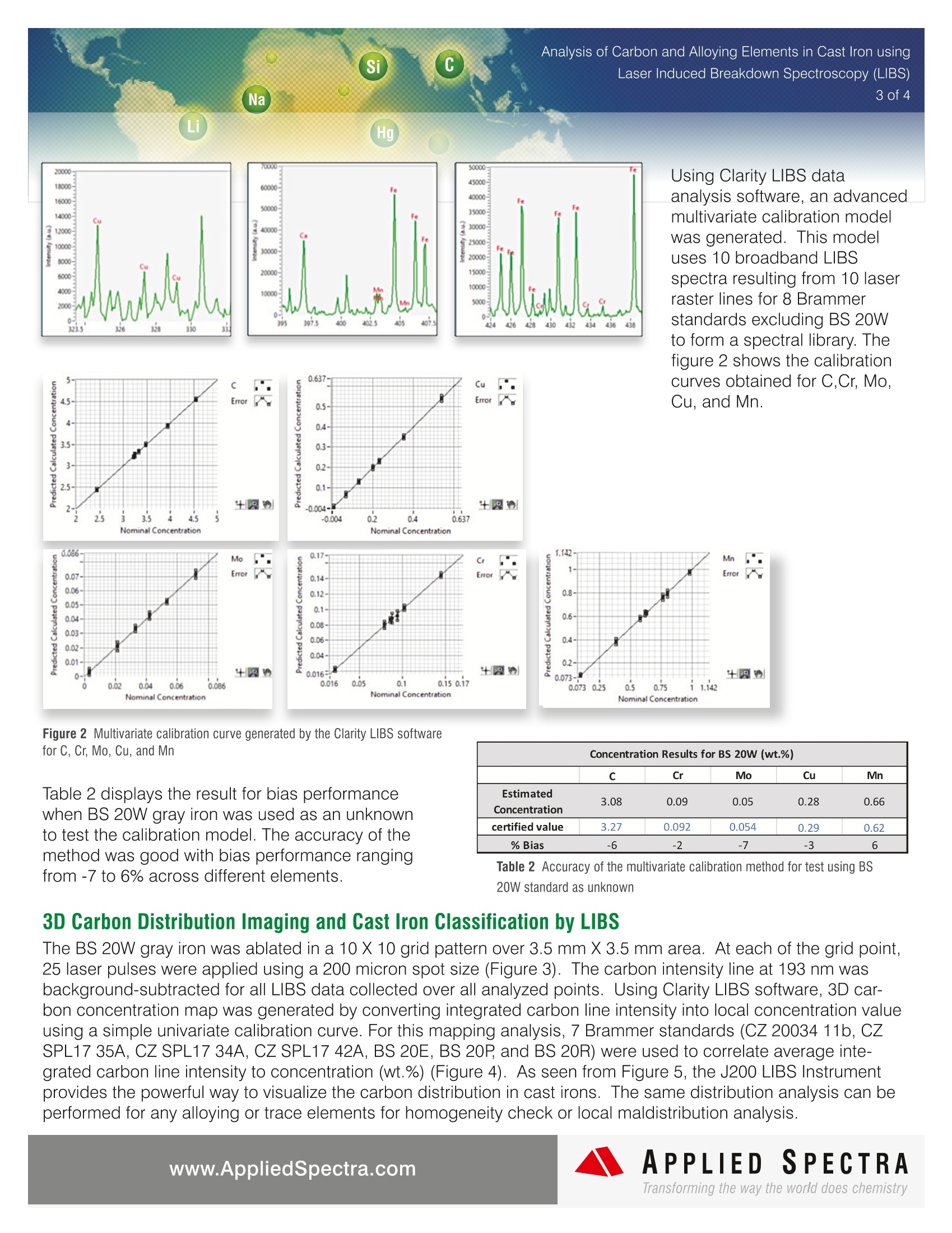
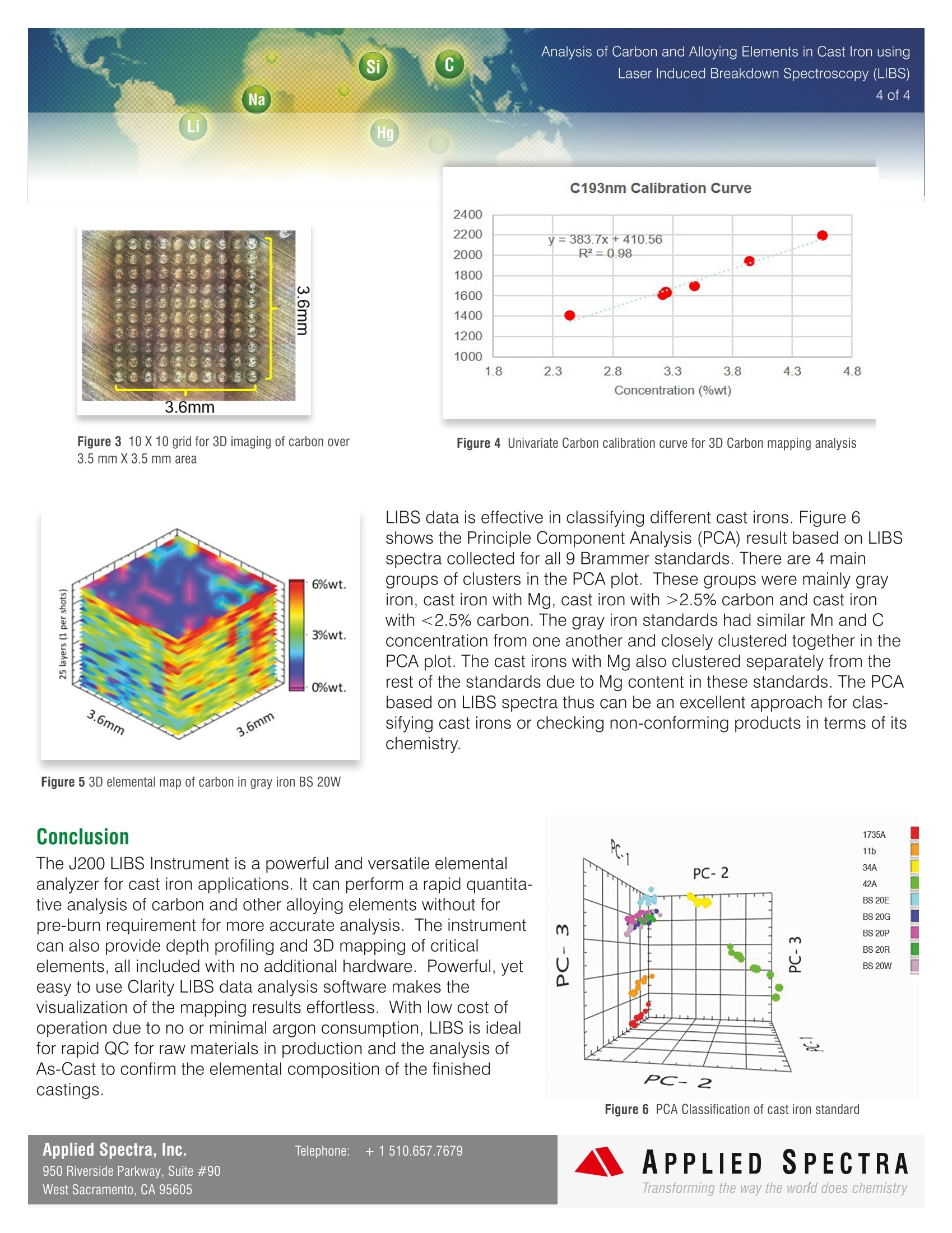
Analysis of Carbon and Alloying Elements in Cast Iron using2 of 4 In today's iron foundries, the labs are faced with a large volumeof daily samples comprised of raw materials, base iron, posttreatment iron, and actual castings. There are various types ofcast irons with different target physical properties such as ten-sile & compressive strength,hardness, machinability, and corro-sion resistance. The production of different cast irons dependson the nature of heat treatment processes and the compositionof carbon and other alloying elements such as Cr, Mo, Cu, andNi. Cast iron and As-Cast analysis have proven to be challengingto produce accurate and reproducible results. For example,carbon which is typically present from 2 to 4% in cast irons is present in various forms that range from tiny graphite spheroids (nodular cast iron) to large flakes (gray iron). Thepopular Spark/Arc OES technique requires a pre-burn time for surface homogenization, but some of free carbonpreferentially evaporates during pre-spark and inaccuracy in quantitative result arises. For GDS (Glow DischargeSpectrometry), a long pre-burn time is necessary to obtain stable signals of carbon and other elements in the fer-rous material. The J200 LIBS (Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) Instrument from Applied Spectra provides an alternateapproach for performing quantitative analysis of carbon and other elements in all cast irons. The J200 LIBS usesshort laser pulses to deliver high power density into the sample surface and directly excite tough materials likecarbon flakes for rapid OES analysis. The effective excitation of all phases of materials in the cast irons allows theJ200 LIBS Instrument to perform accurate and rapid quantitative analysis of carbon and other important elementsfor the cast iron samples without necessity for a long pre-burn. The J200 LIBS Instrument also analyzes all other elements in the periodic table from Hydrogen to Plutonium,including lighter elements and non-metals such as Li, B, H, N, O, S, and F. The measurements can be performedin air or using low flow of Argon purge gas (mls/min versus liters/min), significantly reducing the cost of operation(COO). The J200 LIBS provides high versatility in performing spatially resolved analysis with a laser spot size assmall as 10 micron for 2D and 3D mapping analysis. Finally, the J200 LIBS is an excellent QC tool with the capabil-ity to classify metal and metal alloy samples based on fingerprint-like LIBS spectra associated with specific metalproducts. In this current study, the J200 LIBS Instrument was used to demonstrate the quantitative analysis of carbon andother alloying elements in cast iron samples. A powerful LIBS capability to perform 3D elemental imaging andclassify different type of cast irons was also demonstrated. Si C Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) Na Li Hg Operating Parameters Applied Spectra's J200 LIBS Instrument 266 nm Nd:YAG laser Broadband CCD ES detector Applied Spectra AxiomOperating System Software Flex'M LIBS sample chamber Quantitative Analysis Table 1 summarizes the Brammerstandards used for the analysis ofcarbon and 4 other alloying elements(C, Cr, Mo, Cu, and Mn). Thesestandards cover carbon concentrationrange from 2.4% to 4.5%. Five ofthese standards are gray irons whiletwo represent the cast irons with Mg. Air environment 9 Brammer cast ironstandards Clarity LIBS software for quan-titative analysis,3D elementalmapping, and PCA analysis. Applied Spectra's J200 LIBS Instrument (ES model) LIBS emission spectra (190 to 1040 nm)was collected using the J200 LIBS Instru-ment. A laser beam at a spot size of 200micron was rastered in a line pattern. Table 1 Certified concentration of elements for Brammer standards (cast iron) Figure 1 shows an example of entire BS W20 LIBS spectrum resulting from this line raster together with severalzoom-in spectral regions for C, Cr, Mo, Cu, and Mn. As seen from the figure, LIBS is effective in detection of alltarget elements including carbon.30000 Figure 1 Example LIBS spectrum for sample BS 20W (grey iron) (C at 3.27% wt., Cr at 0.092% wt., Mo at 0.054% wt., Cu at 0.29% wt., andMn at 0.62% wt.) Si C Analysis of Carbon and Alloying Elements in Cast Iron usingLaser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) Na 3 of 4 Li Hg 70000 50000: 20000· 45000 18000- 60000- 40000- 16000- 50000 35000 14000- 312900 10000: 10000- 300008000-从从 112500( 10000 20000: 20000 15000- 6000 10000 4000- 10000 5000 2000 0- 02 395 397.5 400 4025 405 407.5 424 264is 424i4436 438 321.5 0.637- ocvC一 七 4.45· 0.5- Using Clarity LIBS dataanalysis software, an advancedmultivariate calibration modelwas generated. This modeluses 10 broadband LIBSspectra resulting from 10 laserraster lines for 8 Brammerstandards excluding BS 20Wto form a spectral library. Thefigure 2 shows the calibrationcurves obtained for C,Cr, Mo,Cu, and Mn. 4- 0.4- v c o 3.31.5- 0.3-a 3 0.2- 2.5 0.1- -0.004- 出阅 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 -0.004 0.2 0.4 0.637 Nominal Concentration Nominal Concentration 0.086- 0.17- Mo Crccu a 0.07- ¥ Error 0.14- Ertor 0.06- 0.12- 0.05- 0.1- 0.04- 0.08- 0.03- 0.06- 0.02- 0.04- 0.01- 4圆 0.016- 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.086 0.016 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.17 Nominal Concentration Nominal Concentration Figure 2 Multivariate calibration curve generated by the Clarity LIBS softwarefor C, Cr, Mo, Cu, and Mn Table 2 displays the result for bias performancewhen BS 20W gray iron was used as an unknownto test the calibration model. The accuracy of themethod was good with bias performance rangingfrom -7 to 6% across different elements. Concentration Results for BS 20W (wt.%) C Cr Mo Cu Mn Estimated 3.08 0.09 0.05 0.28 0.66 Concentration certified value 3.27 0.092 0.054 0.29 0.62 %Bias -6 -2 -7 -3 6 Table 2 Accuracy of the multivariate calibration method for test using BS 20W standard as unknown 3D Carbon Distribution Imaging and Cast Iron Classification by LIBS The BS 20W gray iron was ablated in a 10 X 10 grid pattern over 3.5 mm X 3.5 mm area. At each of the grid point,25 laser pulses were applied using a 200 micron spot size (Figure 3). The carbon intensity line at 193 nm wasbackground-subtracted for all LIBS data collected over all analyzed points. Using Clarity LIBS software, 3D car-bon concentration map was generated by converting integrated carbon line intensity into local concentration valueusing a simple univariate calibration curve. For this mapping analysis, 7 Brammer standards (CZ 20034 11b, CZSPL17 35A, CZ SPL17 34A, CZ SPL17 42A, BS 20E, BS 20P and BS 20R) were used to correlate average inte-grated carbon line intensity to concentration (wt.%) (Figure 4). As seen from Figure 5, the J200 LIBS Instrumentprovides the powerful way to visualize the carbon distribution in cast irons. The same distribution analysis can beperformed for any alloying or trace elements for homogeneity check or local maldistribution analysis. Si C Na Li Hg Figure 3 10 X10 grid for 3D imaging of carbon over3.5 mm X 3.5 mm area Figure 4 Univariate Carbon calibration curve for 3D Carbon mapping analysis LIBS data is effective in classifying different cast irons. Figure 6shows the Principle Component Analysis (PCA) result based on LIBSspectra collected for all 9 Brammer standards. There are 4 maingroups of clusters in the PCA plot. These groups were mainly grayiron, cast iron with Mg, cast iron with >2.5% carbon and cast ironwith <2.5% carbon. The gray iron standards had similar Mn and Cconcentration from one another and closely clustered together in thePCA plot. The cast irons with Mg also clustered separately from therest of the standards due to Mg content in these standards. The PCAbased on LIBS spectra thus can be an excellent approach for clas-sifying cast irons or checking non-conforming products in terms of itschemistry. Figure 5 3D elemental map of carbon in gray iron BS 20W Conclusion The J200 LIBS Instrument is a powerful and versatile elementalanalyzer for cast iron applications. It can perform a rapid quantita-tive analysis of carbon and other alloying elements without forpre-burn requirement for more accurate analysis. The instrumentcan also provide depth profiling and 3D mapping of criticalelements, all included with no additional hardware. Powerful, yeteasy to use Clarity LIBS data analysis software makes thevisualization of the mapping results effortless. With low cost ofoperation due to no or minimal argon consumption, LIBS is idealfor rapid QC for raw materials in production and the analysis ofAs-Cast to confirm the elemental composition of the finishedcastings. Figure 6 PCA Classification of cast iron standard APPLIEDSPECTRAwww.AppliedSpectra.comTransforming the way the world does chemistry LIBS(激光诱导击穿光谱)仪器为对所有铸铁中的碳和其他元素进行定量分析提供了另一种方法。J200 LIBS采用短激光脉冲将高功率密度传输到样品表面,并直接激发像碳薄片这样的坚韧材料进行快速的原子发射光谱分析。对铸铁中所有材料相的有效激发使J200 LIBS仪器能够对铸铁样品进行准确、快速的碳和其他重要元素的定量分析,而不需要进行长时间的预燃。该仪器还可以提供深度剖析和关键元素的3D地图,所有这些都不需要额外的硬件。功能强大,易于使用的Clarity LIBS数据分析软件,使可视化的地图结果毫不费力。由于没有或极少量的氩气消耗,操作成本很低,LIBS是对生产中的原材料进行快速QC和对铸件进行分析以确定铸件成品的元素组成的理想选择。
确定

还剩2页未读,是否继续阅读?
北京富尔邦科技发展有限责任公司为您提供《铸铁中碳和合金元素检测方案(激光诱导击穿)》,该方案主要用于铁中含量分析检测,参考标准--,《铸铁中碳和合金元素检测方案(激光诱导击穿)》用到的仪器有美国ASI 激光诱导击穿光谱仪(LIBS)
推荐专场
相关方案
更多














