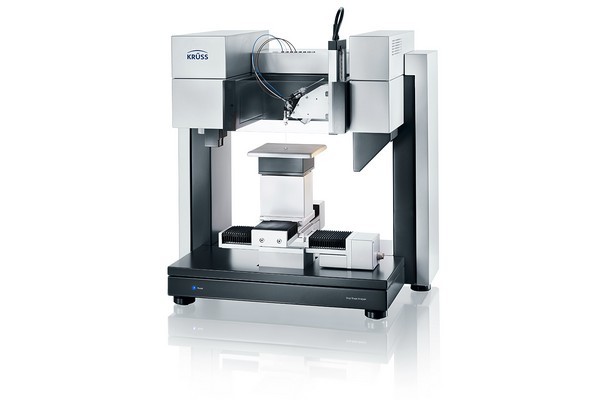
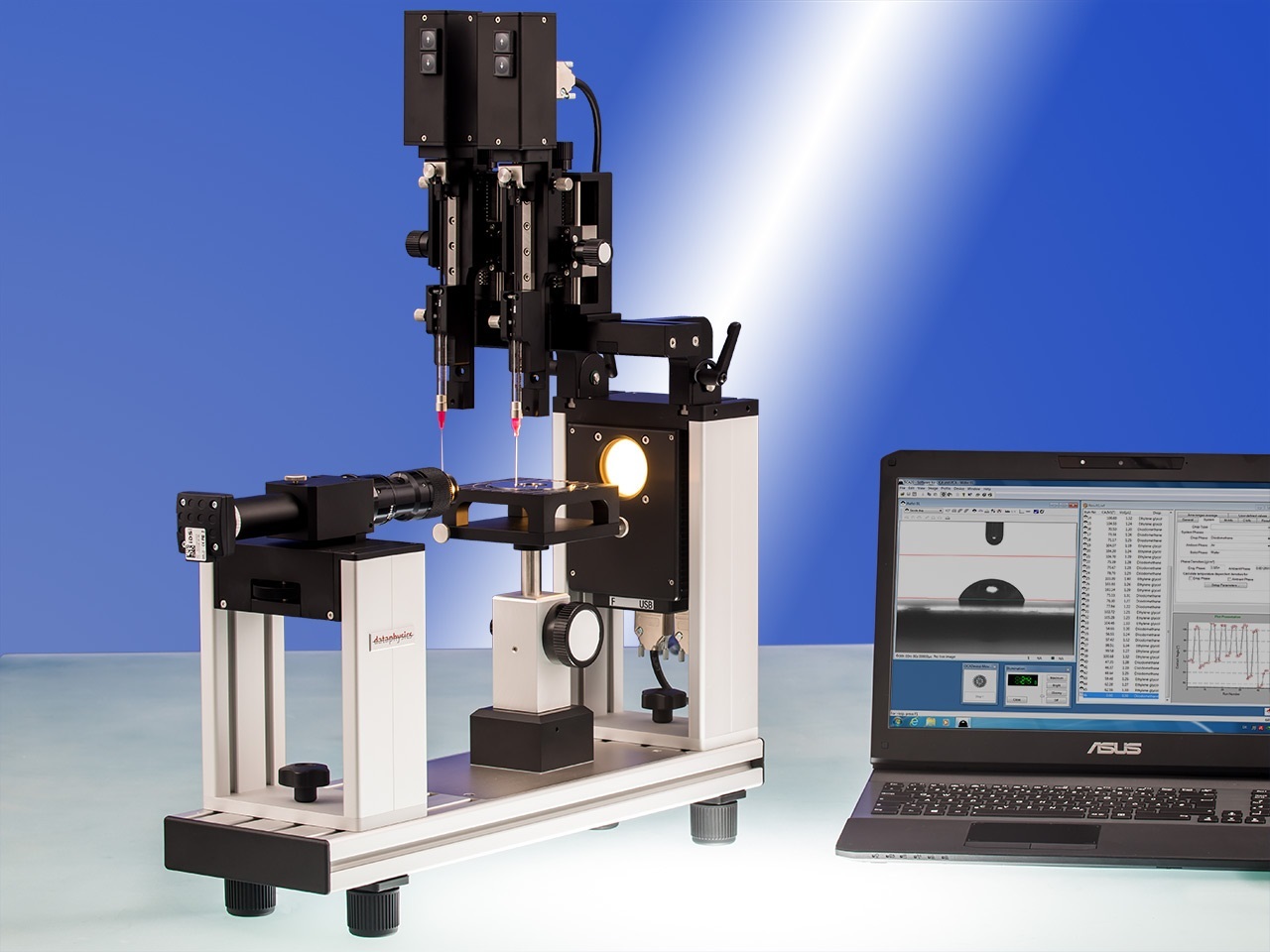
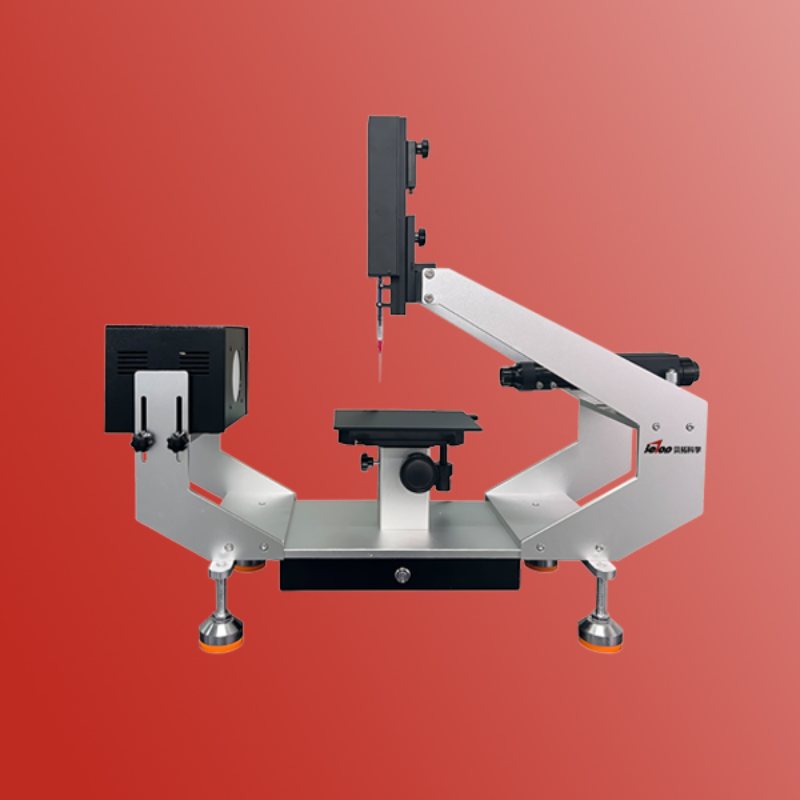
方案详情
文
由于表面极不均匀易于吸收液体,标准接触角测量方法难以量化纺织品的润湿行为。而捕泡法容许润湿样品的接触角测量。混有合成纤维的棉质材料可通过捕泡法测得表面能及其组成部分。因此,可精确测量高分子添加剂产生的水润湿性变化。
方案详情

KRUSS Application Report Surface energy of textiles Application report: AR251e Industry section: Textiles 咖 Authors: F.Thomsen, Date: C. Bilke-Krause02/2006 Method: Drop Shape Analyzer-DSA100 captive bubble Keywords: fibers, textiles,contact angle, surface free energy, wettability, captive bubble, compound materials,polymers Upside down: Surface energy measurement of textiles by captive bubblemethod Abstract The wetting behavior of textiles can hardly be quantified by standard contact angle measurements due to unevenness ofthe sample and rapid ad- or absorption of sample liquids. This may be remedied by the captive bubble method whichallows contact angle measurements on wetted samples. By means of this method, the surface energy and its polar anddisperse part of two cotton materials, one mixed with synthetic fibers, could be measured. Thereby, the changes of waterwettability occurring from this polymeric additive could be measured exactly. Whoever wants topperform ordinary contact anglemeasurements on textiles will face a couple of difficulties.First, textile samples easily absorb the drop liquid so thatthe measurement must be done in only a fewmilliseconds and no one can talk of a stationary value.Second, a tissue sample often is uneven due toprotruding fibers and it is difficult to determine abaseline. Both problems can be minimized by the captivebubble method. As for the standard method, i.e. measurement at thesessile drop, the sample liquid is dosed on to the samplefrom above, normally in a phase of ambient air. However,apart from the contact angle between liquid and solid,there also is a second contact angle, which most usersare normally not interested in: the complementary anglejointly formed by solid and gas phase at the three phasepoint. Both angles together add up to 180°. The captive bubble method puts everything upsidedown. The solid is initially wetted from below by theadjoined sample liquid. Then, a bubble is produced in theliquid below the sample which mounts and forms acontact angle at the bottom side of the sample. Thisbubble contact angle is - like the one of a liquid -determined by video evaluation. The liquid contact angleresults from the difference between this angle and 180°and will be calculated automatically by the software. In case of ad- or absorbing samples, what appears to bea detour actually is the easiest way. On the one hand, theangle can be determined when the sorption process isfinished -you easily get a stationary. On the other hand,wetting by liquid smoothes the sample and one gets aneven baseline. Fig. 1: Schematic view of the captive-bubble arrangement Experiment By means of this arrangement, a comparison could bemade between the surface energy oftwo textile samples:one of a pure cotton material and one of a compoundmaterial with synthetic fibers. Measurements were madewith the three standard test liquids: water, ethyleneglycol and diiodomethane. Calculation of the surfaceenergy from the contact angle data was done as perOwens-Wendt-Rabel-Kaelble. Results It could be shown that the surface energy of the textilematerial decreases in relation to its content of polymers.It also became obvious that the main difference lies inthe polar part of the surface energy which is reduced bythe synthetic fiber. As for the macroscopic behavior thismeans that compound materials show a minor wettabilityby polar liquids like water and are, e.g. more suitable forrainwear. Following pictures show both contact angle evaluations,below listedaare the results of the surface energydetermination. Fig. 2: Evaluation according to OWRK for pure cotton (top)and polymeric compound material (bottom) Pure cottonmaterial Polymeric compound material Surface energy(mN/m) 46.2 39.4 Polar part (mN/m) 34.5 29.3 Dispersive part(mN/m) 11.7 10.1 Tab.1: Surface energy of two textile samples Summary The captive bubble method allows via a detour ofmeasuring the contact angle of a bubble with a solidsample in liquid phase to determine the surface energyof samples that normally are difficult to be measured.The possibilities and advantages of the captive bubblemethod could be demonstrated for two textile samples.It could be shown how the surface energy of cotton canbe reduced by the concentration of added polymericfibers. Especially the polar part of the surface energy andwith it the water wettability can be influenced by addingsynthetic fibers. KRUSS GmbH|lBorsteler Chaussee Hamburg |Germany|www.kruss.de|
确定
还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
克吕士科学仪器(上海)有限公司为您提供《纺织品中表面能检测方案(接触角测量仪)》,该方案主要用于纺织品/服装/帽中表面能检测,参考标准--,《纺织品中表面能检测方案(接触角测量仪)》用到的仪器有KRUSS DSA100接触角测量仪
推荐专场
相关方案
更多