方案详情
文
清洗掉表面的脂类对于日常生活来说是再普通不过的事情。在本文中作者采用石英晶体微天平技术研究了脂肪酶对磷脂膜的降解过程。
方案详情

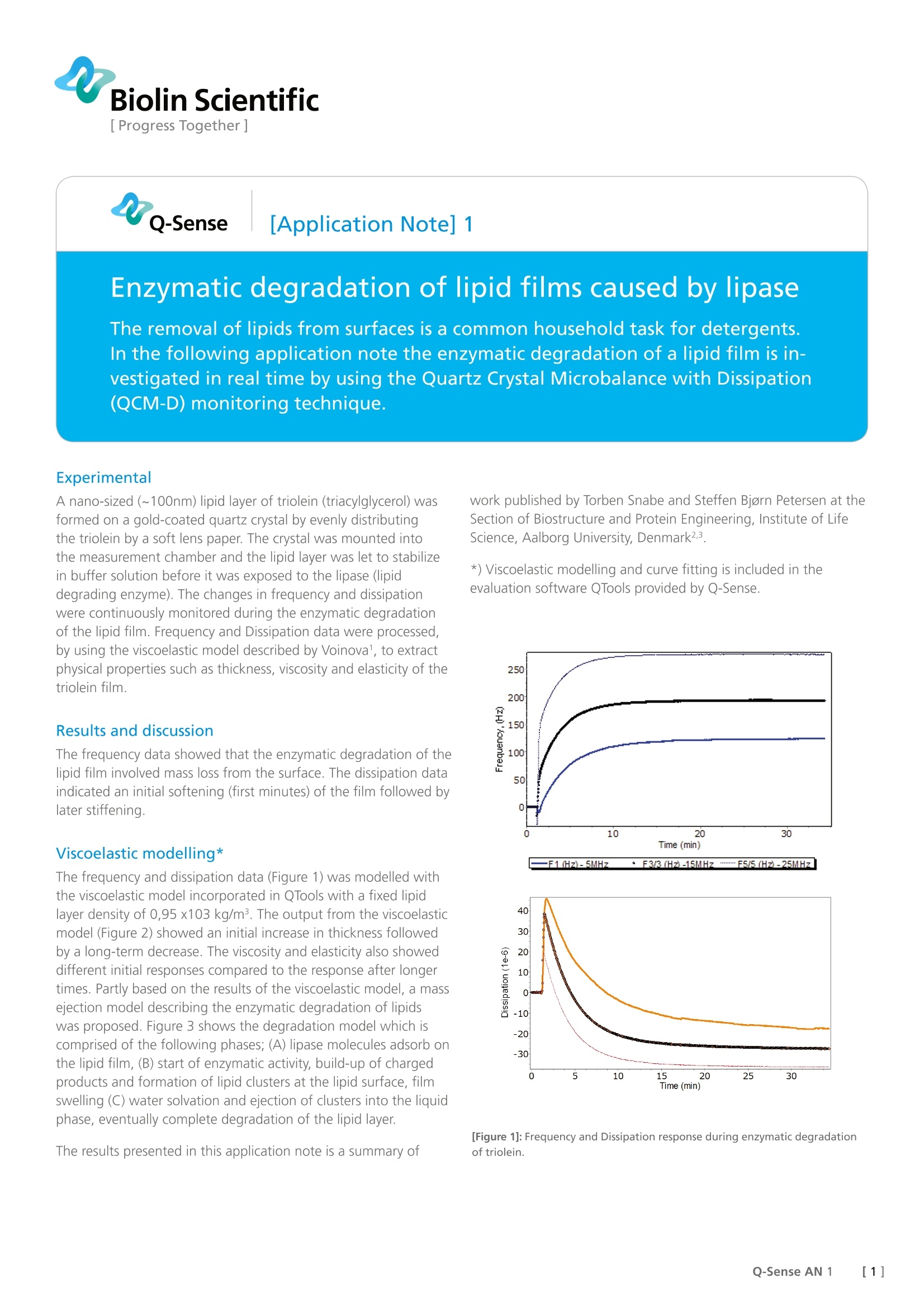
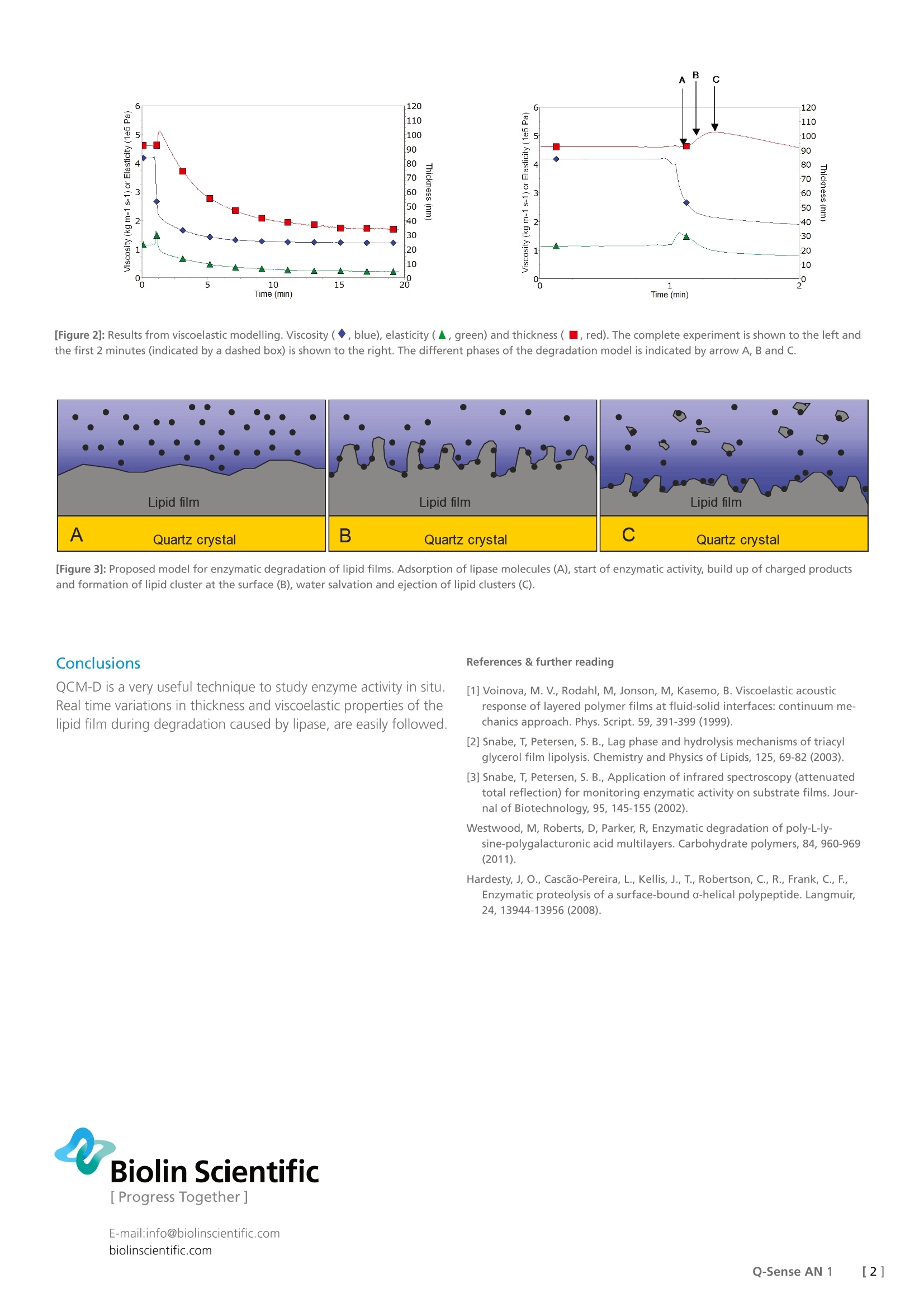
Biolin Scientific[ Progress Together ] [Application Note] 1 Enzymatic degradation of lipid films caused by lipase The removal of lipids from surfaces is a common household task for detergents.In the following application note the enzymatic degradation of a lipid film is in-vestigated in real time by using the Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D) monitoring technique. Experimental A nano-sized (~100nm) lipid layer of triolein (triacylglycerol) wasformed on a gold-coated quartz crystal by evenly distributingthe triolein by a soft lens paper. The crystal was mounted intothe measurement chamber and the lipid layer was let to stabilizein buffer solution before it was exposed to the lipase (lipiddegrading enzyme). The changes in frequency and dissipationwere continuously monitored during the enzymatic degradationof the lipid film. Frequency and Dissipation data were processed,by using the viscoelastic model described by Voinoval, to extractphysical properties such as thickness, viscosity and elasticity of thetriolein film. Results and discussion The frequency data showed that the enzymatic degradation of thelipid film involved mass loss from the surface. The dissipation dataindicated an initial softening (first minutes) of the film followed bylater stiffening. Viscoelastic modelling* The frequency and dissipation data (Figure 1) was modelled withthe viscoelastic model incorporated in QTools with a fixed lipidlayer density of 0,95 x103 kg/m3. The output from the viscoelasticmodel (Figure 2) showed an initial increase in thickness followedby a long-term decrease. The viscosity and elasticity also showeddifferent initial responses compared to the response after longertimes. Partly based on the results of the viscoelastic model, a massejection model describing the enzymatic degradation of lipidswas proposed. Figure 3 shows the degradation model which iscomprised of the following phases; (A) lipase molecules adsorb onthe lipid film, (B) start of enzymatic activity, build-up of chargedproducts and formation of lipid clusters at the lipid surface, filmswelling (C) water solvation and ejection of clusters into the liquidphase, eventually complete degradation of the lipid layer. The results presented in this application note is a summary of work published by Torben Snabe and Steffen Bjorn Petersen at theSection of Biostructure and Protein Engineering, Institute of LifeScience, Aalborg University, Denmark23. *) Viscoelastic modelling and curve fitting is included in theevaluation software QTools provided by Q-Sense. [Figure 1]: Frequency and Dissipation response during enzymatic degradationof triolein. 3 Time (min) [Figure 2]: Results from viscoelastic modelling. Viscosity (◆, blue), elasticity (▲, green) and thickness (■, red). The complete experiment is shown to the left andthe first 2 minutes (indicated by a dashed box) is shown to the right. The different phases of the degradation model is indicated by arrow A, B and C. [Figure 3]: Proposed model for enzymatic degradation of lipid films. Adsorption of lipase molecules (A), start of enzymatic activity,build up of charged productsand formation of lipid cluster at the surface (B), water salvation and ejection of lipid clusters (C). Conclusions QCM-D is a very useful technique to study enzyme activity in situ.Real time variations in thickness and viscoelastic properties of thelipid film during degradation caused by lipase, are easily followed. ( R eferences & further readina ) [1] Voinova, M. V., Rodahl,M, Jonson, M, Kasemo, B. Viscoelastic acousticresponse of layered polymer films at fluid-solid interfaces: continuum me-chanics approach. Phys. Script. 59, 391-399 (1999). [2] Snabe, T, Petersen, S. B., Lag phase and hydrolysis mechanisms of triacylglycerol film lipolysis. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 125, 69-82(2003). [3] Snabe, T, Petersen, S. B., Application of infrared spectroscopy (attenuatedtotal reflection) for monitoring enzymatic activity on substrate films. Jour-nal of Biotechnology, 95, 145-155(2002). Westwood, M, Roberts, D, Parker, R, Enzymatic degradation of poly-L-ly-sine-polygalacturonic acid multilayers. Carbohydrate polymers, 84, 960-969(2011). Hardesty, J, O.,Cascao-Pereira, L., Kellis, J.,T., Robertson, C., R., Frank, C., F.,Enzymatic proteolysis of a surface-bound a-helical polypeptide. Langmuir,24, 13944-13956 (2008). []Q-Sense AN
确定
还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
瑞典百欧林科技有限公司为您提供《脂肪酶中降解脂类过程检测方案 》,该方案主要用于酯中降解脂类过程检测,参考标准--,《脂肪酶中降解脂类过程检测方案 》用到的仪器有QSense卓越版四通道石英晶体微天平、QSense Explorer扩展版石英晶体微天平、QSense全自动八通道石英晶体微天平
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多