原油在生产处理过程中会在固体或液体表面吸附,采用具有耗散性能的石英晶体微天平对沥青与原油表面吸附性能进行了研究,比较了溶剂与产地的影响。
方案详情

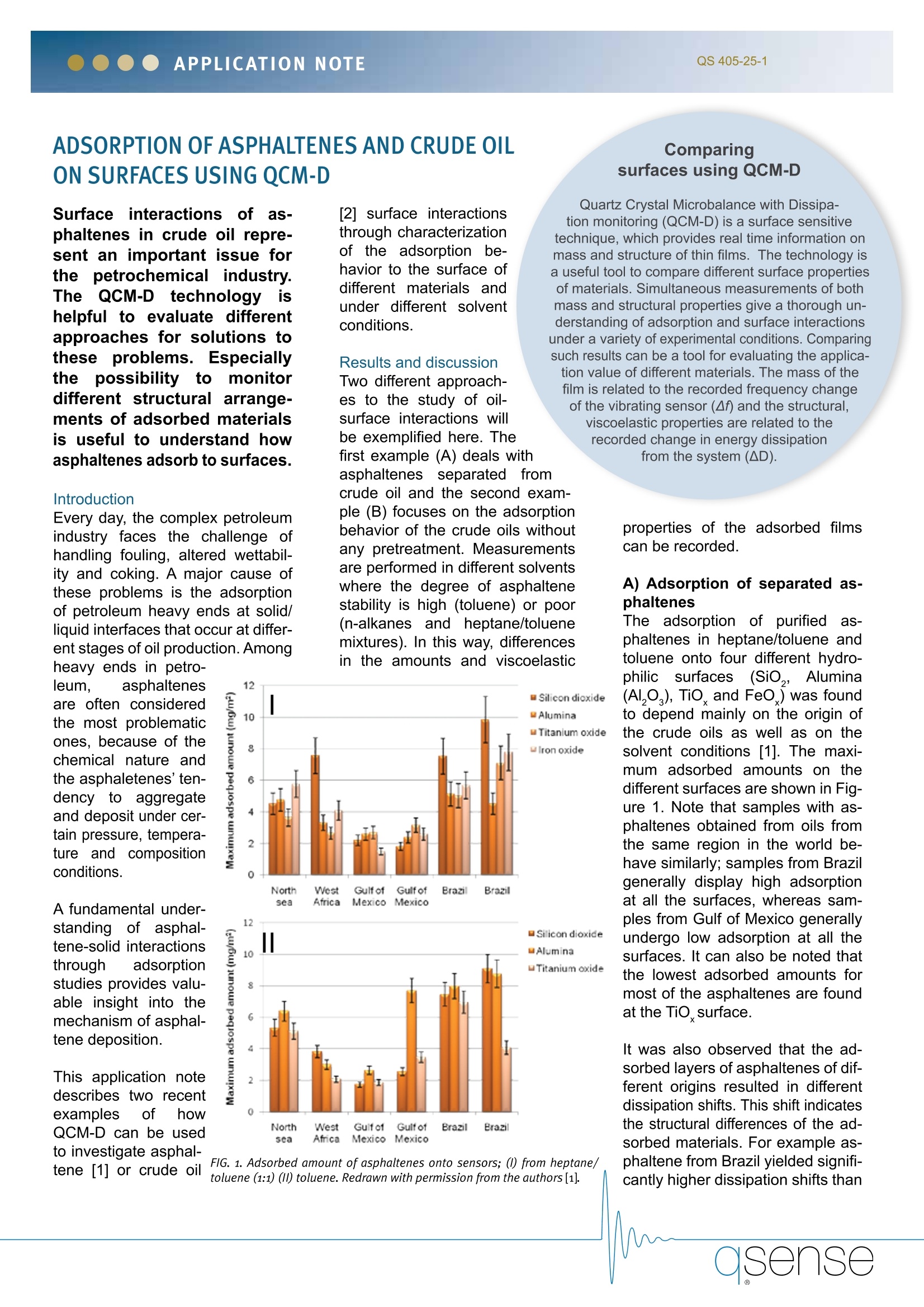
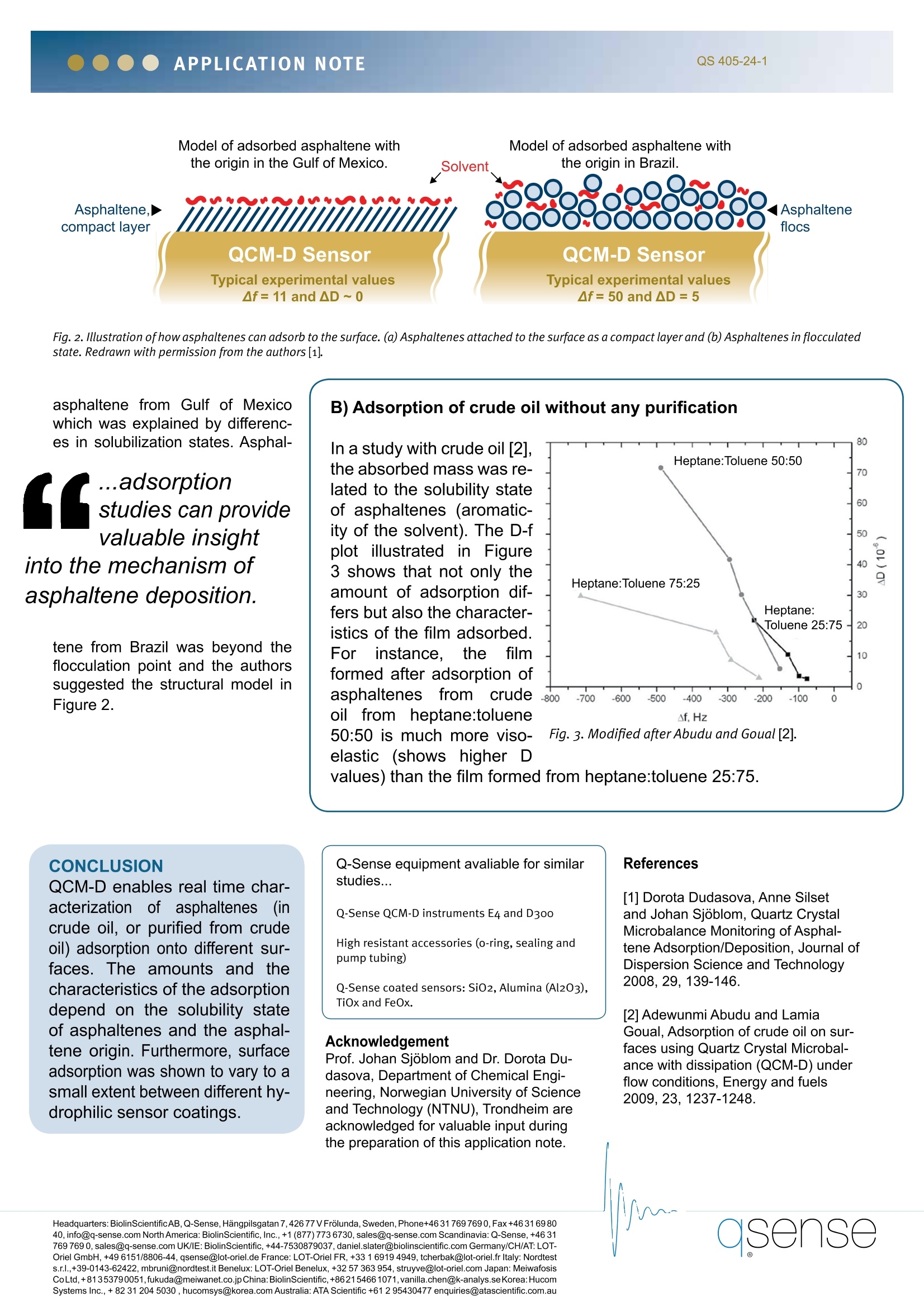
APPLICATION NOTEQS 405-25-1 Osense ADSORPTION OF ASPHALTENES AND CRUDE OILON SURFACES USING QCM-D Surface interactions ofas-phaltenes in crude oil repre-sent an important issue forthe petrochemical industry.The QCM-D technologyishelpful to evaluate differentapproaches for solutions tothese problems.Especiallythe possibility to monitordifferent structural arrange-ments of adsorbed materialsis useful to understand howasphaltenes adsorb to surfaces. Introduction Every day, the complex petroleumindustry faces the challenge ofhandling fouling, altered wettabil-ity and coking. A major cause ofthese problems is the adsorptionof petroleum heavy ends at solid/liquid interfaces that occur at differ-ent stages of oil production.Among 12 [2] surface interactionsthrough characterizationof the adsorption be-havior to the surface ofdifferent materials andunder different solventconditions. Results and discussionTwo different approach-es to the study of oil-surface interactions willbe exemplified here. Thefirst example (A) deals withasphaltenes separated fromcrude oil and the second exam-ple (B) focuses on the adsorptionbehavior of the crude oils withoutany pretreatment. Measurementsare performed in different solventswhere the degree of asphaltenestability is high (toluene) or poor(n-alkanes and heptane/toluenemixtures). In this way, differencesin the amounts and viscoelastic Comparingsurfaces using QCM-D Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipa-tion monitoring (QCM-D) is a surface sensitivetechnique, which provides real time information onmass and structure of thin films. The technology isa useful tool to compare different surface propertiesof materials. Simultaneous measurements of bothmass and structural properties give a thorough un-derstanding of adsorption and surface interactionsunder a variety of experimental conditions. Comparingsuch results can be a tool for evaluating the applica-tion value of different materials.The mass of thefilm is related to the recorded frequency changeof the vibrating sensor (Af) and the structural,viscoelastic properties are related to therecorded change in energy dissipation from the system (AD). heavy ends in petro-leum, asphaltenesare often consideredthe most problematicones, because of thechemical nature andthe asphaletenes'ten-dency to aggregateand deposit under cer-tain pressure, tempera-tureanddcompositionconditions. A fundamental under-standing of asphal-tene-solid interactionsthrough adsorptionstudies provides valu-able insight into themechanism of asphal-tene deposition. This application notedescribes two recentexamplesofhowQCM-D can be usedto investigate asphal-tene [1] or crude oil FIG. 1. Adsorbed amount of asphaltenes onto sensors; (1) from heptane/toluene (1:1)(1I) toluene. Redrawn with permission from the authors [1]. properties of the adsorbed filmscan be recorded. A) Adsorption of separated as-phaltenes The adsorption of purifiedlias-phaltenes in heptane/toluene andtoluene onto four different hydro-philic surfaces(SiO,, Alumina(AI,O), Tio, and FeO) was foundto depend mainly on the origin ofthe crude oils as well as on thesolvent conditions [1]. The maxi-mum adsorbed amounts on thedifferent surfaces are shown in Fig-ure 1. Note that samples with as-phaltenes obtained from oils fromthe same region in the world be-have similarly; samples from Brazilgenerally display high adsorptionat all the surfaces, whereas sam-ples from Gulf of Mexico generallyundergo low adsorption at all thesurfaces. It can also be noted thatthe lowest adsorbed amounts formost of the asphaltenes are foundat the TiO surface. It was also observed that the ad-sorbed layers of asphaltenes of dif-ferent origins resulted in differentdissipation shifts. This shift indicatesthe structural differences of the ad-sorbed materials. For example as-phaltene from Brazil yielded signifi-cantly higher dissipation shifts than Fig.2. Illustration ofhow asphaltenes can adsorb to the surface. (a) Asphaltenes attached to the surface as a compact layer and (b)Asphaltenes in flocculatedstate. Redrawn with permission from the authors[1]. asphaltene from Gulf of Mexicowhich was explained by differenc-es in solubilization states. Asphal- ...adsorptionstudies can providevaluable insightinto the mechanism ofasphaltene deposition. tene from Brazil was beyond theflocculation point and the authorssuggested the structural model inFigure 2. CONCLUSION QCM-D enables real time char-acterization of asphaltenes(1i(incrude oil, or purified from crudeoil) adsorption onto different sur-faces. The amounts and thecharacteristics of the adsorptiondepend on the solubility stateof asphaltenes and the asphal-tene origin. Furthermore, surfaceadsorption was shown to vary to asmall extent between different hy-drophilic sensor coatings. In a study with crude oil [2],the absorbed mass was re-lated to the solubility stateof asphaltenes (aromatic-ity of the solvent). The D-fplot illustrated in Figure3 shows that not only theamount of adsorption dif-fers but also the character-istics of the film adsorbed.Forr instance. thefilmformed after adsorption ofasphaltenes from crudeoil from heptane:toluene50:50 is much more viso-elastic (shows higher D values) than the film formed from heptane:toluene 25:75. Q-Sense equipment avaliable for similarstudies... Q-Sense QCM-D instruments E4 and D300 High resistant accessories (o-ring, sealing andpump tubing) Q-Sense coated sensors: SiO2, Alumina (Al203),TiOx and FeOx. Acknowledgement Prof. Johan Sjoblom and Dr. Dorota Du-dasova, Department of Chemical Engi-neering, Norwegian University of Scienceand Technology (NTNU), Trondheim areacknowledged for valuable input duringthe preparation of this application note. [1] Dorota Dudasova, Anne Silsetand Johan Sjoblom, Quartz CrystalMicrobalance Monitoring of Asphal-tene Adsorption/Deposition, Journal ofDispersion Science and Technology2008,29,139-146. [2] Adewunmi Abudu and LamiaGoual, Adsorption of crude oil on sur-faces using Quartz Crystal Microbal-ance with dissipation (QCM-D) underflow conditions, Energy and fuels2009,23,1237-1248. ( Headquarters: BiolinScientificAB,Q-Sense, Hangpilsgatan 7,42677VFrolunda,Sweden,Phone+4631 7697690,Fax + 46316980 4 0, info@q-sense.com North America: B i olinScientific , Inc.,+1(877) 773 6730,sales@q-sense.com S c andinavia:Q-Sense, +46 3 1 7 69 769 0, sales@q-sense.comUK/IE: BiolinScientific, +44-7530879037, daniel.slater@biolinscientific.com Germany/CH/AT: LOT- O riel GmbH, +49 6151/8806-44,qsense@lot-oriel.de France:LOT-Oriel FR, +33 1 6919 4949, tcherbak@lot-oriel.fr Italy: Nordtest s .r.l.,+39-0143-62422, mbruni@nordtest.it Benelux: LOT-Oriel Benelux, + 32 57 363 954, struyve@lot-oriel.com Japan: Meiwafosis CoLtd,+81353790051,fukuda@meiwanet.co.jpChina:BiolinScientific,+86215466 1071,vanilla.chen@k-analys.seKorea:Hucom S ystems Inc.,+82 31 204 5030, hucomsys@korea.com Australia: ATA Scientific +61 2 95430477 enquiries@atascientific.com.au )
确定
还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
瑞典百欧林科技有限公司为您提供《原油中表面吸附性能检测方案(石英晶体天平)》,该方案主要用于原油中理化分析检测,参考标准--,《原油中表面吸附性能检测方案(石英晶体天平)》用到的仪器有QSense卓越版四通道石英晶体微天平、QSense Explorer扩展版石英晶体微天平、QSense全自动八通道石英晶体微天平
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多