方案详情
文
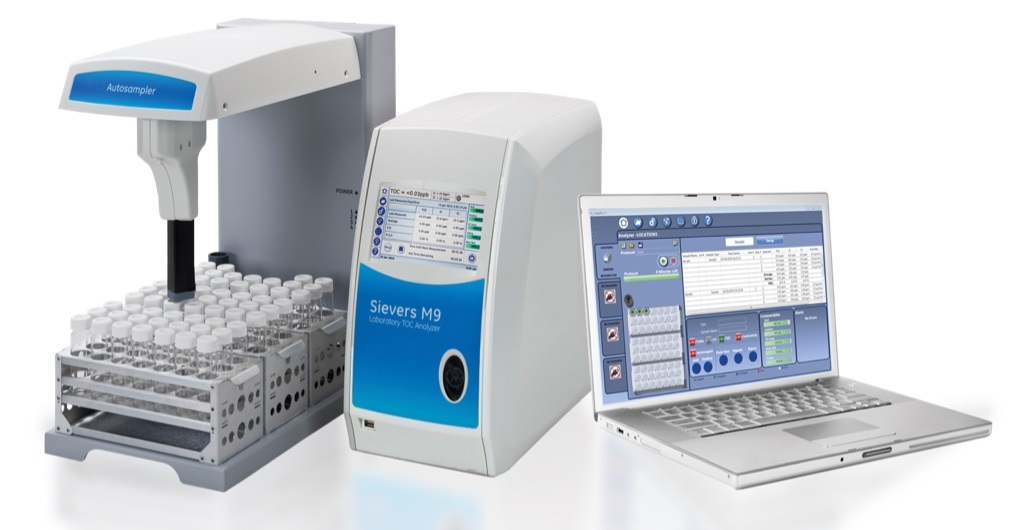
德国耶拿HT1300固体模块,可以与multiN/C系列TOC分析仪,结合使用,消解温度高达1300度,最大进样量3g,绝对C含量达到150mg, 固体分析和液体分析切换方便,可实现最高水平的对固体样品TOC分析。
方案详情

analytikjena Fields of Application / Industry: Chemistry / Polymer Industry Clinical Chemistry / Medicine /Hygiene/ Health Care Electronics Semi-Conductor Technology Energy Environment / Water / Waste Geology / Mining Food / Agriculture Metallurgy / Galvanization Refineries / Petrochemistry Pharmacv Cosmetics Material Analysis Others Determination of TOC in Solids Authors: Sindy Forster, Anja Jungnickel, Analytik Jena AG, Konrad-Zuse-Str.1, 07745 Jena Introduction The determination of TOC(Total Organic Carbon) in solid samples such as waste, soils, sedimentsor manufacturing materials is steadily gaining importance. The (German) Technical Instruction onResidential Waste as revised in 1993 acknowledges the determination of the TOC content in theoriginal sample as a valid alternative to the determination of the loss of weight on ignition. Organiccarbon occurs in waste in various kinds of bond. Given the multitude of possible organic carboncompounds, the quantitative determination of every single organic compound of natural oranthropogenic origin would only be possible at prohibitive expense, if at all. The measurement ofsummary parameters such as TOC is the only sensible alternative, therefore. Principles of the Method All methods of determining total carbon (TC) in solids are based on the conversion of the carboncompounds into carbon dioxide by oxidation or pyrolysis. Thermal digestion is performed at atemperature of at least 1300C. The resulting gas is then purified by filters, dried, and flushed intothe detector by means of a carrier gas flow. The detector is usually of the non-dispersive infraredtype (NDIR).Acidification and pretreatment of the sample before the measurement removes totalinorganic carbon (TIC), so that the measurement ascertains the share of non-volatile organiccarbon (NVOC) only. Inorganic carbon in solids is determined by NDIR detection of the carbon dioxide formed by sampleacidification and subsequent purging. TOC Determination TOC in solids can be determined by either of two methods: the direct and the indirect (differential)one. The latter is based on forming the difference between the TC and TIC parameters, while thedirect method determines TOC as NVOC. Differential method The indirect (differential) method requires two separate measurements -TC and TIC - in order toascertain the organic share as the difference of these. The method is applied if the inorganiccarbon share is smaller than or equal to the organic carbon share in the sample. Carbonates are decomposed in a suitable apparatus (TIC module) at a temperature of about 80°Cby addition of a mineral acid, and the resulting carbon dioxide is detected. In parallel, the untreatedsample is thermally digested at ≥1300 ℃, and the carbon dioxide determined. TOC is then givenby the difference of the two measurements: TOC= TC -TIC. The graph (Figure 1) shows an example of the retrieval of the TOC content of a certified standardby means of the TIC module. The repeatability of the TIC content greatly depends on thehomogeneity of the solid sample. Fig.1 Other methods frequently mentioned in connection with indirect TOC determination in solids aredetection of the residue on ignition or the running of temperature ramps. In the first of these methods, the organic carbon share is combusted at about 600℃ in a mufflefurnace to which oxygen is fed, and TIC is measured in what is called the residue on ignition.Subsequently, a measurement of the original sample is made to determine total carbon. By formingthe difference, one gets TOC = TC - TIC. This method suffers, however, from a number ofuncertainties, which may cause errors. One is that a temperature of 600°C may cause carbonateportions to be decomposed into CO2, depending on the matrix, and thus to be lost for TIC analysis.Another uncertainty is that 600°℃ may not be sufficient to completely oxidize all organiccompounds. The sameproblems also affect TOC determination by temperature ramping.Therefore, these methods should be judged critically, despite the advantage of not having to usewet chemical techniques. Direct method As an alternative to the differential method, the share of non-volatile organic carbon can bedetermined directly. Here, the sample is acidified, while the resulting carbon dioxide is notdetected. 10% HCI is added to the sample drop by drop until the main reaction is over. Thereaction is then completed by the dropwise addition of concentrated HCI until no more gas is seen to develop. The sample thus pretreated is dried at 105℃ for 2 hours. After drying, the sampleshould be kept in a desiccator until analysis to prevent it from taking up any water again. Thesample, now free of TIC, is analyzed by thermal digestion and subsequent NDIR detection of thecarbon dioxide formed. Table 1 lists several sample matrices with the associated weighed quantities and results. The realsamples were pretreated as described. Sample Weighed quantity [mg] TOC [%] Polluted soil 40-1000 6,68 Electroplating sludge, containing Cu 40-1000 1,28 Emulsion sludge 40-1000 19,92 Fly ash 40-1000 2,78 lon-exchange resin 40-1000 24,98 Table 1: Determination of TOC in various sample matrices by the direct method This method is suitable especially for TOC determination in solids with a TIC concentration greaterthan or equal to the TOC content. In such cases, use of the differential method would lead toerroneous results. It should be noted, though, that the direct method does not detect volatileorganic carbon compounds. Comparison of the direct and differential methods Figure 2 compares the TC and TOC contents of a standard and of real samples, determined bydifferent methods. It can be seen that the TOC content determined from the residue on ignition deviates from theresults obtained by the other two methods. This is due to the problems described above. The TOC contents obtained by the differential and direct methods are about comparable. Summary TOC can be determined reliably even in difficult samples containing, for example, volatile organiccarbon compounds or having an unfavourable TIC/TOC ratio. The method to be chosen dependson the proportions of the organic and inorganic carbon shares in the sediment samples. The directmethod of TOC determination is recommendable where samples have high contents of inorganiccarbon. Volatile organic constituents should be determined by the differential method using TICmodule. To characterize solids, TOC is a parameter that can be determined with certainty and convenience. C 2001 Analytik Jena AG ( Publisher: ) Analytik Jena AGKonrad-Zuse-StraBe 107745 Jena Telephone +49 (0)3641/77-70Fax +49 3641 77-92 79 Determination of TOC in SolidsKennziffer: Lit SP_TOC_e|Jn/Foe/
确定



还剩2页未读,是否继续阅读?
耶拿分析仪器(北京)有限公司为您提供《固体中TOC检测方案(TOC分析仪)》,该方案主要用于固体废物中有机污染物检测,参考标准--,《固体中TOC检测方案(TOC分析仪)》用到的仪器有德国耶拿 multi N/C 3100 TOC总有机碳/总氮分析仪、德国耶拿multi N/C 2100 TOC总有机碳/总氮分析仪
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多