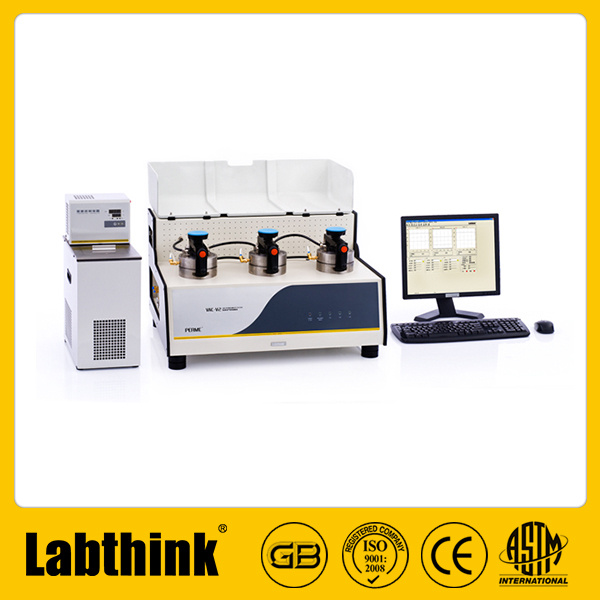
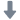
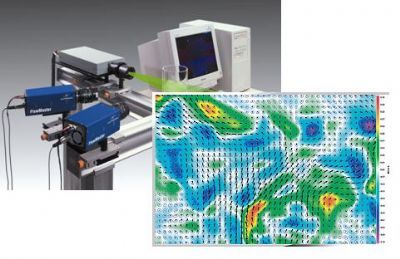
发动机中流场,速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
1.The HARVEST Project
2.2D-2C PIV Measurements
3.NumericalComputation
4.Results
1.ComparisonsPIV / CFD
2.Characterizationof dynamicstall
5.Conclusions
----------------------------------------------------------
Objective:Convertcineticenergyof riversor of tidal flow
Specificity:Vertical axis turbine, radial flux, new generationof Darrieusand Gorlovturbine
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流场,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
台阶中多台阶通道中的爆震衍射检测方案(粒子图像测速)
This research investigated multiple detonation diffraction events in order to better
understand the limits and benefits of diffraction strategies with respect to pulse
detonation engine design. Hydrogen/air detonations were generated using swept
ramp obstacles in a 1.27 m long channel with a cross section of 25.4 mm by 88.9
mm and were diffracted into various multiple-stepped openings. This allowed the
detonation wave diffraction transmission limits to be determined for hydrogen/air
mixtures and to better understand reinitiating mechanisms throughout the
diffraction process. Tests were conducted for area ratios ranging from 2.00–2.60
with varying equivalence ratios from 0.5–1.5.
Computational methods were used to better understand the diffraction
phenomenon using a series of sensitivity studies for different chemistry sets,
computational cell size and equivalence ratio. Experimental tests used combined
optical shadowgraph and particle image velocimetry imaging systems to provide
shock wave detail and velocity information. The images were observed through
a newly designed explosive proof optical section and split flow detonation
channel. It was found that area ratios of 2.0 could survive single and double
diffraction events over a range an equivalence ratio range of 0.8 to 1.14 Area
ratios of 2.3 survived the primary diffraction event for equivalence ratios near
stoichiometric for the given step length. Detonation diffraction for area ratios of
2.6 did not survive the primary diffraction event for any equivalence ratio and
were unable to transmit to a larger combustor.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
多台阶通道中的爆震衍射
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
德国Lambrecht兰博瑞气象站的应用
一体式气象站(5要素),进口气象产品,进口气象站,德国Lambrecht气象站,一体式多功能自动气象站,一体微型气象站
Quatro-ind(工业型)/ Quatro-nav(海洋型)综合一体式气象站,测量温度、湿度、压力、风速、风向。
一体式气象站 性能参数如下:
参数测量范围精度分辨率风速0~80m/s0.2m/s0.1m/s风向0~36003010气温-40~70℃1℃0.1℃气压500~1100hPa1hPa0.4hPa湿度0~100%Rh3%Rh!%Rh
另外:可以计算露点温度值,16bit的计算器用于外部雨量数据输入,模拟输入口(0~10VDC),自动循环自检状态并打印报告,Rs485接口,,测量频率:10HZ。外壳防腐蚀、耐酸,无需维护元件带永久性空气浓度补偿,ASCII数据协议,24VDC供电带有缓冲保护,用外接的meteo-lcd显示屏可以看到测量数据,通过synmet系统和meteoware-nt软件可进行外接数据存储和运算,设备工作温度:-40℃~70℃,体积:302mm高,直径70mm,重量1.5Kg。
一体式气象站使用范围:
1. 各地的路面气象检测
2. 为各种恶劣条件所设计:如沙漠、寒带、热带、高山地区的气象检测
3. 为以下领域检测以及监测气象测量数据
--天气预报以及环境监测部门
--化工厂、大型工厂
--电站、水处理以及垃圾处理厂
--机场、运动场以及度假场所
--国防、军事部门
--消防安全部门
Quatro系列小型气象站的型号有四种,订购号如下
传感器型号订购号用途Quatro-nav(39k)00.16420.100 002海洋型号Quatro-ind(35k)00.16420.200 002工业型号Quatro-mil(34k)00.16420.500 002军事型号Quatro-nbc(42k)00.16420.600 002尖端型号
显示器型号订购号用途Indicator-nav(58k) 海洋型Indicator-ind(48k) 工业型
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
南京欧熙科贸有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
电压击穿试验仪中选择合适量程方法检测方案
2、 如何选择合适量程的电压击穿试验仪:
在材料的标准要求里或者测试报告中,对材料的耐压等级通常用介电强度来表示,即KV/mm,击穿电压和介电强度的关系可以用如下公式表示:
击穿电压值(KV)
介电强度(KV/mm)=------------------------------------------
试样厚度(mm)
由如上公式可以得出结论,选择多大量程的测试仪器,取决于试样的厚度,即:
击穿电压值(KV)=介电强度(KV/mm)* 试样厚度(mm)
由此公式所得出的击穿电压值是按照试样厚度测试时的有效电压值,所以得出击穿电压值后,在此电压值得基础上适当加宽些量程范围比较合理,建议计算出击穿电压值后增加10KV—20KV
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
选择合适量程方法
北京冠测精电仪器设备有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Turbulent jets have been always present in fluid-mechanic researches due to the
large number of applications they have and to the presence of all the turbulence features
on them. Thanks to the use of relative new non-intrusive techniques–such as PIV
(Particle Image Velocimetry)-, the knowledge of turbulence in general, and turbulent
jets in particular has increased.
This work is focused on the assessment of both, the main characteristics of the
turbulent jet and, at the same time, some significant PIV features. For that aim two
experiments are proposed:
-The first one, denominated “Spatial Resolution in PIV”, tries to determine the
best position to place the digital camera that films the movement of the particles
present in the jet, taking into account that we are interested on studying not only
the microscales of the turbulent flow, but also the velocity field and the
recovering of isotropy by evaluating the turbulent parameters (skewness,
kurtosis, square mean derivative ratios,…).
-In the second one, called “Effect of the Reynolds Number in Turbulence”,
starting from the results of the first experiment, the behavior of the jet depending
on the relationship between the inertia forces and the viscous ones is analyzed.
To do this, three different zones along the jet and eight different Reynolds
numbers are to be studied.
This report is structured in four different chapters. The first one corresponds to a
theoretical introduction to turbulence. In the second one the experimental setup is
described after introducing the PIV measurement technique. The third one presents the
results and carries out a deep analysis of them. Finally, in chapter four, the results are
summarized obtaining some important conclusions and considering as well future
challenges of the present work.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场,声场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Although acoustics consists in the propagation of an oscillatory disturbance of local
pressure, particle velocity, density and temperature, sound measurement is often assimilated
to pressure measurement. This is because for decades only pressure fluctuations were
accessible and because their relation with the other oscillatory quantities is well known under
linear acoustic approximation and in simple configurations. Such a correct description of the
origins of sound has long been known from the theory of sound, but there is a bad habit of
acousticians to use the descriptions of sound as acoustic pressure only. Meanwhile, a sound
wave is a form of energy transport in the field and has the vectors features. Sound intensity
(SI) as a vector variable inseparably couples the acoustic particle velocity (called also
acoustic velocity). and acoustic pressure (Ia=p v) and represents a stream of acoustic energy
flowing in the field. This vector parameter of acoustic wave can be measured with special
sound intensity probe and can be easily shown in a graphical form.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,声场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
液体交叉流中气体注入位置对其气泡形成的影响检测方案
Liquid flows incorporating small-size bubbles play a vital role in many industrial applications. In
this work, an experimental investigation is conducted on bubble formation during gas injection from
a microtube into the channel of a downward liquid cross flow. The tip of the air injector has been
located at the wall wall orifice and also at several locations from the wall to channel centerline
nozzle injection. The size, shape, and velocity of the bubbles along with liquid velocity field are
measured using a shadow-particle image velocimetry/particle tracking velocimetry system. The
process of bubble formation for the wall orifice and the nozzle injection configurations is physically
explained. The effect of variation in water and air flow rates on the observed phenomena is also
investigated by considering water average velocities of 0.46, 0.65, and 0.83 m/s and also air average
velocities of 1.32, 1.97, 2.63, and 3.29 m/s. It was observed that shifting the air injector tip toward
the center of the channel resulted in the coalescence of some of the preliminary bubbles and the
formation of larger bubbles termed secondary and multiple bubbles. Increase in air flow rate and
reduction in water flow rate also intensify the rate of bubble coalescence. A correlation-based model
is also suggested to overcome the shortcoming of the available models in the literature which are
developed to only estimate the size of the preliminary bubbles. The model predicts the percent of the
preliminary, secondary, and multiple bubbles along with the average size of secondary and multiple
bubbles as a function of nozzle position within a cross flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
气体注入位置对其气泡形成的影响
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中3D3C速度矢量场,速度场,体视速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
This paper describes the principles of a
novel 3D PIV system based on the illumination,
recording and reconstruction of tracer particles within
a 3D measurement volume. The technique makes use
of several simultaneous views of the illuminated particles
and their 3D reconstruction as a light intensity
distribution by means of optical tomography. The
technique is therefore referred to as tomographic
particle image velocimetry (tomographic-PIV). The
reconstruction is performed with the MART algorithm,
yielding a 3D array of light intensity discretized
over voxels. The reconstructed tomogram pair is then
analyzed by means of 3D cross-correlation with an
iterative multigrid volume deformation technique,
returning the three-component velocity vector distribution
over the measurement volume. The principles
and details of the tomographic algorithm are discussed
and a parametric study is carried out by means of a
computer-simulated tomographic-PIV procedure. The
study focuses on the accuracy of the light intensity field
reconstruction process. The simulation also identifies
the most important parameters governing the experimental
method and the tomographic algorithm
parameters, showing their effect on the reconstruction
accuracy. A computer simulated experiment of a 3D
particle motion field describing a vortex ring demonstrates
the capability and potential of the proposed
system with four cameras. The capability of the technique
in real experimental conditions is assessed with
the measurement of the turbulent flow in the near
wake of a circular cylinder at Reynolds 2,700.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
3D3C速度矢量场,速度场,体视速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
燃烧,火焰,分层火焰,涡流中速度场,流场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Stereoscopic Planar Image Velocimetry (SPIV) has been applied to obtain the three
components of the instantaneous velocity vectors on a vertical plane above the burner
outlet where the flames propagate. The instantaneous temperature fields have been
determined through Laser Induced Rayleigh (LIRay) scattering. Planar Laser Induced
Fluorescence (PLIF) on acetone has been used to calculate the average equivalence ratio
distributions. Instantaneous turbulent burning velocities have been extracted from SPIV
results, while flame curvature and flame thermal thickness values have been calculated
using the instantaneous temperature fields. The probability distributions of these
quantities have been compared considering the separate influence of equivalence ratio
stratification and turbulence. It has been observed that increased levels of turbulence
determine higher turbulent burning velocities and flame front wrinkling. Flames
characterized by stronger fuel stratification showed higher values in turbulent burning
velocities. From the curvature analysis emerged that increased fuel concentration
gradients favour flame wrinkling, especially when associated with positive small radius
of curvature. This determines an increased surface area available for reaction that
promotes a faster propagation of the flame front in the oncoming combustible mixtures.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,流场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
大尺度涡气旋中反气旋对称性检测方案
We performed an experimental study of large-scale wakes in a rotating shallow-water layer.
Standard particle image velocimetry was used to measure the horizontal velocity field, while a
laser-induced fluorescence technique was used to measure the geopotential deviation i.e., the
interface deviation. According to these measurements, we were able to quantify the dynamics in a
wide region of parameter space beyond the quasi-geostrophic regime. For obstacles larger than the
deformation radius and with small Rossby numbers, a significant asymmetry occurs in the wake
between cyclonic and anticyclonic vortices. These parameters correspond to a frontal geostrophic
regime with the relative interface deviation being larger than 0.1–0.2. In this case, anticyclones
remain coherent and circular, whereas cyclones tend to be elongated and distorted. More
surprisingly, for some extreme cases, coherent cyclones do not emerge at all, and only an
anticyclonic vortex street appears several diameters behind the obstacle. The transition from a
quasi-geostrophic to a frontal geostrophic regime is characterized by a strong increase in the
Strouhal number, which can reach a value up to 0.6. Hence, we found that a large-scale wake could
differ strongly from the classical Karman street when the relative geopotential deviation becomes
larger than the Rossby number.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
反气旋对称性
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
赛默飞iCAP 7000 Series 测定高纯氧化钆中镱和镥
高纯氧化钆在现代制造业得到重要的应用,它是特殊发光材料和磁泡记忆存储器的主要原料;氧化钆与镧一起使用,有助于提高玻璃的热稳定性;钆及其合金可作为固态磁致冷介质促进了磁制冷技术的发展。国标GBT18115.7-2006中稀土金属及其氧化物中稀土杂质化学分析方法中,其方法一为ICP 发射光谱法,但Yb 和Lu 的测定下限为0.0010%;方法二中为ICP 质谱法,但Yb 和Lu 都受Gd 各同位素的氧化物离子严重干扰,国标采用了C272 微型分离Gd 基体后测定。本方法使用ICP 光谱水平观测方式,通过对基体效应,谱线选择以及采用基体匹配,可以满足氧化钆中ug/g 级Yb 和Lu 的测定。其它稀土杂质使用iCAP Q ICPMS KED 模式测定,得到理想的结果。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
赛默飞色谱与质谱
查看联系电话
前往展位
水喷射泵转子叶片中尖区流场结构的可视化研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In this paper, we examine the occurrence of cavitation
in the tip region of a waterjet pump, and use the
observations to identify key features of the flow
structure. The rotor, stator and pump casing in our
recently upgraded facility are made of acrylic, whose
refractive index matches that of the working fluid, a
concentrated aqueous solution of sodium iodide. Such
matching makes the blades invisible, enabling flow
structure visualization and optical measurements
without any obstructions. Our initial tests with fresh
water focus on cavitation in the vicinity of the tip
region close to design conditions. Near the leading
edge, cavitation inception near the tip corner of the
pressure side causes accumulation of bubbles along the
pressure side of the corner until mid blade. As roll-up
of the tip leakage vortex (TLV) starts in the mid blade
region, these bubbles travel across the tip-clearance to
the suction side, and become nuclei for cavitation
inception in the TLV. As the TLV migrates to the
vicinity of the pressure side of the neighboring blade it
bursts, generating a cloud of bubbles that spreads over
most of the aft section of the passage. The leakage flow
in the tip gap along the aft side of the blade is strong
enough to cause sheet cavitation within the gap,
starting from the pressure side corner. The paper also
presents preliminary Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV)
data concentrating on the roll-up of TLV. Results are
consistent with observed cavitation phenomena.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
尖区流场结构的可视化研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
空化混合层中速度场分析检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The purpose of this experimental study was to analyze a two-dimensional cavitating shear layer.
The global aim of this work was to improve understanding and modeling of cavitation
phenomena, from a 2D turbulent shear flow to rocket engine turbopomp inducers. This 2D mixing
layer flow provided us with a well documented test case to be used for comparisons between
behavior with and without cavitation. Similarities and differences enabled us to characterize the
effects of cavitation on flow dynamics. The experimental facility enabled us to set up a mixing
layer configuration with different cavitation levels. The development of a velocity gradient was
observed inside a liquid water flow using PIV–LIF (particle image velocimetry–laser induced
fluorescence). Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities developed at the interface and vaporizations and
implosions of cavitating structures inside the vortices were observed. The mixing area grew
linearly, showing a constant growth rate, for the range of cavitation levels studied. The spatial
development of the mixing area seemed hardly to be affected by cavitation. Particularly, the
self-similar behavior of the mean flow was preserved despite the presence of the vapor phase.
Successive vaporizations and condensations of the fluid particles inside the turbulent area
generated additional velocity fluctuations due to the strong density changes. Moreover, when
cavitation developed, the Kelvin-Helmholtz vortex shape was modified, inducing a strong
anisotropy (vortex distortion as ellipsoidal form) due to the vapor phase. The main results of this
study clearly showed that the turbulence-cavitation relationship inside a mixing layer was not
simply a change of compressibility properties of the fluid in the turbulent field, but a mutual
interaction between large and small scales of the flow due to the presence of a two-phase flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场分析
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流场中速度场,速度矢量场,气动声学性能检测方案(粒子图像测速)
One of the major environmental problems facing the aviation industry is that of aircraft noise. The work
presented in this paper, done as part of the EU’s OPENAIR Project, looks at reducing spoiler noise whilst
maintaining aerodynamic performance, through means of large-scale fractal porosity. It is hypothesised that
the highly turbulent flow generated by fractal grids from the way the multiple-length-scales are organised in
space, would reduce the impact of the re-circulation region and with it, the low frequency noise it generates.
In its place, a higher frequency noise is introduced which is more susceptible to atmospheric attenuation and
is less offensive to the human ear. A total of nine laboratory scaled spoilers were looked at, seven of which
had a fractal design, one with a regular grid design and one solid for reference. The spoilers were inclined at
an angle of 30. Force, acoustic and flow visualisation experiments on a flat plate were carried out and it was
found that the present fractal spoilers reduce the low frequency noise by 2.5dB. Results show that it is possible
to improve the acoustic performance by modifying a number of parameters defining the fractal spoiler, some
of them very sensitively. From these experiments, two fractal spoilers were chosen for a detailed aero-acoustic
study on a three-element wing system, where it was found that the fractal spoilers had a reduction of up to 4dB
in the sound pressure level while maintaining similar aerodynamic performances as conventional solid spoilers
on the measured wing system.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场,气动声学性能
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2257篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等