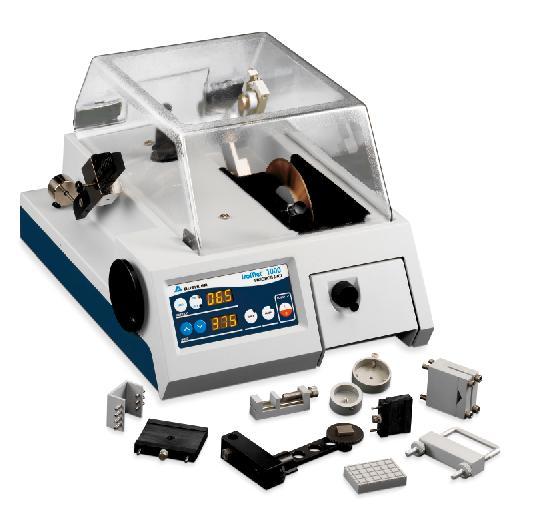
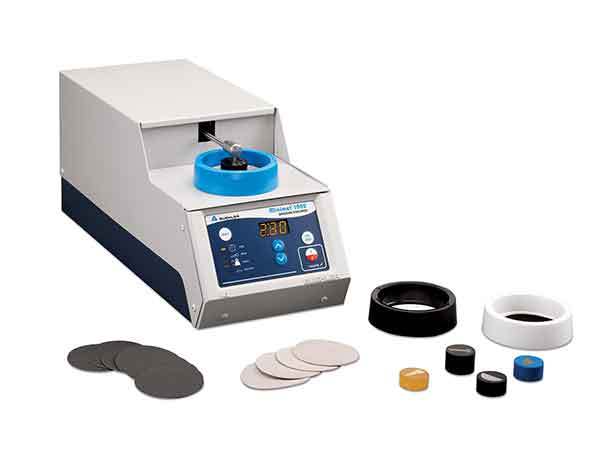
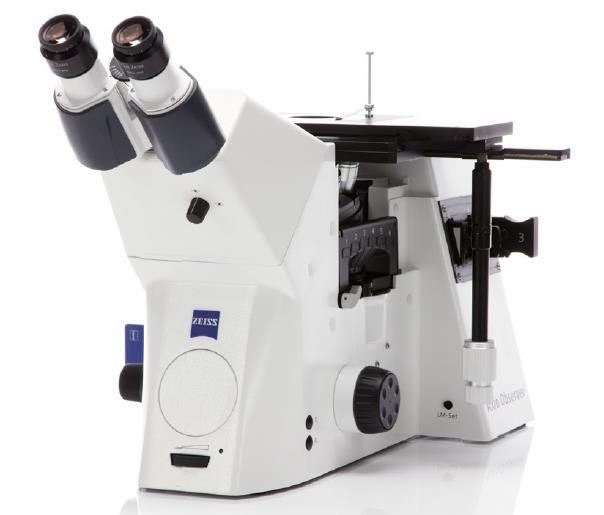
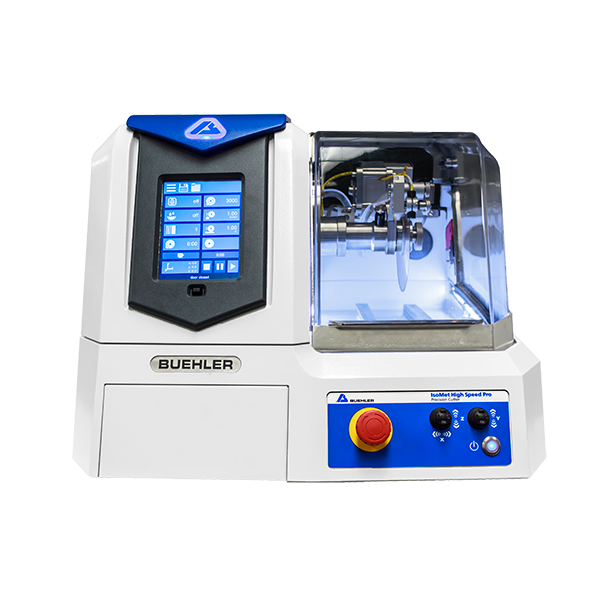
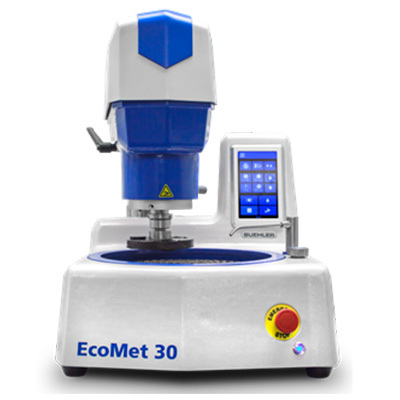
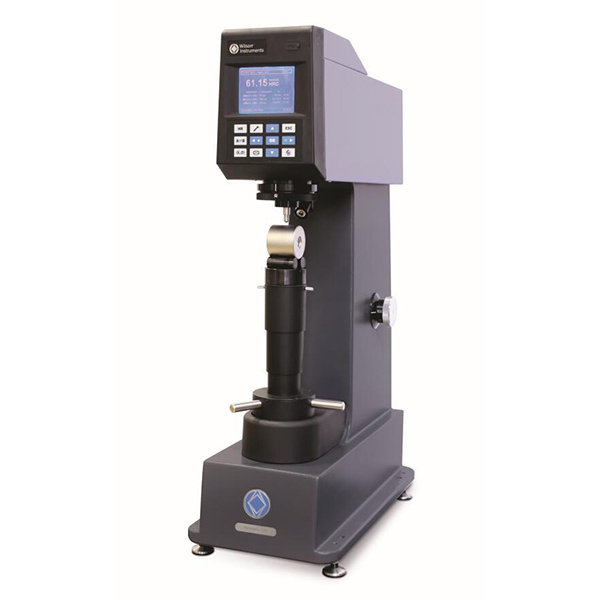
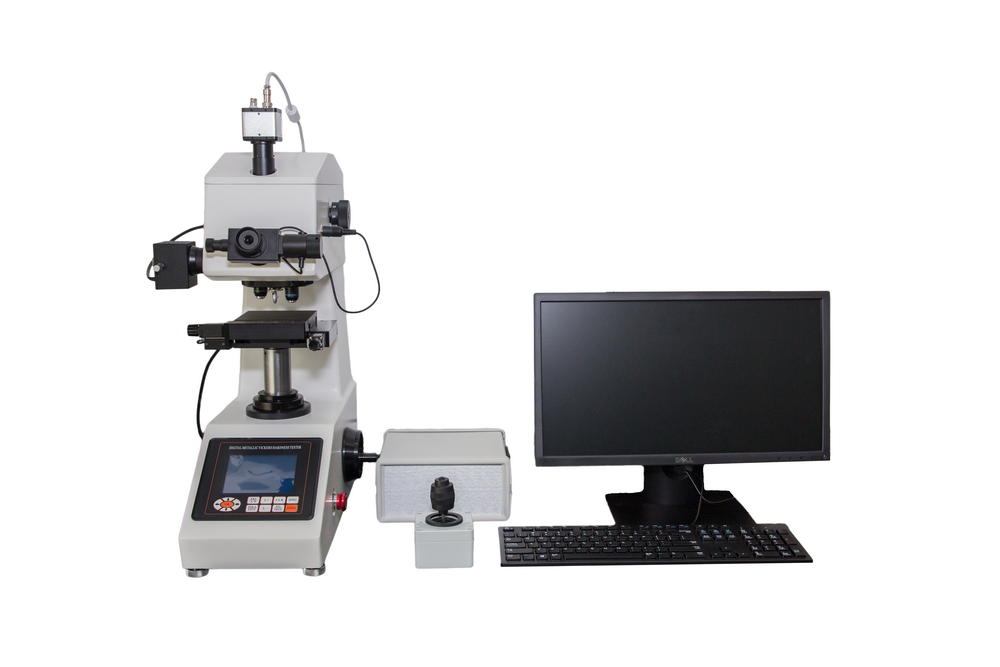
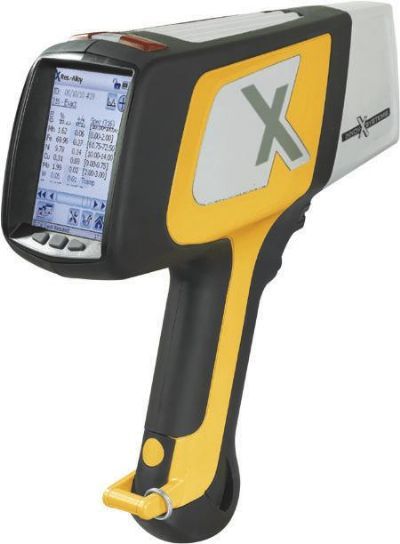
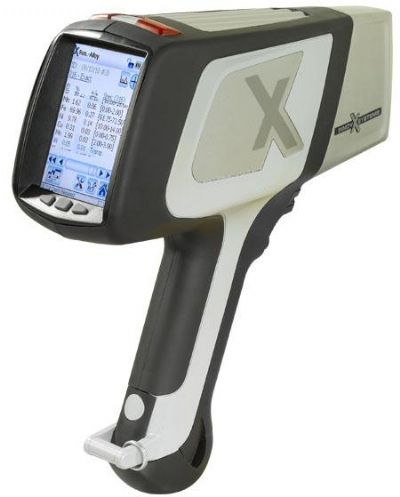
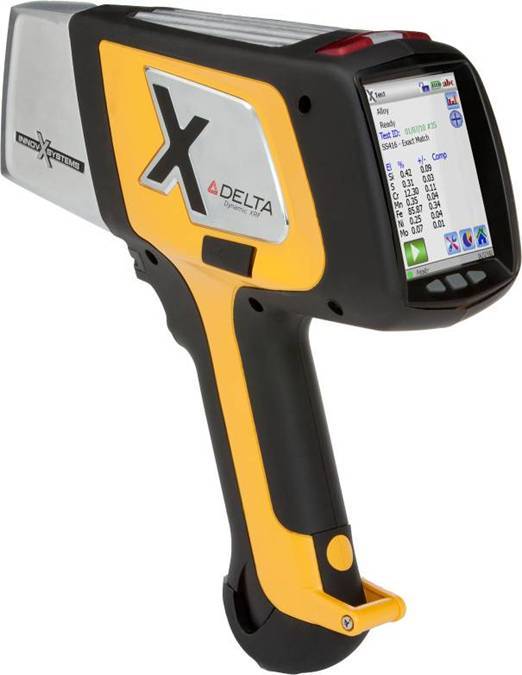
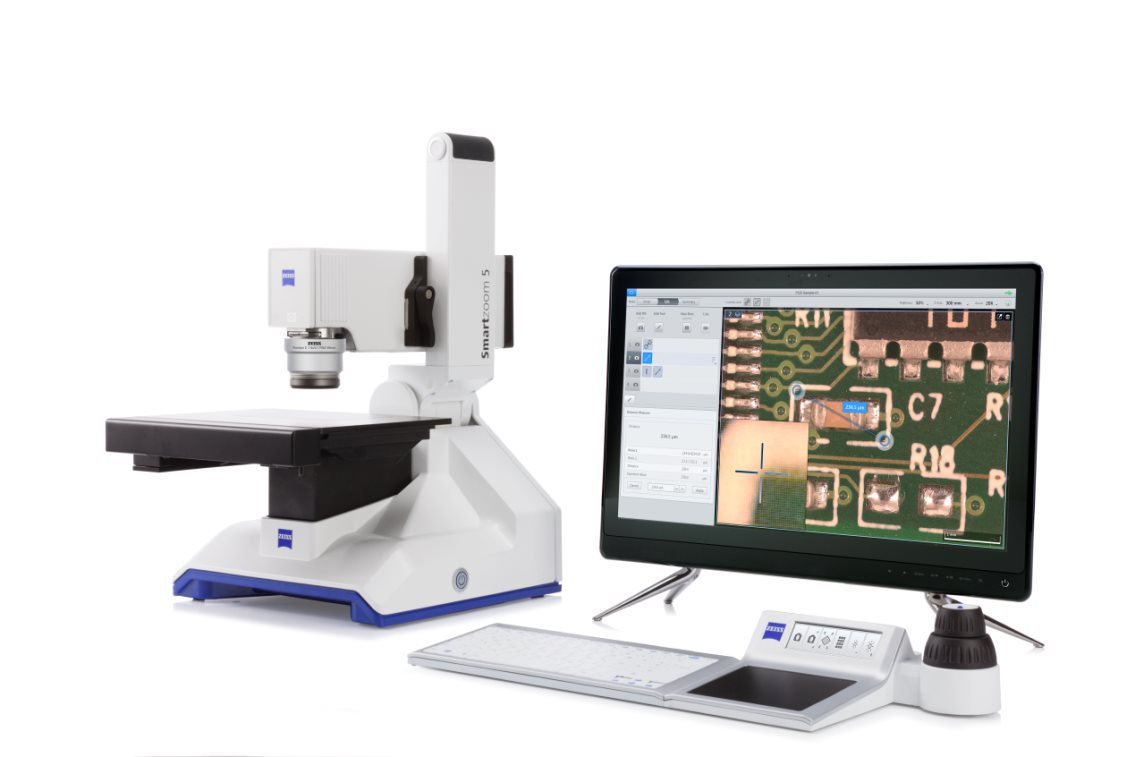
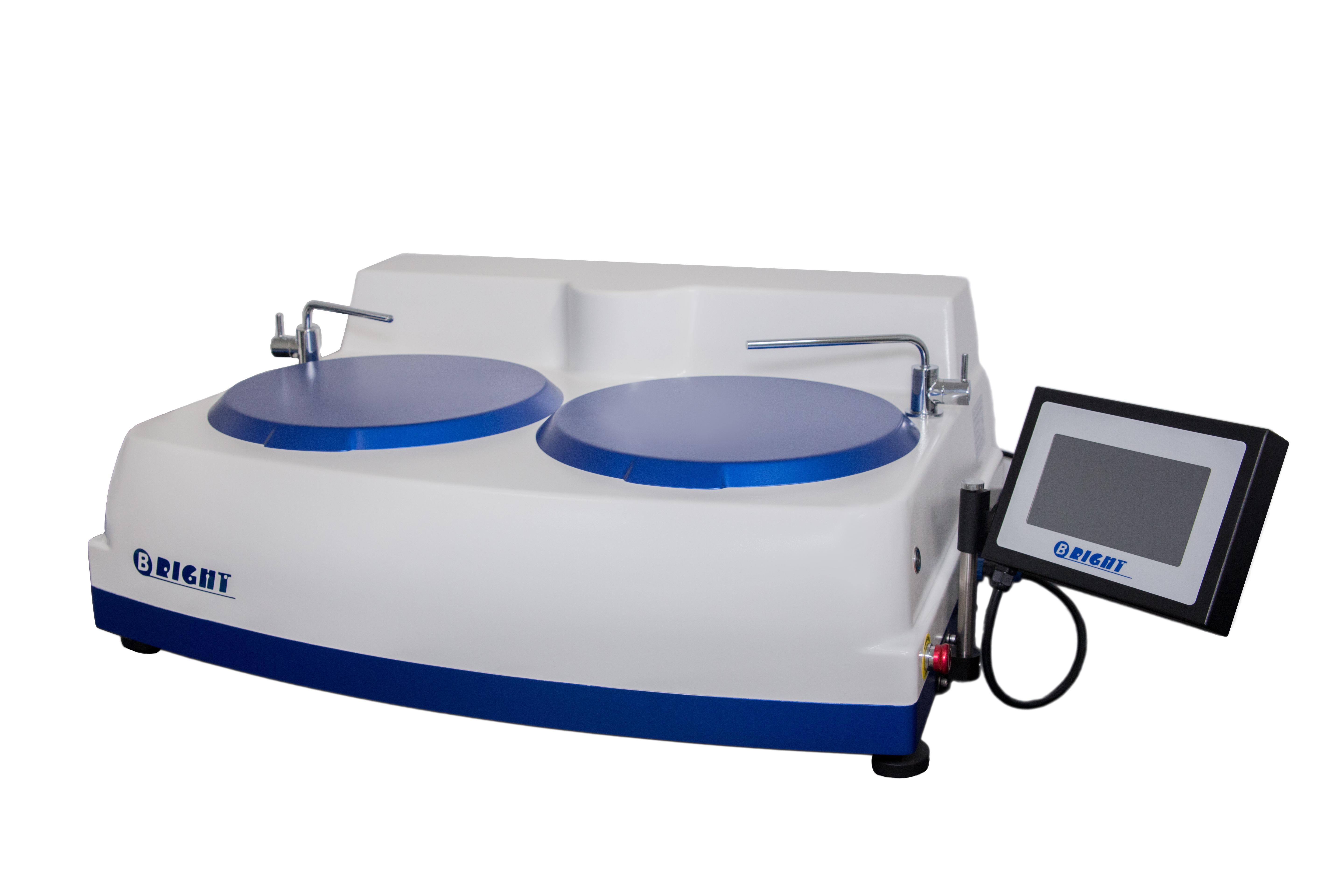
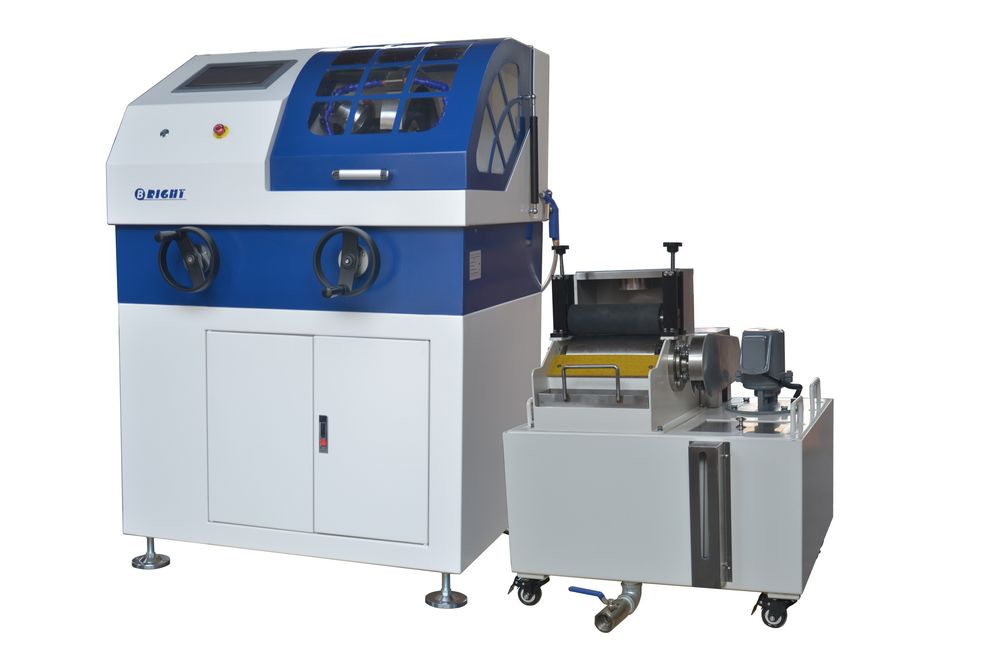
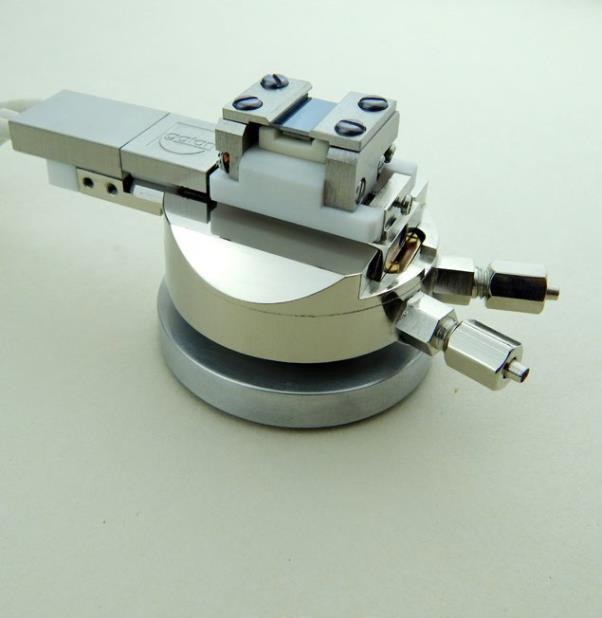
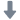
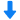
烧结钢中金相制备分析检测方案(切割机)
1、电子产品正变得越来越复杂,工程技术人员总是力图将许多部件放在一个小小的“黑匣子” 中。 毫无疑问,最终产品的质量和可靠性取决于每个部件的性能。然而,这也总是电子工业的一个令人头痛的问题。对电子产品的截面进行金相检验是一种众所周知并通常广为接受的检验方法。
然而,大多数电子产品检验员可能面临的一个问题就是他们需要进行磨光和抛光的材料比预期的复杂和困难。而且他们也许从来没有学习过如何去处理多层基体材料,他们在大学学习时只学过如何恰当地制备均匀的材料,例如钢、铜合金或铝合金。
2、烧结钢零件的横截面试样制备好以后, 不难发现在心部仍然有一些孔隙. 孔隙的面积分数也是该烧结钢零件是否合格的一个重要判据. 然而, 如果试样制备的方法不正确, 测出的孔隙面积分数可能更小或更大.
为了评估试样制备方法对试样中孔隙面积分数的影响, 可将一个烧结钢零件切成两块。其中一个面用传统方法制备, 另一个面用Buehler方法制备.
检测样品:
钢材
检测项:
理化分析
美国标乐
查看联系电话
前往展位
采用OES-PDA 对钢样清洁度分析
当前对钢铁产品质量要求越来越高,尤其是产品的均匀性和清洁度的要求一直在提高。优质钢产品的关键在于其拥有最好的洁净度和最低的氧含量。 传统的检测非金属夹杂物的方法是采用金相显微镜和扫描电镜-能谱分析。这些方法通常很慢或者很贵。而采用发射光谱-脉冲辨别分析技术(OES-PDA)可以快速并有效地对清洁度和氧含量进行分析。在熔化过程中,这些质量指标是必须进行实时控制。此外,该方法可以用于最终产品的快速质量检验。
为了解决该种需求,Bruker研发出MCI(金属清洁度检测)软件包,MCI软件是基于对非金属夹杂物所产生的火花进行的统计分析。
检测样品:
钢材
检测项:
利曼中国
查看联系电话
前往展位
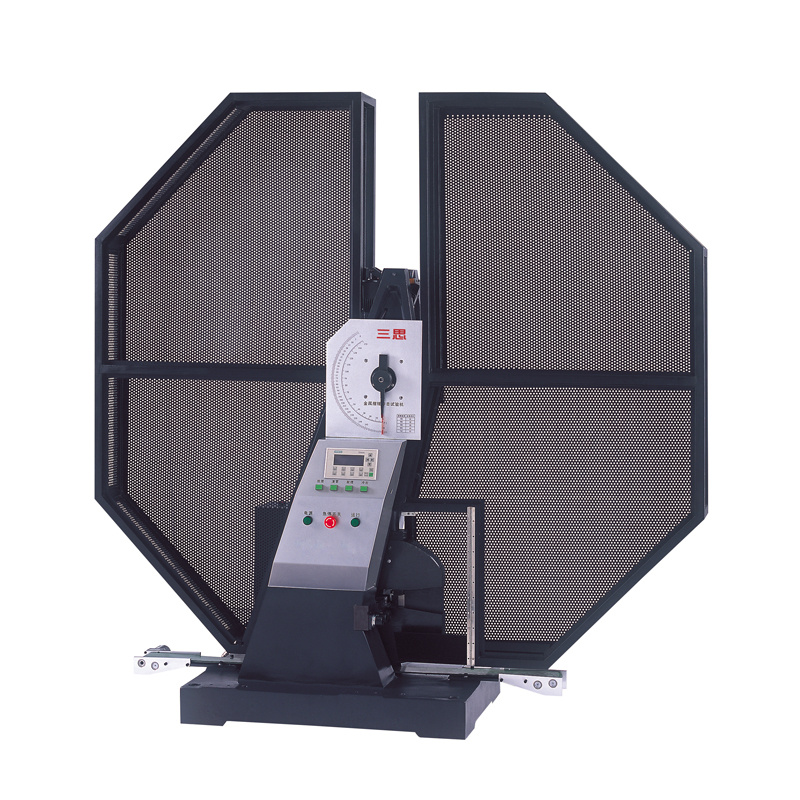
钢板中r 和 n 值检测方案(万能试验机)
我们发现,视频引伸计在这些试验中应用不多,因为金属行业中大多数用户采用传统的 接触式引伸计并相信其结果的可靠性。引伸计技术的发展为金属测试用户提供了其他选择, 例如我们的先进视频引伸计(AVE).该方案不仅允许同时采集轴向和横向应变数据,并减少 因刀口的磨损和撕裂所需的维护,还提高了效率、简化了测试。本测试的目的是为了演示采 用 AVE 测试钢样品的准确性和可靠性。为此,我们采用5982万能试验机、10kN 的载荷传 感器和50kN 的带齿面的楔型夹具。我们采用 Bluehill® 材料测试软件获得试验结果。
检测样品:
钢材
检测项:
机械性能
英斯特朗
查看联系电话
前往展位
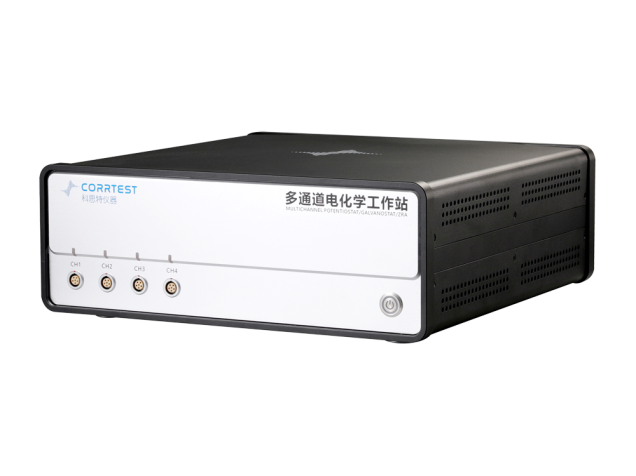
X65管道钢中在油/水乳液的电化学腐蚀检测方案(电化学部件)
The electrochemical corrosion behavior of X65 pipeline steel in the
simulated oil/water emulsion was investigated under controlled
hydrodynamic and electrochemical conditions by rotating disk electrode technique.
Results demonstrated that mass-transfer of
oxygen plays a significant role in the cathodic process of steel in
both oil-free and oil-containing solutions. Electrode rotation
accelerates the oxygen diffusion and thus the cathodic reduction.
The higher limiting diffusive current density measured in
oil-containing solution is due to the elevated solubility of oxygen
in oil/water emulsion. The anodic current density decreases with the
increase of electrode rotating speed, which is attributed to the
accelerated oxygen diffusion and reduction, enhancing the steel
oxidation. Addition of oil decreases the anodic dissolution of steel
due to the formation of a layer of oily phase on steel surface,
increasing the reaction activation energy. The steel electrode
becomes more active at the elevated temperature, indicating that the
enhanced formation of oxide scale is not sufficiently enough to
offset the effect resulting from the enhanced anodic dissolution
reaction kinetics. The corrosion reaction mechanism is changed upon oil addition,
and the interfacial reaction is activation-controlled,
rather than mass-transfer controlled. When sand particles are added
in oil/water emulsion, there is a significant increase of corrosion of the steel.
The presence of sands in the flowing slurry would
impact and damage the oxide film and oily film formed on the steel
surface, exposing the bare steel to the corrosive solution.
检测样品:
钢材
检测项:
可靠性能
理化(香港)有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
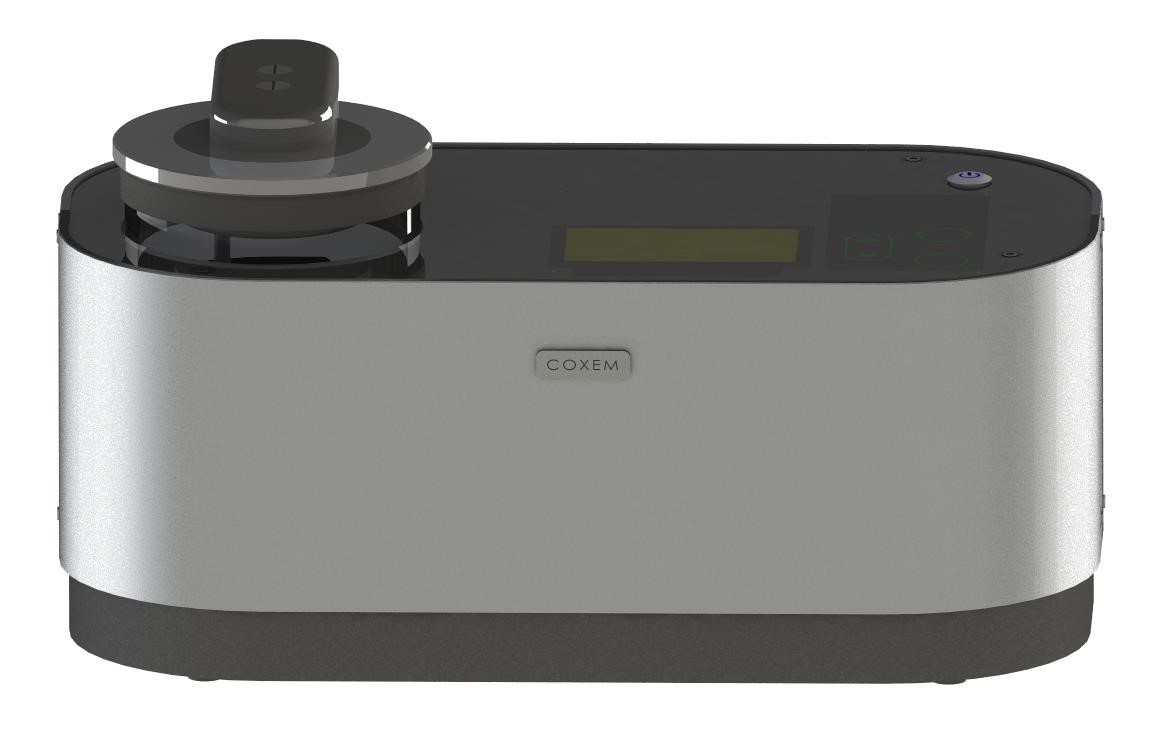
钢帘线用钢盘条中C82D2质量研究检测方案(金相显微镜)
通过试验和检验,分析研究了盘条化学成份、连铸坯中心偏析、非金属夹杂物、钢中 O、N 含量、轧后控冷工艺等 5 种因素对 C82D2 盘条质量的影响。研究表明,应严格控制 C82D2 盘条化学成分的均匀性和有害元素的含量;连铸坯中心偏析严重,易使盘条在拉拔时断裂,产生杯锥状断;盘条中的非金属夹杂物,使盘条在拉拔和捻制变形时,因应力作用而造成钢丝断裂;钢中 O、N 含量过高,会使钢的强度和硬度升高,塑韧性下降;合理的吐丝温度和冷却速度,能保证盘条获得理想的细索氏体组织。为了进一步提高 C82D2 盘条的质量,提出了质量改进建议。
检测样品:
钢材
检测项:
理化分析
北京普瑞赛司仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
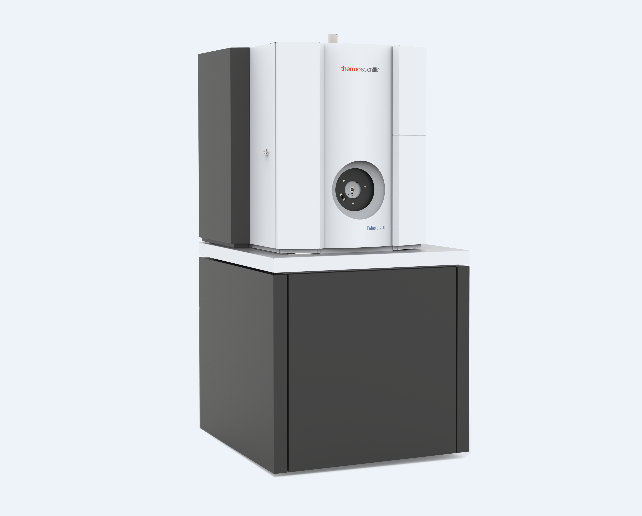
Q&P钢中应变速率对其拉伸变形行为的影响检测方案(扫描电镜)
以汽车用先进高强度 Q&P 钢为研究对象,分析了应变速率对 Q&P 钢拉伸性能及变形行为的影响。结果表明,随应变速率增加,Q&P 钢的强度增加,断裂延伸率则呈先下降(10-4 s-1~101 s-1),后上升至峰值(8×101 s-1),之后再下降(102 s-1~103 s-1)的趋势。变形过程中强度的增加可能同形变回复受限,位错运动受阻有关。而断裂延伸率的变化主要与不同应变速率下 Q&P 钢中残余奥氏体向马氏体转变(即 TRIP 效应)有关。
检测样品:
钢材
检测项:
机械性能
北京欧波同光学技术有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
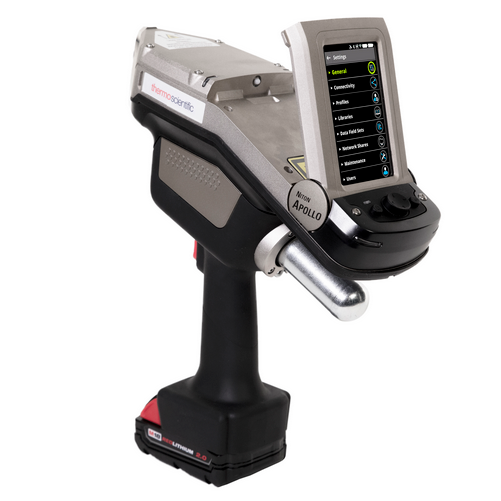
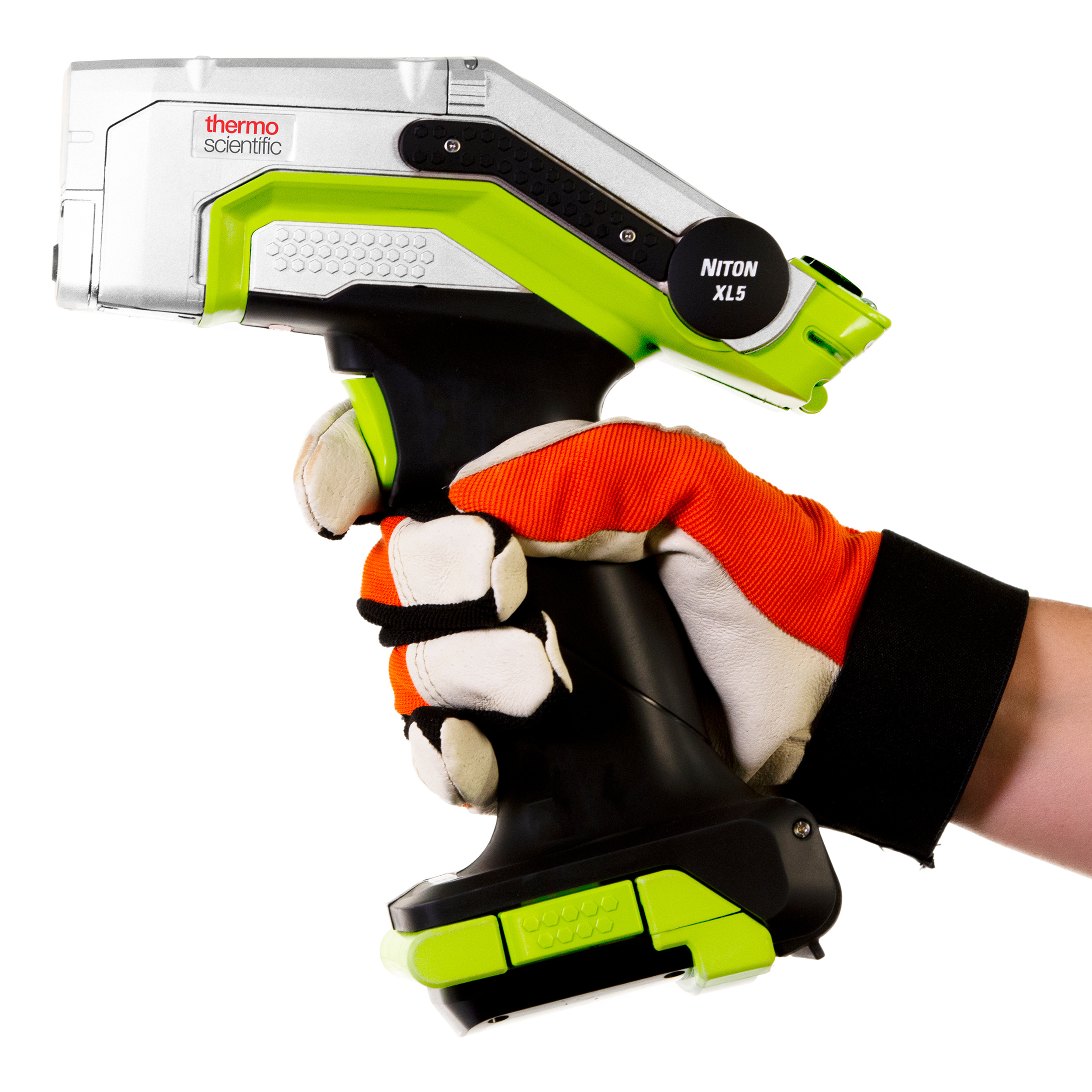
钢构件中碳当量分析检测方案(激光诱导击穿)
钢的焊接性主要受其碳含量的影响。此外,其他元素(例如锰(Mg)、铬(Cr)、钼(Mo)、钒(V)、铜(Cu)、镍(Ni)和硅(Si))的含量也会影响其碳当量(CE)。这些元素在目前占据市场主导地位的、添加了废钢炼制的电弧炉钢中积累,
并进入成品中。
最初,碳当量的提出是为给给定的钢成分指定一个数值,以表明其碳的含量,这将有助于表明该钢材的等效淬透性水平。进一步而言,碳当量代表了物料成分对钢的冷裂(氢裂)敏感性的影响。
在焊接作业中,碳当量计算用于预测热影响区(HAZ)的淬透性。通过碳当量计算了解化学上的任何差异,就可以确定通过填充金属成分连接在一起的两种物料的特性是否适合该工艺。如果成分之间差异过大,或者碳当量值较高接近不可取值(表1),则在焊接操作之前和焊接过程中可能需要采取特殊的预防措施。
焊接预防措施可能包括规定的热处理、使用低氢电极和控制热量输入。这些指南措施很多都已在 NACE(国家腐蚀工程师协会)标准中发布。
检测样品:
钢材
检测项:
含量分析
赛默飞世尔科技分子光谱
查看联系电话
前往展位
新型低碳冷轧搪瓷用钢的组织及性能
在满足性能要求和少添加高价合金元素的前提下, 以开发出高贮氢性能及可适应后期多元化涂搪工艺为目的, 开发出一种含钛低碳冷轧搪瓷用钢。对搪瓷钢不同状态的组织和性能进行了研究, 获得了第二相粒子的析出规律、涂搪前后的晶粒尺寸及析出物的变化规律及退火工艺对强度的影响规律。对钢板的氢渗透时间进行了测定, 试验结果与随后的涂搪试验吻合。搪瓷用钢的室温组织为铁素体, 涂搪后晶粒有一定程度的长大; 钢板中弥散粗大的第二相粒子 T i4C2 S2 是提高钢板贮氢性能的主要因素。730 ?? 保温5h 退火后, 氢渗透时间 tb 大于 18min,氢扩散系数 D 小于 0. 44?? 10- 6 cm2/ s; 钢板与涂层具有良好的密着性, 可承受 110g 钢球在2 m 高度自由落体的冲击。
检测样品:
钢材
检测项:
北京欧波同光学技术有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
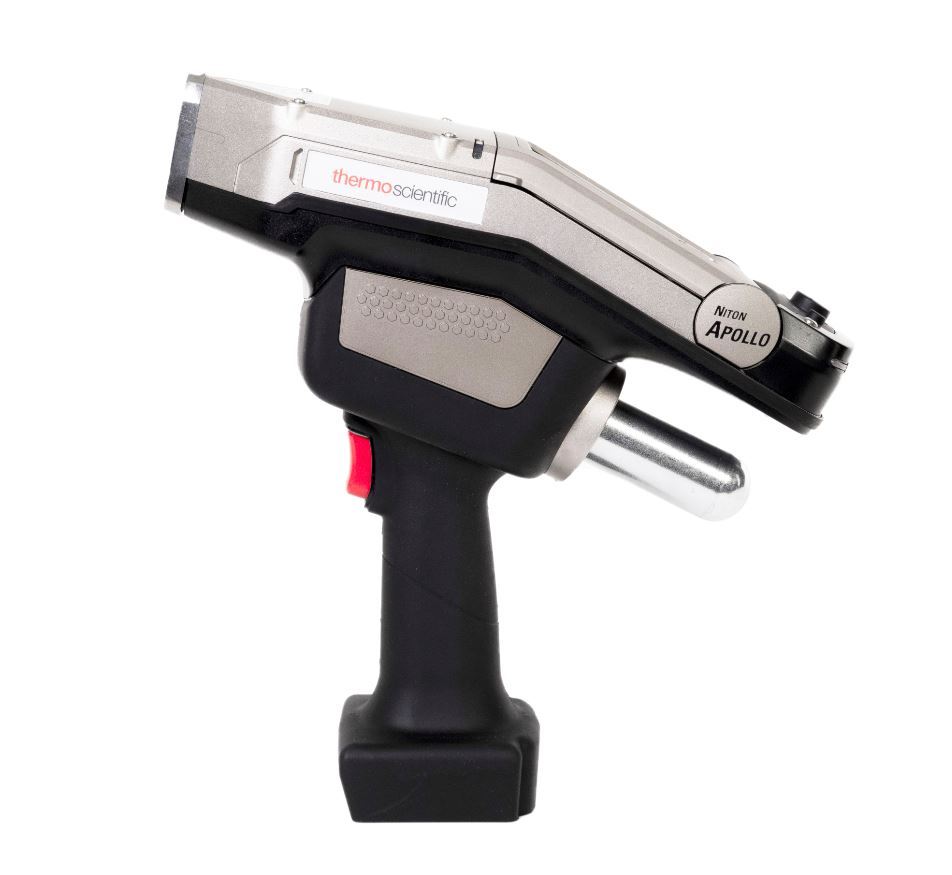
钢板、钢筋、钢条、管材中不锈钢分析检测方案(激光诱导击穿)
测试设备面临的挑战:在过去,XRF (x 射线荧光)和 OES (光发射光谱)都可用于物料验证。在早期的测试作业中,只有实验室配备了物料验证所需的各种仪器。然而,随着实验室技术的小型化,工艺过程中测试和现场测试已经成为现实。
碳(C)是一种重要的合金元素,常常被添加到不锈钢中以增加其硬度和强度。迄今为止,碳的分析一直是一个具有挑战性的工作。最流行的物料验证方法是采用手持式 X 射线荧光(XRF),但其无法检测碳含量。光学发射光谱法(OES)可以检测碳,但需要依托于大型笨重的推车,这也限制了其在棘手的环境中(梯子、狭小通道、沟渠、狭窄的空间等)的应用。
根据不锈钢的等级,碳当量要求在 0.005% 至 1.2% 之间。在某些不锈钢中,不允许碳含量过高,尤其是由于碳化物沉淀而可能威胁焊接性时。由于这些原因,碳含量的测定对于随时间推移全面验证等级和安全操作至关重要。
Niton Apollo 手持式 LIBS 分析仪:现在,我们成功推出新的工具可供专业人员进行物料检验。Thermo Scientific™Niton™Apollo™ 手持式 LIBS 分析仪利用激光诱导击穿光谱技术(LIBS)在生产过程中对物料进行检验。Niton Apollo 分析仪重量仅为 6.4 磅(2.9 千克),专门用于提供方便、便携式碳含量检测方案– 在许多情况下,无需使用笨重的光学发射光谱(OES)推车。Niton Apollo 分析仪具有高效的激光和高纯度的氩气吹扫功能,可以确认或更新错误的MTR 报告,消除与焊接操作时不兼容合金相关的风险,甚至可以区分相似等级的合金。
检测样品:
钢材
检测项:
理化分析
赛默飞世尔科技分子光谱
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供191篇钢材检测方案,可分别用于其他检测,参考标准主要有等