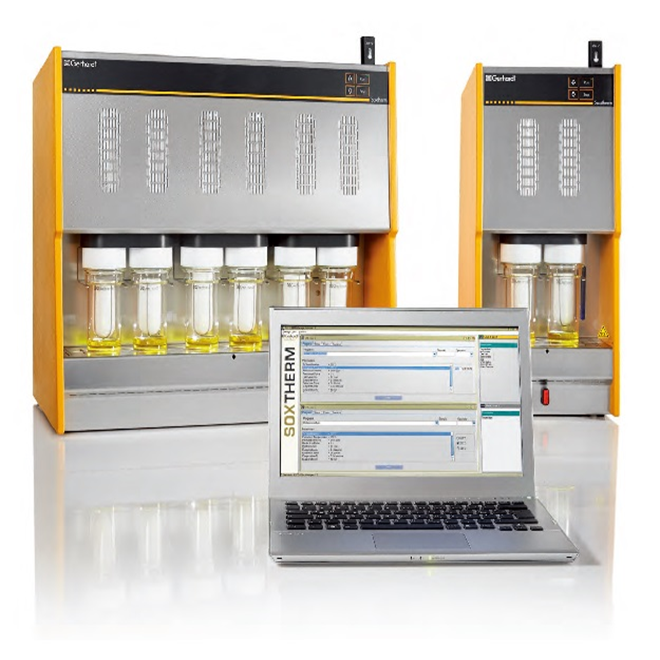
使用格哈特公司的蛋白质测定仪检测复方中草药配方的蛋白质含量,使用格哈特方式的全自动快速脂肪测定仪检测复方中草药配方的脂肪含量。
方案详情

使用格哈特公司的蛋白质测定仪检测复方中草药配方的蛋白质含量,使用格哈特方式的全自动快速脂肪测定仪检测复方中草药配方的脂肪含量。Journal of Ayurvedic and Herbal Medicine 2018;4(3): 132-134 Physico-chemical parameters Journal of Ayurvedic and Herbal Medicine 复方中草药配方的理化及概略分析 Research Article ISSN:2454-5023 Physico-chemical and Proximate Analysis of Poly HerbalFormula-Palakalyana Ghrita J. Ayu. Herb. Med. 2018;4(3):132-134 Kariyakeranage Chandi Pereral, Menuka Arawwawala, Sumeda Wijeratne3, Deepal Mathew4 1 Institute of Indigenous Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka www.ayurvedjournal.com 2 Industrial Technology Institute, Bauddhaloka Mawatha, Colombo 07, Sri Lanka Received: 04-08-2018 3 Department of Obstetrics &Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka Accepted: 12-10-2018 4 Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka ABSTRACT Background: Standardization is necessary in order to assess the quality of herbal formulations. Palakalyana Ghrita (PKG)is an herbal formula used in Ayurveda medical system to enhance fertility and immunity in both genders which consistsnineteen medicinal plants with cow’s ghee and milk. As per available literature PKG formula has not been standardizedalthough it is a commonly used drug by traditional practitioners. Therefore, this study was carried out to evaluate thephysio-chemical properties, nutrition composition and possible toxic elements and microorganisms of PKG formula.Methodology: Physico-chemical properties tested include refractive index, total ash content, acid in soluble ashcontent, water soluble ash content, moisture content, acid value, peroxide value, saponification value. Carbohydrate,protein, fatty acid, vitamin and mineral composition were assessed as nutritional parameters of PKG. Heavy metals andmicroorganisms were tested using standard protocols. Results: Unsaturated fatty acids namely Palmitoleic acid (0.26%),Oleic acid (40.36%) and Linoleic acid (9.19%) and saturated fatty acids; Capric acid (0.63%), Myristic acid (1.68%)Pentadecyclic acid (0.23%) Palmitic acid (42.25%) Margaric acid ((0.26%) and Stearic acid (4.85%) were present in thePKG formulation. The percentages of carbohydrate, protein and fat content of PKG were 0.04±0.0, 98.8±0.2 and 0.7±0.0 respectively. Heavy metals and microbes were not detected. Conclusion: Results obtained could be utilized asreferences standard for quality assurance of PKG. Keywords: Herbal formulation, Palakalyana Ghrita, Physico-chemical, Standardization. INTRODUCTION Palakalyana Ghrita (PKG) is used in traditional medical systemof Sri Lanka, to enhance fertility andimmunity of both males and females. Roots of Asparagus racemosus is the main ingredient in PKG. It isknown to possess medicinally important aphrodisiac, immunomodulatory, anti-ulcer and anti-anemicproperties [1, 2,3,4]. PKG contains 19 medicinal plants along with cow's milk and cow's ghee (Table 1). Mostof these herbal compositions are effective in practice, however are not scientifically validated. Therefore,standardization of PKG is essential to ensure efficacy and stability of its' finished product. In the presentstudy, an attempt was done to standardize PKG using standard protocols. MATERIAL AND METHODS Plant materials All plants materials with pasteurized cow's milk, and fresh cow’s ghee were purchased from the Ayurvedapharmacy adjacent to the, Ayurveda teaching hospital, Borella, Sri Lanka and all were identified andauthenticated by the Department of Materia Medica, in Institute of Indigenous Medicine, University ofColombo, Sri Lanka. Preparation of the drug *Corresponding author: Chandi Nineteen herbal ingredients in the formulation were washed and dried at 60 ℃ using an oven.Concentrated water extract of Asparagus racemosus was prepared using 600 g of the chopped rootsinfused in 20 L water, and boiled at 100 ℃ for 4-6 hours until reduced to 5 L volume of liquid. All the otherherbal materials were separately washed and air dried to a constant weight and powdered using anelectric grinder and passed through the 10 mesh sieve. Fifteen gram of each finely powdered herbalingredients, 5 L of pasteurized cow's milk and 1280 g of fresh cow's ghee were added to the 5 L volume ofliquid. The mixture with all ingredients was boiled until all the water evaporated. The preparation wasstored in glass bottles at room temperature. This formulation was prepared as per the classical procedure[5] at the pharmacy attached to the Institute of Indigenous Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka. Determination of physico-chemical parameters such as total ash, acidinsoluble ash, and water soluble ash were done as per WHO guidelines20116. Moisture content, refractory index, saponification value andperoxide value were determined according to the method mentionedin SLS 340:1975M. Acid value was measured by using titrating methodin an alcoholic medium with aqueous potassium hydroxide (KOH)solution. Nutritional values VitaminB1, B2, and B12 were detected using ROCHE Basle method.Vitamin C was evaluated according to US Pharmacopeia 22nd Edition20048, Vitamin A and E were detected according to a standardprotocol using HPLC [9].Fatty acid composition was analyzed using BF3/Methanol fatty acid ester derivertization [10]. Kjeldahl method wasused for the detection of protein [11]. Carbohydrate was detected usingMolish's test [12]. Total dietary fiber was evaluated using enzymaticgravimetric method. Crude fat content was analyzed using the methoddescribed in AOAC (2000) and the Soxtherm manual 113 Heavy metals Heavy metals such as Mercury, Arsenic, Lead and Cadmium wereestimated by hydride generation technique (coldd vapor atomicabsorption spectrometry)[13], lodine value This was estimated according to SLS 313 Part 2, section 2;2014I14] Microbiological limits Aerobic plate counts, yeast and moulds were observed according toSLS 516/1 and SLS 516/2 [15] methods. Coliforms/ Escherichia coli, andStaphylococcus aureus were observed using methods as described inSLS/3 [16] and SLS/516/6 [17] respectively. TLC fingerprinting Extraction procedure for the sample Sample (10 g) was refluxed with water (50 ml), added to a separatingfunnel containing hexane, shaken well and kept for 15 min. After thatremoved the hexane layer and active ingredients were extracted intodichloromethane and concentrated. Extraction procedure for the active ingredients Plant ingredients mentioned in Table 1, mixed in a ratio of 1:1 (w/w)and extracted into dichloromethane and concentrated. Both sample (5ul) and mixture of raw materials (5 ul) were spotted on the same TLCplate. A mixture of solvent system consist of methanol, cyclohexaneand dichloromethane in a ratio of 0.2:2:9.8 v/v was used as the mobilephase. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Very minor quantities total ash, water soluble ash or acid insoluble ashwere present in PKG (Table 2). That indicates fewer impurities in thefinal product of PKG. Less moisture content (0.12% w/w) shows thatthere is less chance of microbial growth. Acid value of the amount ofpotassium hydroxide in milligrams required to neutralize the acidpresent with any formulation. During the process of oxidation acidityincreases because triglycerides are converted into fatty acids andglycerol. Releasing of fatty acid is result of hydrolysis, and thermaleffects. Further there is direct relationship of acid value with rancidity. The less acid value (1.8mg/KoH/g Oil) indicate better quality andsuitability for human use. Further these results are supported toprevious studies on standardization of Ghrita preparations in Ayurvedamedicine [18] (Table 3). Table 1: Medicinal plants in Palakalyana Ghrita Plant Ingredients Family Part of the plant Terminalia chebula(Retz) Combretaceae fruits Terminalia bellirica (Roxb) Combretaceae truits Phyllanthus emblica (L[']) Phyllanthaceae fruits Picrorhiza kurroa (L门) Plantaginaceae rhizomes Curcuma domestica (L[']) Zingiberaceae rhizomes Rubia cordifolia(L) Rubiaceae roots Vitis vinifera(L) Vitaceae fruits Nymphoides cristata (Roxb) Menyanthaceae flowers Santalum album (L) Santalaceae wood Saussure lappa (Decne) Asteraceae roots Withania somnifera (L) Solanaceae roots Dunal Sida cordifolia (L) Malvaceae roots Ipomoea peniculata (L) Convolvulaceae tubers Pterocarpus santalinus (L.f) Fabeceae wood Coscinium fenestratum Menispermaceae stem (Goetgh) Sacchrum officinarum (L) Poaceae stem Glycyrrhiza glabra (L[') Fabeceae rhizomes Vernonina cineria (H Rob) Asteraceae Whole plant Asparagus recemosus Asparagaceae roots (willd[) Table 2: Medicinal plants in Palakalyana Ghrita Test Result 1. Refractive index 1.4666 at 40°℃ 2. Total ash 0.03% w/w 3. Acid insoluble ash Not detected <0.01% 4. Water soluble ash Not detected <0.01% 5. Moisture content 0.12%w/w 6. Acid value 1.8 mg/KOH/g Oil 7. Peroxide value 7.5 milliequvillent/kg 8. Saponification value 212.0 9. lodine value 52.6 g per 100 n=6 PKG consists with Capric acid (0.63%) and Myristic acid (1.68%) (Table3). Medium chain fatty acids possess antioxidant properties whichcounter negative results of premature gray hair, macular degenerationand sagging of the pores and skin. Both unsaturated and saturatedfatty acids included in PKG are coronary heart pleasant fatty acids,increases the fee of metabolism that helping in weight loss ,increasethe extent of true cholesterol (high density lipoproteins) and decreasethe bad cholesterol (low density lipoproteins) in human frame .Thoseare great sources of energy[19]. Microbes such as aerobic microbes,yeast and moulds, coliforms/Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureuswere not detected in PKG. Name of the Fatty acid percentage 1. Capric acid 0.63% 2. Myristic acid 1.68% 3. Pentadecyclic acid 0.23% 4 Palmitic acid 42.25% 5. Palmitoleic acid 0.54% 6. Magaric acid 0.26% 7. Stearic acid 4.85% 8. Vaccenic acid 40.36% 9. Linoleic acid 9.19% n=6 Table 4: Nutritional composition in Palakalyana Ghrita Phytoconstituents Results (%) 1. Carbohydrate 0.04±0.0% 2 Fat 98.8±0.2% 3. Protein 0.7±0.0% 4. Vitamin A 1.0(mg/100g) 5. Vitamin E 2.5 (mg/100g) 6. Vitamin B12 0.041 (mg/100g) n=6 Figure 1: TLC profile of Palakalyana Ghrita (PKG) TLC fingerprint profile is showed in (Figure 1). The sample has similarities interms of Rf values and colour of PKG sample to the Rf values and colour of theraw materials. It is proved homogeneity of a final product. Nutritional analysis indicates good amount of vitamins as vitamin A, Eand B12. Due to high oily base in PKG enhance the absorption ofvitamins A and E which are fat soluble vitamins consisted. Ancientphysician were prescribed PKG as fertility enhancing treatment.Nutritional analysis of PKG shows evidence to prove that claim (Table4). Mercury, lead and cadmium were not present in PKG. Results haveshown that concentration of arsenic was 0.3 mg/kg in PKG. However,the observed arseniIcCCconcentration Was within the WHOrecommended limits. These evidences confirm the nontoxic effect ofPKG. The iodine value of PKG was 52.6 g per 100. Higher iodine valueindicates the grater the number of unsaturated fatty acids. Rf values ofsample and mixture of raw materials were similar to each other (0.06,0.15,0.18, 0.21,0.31,0.41,0.46,0.48,0.53, 0.62, 0.75 and 0.82). Palakalyana Ghrita was standardized for the first time using standardprotocols and output of the present study could be utilized asreferences standard for quality assurance of Palakalyana Ghrita. Conflict of interest-None declared Acknowledgement The authors are sincerely thankful to the Institute of IndustrialTechnology, Colombo 07, Sri Lanka, for providing facilities for theexperimentation. Their special thanks go to the University of Colombo,Sri Lanka and NCAS, Sri Lanka for providing the financial assistance forthe study. REFERENCES 1. Sastri V.S.D.A., Bahisajja Ratnavali Yoni vyapad Chikithsa. ChaukambaSanskrit Sansthana, Varanasi, India.2006 ;(I); 373. 2. Dan B., Clary S., Erich S., Andrew G. Chinese Herbal Medicine:Materia Medica, 3rd Ed. Eastland Press. 2004. 3. Gautam M., Diwany S., Gairola S., Sinde Y. Immuno adjuvantpotential of Asparagus resemosus aqueous extract in experimentalsystem. Eth.J.2009;91:251-5. 4 Thakur R.S., Puri H.S., Husain A. Major Medicinal Plants of India.Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, Lucknow, UttarPradesh.1992. 5. Ayurveda Pharmacopeia, Department of Ayurveda Colombo. 1975;1:(1),63. 6. WHO general guidelines for Methodologies on research andevaluation of Traditional Medicine, World Health OrganizationGeneva, 2011. 7. Sri Lanka standard publication of Sri Lanka Standards Institution, SriLanka 340:1975. 8. United states Pharmacopeia (USP 27th revision) the nationalformulatory(NF 22ndedition) Rock Ville; United StatesPharmacopeia convention 2004. 9. Leenheer De A.P., Nelis H.J., Lambert W.E., Bauwen. R.M.,Chromatography of fat-soluble Vitamins in clinical Chemistry. Journalof Chromatography, 1988;429:3-58. 10. Morrison W.R., Smith L.M., Preparation of fatty acid methyl estersand dimethyl acetyls from lipid with boron fluoride methanol.J.Lipid.Res1964;5:600-608. 11. AOAC official methods of analysis, Association. Official Analyticalchemists, Washington DC, USA, 15th Edition, 1990;807-828. 12. Harbone J.B. Phytochemicals method. A guide to modern techniquesof plant analysis, 1998.3rd Ed.chapman and Hall Int, New York. 13. Official methods of Analysis of AOAC international1..AOACinternational, Gaithersburg MD, USA, Official Methods 2000. 14 Sri Lanka standard publication of Sri Lanka Standards Institution, SriLanka 2014; 313:2. 15. Sri Lanka standard publication of Sri Lanka Standards Institution, SriLanka 516/2; 1991. 16. Sri Lanka standard publication of Sri Lanka Standards Institution, SriLanka. 3;1982. 17. Sri Lanka standard publication of Sri Lanka Standards Institution, SriLanka 516/6 .1992. 18. Pronab H, Mahapatra BN. Agrawal D, Singh AK.Pharmaceuticoanalytical study and standardization of Panchtiktaghrita.Int.Res.J.Pharm.2013;4:(9).173-179. 19. Groff J.L., Gropper S.S., Hunt S.M. Advanced Nutrition and HumanMetabolism. New York: West Publishing Company; 1995. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE Perera KC, Arawwawala M, Wijeratne S, Mathew D. Physico-chemical andProximate Analysis of Poly Herbal Formula- Palakalyana Ghrita. J Ayu HerbMed 2018;4(3):132-134.
确定



还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
中国格哈特为您提供《复方中草药配方的蛋白质及脂肪含量检测》,该方案主要用于中药制剂中含量测定检测,参考标准--,《复方中草药配方的蛋白质及脂肪含量检测》用到的仪器有格哈特全自动快速索氏提取SOXTHERM、格哈特凯氏消化系统KT8S、格哈特维克松废气实验室废物处理系统涤气VS、格哈特带自动进样器凯氏定氮仪VAP500C、德国加液器MM、滤纸筒
该厂商其他方案
更多