方案详情
文
在调查枪击类犯罪时,是否可以在犯罪现场或可能使用的武器上找到枪弹残留物(GSR)至关重要。侦探可以识别或是排除被发现枪支是否是作案的武器,并可以将其与嫌疑人联系起来。此外如果使用正确的技术,通过化学分析可以揭示武器的使用时间。
瑞士洛桑大学,意大利罗马的Sapienza大学和英国伦敦的国王学院的科学家们对广泛使用的基于气质检测(GC / MS)和固相微萃取(SPME)的分析方法进行了评估。此外,他们也对使用顶空吸附萃取(HSSE)然后进行热解吸-气质联用(TD-GC / MS)的新方法与基于SPME的方法进行了比较。科学家们对结果很满意。
方案详情

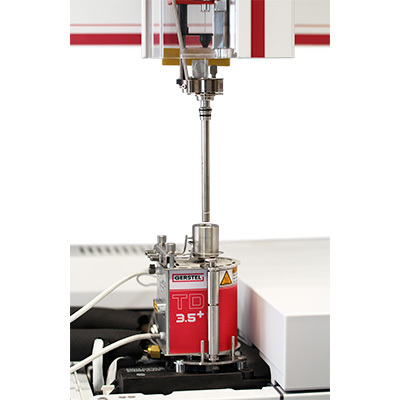
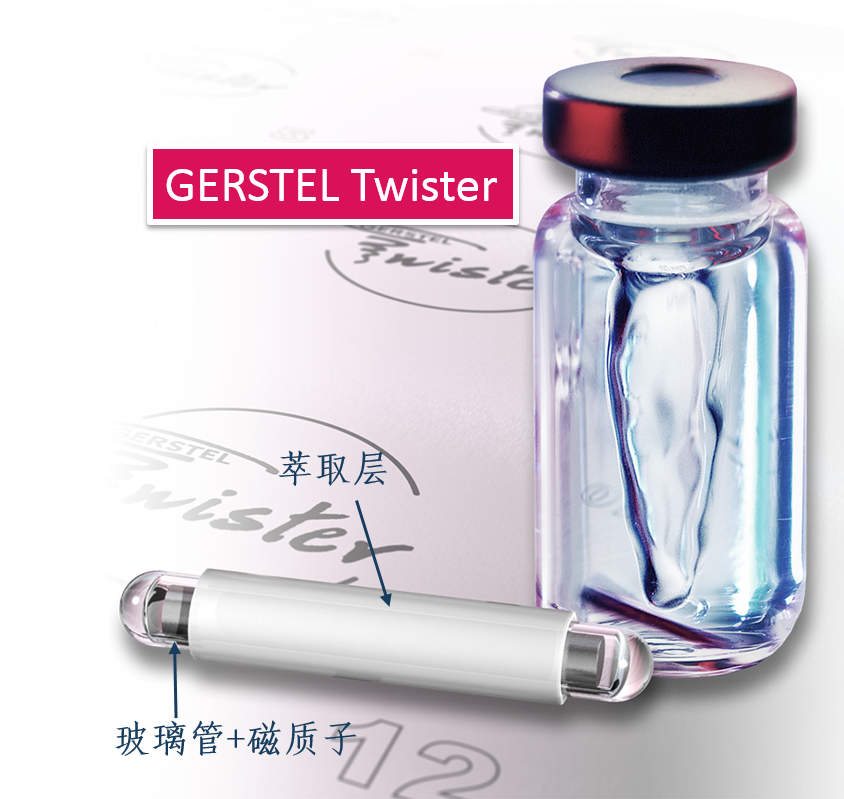
Forensic Dating Services Gunshot Residue Dating To determine if and when a handgun has been fired, forensic scientists are searching for and analyzingGunshot Residue (GSR) deposits. GSR can be found directly on firearms, spent cartridges, or on persons,clothing or materials that were near the firearm at the time it was discharged. One highly interestingaspect of GSR is the presence of volatile organic chemical residues, which can offer clues as to when aweapon was fired. An innovative extraction technique based on Headspace Sorptive Extraction (HSSE) has now been shown to extract additional information from spent cartridges. By Guido Deussing hen investigating a crime that was carried out us-ing a firearm, it is often of critical importance todetermine whether gunshot residue (GSR) can be foundat the crime scene or on weapons potentially used. Sucha finding can enable detectives to identify- or rule out-a firearm as the weapon used and potentially link it to asuspect. Further, given the right technique,chemical ana-lysis can shed light on the time elapsed since a weaponwas last fired. Widely used analysis methods based on gas chroma-tography with mass spectrometry detection (GC/MS)and Solid Phase Micro-Extraction (SPME) have been GERSTEL Solutions worldwide-No. 18 evaluated by collaborating scientists at the Universityof Lausanne, Switzerland; the Sapienza University inRome, Italy; and King’s College in London,England. Inaddition, a novel method using Headspace Sorptive Ex-traction (HSSE) followed by thermal desorption-GC/MS (TD-GC/MS) was compared with the SPME basedmethod. The scientists were pleased with the results.[1]. The Content of Gunshot Residue Every firearm emits gunshot residue when discharged.The compounds involved are released at explosive speedand deposited or adsorbed on the hand, body and cloth-ing of the shooter. Depending on the distance to the fire-arm, residue can also be found on the victim and,obvi-ously, on the weapon used and on spent cartridges thatwere ejected. Sources of GSR are the ignition- and propellantcharge powders in the cartridge. In addition, metallicpowder is formed by abrasion from the bullet and car- To perform Headspace Sorptive Extraction (HSSE), a GERSTEL Twister is suspendedinside a sealed vial placed in the headspace above the sample. In the case shownhere, a spent handgun cartridge (left) is being analyzed. During extraction, volatileand semi-volatile organic compounds (VOCs and SVOCs) are concentrated in thesorption phase of the Twister. The Twister shown here is the Polydimethylsiloxane(PDMS) version. Following the extraction period, the Twister is removed, placed ina glass liner, and analyzed by thermal desorption-GC/MS. The GERSTEL ThermalDesorption Unit combined with a GC/MS-System (Agilent Technologies) was usedin the work reported here. tridge and added to the mix. GSR consists of variousinorganic and organic chemicals. Due to aging processesand volatilization, changes in the concentrations andamounts of organic chemicals as well as certain com-pound to compound ratios of amounts can be helpful indetermining the time of discharge of a weapon accordingto Gallidabino et al. as reported in their paper in Analyti-cal Chemistry [1]. The compounds identified as GSR from literaturereferences are, among others, nitroglycerine, diphenyl-amine, ethylcentralite, dibutylphthalate and 3-Ethyl-1-Hexanol as well as organic reaction byproducts, espe- cially derivatives of benzene, and polycyclic aromatichydrocarbons (PAHs). To determine these, the SPMEtechnique has been widely used in combination withGC/MS. To perform GSR-based dating, Gallidabinoet al. performed repeat extractions of analytes from theinterior of a firearm and/or spent ammunition withthe aim of establishing an aging profile, which can becompared with reference profiles.Naphthalene and de-composition products of nitrocellulose were proposedas target reference compounds. The problem with handguns - and thesolution SPME is an established technique for time estimatesconcerning discharge of ammunition from rifles andother larger firearms. However, its usefulness for foren-sic dating of firing of smaller handguns is more limited.The repeatability is insufficient, as reported by the sci-entists, and degradation curves for the target analytesquickly fall below their limits of detection with SPME,as Gallidabino et al. [1] report. For these reasons,SPME is not the ideal technique for the investigationof GSR in combination with handguns. In their search for an alternative extraction andanalysis method with significantly higher sensitiv-ity for the target analytes, the scientists'attention wascaught by Headspace Sorptive Extraction (HSSE).HSSE is based on the GERSTEL Twister, a glasscoated magnetic stir bar with a PDMS sorption phase.The Twister is most often used for Stir Bar SorptiveExtraction (SBSE) of aqueous samples. In HSSE,the Twister is suspended in the Headspace above thesample inside a sealed 20 mL headspace vial. HSSEis thus very similar in principle to Headspace SolidPhase Micro-Extraction (HS-SPME). The main dif-ference is that the Twister offers a much larger sorp-tion phase volume than SPME fibers which consistof a thin sorption phase coating on a metal or glassfiber contained within a syringe needle. Consequently,SBSE provides better recovery, better repeatability, andlower limits of detection. After the extraction step,analytes are released from the Twister by thermal de-sorption in the GERSTEL Thermal Desorption Unit(TDU2) immediately followed by GC/MS determi-nation of the analytes. These steps are fully automatedusing the GERSTEL MultiPurpose Sampler (MPS)under MAESTRO software control.“The Twistercan provide up to 1000 times higher sensitivity thanSPME, depending on the application", says Oliver Le-rch, Ph.D., Application Scientist from GERSTEL. SBSE can be performed with different Twisters tocover a wide range of analytes from non-polar to polar.Desorption can be performed by thermal desorption- as is most often the case - or by liquid desorptioncombined with either GC/MS or LC/MS. Preparing the GSR analysis To determine whether HSSE is a suitable extraction tech-nique for the analysis of GSR, different types of cartridg-es were inserted into a semi-automatic pistol, discharged,1,and the spent cartridges placed in sealed HS vials withGERSTEL Twisters suspended in the headspace abovethe sample. The cartridges contained propellant chargesbased on either nitrocellulose or a combination of nitro-cellulose and nitroglycerine. The results from the HSSE-TD-GC/MS analysis were compared with results fromthe analysis of a reference mixture based on 55 selected GSR target analytes from discharged cartridges. HSSEproved to be significantly more sensitive while deliveringbetter reproducibility than SPME. Among the 4 com-pounds not found were thermally labile compounds suchas nitroglycerine that are decomposed during thermal de-sorption. Further studies are to be performed to optimizethe analysis method parameters with the aim of increas-ing the number of target analytes that can be determined. As part of their project, Gallidabino et al. generatedaging curves in order to develop a method for determin-ing the approximate time of discharge including deter-mining whether the firearm was discharged at all. These substances,identified as GSR com-pounds. This is how Gallidabino etal. approached the analysis: In theheadspace above the spent cartridgeto be analyzed, a perforated glassinsert containinga conditionedTwister was positioned and theheadspace vial was sealed. Differ-ent Twister techniques enable dif-ferent sampling approaches alongwith the use of different phases tocollect a wider range of analytes.In this case, the analytes were ex-tracted at 80°C for 72 hours. TheTwisters were removed from thevial and placed in individual sealedglass tubes ready for Thermal De-sorption-GC/MSanalysis.Theglass tubes were fitted with individ-ual transport adaptors, which seal Extracted lon Chromatogramm (EIC) of the standard solution containing 55 substances injected by Gallidabino et al.Using HSSE-GC/MS, the researchers were able to determine 51 of the 55 compounds in GSR. The "missing com-pounds" were thermally labile substances induding nitroglycerine and N-nitrosophenylamine. the tubes and enable the MultiPurpose Sampler (MPS)gripper to transfer them to the Thermal Desorption Unit(TDU) for temperature programmed desorption. The re-leased analytes are focused in the GERSTEL Cooled In-jection System (CIS) PTV type GC inlet at -80℃. TheCIS is then heated using a temperature program and theanalytes transferred to the GC column in splitless modeusing a helium carrier gas flow of 1.3 mL/min for highlysensitive GC/MS determination.The CIS was installedin a gas chromatograph (Agilent GC 7890A) connectedto an Agilent 5975 Mass Selective Detector(MSD). Thecolumn used was an Agilent HP-5MS (30 m x 0.25 mmx 0.25 um). The GC oven initial temperature was 40 ℃,the program progressing to a final temperature of 280 ℃.The GC run including cool-down and equilibration last-ed 46 minutes. Mass Selective Detection (Agilent 5975CMSD) was performed in EI mode in full scan modeacross a range of m/z 40 to 500. HSSE delivers The results of their study clearly showed that by usingHSSE, the scientists were able to determine and track theconcentration degradation curves of 51 of the selected 55 aging curves are based on GSR compound concentra-tions on spent cartridges from handguns and their degra-dation curves. The scientists report that based on the useof HSSE on aged samples, several GSR compounds haveshown significant aging profiles. In addition, compound-to-compound ratios can be used to extend the time pe-riods that can be covered. This approach also contributesto making the determination more rugged and to reduc-ing variability, making the method more useful for the forensic scientist entrusted with the case. Gallidabino and his colleagues concludedthat their results were very encouragingfor the development of a new and com-plete forensic dating technique basedon GSR. Reference [1] M. Gallidabino, F. S. Romolo, K. Bylenga andC. Weyermann, Development of a NovelHeadspace Sorptive Extraction Method toStudy the Aging of Volatile Compoundsin Spent Handgun Cartridges, AnalyticalChemistry 86 (2014) 4471-4478 GERSTEL Solutions worldwide -No. 在调查枪击类犯罪时,是否可以在犯罪现场或可能使用的武器上找到枪弹残留物(GSR)至关重要。侦探可以识别或是排除被发现枪支是否是作案的武器,并可以将其与嫌疑人联系起来。此外如果使用正确的技术,通过化学分析可以揭示武器的使用时间。瑞士洛桑大学,意大利罗马的Sapienza大学和英国伦敦的国王学院的科学家们对广泛使用的基于气质检测(GC / MS)和固相微萃取(SPME)的分析方法进行了评估。此外,他们也对使用顶空吸附萃取(HSSE)然后进行热解吸-气质联用(TD-GC / MS)的新方法与基于SPME的方法进行了比较。科学家们对结果很满意[1]。枪弹残留每个枪支在射击后时都会留下枪击残留物。所涉及的化合物以爆炸性速度释放并沉积或吸附在枪手的手,身体和衣服上,还有在使用的武器和弹出的废弹药筒上。根据与枪械的距离,也可以在受害者身上找到残留物。GSR的来源是弹药筒中的点火和推进剂装料粉末,另外还有通过子弹和弹药筒的磨损形成金属粉末。 GSR由各种无机和有机化学品组成。根据Gallidabino等人的研究,由于老化过程和挥发,有机化学品的浓度和数量的变化以及某些化合物与化合物的比例的变化可能有助于确定武器的排放时间[1].从文献中鉴定为GSR的化合物尤其是硝化甘油,二苯胺,乙基中定剂,邻苯二甲酸二丁酯和3-乙基-1-己醇以及有机反应副产物,尤其是苯的衍生物和多环芳烃(PAHs)。为了确定这些化合物,SPME技术已广泛用于GC / MS。为了进行基于GSR的数据研究,Gallidabino等人从枪支内部和/或用过的弹药中重复提取分析物,目的是建立老化曲线来与参考曲线进行比较。他们使用的目标参考化合物是萘和硝酸纤维素的分解产物。手枪的问题和解决方案SPME是一种用于估计步枪和其他大型枪械中释放弹药的时间曲线的成熟技术。然而它对于研究小型枪械使用的法医数据有其局限性。如科学家所报告的那样,SPME的重复性不足,目标分析物的降解曲线迅速会低于其用SPME检测的极限 [1]。正因如此,SPME不适合研究手枪的枪弹残留物。在寻找对目标分析物具有显着更高灵敏度的替代萃取和分析方法时,科学家的注意力被顶空吸附萃取(HSSE)捕获。 HSSE基于GERSTEL Twister,是一种带有PDMS吸附相的玻璃涂层磁力搅拌棒。 Twister最常用于水样的搅拌棒吸附萃取(SBSE)。在HSSE中,Twister悬浮在密封的20 mL顶空样品瓶内的样品上方的顶空中。因此,HSSE原理上与顶空固相微萃取(HS-SPME)非常相似。主要区别在于Twister提供比SPME纤维大得多的吸附相体积。因此,SBSE有更好回收率,更好的可重复性和更低的检测限。在萃取步骤之后,通过GERSTEL热解吸单元(TDU 2)中的热脱附立即从Twister中释放分析物,紧接着通过GC / MS测定分析物。使用MAESTRO软件控制下的GERSTEL 多功能全自动样品前处理平台(MPS)可以完全自动化这些步骤。 GERSTEL的应用科学家Oliver Lerch博士说:“根据不同的应用,Twister的灵敏度可以比SPME高出1000倍”。SBSE可以使用不同的Twister进行,以涵盖从非极性到极性的各种分析物。利用HSSE对GSR分析为了进行顶空吸附萃取(HSSE),将GERSTEL Twister悬浮在置于样品上方顶空中的密封小瓶内。如图正在分析用过的手枪弹药筒(左)。在萃取过程中,挥发性和半挥发性有机化合物(VOCs和SVOCs)在Twister的吸附阶段被浓缩。这里显示的Twister是聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)版本。在提取期后,取出Twister,置于玻璃衬里中,并通过热解吸-GC / MS分析。 GERSTEL热解吸单元与GC / MS系统(Agilent Technologies)结合使用。为了确定HSSE是否合适用于分析GSR,将不同类型的弹药筒插入半自动手枪中并射击,并将用过的弹药筒置于密封的顶空小瓶中,其中Twister悬浮在样品上方的顶部空间中。该弹药筒中含有基于硝酸纤维素或硝酸纤维素和硝化甘油的混合物的推进剂装药。将HSSE-TD-GC / MS分析的结果与基于55种GSR化合物的参考混合物的分析结果进行比较。分析步骤:将Twister放在待分析的用过的弹药筒上方的顶部空间中,然后密封顶部空间小瓶。然后将分析物在80℃下萃取72小时。将Twister从小瓶中取出并置于单独的密封玻璃管中,准备进行热脱附-GC / MS分析。玻璃管配有单独的运输适配器,多功能进样器(MPS)抓手能够将它们转移到热解吸单元(TDU2)进行程序升温脱附。释放的分析物集中在-80°C的GERSTEL冷进样系统(CIS:PTV型GC进样口),然后使用温度程序加热CIS,并使用1.3 mL / min的氦载气流将分析物以不分流模式转移至GC色谱柱,以进行高灵敏度GC / MS测定。 CIS安装在连接Agilent 5975质量选择检测器(MSD)的气相色谱仪(Agilent GC 7890A)中。使用的柱是AgilentHP-5MS(30m×0.25mm×0.25μm)。 GC柱箱初始温度为40°C,程序进展到最终温度280°C。 GC运行包括冷却和平衡持续46分钟。质量选择性检测(Agilent5975C MSD)在EI模式下以全扫描模式在m / z40至500的范围内进行。提取的离子色谱图(EIC)含有由Gallidabino等人注射的55种物质的标准溶液。使用HSSE-GC / MS,研究人员能够确定GSR中55种化合物中的51种。“缺失的化合物”是热不稳定物质,包括硝化甘油和N-亚硝基苯胺。HSSE的结果他们的研究结果清楚地表明,通过使用HSSE,科学家能够确定和跟踪51个选定的55 GSR目标分析物的浓度降解曲线。事实证明,HSSE比SPME具有更高的重现性,同时提供更好的重现性。在未发现的4种化合物中,热不稳定化合物如硝酸甘油在热解吸过程中分解。接下来他们将进行进一步的研究以优化分析方法参数,目的是增加可以确定的目标分析物的数量。作为他们项目的一部分,Gallidabino等人制作了老化曲线以开发确定大致射击时间的方法,包括确定枪械是否被使用过。这些老化曲线基于来自手枪的废弹药筒上的GSR化合物浓度及其降解曲线。科学家报告说,在老化的样品上使用HSSE,几种GSR化合物已显示出明显的老化特征。此外,使用化合物 - 化合物比率可用于延长检测的时间段。这种方法也有助于使判断更加可靠并减少变量,使该方法对委托案件的法医科学家非常有用。 Gallidabino和他的同事的新方法对于开发基于GSR的新的完整的法医数据技术非常有用,结果也鼓舞人心。文献[1] M. Gallidabino, F. S. Romolo, K. Bylenga and C.Weyermann, Development of a Novel Headspace Sorptive Extraction Method to Studythe Aging of Volatile Compounds in Spent Handgun Cartridges, AnalyticalChemistry 86 (2014) 4471-4478
确定



还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
GERSTEL(哲斯泰)为您提供《子弹中VOC检测方案(其它萃取设备)》,该方案主要用于刑侦中VOC检测,参考标准--,《子弹中VOC检测方案(其它萃取设备)》用到的仪器有GERSTEL 搅拌棒Twister (萃取、固相微萃取)、GERSTEL热脱附单元TDU2 (热解吸,热解析)
推荐专场
固相微萃取仪、固相微萃取装置
更多
相关方案
更多