土壤中氮含量的测定对于有机质的评价和肥料用量的计算具有重要意义。氮含量的测定提供了有关植物生长所需营养元素缺乏或过剩的信息。氮含量是各种农作物在种植及生产过程中的重要指标,也是农业和环境研究中氮循环和氮固定监测的重要指标。
采用传统方法可以进行氮含量的分析,但随着样品量越来越多,以及对运行费用较低的客观要求来看,有必要采用自动化程度高的仪器,用来提高分析速度以及得到良好的重复性。
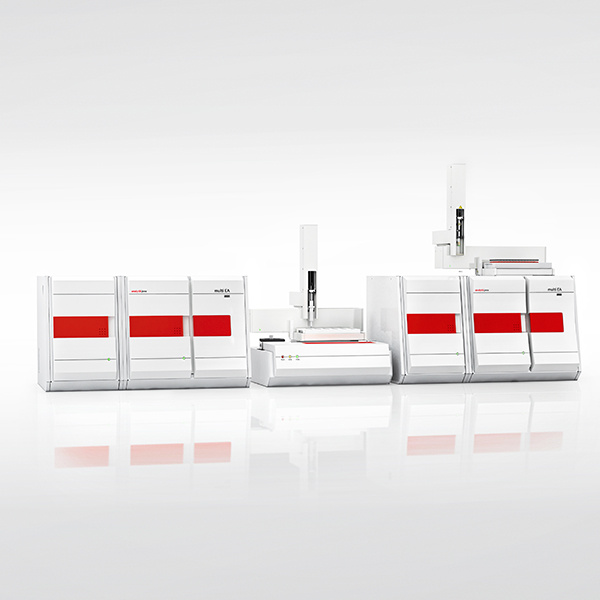
热电FlashSmart元素分析仪完全可以满足现代实验室的这些需要,采用动态+瞬时闪烧技术,其准确度、重现性以及大处理量使得样品分析工作得心应手。
方案详情

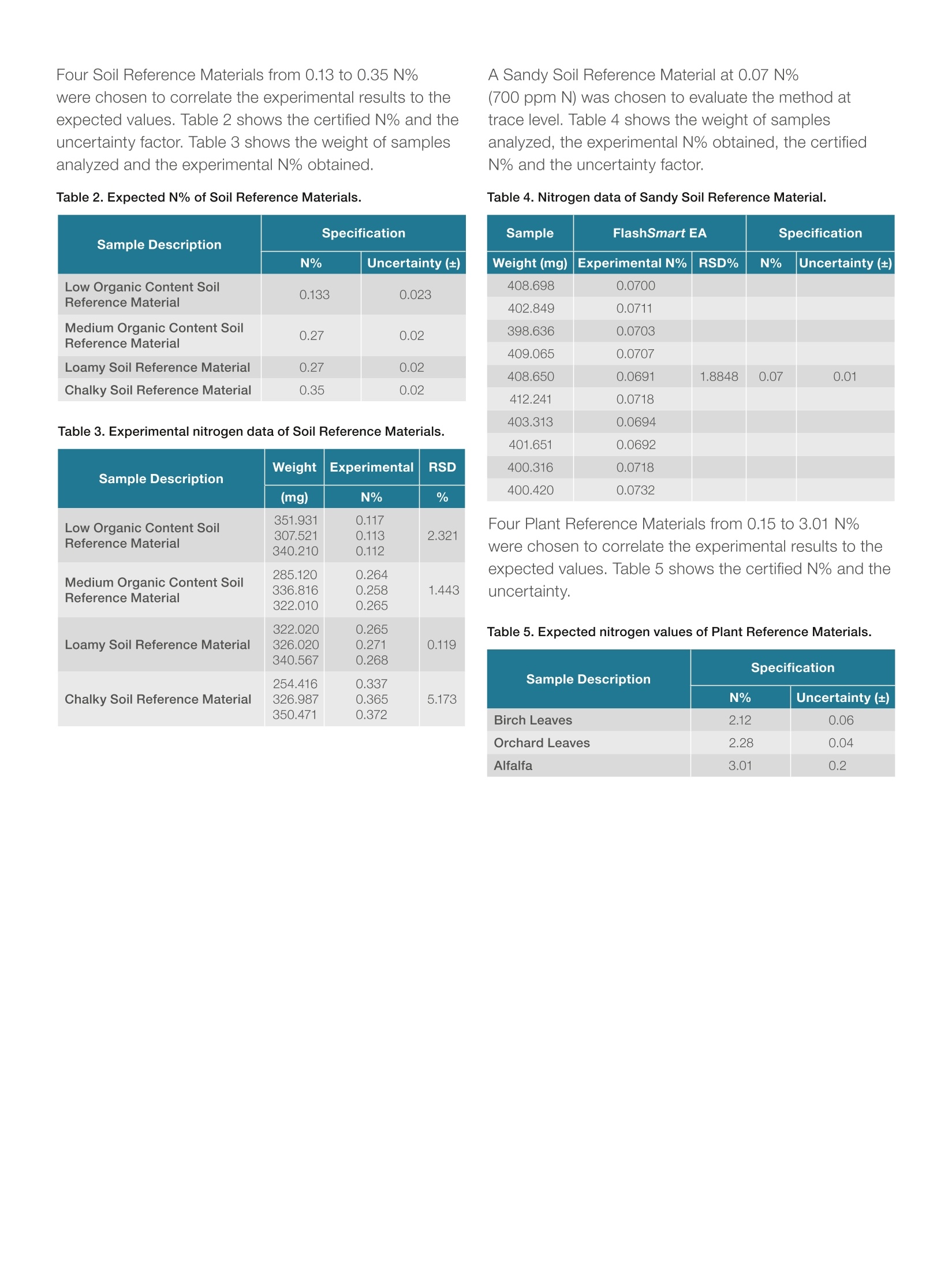
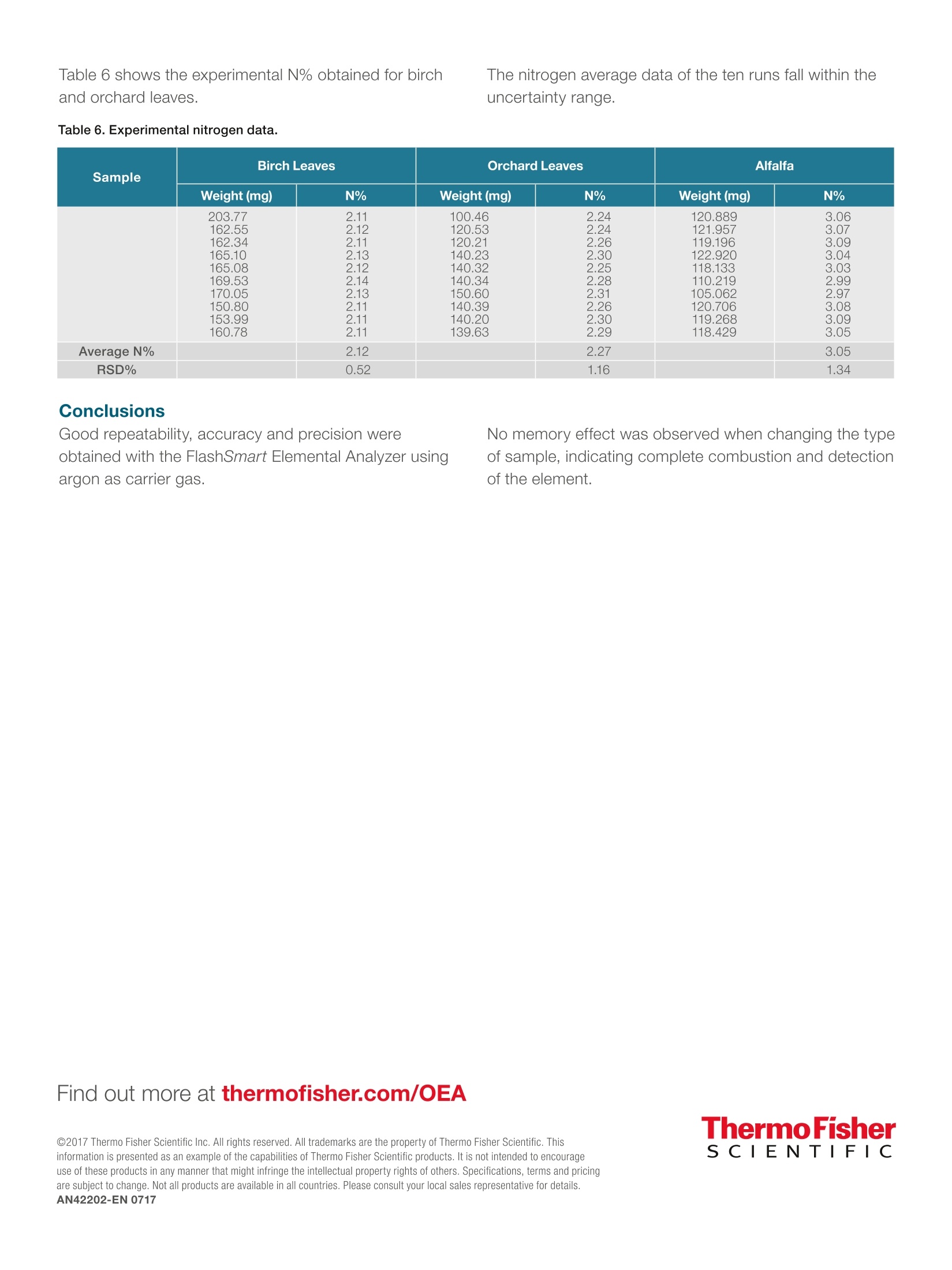
Elemental Analysis: Nitrogen determination in soilsand plants using argon as carrierergas Dr. Liliana Krotz, Walter Galotta,and Dr. Guido Giazzi,OEAThermo Fisher Scientific, Milan, Italy Keywords Argon, Carrier Gas, Combustion, Elemental Analysis, NC, Plants, Soils Goal This application note presentsdata on nitrogen determinationin soil and plant referencematerials with different nitrogenconcentrations to demonstratethe performance of theFlashSmart EA using argon asan alternative carrier gas andshow the reproducibility of theresults obtained. Nitrogen determination in soils is important for the evaluation of theorganic matter and the calculation of the amount of fertilizer needed.The determination of nitrogen content provides information regarding thedeficiency or excess of nutritional elements important for plant growth.Nitrogen content is important for determining the quality of various typesof crops for feeding and processing, as well as for N-cycle and N-fixationmonitoring in agricultural and environmental research. As the demand for improved sample throughput and reduction of operationalcosts is increasing, it is essential to have an automated technique, whichallows fast analysis with excellent reproducibility. The Thermo ScientificFlashSmartElemental Analyzer (Figure 1), copes withmodern laboratory requirements such as accuracy, day to day reproducibilityand high sample throughput. It operates according to the dynamic flashcombustion of the sample and typically uses helium as carrier gas. Considering the need for cost efficiencies and the likelyincrease in helium gas cost, an alternative gas to beused as carrier gas is needed. Argon can be used asalternative to helium in the FlashSmart EA. Figure 1. Thermo Scientific FlashSmart Elemental Analyzer. Methods Samples are weighed in tin containers and introducedinto the combustion reactor via the Thermo ScientificMAS Plus Autosampler with oxygen.After combustion,the resultant gases are carried by an argon flow to asecond reactor filled with copper, then swept throughCO, and H,O traps, a GC column and are finallydetected by a Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD).The analytical configuration as well as the TCD Detectorare the same as those used with helium as the carriergas (see Figure 2). A complete report is automatically generated by theThermo ScientificEagerSmartData Handling Software.The EagerSmart Data Handling Software provides theoption AGO (Argon Gas Option),enabling to modify theargon carrier flow during the run. Analytical Conditions Combustion Furnace Temperature 950°℃ Reduction Furnace Temperature 840°C Oven Temperature 50°C (GC column inside the oven) Argon Carrier Flow 60 ml/min Argon Reference Flow 60 ml/min Oxygen Flow 300 ml/min Sample Delay 10 sec Run Time 10 minutes Note: The oxygen amount necessary for the complete combustion of samples is calculatedautomatically by the dedicated feature (0xyTune Function) of the EagerSmart Data HandlingSoftware: Results To evaluate the performance of the system for soils andplants analysis, relative reference materials with differentnitrogen concentrations were chosen. Instrumentcalibration was performed with approximately 50 - 70 mgof aspartic acid (10.52 N%) standard, using K factor asthe calibration method. Table 1 shows the nitrogen data obtained of the analysisof Thermo Scientific Soil Reference Material. The samplewas weighed at 250-350 mg. The certified N% is 0.21and the accepted range according to the technicalspecification is 0.19 - 0.23 N%. The average of the12 runs is 0.19 N% with an RSD% of 2.55. Table 1. Nitrogen data of Soil Reference Material. Weight (mg) N% 250.224 0.20 260.746 0.20 270.494 0.19 300.714 0.19 310.893 0.19 320.423 0.19 270.794 0.19 280.101 0.19 290.134 0.19 300.844 0.19 320.242 0.20 350.896 0.20 Four Soil Reference Materials from 0.13 to 0.35 N%were chosen to correlate the experimental results to theexpected values. Table 2 shows the certified N% and theuncertainty factor. Table 3 shows the weight of samplesanalyzed and the experimental N% obtained Table 2. Expected N% of Soil Reference Materials. Sample Description Specification N% Uncertainty(±) Low Organic Content Soil Reference Material 0.133 0.023 Medium Organic Content SoilReference Material 0.27 0.02 Loamy Soil Reference Material 0.27 0.02 Chalky Soil Reference Material 0.35 0.02 Table 3. Experimental nitrogen data of Soil Reference Materials. Sample Description Weight Experimental RSD (mg) N% % Low Organic Content SoilReference Material 351.931 0.117 2.321 307.521340.210 0.1130.112 Medium Organic Content SoilReference Material 285.120336.816322.010 0.2640.2580.265 1.443 322.020 326.020340.567 0.2650.2710.268 0.119 Loamy Soil Reference Material Chalky Soil Reference Material 254.416326.987350.471 0.337 5.173 0.3650.372 .A Sandy Soil Reference Material at 0.07 N%(700 ppm N) was chosen to evaluate the method attrace level. Table 4 shows the weight of samplesanalyzed, the experimental N% obtained, the certifiedN% and the uncertainty factor. Table 4. Nitrogen data of Sandy Soil Reference Material. Sample FlashSmart EA Specification Weight (mg) Experimental N% RSD% N% Uncertainty (±) 408.698 0.0700 402.849 0.0711 398.636 0.0703 409.065 0.0707 408.650 0.0691 1.8848 0.07 0.01 412.241 0.0718 403.313 0.0694 401.651 0.0692 400.316 0.0718 400.420 0.0732 Four Plant Reference Materials from 0.15 to 3.01 N%were chosen to correlate the experimental results to theexpected values. Table 5 shows the certified N% and theuncertainty. Table 5. Expected nitrogen values of Plant Reference Materials. Sample Description Specification N% Uncertainty(±) Birch Leaves 2.12 0.06 Orchard Leaves 2.28 0.04 Alfalfa 3.01 0.2 Table 6 shows the experimental N% obtained for birch.and orchard leaves. Table 6. Experimental nitrogen data. The nitrogen average data of the ten runs fall within theuncertainty range. Sample Birch Leaves Orchard Leaves Alfalfa Weight (mg) N% Weight (mg) N% Weight (mg) N% 203.77 2.11 100.46 2.24 120.889 3.06 162.55 2.12 120.53 2.24 121.957 3.07 162.34 2.11 120.21 2.26 119.196 3.09 165.10 2.13 140.23 2.30 122.920 3.04 165.08 2.12 140.32 2.25 118.133 3.03 169.53 2.14 140.34 2.28 110.219 2.99 170.05 2.13 150.60 2.31 105.062 2.97 150.80 2.11 140.39 2.26 120.706 3.08 153.99 2.11 140.20 2.30 119.268 3.09 160.78 2.11 139.63 2.29 118.429 3.05 Average N% 2.12 2.27 3.05 RSD% 0.52 1.16 1.34 Conclusions Good repeatability, accuracy and precision wereobtained with the FlashSmart Elemental Analyzer usingargon as carrier gas No memory effect was observed when changing the typeof sample, indicating complete combustion and detectionof the element. Find out more at thermofisher.com/OEA ◎2017 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. All trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific. Thisinformation is presented as an example of the capabilities of Thermo Fisher Scientific products. It is not intended to encourageuse of these products in any manner that might infringe the intellectual property rights of others. Specifications, terms and pricingare subject to change. Not all products are available in all countries. Please consult your local sales representative for details.AN42202-EN 0717 土壤中氮含量的测定对于有机质的评价和肥料用量的计算具有重要意义。氮含量的测定提供了有关植物生长所需营养元素缺乏或过剩的信息。氮含量是各种农作物在种植及生产过程中的重要指标,也是农业和环境研究中氮循环和氮固定监测的重要指标。采用传统方法可以进行氮含量的分析,但随着样品量越来越多,以及对运行费用较低的客观要求来看,有必要采用自动化程度高的仪器,用来提高分析速度以及得到良好的重复性。热电FlashSmart元素分析仪完全可以满足现代实验室的这些需要,采用动态+瞬时闪烧技术,其准确度、重现性以及大处理量使得样品分析工作得心应手。
确定


还剩2页未读,是否继续阅读?
大昌华嘉科学仪器为您提供《土壤和植物中氮元素含量检测方案(有机元素分析)》,该方案主要用于土壤中营养盐检测,参考标准--,《土壤和植物中氮元素含量检测方案(有机元素分析)》用到的仪器有有机元素分析仪(碳氢氧氮硫)、元素分析仪(CN/CNS)、全自动元素分析仪(CHN)、总氮分析仪(杜马斯燃烧法)、杜马斯蛋白质分析仪(定氮仪)
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多