单一的微流控毛细管电泳芯片与质谱联用系统,实现小分子和完整的蛋白质生物标记物的分析。采用ZipChip微流控毛细管电泳芯片与质谱联用技术,对新生儿筛查过程中常见的小分子和蛋白质生物标志物进行了有效分析。
方案详情

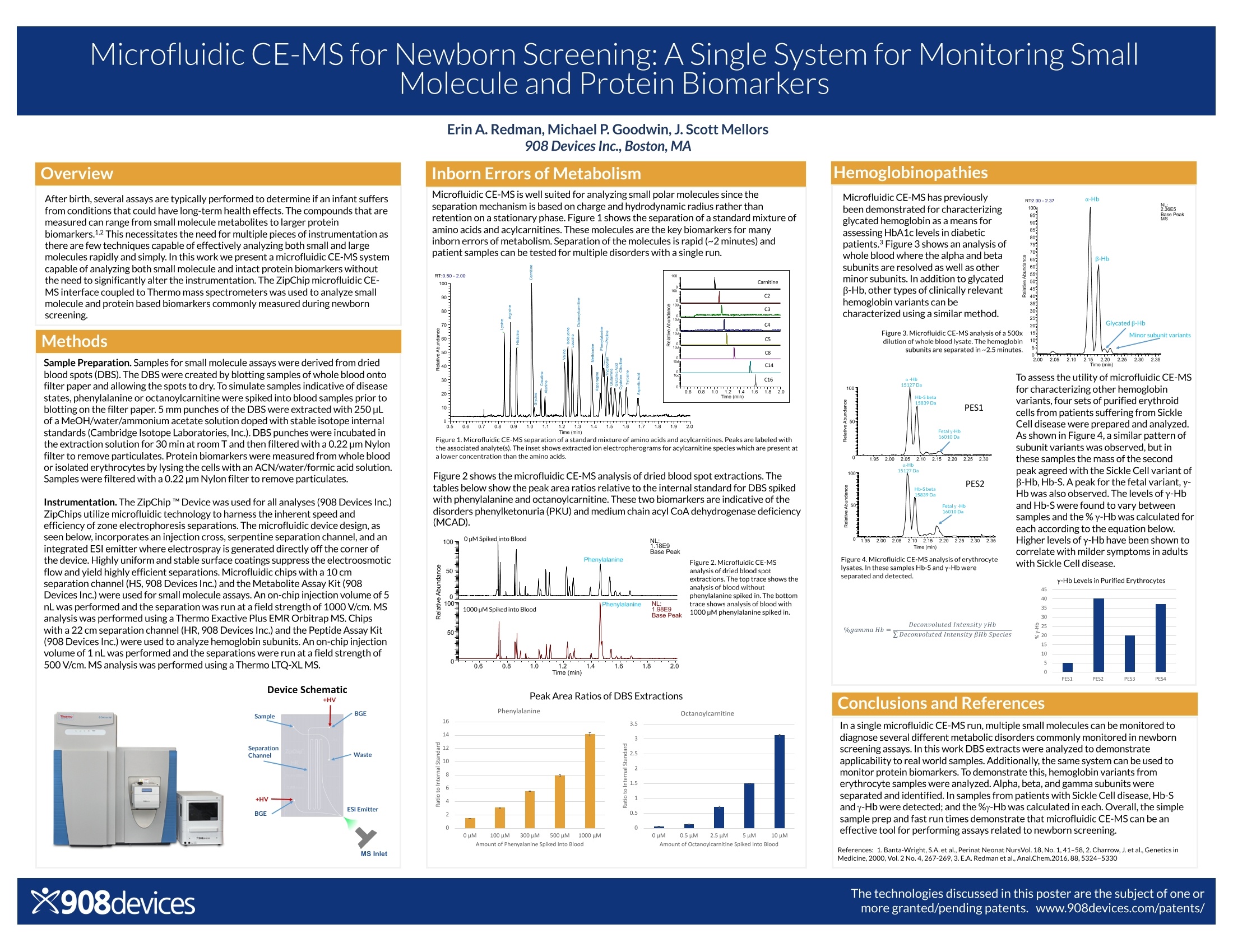
Microfluidic CE-MS for Newborn Screening: A Single System for Monitoring SmallMolecule and Protein Biomarkers After birth, several assays are typically performed to determine if an infant suffersfrom conditions that could have long-term health effects. The compounds that aremeasured can range from small molecule metabolites to larger proteinbiomarkers.1.2 This necessitates the need for multiple pieces of instrumentation asthere are few techniques capable of effectively analyzing both small and largemolecules rapidly and simply. In this work we present a microfluidic CE-MS systemcapable of analyzing both small molecule and intact protein biomarkers withoutthe need to significantly alter the instrumentation.The ZipChip microfluidic CE-MS interface coupled to Thermo mass spectrometers was used to analyze smallmolecule and protein based biomarkers commonly measured during newbornscreening. Methods Sample Preparation. Samples for small molecule assays were derived from driedblood spots (DBS). The DBS were created by blotting samples of whole blood ontofilter paper and allowing the spots to dry. To simulate samples indicative of diseasestates,phenylalanine or octanoylcarnitine were spiked into blood samples prior toblotting on the filter paper. 5 mm punches of the DBS were extracted with 250pLof a MeOH/water/ammonium acetate solution doped with stable isotope internalstandards (Cambridge Isotope Laboratories,Inc.).DBS punches were incubatedinthe extraction solution for 30 min at room T and then filtered with a 0.22 pm Nylonfilter to remove particulates.Protein biomarkers were measured from whole bloodor isolated erythrocytes by lysing the cells with an ACN/water/formic acid solution.Samples were filtered with a 0.22pm Nylon filter to remove particulates. Instrumentation. The ZipChip M Device was used for all analyses (908 Devices Inc.) ZipChips utilize microfluidic technology to harness the inherent speed andefficiency of zone electrophoresis separations. The microfluidic device design,asseen below, incorporates an injection cross, serpentine separation channel, and anintegrated ESl emitter where electrospray is generated directly off the corner ofthe device. Highly uniform and stable surface coatings suppress the electroosmoticflow and yield highly efficient separations. Microfluidic chips with a 10 cmseparation channel (HS, 908 Devices Inc.) and the Metabolite Assay Kit (908Devices Inc.) were used for small molecule assays. An on-chip injection volume of 5nL was performed and the separation was run at a field strength of 1000 V/cm.MSanalysis was performed using a Thermo Exactive Plus EMR Orbitrap MS. Chipswith a 22 cm separation channel (HR, 908 Devices Inc.) and the Peptide Assay Kit(908 Devices Inc.) were used to analyze hemoglobin subunits. An on-chipinjectionvolume of 1 nL was performed and the separations were run at a field strength of500 V/cm.MS analysis was performed using a Thermo LTQ-XLMS. Device Schematic Inborn Errors of Metabolism Microfluidic CE-MS is well suited for analyzing small polar molecules since theseparation mechanism is based on charge and hydrodynamic radius rather thanretention on a stationary phase.Figure 1 shows the separation of a standard mixture ofamino acids and acylcarnitines. These molecules are the key biomarkers for manyinborn errors of metabolism. Separation of the molecules is rapid (~2 minutes) and patient samples can be tested for multiple disorders with a singlerun. Figure 1.Microfluidic CE-MS separation of a standard mixture of amino acids and acylcarnitines. Peaks are labeled withthe associated analyte(s). The inset shows extracted ion electropherograms for acylcarnitine species which are present ata lower concentration than the amino acids. Figure 2 shows the microfluidic CE-MS analysis of dried blood spot extractions. Thetables below show the peak area ratios relative to the internal standard for DBS spikedwith phenylalanine and octanoylcarnitine. These two biomarkers are indicative of thedisorders phenylketonuria (PKU) and medium chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency(MCAD). Figure 2. Microfluidic CE-MS analysis of dried blood spot extractions. The top trace shows the analysis of blood without phenylalanine spiked in. The bottom trace shows analysis of blood with 1000 pM phenylalanine spiked in. Peak Area Ratios of DBS Extractions Microfluidic CE-MS has previouslybeen demonstrated for characterizingglycated hemoglobin as a means forassessing HbA1c levels in diabeticpatients.Figure 3 shows an analysis ofwhole blood where the alpha and betasubunits are resolved as well as otherminor subunits. In addition to glycatedβ-Hb, other types of clinically relevanthemoglobin variants can becharacterized using a similar method. Figure 3.Microfluidic CE-MS analysis of a 500xdilution of whole blood lysate. The hemoglobinsubunits are separated in~2.5 minutes 2.002.052.10 2.202.252.302.35ne (min) To assess the utility of microfluidic CE-MSfor characterizing other hemoglobinvariants, four sets of purified erythroidcells from patients suffering from SickleCell disease were prepared and analyzed.As shown in Figure 4, a similar pattern ofsubunit variants was observed, but inthese samples the mass of the secondpeak agreed with the Sickle Cell variant ofB-Hb, Hb-S. A peak for the fetal variant,y-Hb was alsoobserved. The levels of y-Hband Hb-S were found to vary betweensamples and the % y-Hb was calculated foreach according to the equation below.Higher levels of y-Hb have been shown tocorrelate with milder symptoms in adultswith Sickle Cell disease. Figure 4. Microfluidic CE-MS analysis of erythrocytelysates. In these samples Hb-S and y-Hb wereseparated and detected. Deconvoluted Intensity yHb%gamma Hb:2Deconvoluted Intensity BHb Species Conclusions and References In a single microfluidic CE-MS run, multiple small molecules can be monitored todiagnose several different metabolic disorders commonly monitored in newbornscreening assays.In this work DBS extracts were analyzed to demonstrateapplicability to real world samples. Additionally, the same system can be used tomonitor protein biomarkers. To demonstrate this, hemoglobin variants fromerythrocyte samples were analyzed.Alpha, beta, and gamma subunits wereseparated and identified. In samples from patients with Sickle Cell disease,Hb-Sand y-Hb were detected; and the %y-Hb was calculated in each. Overall,the simplesample prep and fast run times demonstrate that microfluidic CE-MS canbe aneffective tool for performing assays related to newborn screening. References: 1.Banta-Wright, S.A. et al., Perinat Neonat NursVol. 18,No.1,41-58,2. Charrow,J.et al.,Genetics inMedicine,2000,Vol.2 No.4,267-269,3.E.A. Redmanet al., Anal.Chem.2016,88,5324-5330 新生儿出生后,通常会进行若干项检测,以确定婴儿是否患有可能对健康产生长期影响的疾病。所测量的化合物可以从小分子代谢物到较大的蛋白质生物标记物。满足这些测试需要多个仪器,因为很少有技术能够快速和简单有效的实现对小分子和大分子的分析。 在本方案中,我们提出了一个微流控毛细管电泳芯片与质谱联用系统,可以兼具分析小分子和完整的蛋白质生物标记物的性能,而不需要对现有仪器进行大的改动。采用ZipChip微流控毛细管电泳芯片与质谱联用技术,对新生儿筛查过程中常见的小分子和蛋白质生物标志物进行了分析。 本方案中详细描述了实验测试的方法(主要是样品的制备)、实验装置以及初步的实验结果。 实验结果表明,在单次的微流控毛细管电泳-质谱联用分析过程中,可以实现多个小分子的监测,从而诊断新生儿筛查中常见的几种不同的代谢紊乱。本文对DBS提取液进行了分析,验证了DBS提取物在实际样品中的适用性。此外,同样的系统可以用来监测蛋白质生物标记物。为了证明这一点,从红细胞样本中分析了血红蛋白变异体。α、β 和 γ 亚基单元被有效分离和识别。在Sickle细胞病患者标本中,检测到Hb-S和g-Hb,并计算g-Hb的百分比。总之,简单的样本准备和快速运行时间表明,ZipChip微流控毛细管电泳芯片与质谱联用技术可以作为执行与新生儿筛查相关的检测的有效工具。
确定
还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
908 Devices为您提供《新生儿血样 (dried blood spots,DBS)中氨基酸,蛋白标记物检测方案(自动进样器)》,该方案主要用于全血/血清/血浆中氨基酸,蛋白标记物检测,参考标准--,《新生儿血样 (dried blood spots,DBS)中氨基酸,蛋白标记物检测方案(自动进样器)》用到的仪器有908Devices ZipChip 自动进样器、908Devices ZipChip AS 毛细管电泳质谱联用系统 (自动进样款)、ZipChip 肽段分析试剂盒
推荐专场
相关方案
更多