方案详情
文
随着生活水平的提高,食品质量和安全问题越来越受到人们的关注。蜂蜜是一种广受人民欢迎的天然保健食品,在蜜蜂饲养中,为了降低蜜蜂死亡率,提高蜂蜜产量,多种药物从而被使用,其中喹诺酮和大环内酯类药物就是经常被使用的两种。在欧盟,已经建立了对蜂蜜中兽药残留“零容忍”的检测标准。要做到“零容忍”检测标准,必须使检测限尽可能的降低。目前使用串联质谱的方式已经可以使检测线降低到ppb 范围以下。而为了保持蜂蜜中兽残分析的
灵敏性,必须除去其中的糖类,以避免污染。
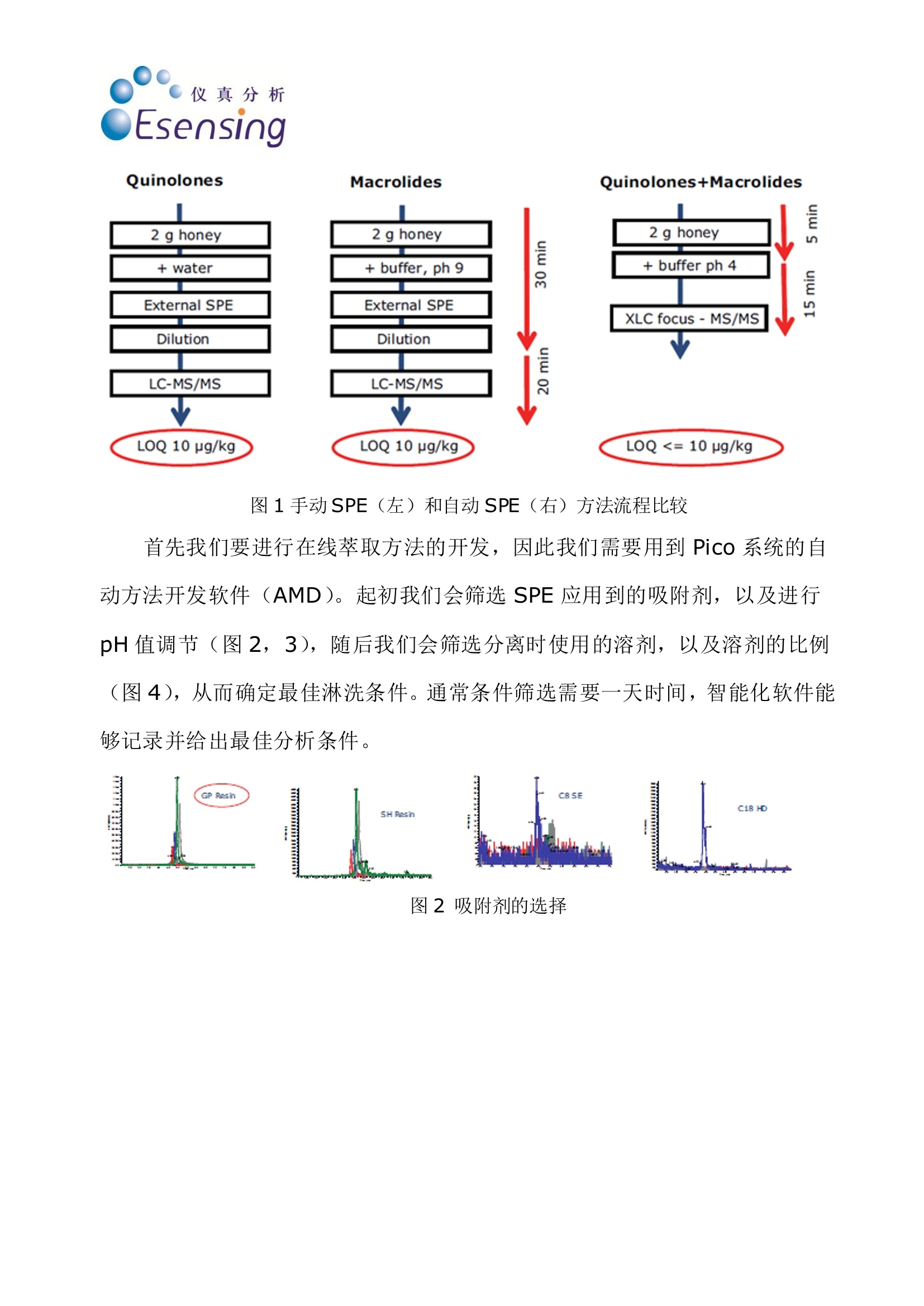
传统蜂蜜中兽残的分析方法主要是将2g 蜂蜜加入水中,通过SPE 净化,稀释样品后进入LC-MS/MS 方法进行分析,检测限在10μg/kg,而通过全自动在线SPE 方法串联LC-MS/MS 法进行检测,不仅可以省去与SPE 相关的所有人工步骤,节约时间,还能将检测限降至10μg/kg 以下,同时喹诺酮和大环内酯类药物可以在同一批次检出。通过全自动在线SPE 方法,只要将蜂蜜加入SPE 柱即可,后续即能自动完成
方案详情

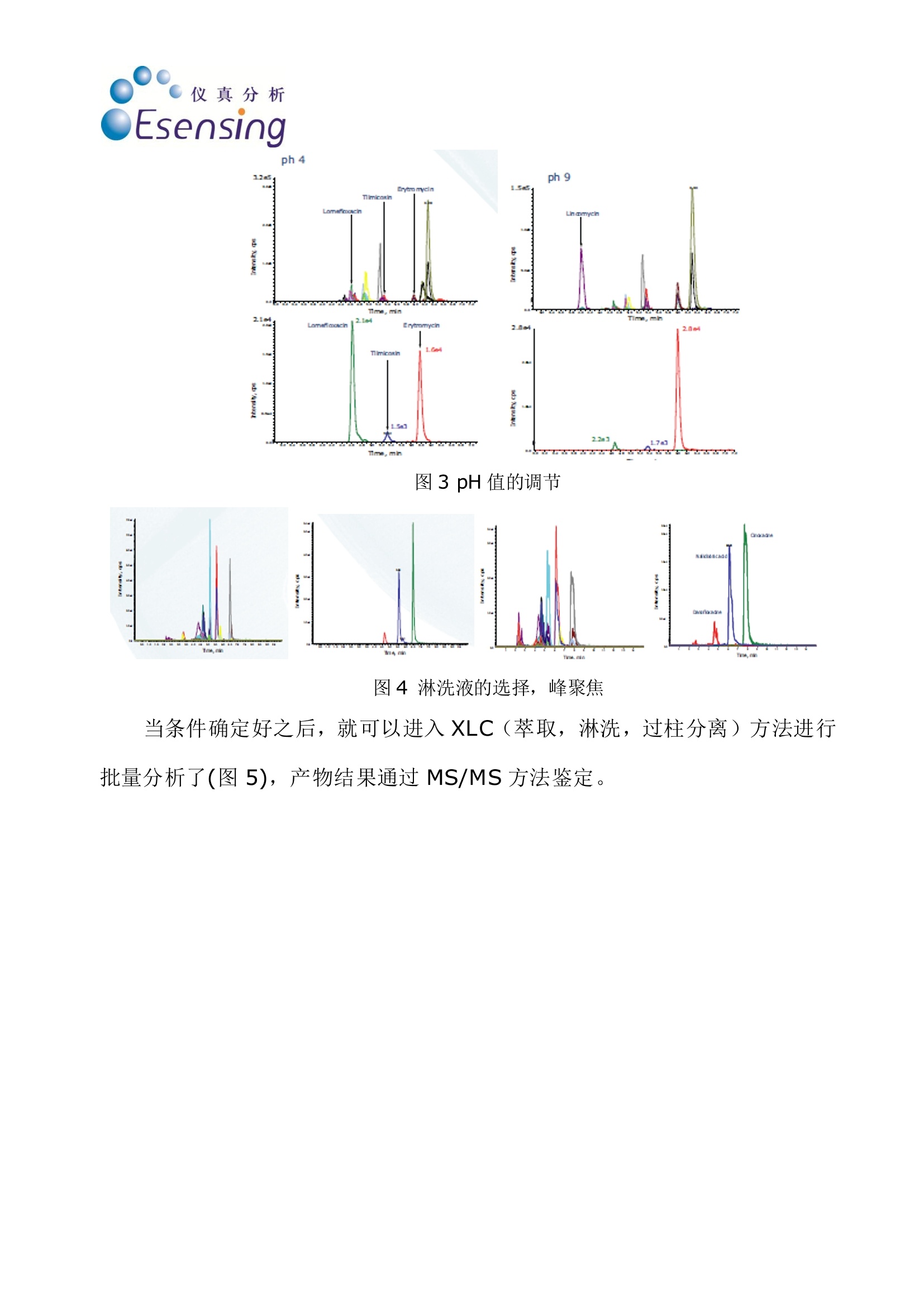
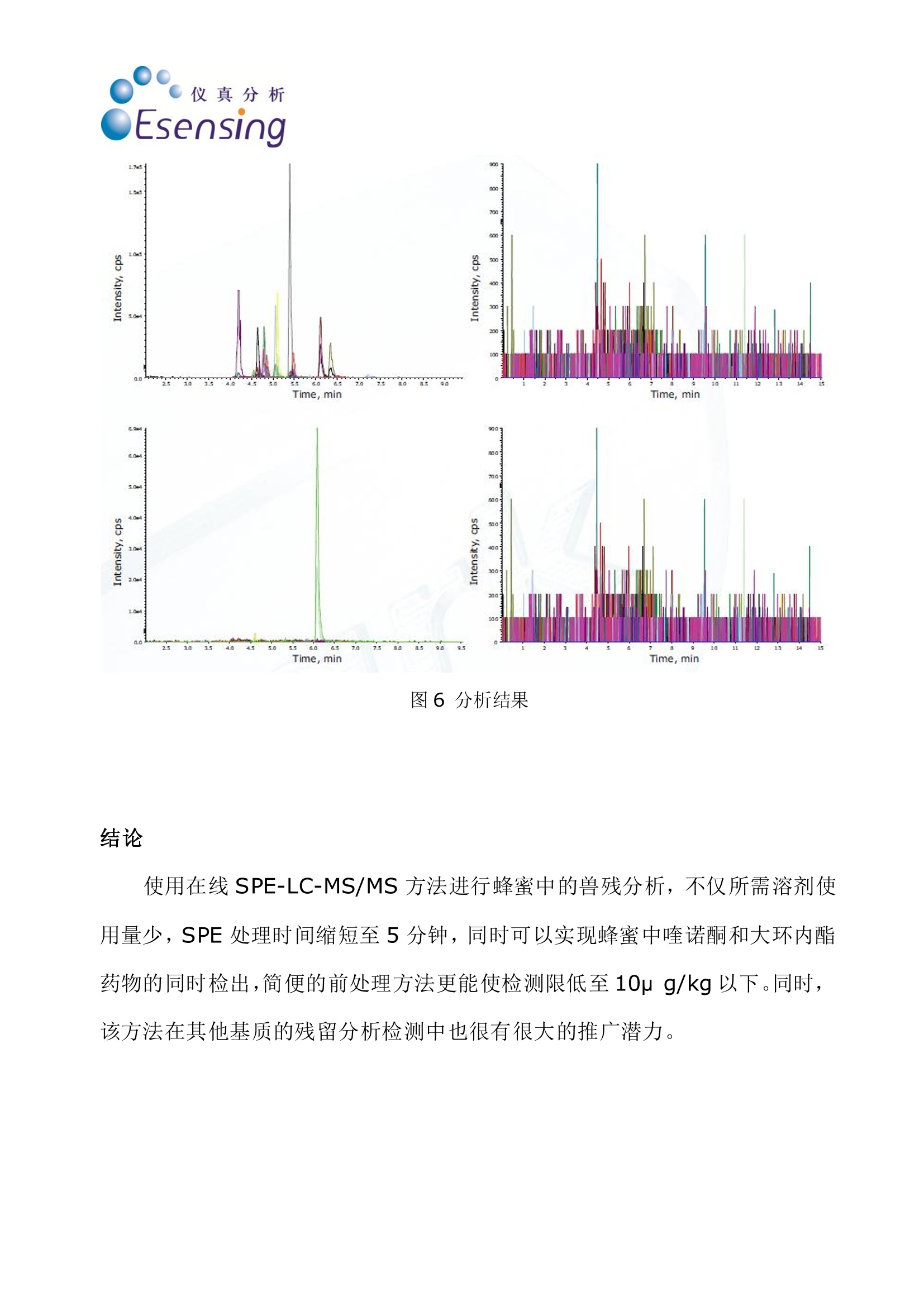
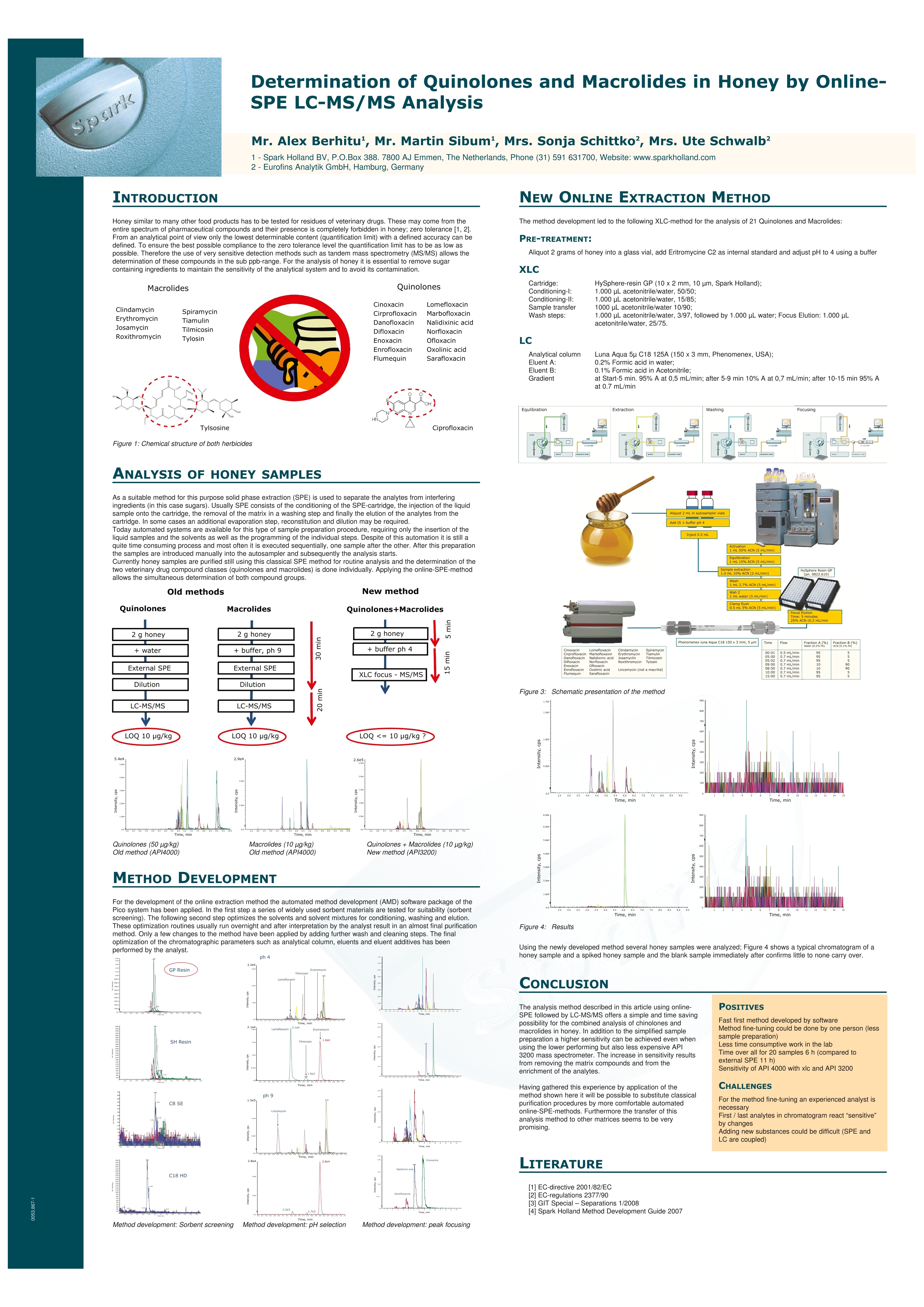
仪真分析Esensing 仪真分析Esensing 蜂蜜中的喹诺酮和大环内酯类抗生素的检测 背景: 随着生活水平的提高,食品质量和安全问题越来越受到人们的关注。蜂蜜是一种广受人民欢迎的天然保健食品,在蜜蜂饲养中,为了降低蜜蜂死亡率,提高蜂蜜产量,多种药物从而被使用,其中喹诺酮和大环内酯类药物就是经常被使用的两种。在欧盟,已经建立了对蜂蜜中兽药残留“零容忍”的检测标准。要做到“零容忍”检测标准,必须使检测限尽可能的降低。目前使用串联质谱的方式已经可以使检测线降低到 ppb 范围以下。而为了保持蜂蜜中兽残分析的灵敏性,必须除去其中的糖类,,以以避免污染。 一般蜂蜜的兽残分析都需要将蜂蜜通过 SPE 进行前处理,传统手统的 SPE方法包括:SPE填料的筛选,将蜂蜜加入 SPE 柱中并选择合适的淋洗剂将基质去除并洗脱分析产物,有些情况下,还需要旋蒸和重新定容。 实验过程: 传统蜂蜜中兽残的分析方法主要是将2g蜂蜜加入水中,通过 SPE 净净,稀释样品后进入 LC-MS/MS 方法进行分析,检测限在10ug/kg,而通过全自动在线 SPE 方法串联 LC-MS/MS 法进行检测,不仅可以省去与 SPE 相关的所有人工步骤,节约时间,还能将检测限降至10pg/kg 以下,同时喹诺酮和大环内酯类药物可以在同一批次检出。通过全自动在线 SPE 方法,只要将蜂蜜加入SPE 柱即可,后续即能自动完成(图1)。 仪真分析 Esensing 图1手动SPE(左)和自动SPE (右)方法流程比较 首先我们要进行行线萃取方法的开发,因此我们需要用到 Pico 系统的自动方法开发软件(AMD)。起初我们会筛选 SPE 应用到的吸附剂,以及进行pH值调节(图2,3),随后我们会筛选分离时使用的溶剂,以及溶剂的比例(图4),从而确定最佳淋洗条件。通常条件筛选需要一天时间,智能化软件能够记录并给出最佳分析条件。 图2吸附剂的选择 ph 4 图3 pH值的调节 图4淋洗液的选择,峰聚焦 当条件确定好之后,就可以进入XLC(萃取,淋洗,过柱分离)方法进行批量分析了(图5),产物结果通过 MS/MS 方法鉴定。 图5大批量分析流程图 Time, min Time, min 图6分析结果 结论 使用在线SPE-LC-MS/MS 方法进行蜂蜜中的兽残分析,不仅所需溶剂使用量少, SPE 处理时间缩短至5分钟,同时可以实现蜂蜜中喹诺酮和大环内酯药物的同时检出,简便的前处理方法更能更检测限低至10p g/kg以下。同时,该方法在其他基质的残留分析检测中也很有很大的推广潜力。 Online-SPE-LC-MS/MS Determination of 22 Quinolones and Macrolides in Honey Honey similar to many other food stuffs has to be tested for residues ofveterinary drugs. These may come from the entire spectrum of pharmaceuticalcompounds and their presence is completely forbidden in honey (zero toler-ance limit [1, 2]). From an analytical point of view only the lowest determin-able content (limit of quantification, LOQ) with a defined accuracy can bedefined. To ensure the best possible compliance to the zero tolerance level thequantification limit has to be as low as possible. Therefore the use of very sen-sitive detection methods such as tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) allowsthe determination of these compounds in the sub ppb-range. For the analysisof honey it is essential to remove sugar containing ingredients to maintainthe sensitivity of the analytical system and to avoid its contamination. As a suitable method for this purpose solidphase extraction (SPE) is used to separate theanalytes from interfering ingredients (in thiscase sugars). Usually SPE consists of the condi-tioning of the SPE-cartridge, the injection of theliquid sample onto the cartridge, the removal ofthe matrix in a washing step and finally the elu-tion of the analytes from the cartridqe. In somecases an additional evaporation step, reconstitu-tion and dilution may be required. Today automated systems are available forthis type of sample preparation procedure, re-quiring only the insertion of the liquid samplesand the solvents as well as the programming ofthe individual steps. Despite of this automationit is still a quite time consuming process andmost often it is executed sequentially, one sam-ple after the other. After this preparation thesamples are placed manually into the autosam-pler and subsequently the analysis starts. Thisprocedure is currently used in routine. The method described here uses online-SPE di-rectly automatically executed prior to analysis.The samples are placed in the autosampler andthe XLC-program (XLC=eXtraction Liquid Chro-matography) is selected. It consists of two parts:the extraction that finally elutes the analytesfrom the cartridge onto the analytical column ofthe directly following LC-MS/MS (liquid chroma-tography coupled with MS/MS detection). For the analyses described here a mass spec-trometer (API 3200, Applied Biosystems, USA) ishyphenated with the online-SPE unit SymbiosisPico (Spark Holland, The Netherlands). The on-line-SPE-LC-system consists of an autosampler,high pressure LC gradient pumps, a high pres-sure dispenser (HPD), valves and the XLC-unitfor the solid phase extraction. Figure 1 demon-strates the principle of online-SPE. In the firststep a gripper inserts a cartridge into the left Sonja Schittko, project leader and Ute Schwalb,project assistant; LC-MS Analytics at Eurofins /WEJ. clamp of the XLC-unit. That’s where the condi-tioning of the cartridge, the sample introductionand the wash step to remove the matrix com-pounds are executed. Afterwards the grippertransfers the SPE-cartridge to the right clamp ofthe XLC-unit. There the elution directly onto theanalytical column and the chromatographic runstake place. This may be done by two differentmeans: either by elution using the LC-gradientor by elution using the high pressure dispenser(HPD) with the so called "focusing". Focusing isa concentration step of the analytes at the topof the analytical column in a small spot. Themethod described here uses the focusing toachieve an enrichment and a better chromato-graphic behavior of the very different analytes(22 quinolones and macrolides, see fig. 2) on theanalytical column. One cycle consisting of SPE-purification andLC-MS/MS analysis has a runtime of 20 minutesin total. Immediately after the end of the extrac- tion of sample #1 (in the rightclamp) and the cleaning of theXLC-unit the conditioning of thenext cartridge and injection ofsample #2 starts (in the left clamp)Applying this overlapping proce-dure only six hours are required forthe total analysis of 20 samplesThis results into a gain of five hoursversus the classical (offline) SPEpurification. Method For the development of the extrac-. tion method the automated meth-od development (AMD) softwarepackage of the Pico system hasbeen applied. In the first step a se-ries of widely used sorbent materi-als are tested for suitability (sor-bent screening). The followingsecond step optimizes the solventsand solvent mixtures for condition-ing, washing and elution. Theseoptimization routines usually runovernight and after interpretationby the analyst result in an almostfinal purification method. Only afew changes to the method havebeen applied by adding furtherwash and cleaning steps. The finaloptimization of the chromato-graphic parameters such as analyt-ical column,eluents and eluent ad-ditives has been performed by theanalyst. The automated methoddevelopment led to the followingXLC-method for the analysis of 22quinolones and macrolides: XLC: Cartridge: HySphere-resinGP (10 x 2 mm, 10 pm, 13,74 mg,Spark Holland); Conditioning:1.000 pL acetonitrile (ACN)/water,15/85; sample injection (2 g honeyin 2 mL buffer at pH 4) 500 pL;wash steps: 1.000 pL water/ACN,97/3, followed by 1.000 pL water;Elution: 1.000 pL ACN/water, 25/75with 0,1% formic acid (FA). LC: Analytical column Aqua 5pC18 125A (150x3 mm, Phenome-nex, USA); Eluent A: ACN (0,1%FA); Eluent B: water (0,2% FA);Start: 95 % A, 0,5 mL/min, after 2min 0,7 mL/min, 9 min 10% A, 10to 15 min 10% A, 10 to 15 min95%A. Analysis of Honey Samples Currently honey samples are puri-fied still using the classical SPEmethod for routine analysis and Fig. 1: Function of the Pico SystemA: conditioning of the SPE-cartridgeB: Sample applicationC: recycling of the SPE-cartridge,D: Elution and LC-run, sample transfer to the right side Fig. 2: Chemical structure of Ciprofloxacine and Tylosine and the list of ana-lytes that can be determined with online-SPE and LC-MS/MS Fig. 3: Chromatograms of spiked honey samples; Left side: quinolones at 50ug/kg, analyzed by offline-SPE and API 4000 MS; Right side: online-SPE withSymbiosis Pico and API 3200 MS, quinolones and macrolides each at 10 pg/kg the determination of the two vet-erinary drug compound classes(quinolones and macrolides) isdone individually. Applying the on-line-SPE-method allows the simul- taneous determination of bothcompound groups (except for Lin-comycin, requiring a basic buffer). Figure 3 shows the chromato-grams (and several mass traces) of honey samples. Both, the analysisusing an API 4000 MS after offlineSPE (left side of fig. 3) and theanalysis using the API 3200 MScoupled to the Symbiosis Pico on-line-SPE system, are displayed. In figure 3 it becomes obviousthat the samples analyzed with thePico system show larger peakheights. Despite the use of the lesssensitive API 3200 MS the combi-nation with online-SPE-purificationgives a higher sensitivity and a re-duction of the quantification limitdown to 5 pg/kg for the majority ofthe analytes Conclusion The analysis method described inthis article using online-SPE fol-lowed by LC-MS/MS offers a simpleand time saving possibility for thecombined analysis of quinolonesand macrolides in honey. In addi-tion to the simplified sample prep-aration a higher sensitivity can beachieved even when using the low-er performing but also less expen-sive API 3200 mass spectrometer.The increase in sensitivity resultsfrom removing the matrix com-pounds and from the enrichmentof the analytes. Having gathered this experi-ence by application of the methodshown here it will be possible tosubstituteeclassical purificationprocedures by more comfortableautomatedonline-SPE-methods.Furthermore the transfer of thisanalysis method to other matricesseems to be very promising. . References [1] EC-directive 2001/82/EC [2] EC-regulations 2377/90 [3] GIT Special- Separation 1, 8 (2008) Contact: Sonja Schittko eurofins /WEJ Hamburg, Germany Tel.:+49 40 49294 274Fax: +49 40 49294 111sonjaschittko@eurofins.dewww.wej.dewww.eurofins.de Spark Holland B.V.Emmen, The NetherlandsTel.:+31 591 631700Fax: +31 591 645900 solutions@sparkholland.comwww.sparkholland.com Determination of Quinolones and Macrolides in Honey by Online-SPE LC-MS/MS Analysis INTRODUCTION Honey similar to many other food products has to be tested for residues of veterinary drugs. These may come from theentire spectrum of pharmaceutical compounds and their presence is completely forbidden in honey;zero tolerance [1, 2].From an analytical point of view only the lowest determinable content (quantification limit) with a defined accuracy can bedefined. To ensure the best possible compliance to the zero tolerance level the quantification limit has to be as low aspossible. Therefore the use of very sensitive detection methods such as tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) allows thedetermination of these compounds in the sub ppb-range. For the analysis of honey it is essential to remove sugarcontaining ingredients to maintain the sensitivity of the analytical system and to avoid its contamination. Macrolides Quinolones Cinoxacin Lomefloxaciirn Cirprofloxacirin Marbofloxacin Danofloxacin Nalidixinic acic Difloxacin Norfloxacir Enoxacirin Ofloxacin Enrofloxacir Oxolinic acid Flumequin Sarafloxacin Ciprofloxacir Figure 1: Chemical structure of both herbicides ANALYSIS OF HONEY SAMPLES i As a suitable method for this purpose solid phase extraction (SPE) is used to separate the analytes from interferingingredients (in this case sugars). Usually SPE consists of the conditioning of the SPE-cartridge, the injection of the liquidsample onto the cartridge, the removal of the matrix in a washing step and finally the elution of the analytes from thecartridge. In some cases an additional evaporation step, reconstitution and dilution may be required.Today automated systems are available for this type of sample preparation procedure, requiring only the insertion of theliquid samples and the solvents as well as the programming of the individual steps. Despite of this automation it is still aquite time consuming process and most often it is executed sequentially, one sample after the other. After this preparationthe samples are introduced manually into the autosampler and subsequently the analysis starts.Currently honey samples are purified still using this classical SPE method for routine analysis and the determination of thetwo veterinary drug compound classes (quinolones and macrolides) is done individually. Applying the online-SPE-method allows the simultaneous determination of both compound groups.New method Old methods METHOD DEVELOPMENT For the development of the online extraction method the automated method development (AMD) software package of thePico system has been applied. In the first step a series of widely used sorbent materials are tested for suitability (sorbentscreening). The following second step optimizes the solvents and solvent mixtures for conditioning, washing and elution.These optimization routines usually run overnight and after interpretation by the analyst result in an almost final purificationmethod. Only a few changes to the method have been applied by adding further wash and cleaning steps. The finaloptimization of the chromatographic parameters such as analytical column, eluents and eluent additives has been NEW ONLINE EXTRACTION METHOD The method development led to the following XLC-method for the analysis of 21 Quinolones and Macrolides:PRE-TREATMENT: Aliquot 2 grams of honey into a glass vial, add Eritromycine C2 as internal standard and adjust pH to 4 using a buffeXLC Cartridge HySphere-resin GP (10x 2 mm, 10 pm, Spark Holland); cConditioning--l: 1.000 uL acetonitrile/water, 50/50; Conditioning-ll: 1.000 pL acetonitrile/water, 15/85Sample transfe 1000 pL acetonitrile/water 10/900;Wash steps: 1.000 pL acetonitrile/water, 3/97, followed by 1.000 pL water; Focus Elution: 1.000uLafiifacetonitrile/water, 25/75. LC Figure 4: Results Using the newly developed method several honey samples were analyzed; Figure 4 shows a typical chromatogram of ahoney sample and a spiked honey sample and the blank sample immediately after confirms little to none carry over. CONCLUSION The analysis method described in this article using online-SPE followed by LC-MS/MS offers a simple and time savingpossibility for the combined analysis of chinolones andmacrolides in honey. In addition to the simplified samplepreparation a higher sensitivity can be achieved even whenusing the lower performing but also less expensive API3200 mass spectrometer. The increase in sensitivity resultsfrom removing the matrix compounds and from theenrichment of the analytes. POsITIVES Fast first method developed by software Method fine-tuning could be done by one person (less Having gathered this experience by application of themethod shown here it will be possible to substitute classicalpurification procedures by more comfortable automatedonline-SPE-methods. Furthermore the transfer of thisanalysis method to other matrices seems to be very sample preparation)Less time consumptive work in the labTime over all for 20 samples 6 h (compared toexternal SPE 11 h)Sensitivity of API 4000 with xlc and API 3200CHALLENGESFor the method fine-tuning an experienced analyst isnecessaryFirst /last analytes in chromatogram react "sensitive' promising. by changes Adding new substances could be difficult (SPE and LC are coupled) LITERATURE ( [ 1 ] EC- d irectiv e 2001/82 / EC [ 2 ] EC-regulations 2377/90 [ 3 ] GIT S pecial - Separations 1 / 2008 [ 4 ] Spark Hol l and Meth o d D evelopment G u id e 2007 ) G.I.T. Laboratory Journal -/ G.I.T. Laboratory Journal -/ 随着生活水平的提高,食品质量和安全问题越来越受到人们的关注。蜂蜜是一种广受人民欢迎的天然保健食品,在蜜蜂饲养中,为了降低蜜蜂死亡率,提高蜂蜜产量,多种药物从而被使用,其中喹诺酮和大环内酯类药物就是经常被使用的两种。在欧盟,已经建立了对蜂蜜中兽药残留“零容忍”的检测标准。要做到“零容忍”检测标准,必须使检测限尽可能的降低。目前使用串联质谱的方式已经可以使检测线降低到ppb 范围以下。而为了保持蜂蜜中兽残分析的灵敏性,必须除去其中的糖类,以避免污染。传统蜂蜜中兽残的分析方法主要是将2g 蜂蜜加入水中,通过SPE 净化,稀释样品后进入LC-MS/MS 方法进行分析,检测限在10μg/kg,而通过全自动在线SPE 方法串联LC-MS/MS 法进行检测,不仅可以省去与SPE 相关的所有人工步骤,节约时间,还能将检测限降至10μg/kg 以下,同时喹诺酮和大环内酯类药物可以在同一批次检出。通过全自动在线SPE 方法,只要将蜂蜜加入SPE 柱即可,后续即能自动完成
确定




还剩6页未读,是否继续阅读?
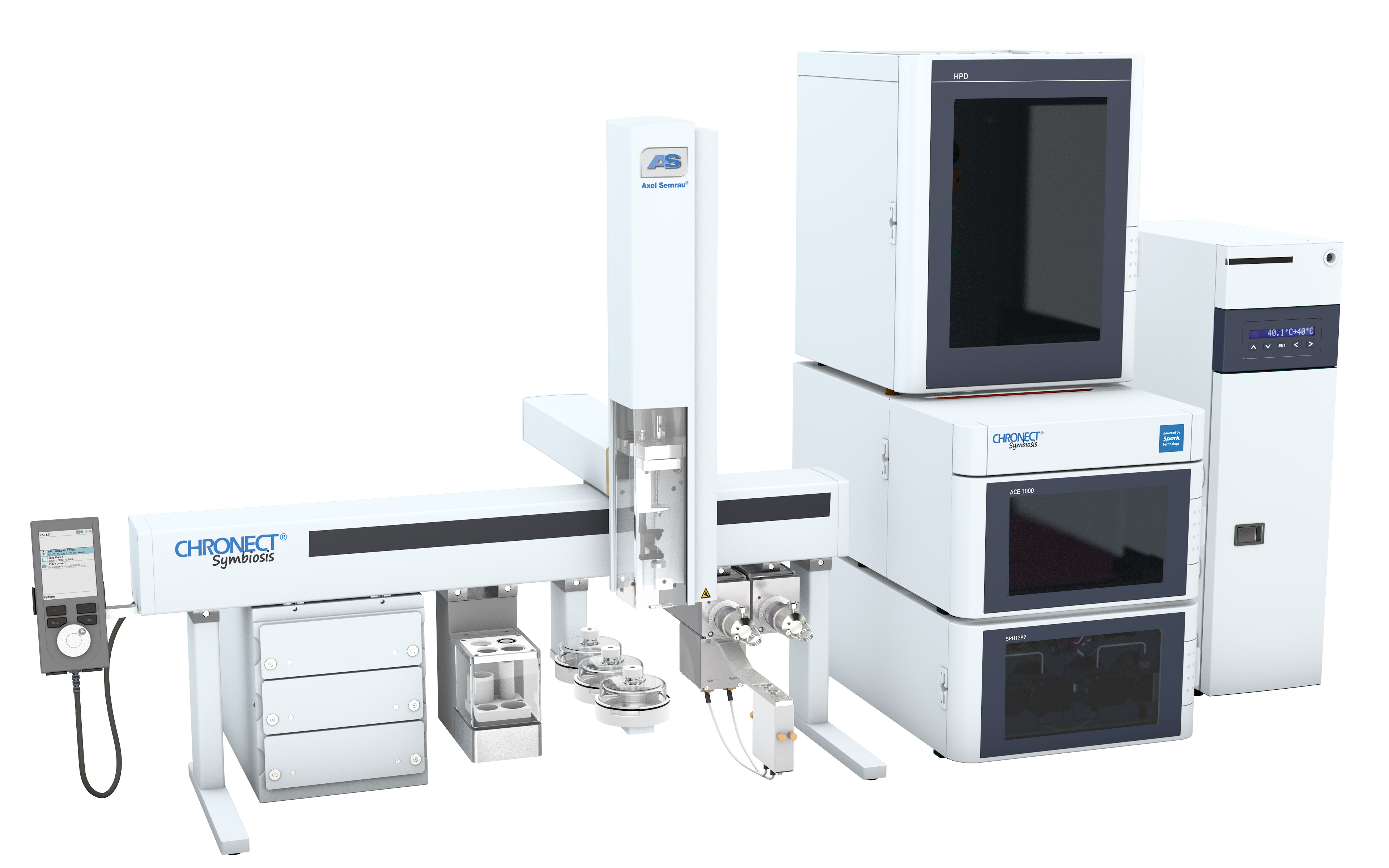
仪真分析仪器有限公司为您提供《蜂蜜中喹诺酮检测方案(液相色谱仪)》,该方案主要用于蜂蜜中兽药残留检测,参考标准--,《蜂蜜中喹诺酮检测方案(液相色谱仪)》用到的仪器有超高压液相在线SPE色谱联用系统CHRONECT Symbiosis
推荐专场
该厂商其他方案
更多















