方案详情
文
The ability to monitor kinetic process occurring on the millisecond timescale has been demonstrated by the simple addition of a stopped flow accessory to the DeltaFlex system. This was operated in the kinetic TCSPC measurement mode and was aided by the use of a high repetition rate excitation source coupled with very low dead time electronics to efficiency collect the data. The data obtained clearly shows the advantage of using the fluorescence lifetime in this case, to obtain obtain kinetics unaffected by sample photobleaching.
方案详情

HORIBAScientificTime-Resolved Fluorescence Application Note TRFA-14 Stopped flow time-resolved fluorescence study of serum albumin-curcuminoid binding Rapid mixing accessories to perform stopped flow measurements have found application in characterisinginteractions and reactions occurring in solution. Reactants are expelled from syringes, mixed and injected into aflowcell. The flow is then stopped with the ensuing reaction / interaction monitored. lf one of the reactants isfluorescent this phenomenon maybe used to follow the interaction. However, intensity based approaches can beinfluenced by fluctuations in the detected signal, eg. caused by photobleaching. This can be avoided by making use ofthe fluorescence lifetime, but data collection times have limited its usage. The recent introduction of very lowdeadtime electronics coupled with high repetition rate excitation sources have now allowed efficient and fastmeasurement of fluorescence decays. Here we monitor the interaction of a fluorescent curcuminoid mixture withserum albumin using a stopped flow accessory on a DeltaFlex system with DeltaDiode excitation at 100MHz. Stopped flow-kinetic TCSPC measurements A typical stopped flow accessory is shown, schematically,inFig. 1. Driving the reactant syringes, either manually ormechanically, expels the reactants with are rapidly mixed andenter the flowcell, replacing the existing liquid volume. Thereis a stop that limits the volume entering the syringe and canbe used to provide an electronic signal to start datacollection, if configured. Fig. 1. Schematic representation of a stopped flow set up Mixing reactions that occur on the millisecond timescale canbe monitored using this technique and, if using fluorescence,this has previously involved an intensity based approach.However, these kinds of measurements can be influenced byfluctuations in excitation source intensity andl samplephotobleaching. The fluorescence lifetime is advantageoussince, as well as its inherent sensitivity, it is an absolutemeasurement (not relative as in the case of steady statefluorescence) and the lifetime is not affected by dilution asthe reactant liquids mix or if the sample photobleaches. Untilrecently instrumentation was not efficient enough to collectsufficient data on these timescales. However, with the introduction of very low deadtime electronics, coupled withhigh repetition rate excitation sources this has now becomepossible. The kinetic TCSPC measurement mode, available in bothDeltaFlex and DeltaPro systems, enables up to 10,000 time-resolved fluorescence decays to be obtained; with eachhistogram seamlessly collected in as little as 1ms. The100MHz capability of the DeltaDiode, is well matched to thevery low dead time of the DeltaHub (10ns). When short datacollection times are employed, this efficiency is required inorder to obtain sufficient data quality. The stopped flowaccessory fits into the standard cuvette (10mm pathlength)holder of the DeltaFlex (Fig. 2) via a modified samplechamber lid. Fig. 2. DeltaFlex with stopped flow accessory entering via a“split"sample chamber lid. Using the DataStation control software, data collection canbe started either using an external TTL signal from thestopped flow accessory (if configured) or manually, within thesoftware, in the kinetic TCSPC measurement mode. Curcuminoid-serum albumin binding The study of the interaction of curcuminoids with proteins isof interest as these compounds are being promoted as havingpotential health benefits. The role of serum albumin in theblood makes it an ideal choice for a model protein with whichto observe this interaction. In the experiment performedhere a solution of curcuminoid in DMSO / buffer was placedin one syringe, with the other reactant syringe filled withserum albumin in buffer. In this solvent mixture thecurcuminoids are weakly fluorescent and exhibit a shortfluorescence lifetime. Upon interaction with the protein boththe fluorescence quantum yield and lifetime increase. Inorder to obtain as many photons as possible a repetition rateof 100MHz was used and a 2ms collection time per decayemployed. The data acquisition was started in DataStation toprovide a "background" and the reactants expelled manually.After analysis using DAS6 software the change in averagelifetime during the course of the experiment was plotted andthis is displayed in Fig. 3. From this plot it is possible todetermine kinetic rates, if required. Fig. 3. Change in average fluorescence lifetime with time. Theexcitation source was a DD-395L operating at 100MHz withdecay histograms collected every 2ms. Stopped flowaccessory operated manually. There can be a problem when using these compounds in asmall volume flowcell with a high intensity (and repetitionrate) excitation source. As they are not very photostable,photobleachingcannbee seen to occur. Althoughhthefluorescence lifetime is unaffected, a measurement of theintensity (obtained from the TCSPC measurement) will exhibit a decrease with time. This is demonstrated in a secondmeasurement (performed under similar conditions), butusing 5ms per decay data collection time for the acquisitionof the 10,000 time-resolved fluorescence decay curves. This isshown in Fig. 4. Fig. 4. Comparison between intensity and lifetime dataobtained from a stopped flow measurement with datacollected every 5ms. From this figure it can be clearly seen that the fluorescenceintensity decreases with time after the initial rise relating tothe curcuminoids binding to the serum albumin. This isattributed to photobleaching. However it is noteworthy thatthe fluorescence lifetime remains stable. The influence ofphotobleaching obviously has implications if the analysis ofthis kinetic process were to be performed using the intensitybased measurement. Summary The ability to monitor kinetic processes occurring on themillisecond timescale has been demonstrated by the simpleaddition of a stopped flow accessory to the DeltaFlex system.This was operated in the kinetic TCSPC measurement modeand was aided by the use of a high repetition rate excitationsource coupled with very low dead time electronics toefficiency collect the data. The data obtained clearly showsthe advantage of using the fluorescence lifetime in this case,to obtain kinetics unaffected by sample photobleaching. www.horiba.com/scientific HORIBAExplore the futureAutomotive Test Systems Process & Environmental Medical lSemiconductor Scientific JOBIN YVONTechnologyinfo.sci@horiba.comUSA: + K:+()hina:+()ORIBAExplore the futureAutomotive Test Systems Process & EnvironmentalMedical Semiconductor Scientific The ability to monitor kinetic process occurring on the millisecond timescale has been demonstrated by the simple addition of a stopped flow accessory to the DeltaFlex system. This was operated in the kinetic TCSPC measurement mode and was aided by the use of a high repetition rate excitation source coupled with very low dead time electronics to efficiency collect the data. The data obtained clearly shows the advantage of using the fluorescence lifetime in this case, to obtain obtain kinetics unaffected by sample photobleaching.
确定

还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
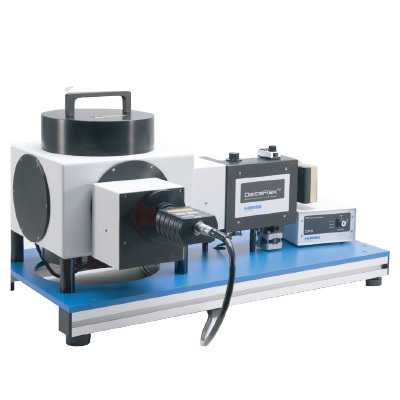
HORIBA(中国)为您提供《姜黄素,血清白蛋白中监控动力学过程(荧光研究)检测方案(分子荧光光谱)》,该方案主要用于其他中监控动力学过程(荧光研究)检测,参考标准--,《姜黄素,血清白蛋白中监控动力学过程(荧光研究)检测方案(分子荧光光谱)》用到的仪器有HORIBA DeltaFlex超快时间分辨荧光光谱仪
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多