方案详情
文
表面涂层可以被用在很广泛的材料上,用以增加特殊的性能,如生物相容性,激素响应,药物运输或者抗细菌性能。对于温度,酸碱度,离子浓度有响应的高分子刷已经在生物医药和生物应用方面有了广泛的使用。在本文中,QCM-D技术,高分子刷的溶胀和坍塌被详细的解释。
方案详情

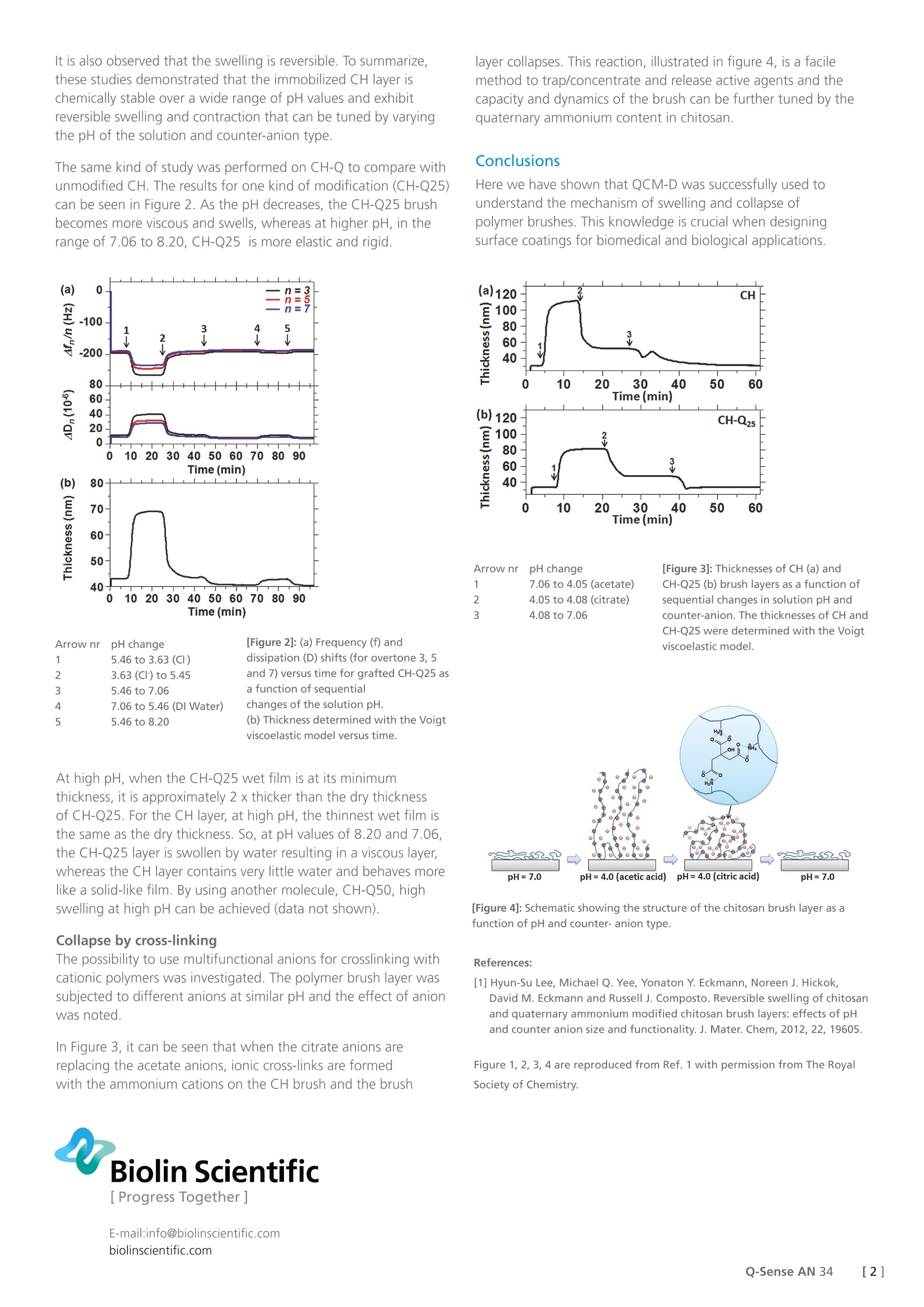
Biolin Scientific[ Progress Together] [Application Note] 34 Characterization of polymer layer swelling and collapse by the QCM-D technology Surface coatings can be applied to a bulk material to add desirable properties suchas biocompatibility, responsiveness to various stimuli, drug delivery capabilities andantibacterial qualities. Polymer brushes, which respond to changes in temperature,pH and ionic strength have been of great interest as surface coatings for biomedicaland biological applications. In this study, the QCM-D technology was successfullyused to track and understand the mechanism of swelling and collapse of polymerbrushes. Chitosan (CH) brush layers are an attractive coating becausechitosan is both bio-compatible and biodegradable. Chitosan iswater-soluble at low pH but is a collapsed coil that is insolublein water at pH above 6.5. The rheological properties, solubilityand swelling of chitosan depend on pH and counter-anion size,because both parameters directly affect the extent of intra- andintermolecular electrostatic repulsions. Due to its limited solubilitynear physiological conditions (pH~7), chitosan has not been fullyutilized as a biomaterial coating. To make chitosan water-solubleabove pH 6.5 the molecule can be modified with quaternaryammonium salts (CH-Q). In the study reviewed here, the aimwas to understand the mechanism of brush swelling for chitosanand modified chitosans. The Quartz Crystal Microbalance withDissipation (QCM-D) technology was used to study the thicknessof the polymer brushes as they were exposed to different ambientconditions. Experimental Reference measurements The E4 QCM-D instrument was used with silicon dioxide sensors.The sensors were subjected to silane deposition and CH andCH-Q were grafted onto the silane layer. In order to calculate theextent of swelling in aqueous media, the initial dry thickness ofthe polymer brush was determined by QCM-D measurements andthe Sauerbrey equation that relates mass changes to frequencychanges. Results In situ swelling of the polymer brushes - effect of pH andcounteranion type The chitosan polymer brush coated sensor was subjected tosolutions of different pH and counter-anion type. The measuredfrequency (related to mass) and dissipation (related to rigidity)values were used in the Voigt viscoelastic model to determine the thickness of the layer during swelling and contraction (Figure1). At low pH, the CH layer swells and becomes more viscous,whereas at higher pH (pH 7.06 and 8.20), the CH layer is elasticand rigid. In order to study the effect of counter-anion type on theviscoelastic and swelling properties of the CH brush layer, itwas exposed to a solution at pH 3.85 containing acetate anions(CH,CO, ) (arrow 6) for comparison with the behavior whenexposed to a solution at pH 3.63 containing chloride anions(arrow 1). The larger counter-anions (CH,CO,) induce the layer to becomemore viscous and swell to a greater extent than the smallercounter-anions (CF). [Figure 1]: (a) Frequency (f) and dissipation (D) shifts (for overtone 3, 5 and 7)of a CH brush versus time as a function of sequential changes of solution pHand counter-anion type. (b) Thickness determined with the Voigt viscoelasticmodel versus time. (c) Illustrations showing collapsed (left) and swollen brushes(right), respectively. It is also observed that the swelling is reversible. To summarize,these studies demonstrated that the immobilized CH layer ischemically stable over a wide range of pH values and exhibitreversible swelling and contraction that can be tuned by varyingthe pH of the solution and counter-anion type. The same kind of study was performed on CH-Q to compare withunmodified CH. The results for one kind of modification (CH-Q25)can be seen in Figure 2. As the pH decreases, the CH-Q25 brushbecomes more viscous and swells, whereas at higher pH, in therange of 7.06 to 8.20, CH-Q25 is more elastic and rigid. Arrow nrpHchange7.06 to 4.05 (acetate)2 4.05 to 4.08 (citrate)3 4.08 to 7.06 [Figure 3]: Thicknesses of CH (a) andCH-Q25(b) brush layers as a function ofsequential changes in solution pH andcounter-anion. The thicknesses of CH andCH-Q25 were determined with the Voigtviscoelastic model. [Figure 4]: Schematic showing the structure of the chitosan brush layer as afunction of pH and counter- anion type. References: [1] Hyun-Su Lee, Michael Q. Yee, Yonaton Y. Eckmann, Noreen J. Hickok,David M. Eckmann and Russell J. Composto. Reversible swelling of chitosanand quaternary ammonium modified chitosan brush layers: effects of pHand counter anion size and functionality. J. Mater. Chem, 2012, 22, 19605. []Q-Sense AN
确定

还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
瑞典百欧林科技有限公司为您提供《QCM-D技术检测高分子层溶胀和坍塌性》,该方案主要用于其他中--检测,参考标准--,《QCM-D技术检测高分子层溶胀和坍塌性》用到的仪器有QSense卓越版四通道石英晶体微天平、QSense Explorer扩展版石英晶体微天平、QSense全自动八通道石英晶体微天平
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多