方案详情
文
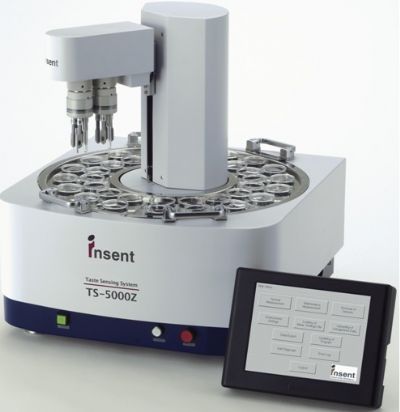
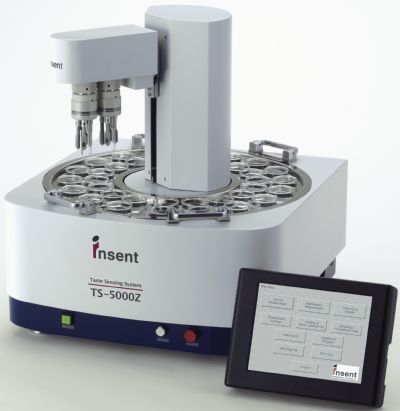
在医药品行业,开发易于服用的剂型是保证遵医嘱服药的前提,但因为药物副作用等原因,口尝试验受到很大的制约,难以把握样本的实际苦度。 近年来,随国际化趋势的增强,非常需要有一个苦度评价标准,以解决由于地域引起的苦味感知差异的问题。具备价格优势的后发药品逐渐占领市场的前提下,开发比竞争对手的产品更具备易服用性的产品势在必行。
使用TS5000Z味觉传感器定量苦度,可以推测哪种剂型的苦味抑制效果 好,不受国家地域等因素的限制,成为客观的评价标准,并客观的宣传产品的易服用的特征,强调相对竞争对手的产品的优势。
GB.NO
方案详情

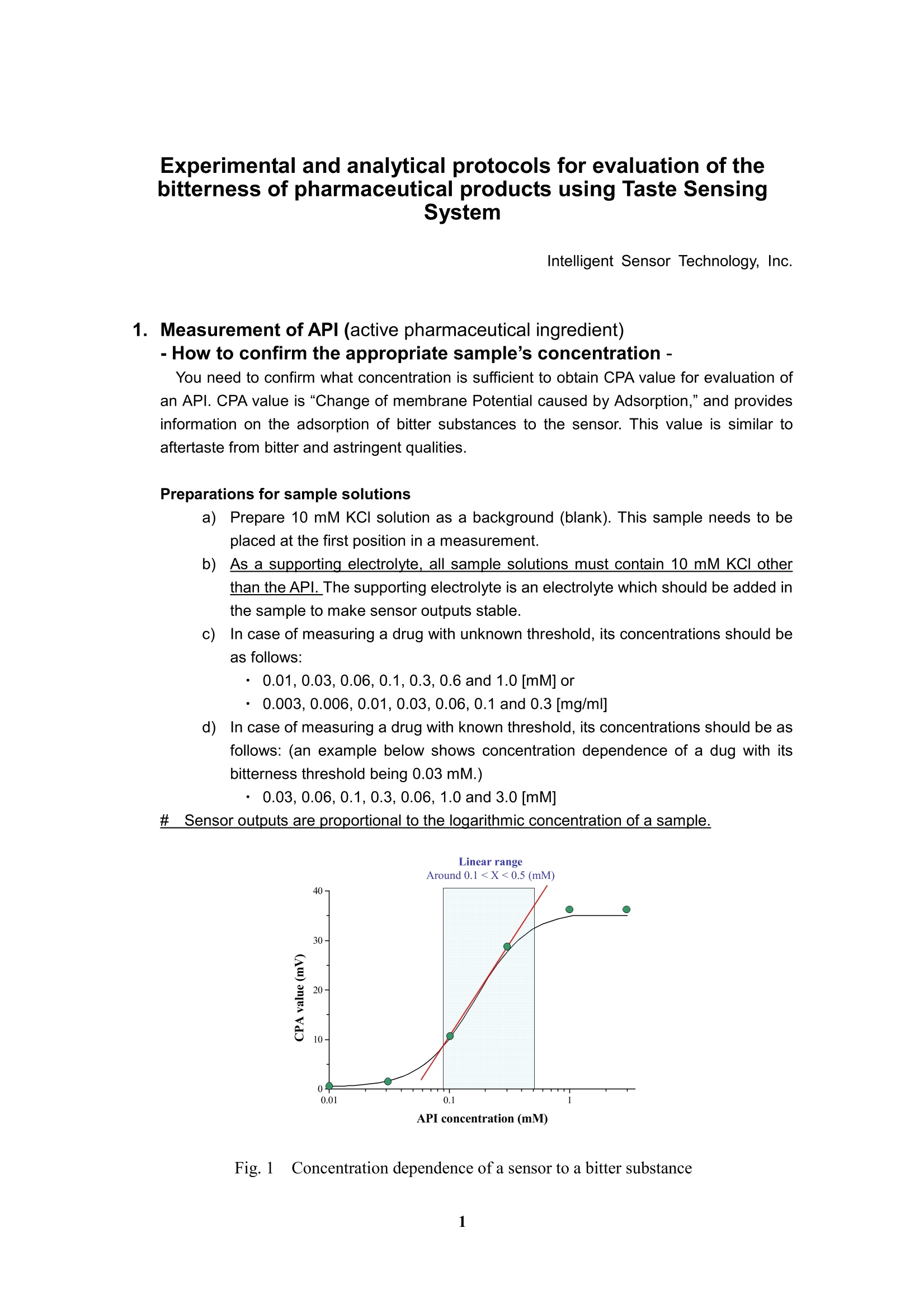
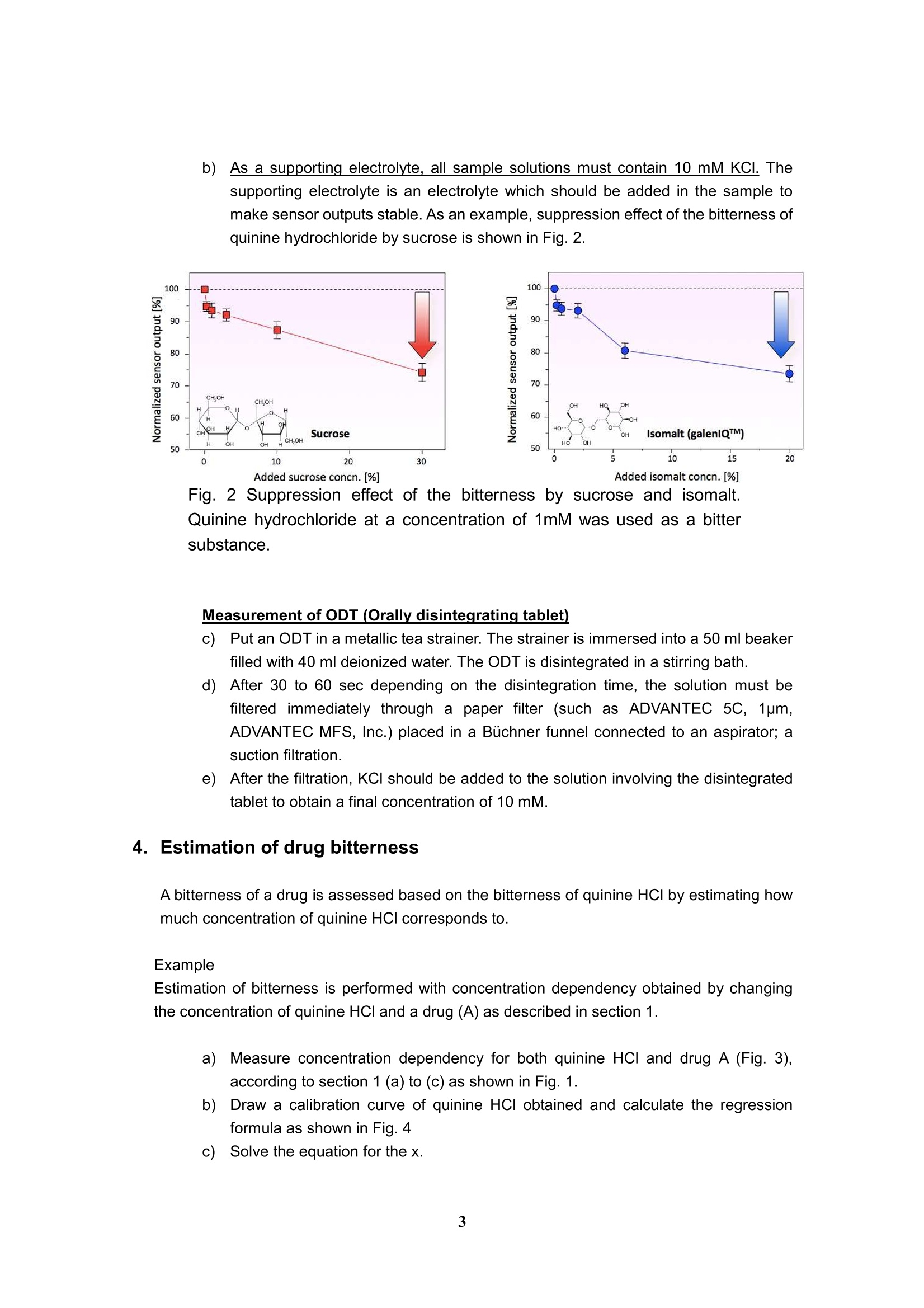
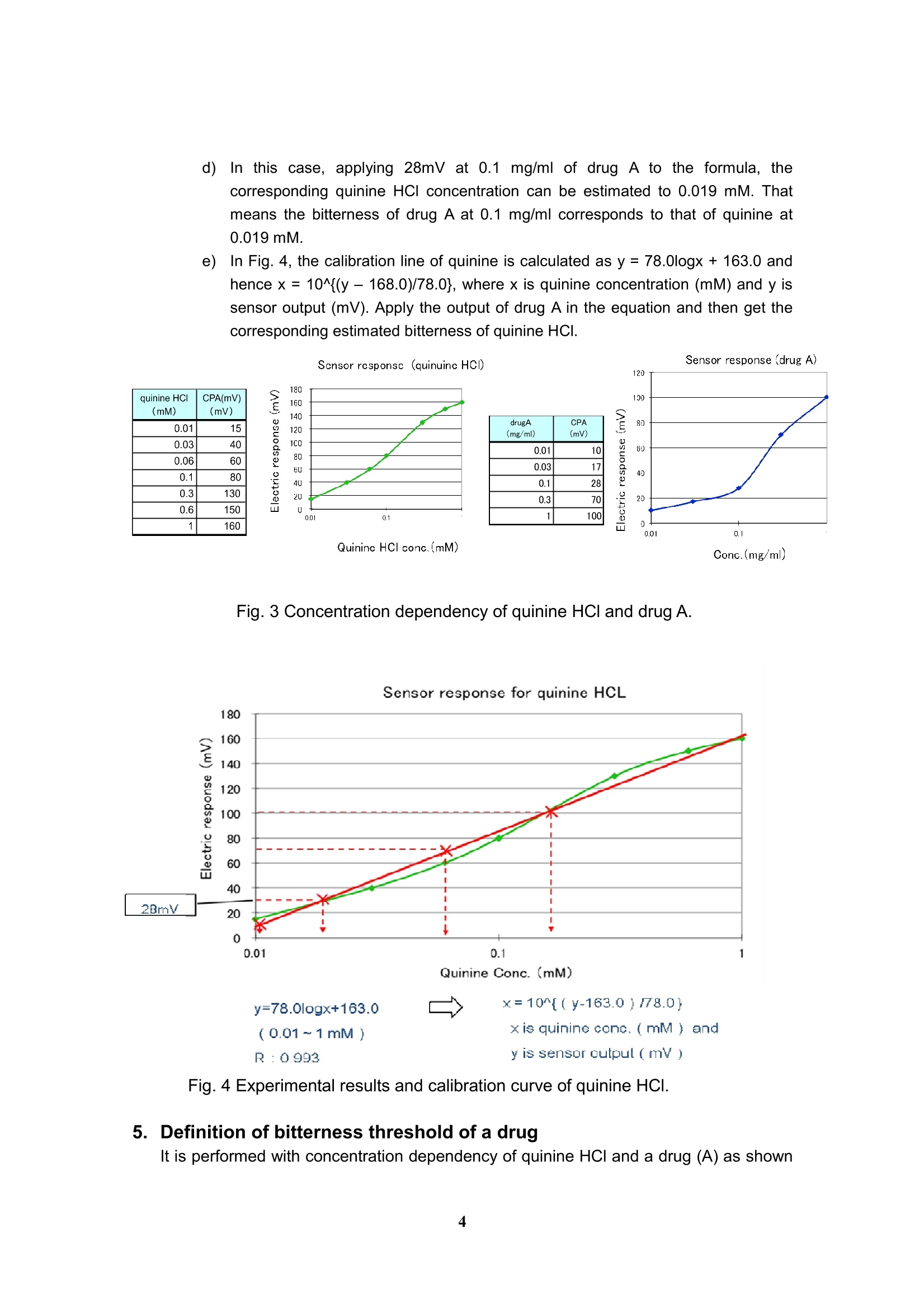
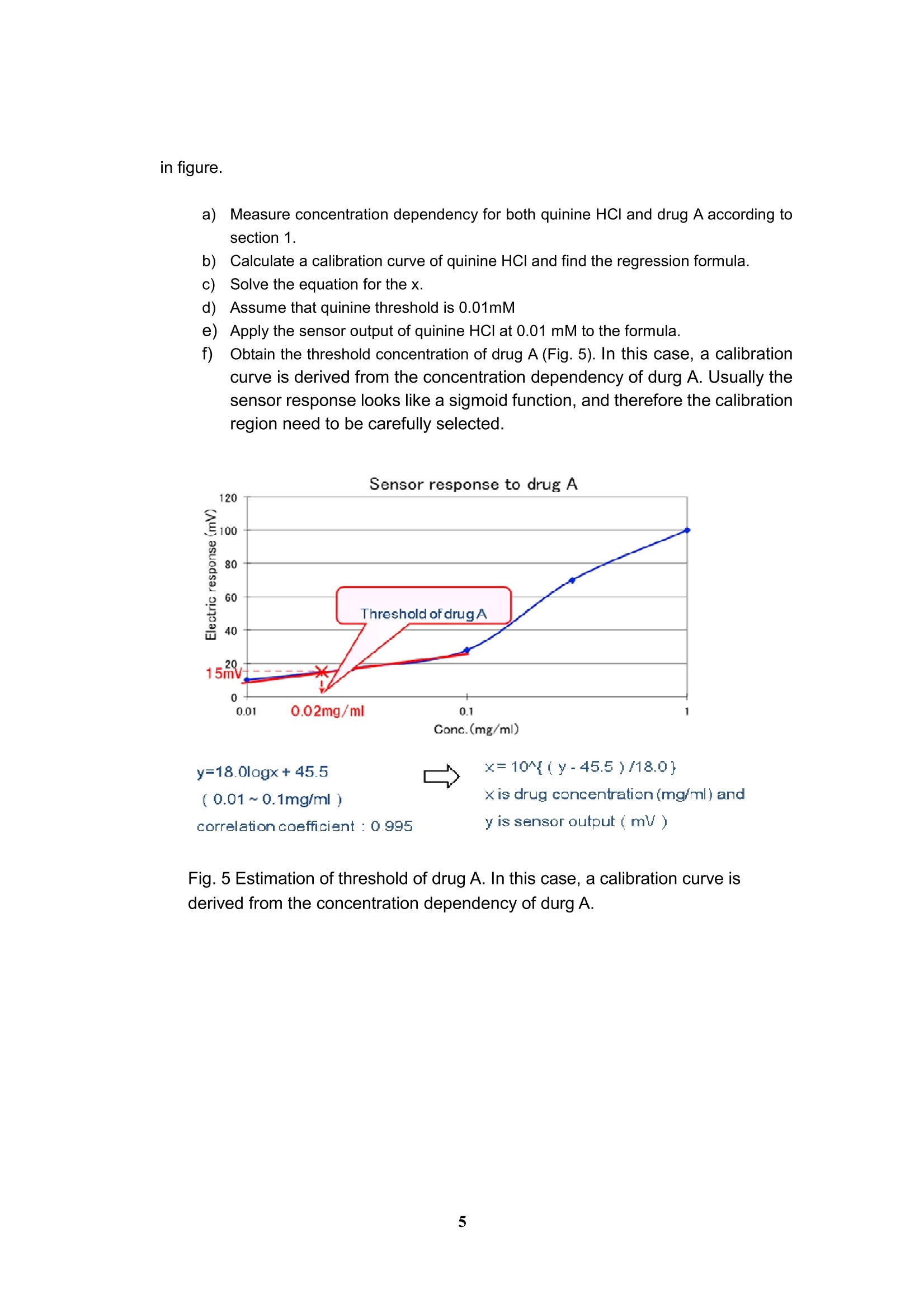
Experimental and analytical protocols for evaluation of thebitterness of pharmaceutical products using Taste SensingSystem Intelligent Sensor Technology, Inc. 1. Measurement of API (active pharmaceutical ingredient) -How to confirm the appropriate sample's concentration- You need to confirm what concentration is sufficient to obtain CPA value for evaluation ofan API. CPA value is "Change of membrane Potential caused by Adsorption,” and providesinformation on the adsorption of bitter substances to the sensor. This value is similar toaftertaste from bitter and astringent qualities. Preparations for sample solutions a)Prepare 10 mM KCl solution as a background (blank). This sample needs to beplaced at the first position in a measurement. b))As a supporting electrolyte, all sample solutions must contain 10 mM KCl otherthan the API. The supporting electrolyte is an electrolyte which should be added inthe sample to make sensor outputs stable. c)In case of measuring a drug with unknown threshold, its concentrations should beas follows: ·0.01,0.03,0.06,0.1,0.3, 0.6 and 1.0 [mM] or ·0.003,0.006,0.01,0.03,0.06,0.1 and 0.3[mg/ml] d))In case of measuring a drug with known threshold, its concentrations should be asfollows: (an example below shows concentration dependence of a dug with itsbitterness threshold being 0.03 mM.) ·0.03,0.06,0.1,0.3,0.06, 1.0 and 3.0 [mM] #Sensor outputs are proportional to the logarithmic concentration of a sample. Fig. 1Concentration dependence of a sensor to a bitter substance As an example, Figure 1 shows concentration dependence of a sensor to an APl, indicatinga linear relation between API's concentration and CPA value in the range from about 0.1 to0.5 mM.. Therefore, samples of the concentrations above are appropriate for themeasurement. In addition, significantly high CPA value should be avoided because it meansthat a large amount of bitter substances adsorbed on the membrane, probably leading to thedeterioration of the sensor. Therefore, samples should be measured at lower CPA value than50 mV for BT0, 30 mV for AN0,-50 mV for C00 and -50 mV for AE1. If no CPA value is observed in the range above, the relative value may be used as analternativeway. Poorly water-soluble drugs, which are soluble in a buffer solution at a pH range 3.5 to 8,could be measured with sensors. In this case, 10 mM KCI solution needs to be placed at thefirst position in a measurement. 2. Measurement of Diluents - To confirm that sensors do not respond to diluents or bitternessmasking materials · To evaluate the suppression effect of the bitterness of an API, it is required to confirm thatsensors do not respond to diluents or bitterness masking materials. You can skip this sectionif you will measure sugars or sugar alcohols as bitterness masking materials because theydo not show any CPA difference in potential. Preparations for sample solutions a))Prepare 10 mM KCI solution as a background (blank). This sample needs to beplaced at the first position in a measurement. b))As a supporting electrolyte, all sample solutions must contain 10 mM KCl. Thesupporting electrolyte is an electrolyte which should be added in the sample tomake sensor outputs stable. c)Three different concentrations with regard to the concentration of formulationshould be measured to confirm no potential change obtained. For example, ifbitterness masking material 3 mg/mlof bitterness masking materials contained informulation, three concentrations such as 1, 3 and 10mg/ml masking materialsshould be taken. d)If an excipient exhibited some sensor outputs, you might estimate a true value ofbitterness masking effect of formulation by subtracting the results of drugformulations. 3. Measurement of formulations - How to evaluate the suppression effect on the bitterness by diluents - Preparations for sample solutions and measurement a))Prepare 10 mM KCI solution as a background (blank). This sample needs to beplaced at the first position in a measurement. b))As a supporting electrolyte, all sample solutions must contain 10 mM KCI. Thesupporting electrolyte is an electrolyte which should be added in the sample tomake sensor outputs stable. As an example, suppression effect of the bitterness ofquinine hydrochloride by sucrose is shown in Fig. 2. Fig. 2 Suppression effect of the bitterness by sucrose and isomalt.Quinine hydrochloride at a concentration of 1mM was used as a bittersubstance. Measurement of ODT (Orally disintegrating tablet) c)Put an ODT in a metallic tea strainer. The strainer is immersed into a 50 ml beakerfilled with 40 ml deionized water. The ODT is disintegrated in a stirring bath. d)After 30 to 60 sec depending on the disintegration time, the solution must befiltered immediately through a paper filter (such as ADVANTEC 5C, 1pm,ADVANTEC MFS, Inc.) placed in a Buchner funnel connected to an aspirator; asuction filtration. e))After the filtration, KCl should be added to the solution involving the disintegratedtablet to obtain a final concentration of 10 mM. 4. Estimation of drug bitterness A bitterness of a drug is assessed based on the bitterness of quinine HCI by estimating howmuch concentration of quinine HCl corresponds to. Example Estimation of bitterness is performed with concentration dependency obtained by changingthe concentration of quinine HCl and a drug (A) as described in section 1. a)Measure concentration dependency for both quinine HCI and drug A (Fig. 3),according to section 1 (a) to (c) as shown in Fig. 1. b)Draw a calibration curve of quinine HCI obtained and calculate the regressionformula as shown in Fig. 4 c)Solve the equation for thex. d)In this case, applying 28mV at 0.1l mg/ml of drug A to the formula, thecorresponding quinine HCI concentration can be estimated to 0.019 mM. Thatmeans the bitterness of drug A at 0.1 mg/ml corresponds to that of quinine at0.019 mM e)In Fig. 4, the calibration line of quinine is calculated as y= 78.0logx+163.0 andhence x = 10^{(y-168.0)/78.0}, where x is quinine concentration (mM) and y issensor output (mV). Apply the output of drug A in the equation and then get thecorresponding estimated bitterness of quinine HCl. Fig. 3 Concentration dependency of quinine HCI and drug A. Quinine Conc.(mM) y=78.0logx+163.0 x=10^{(y-163.0)/78.0} (0.01~1mM】 x is quinine canc.(mM) and .R : 0.993 y is sensor output (mV) Fig. 4 Experimental results and calibration curve of quinine HCI. 5. Definition of bitterness threshold of a drug It is performed with concentration dependency of quinine HCI and a drug (A) as shown in figure. a)Measure concentration dependency for both quinine HCI and drug A according tosection 1. Calculate a calibration curve of quinine HCl and find the regression formula. Solve the equation for the x. Assume that quinine threshold is 0.01mM )Apply the sensor output of quinine HCI at 0.01 mM to the formula. Obtain the threshold concentration of drug A (Fig.5). In this case, a calibrationcurve is derived from the concentration dependency of durg A. Usually thesensor response looks like a sigmoid function, and therefore the calibrationregion need to be carefully selected. Sensor response to drug A y=18.0logx+45.5 x=10^{(y-45.5)/18.0}(0.01~0.1mg/ml) x is drug concentration(mg/ml) andcorrelation coefficient : 0.995y is sensor output (mV) Fig.5 Estimation of threshold of drug A. In this case, a calibration curve isderived from the concentration dependency of durg A.
确定

还剩3页未读,是否继续阅读?
产品配置单
北京盈盛恒泰科技有限责任公司为您提供《化学药中主要物质含量分析检测方案 》,该方案主要用于中药材和饮片中其他检测,参考标准--,《化学药中主要物质含量分析检测方案 》用到的仪器有电子舌、日本INSENT味觉分析系统(电子舌)
推荐专场
感官智能分析系统(电子鼻/电子舌)
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多















