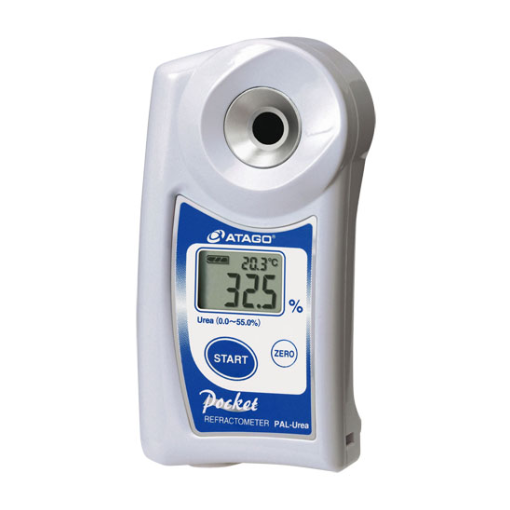
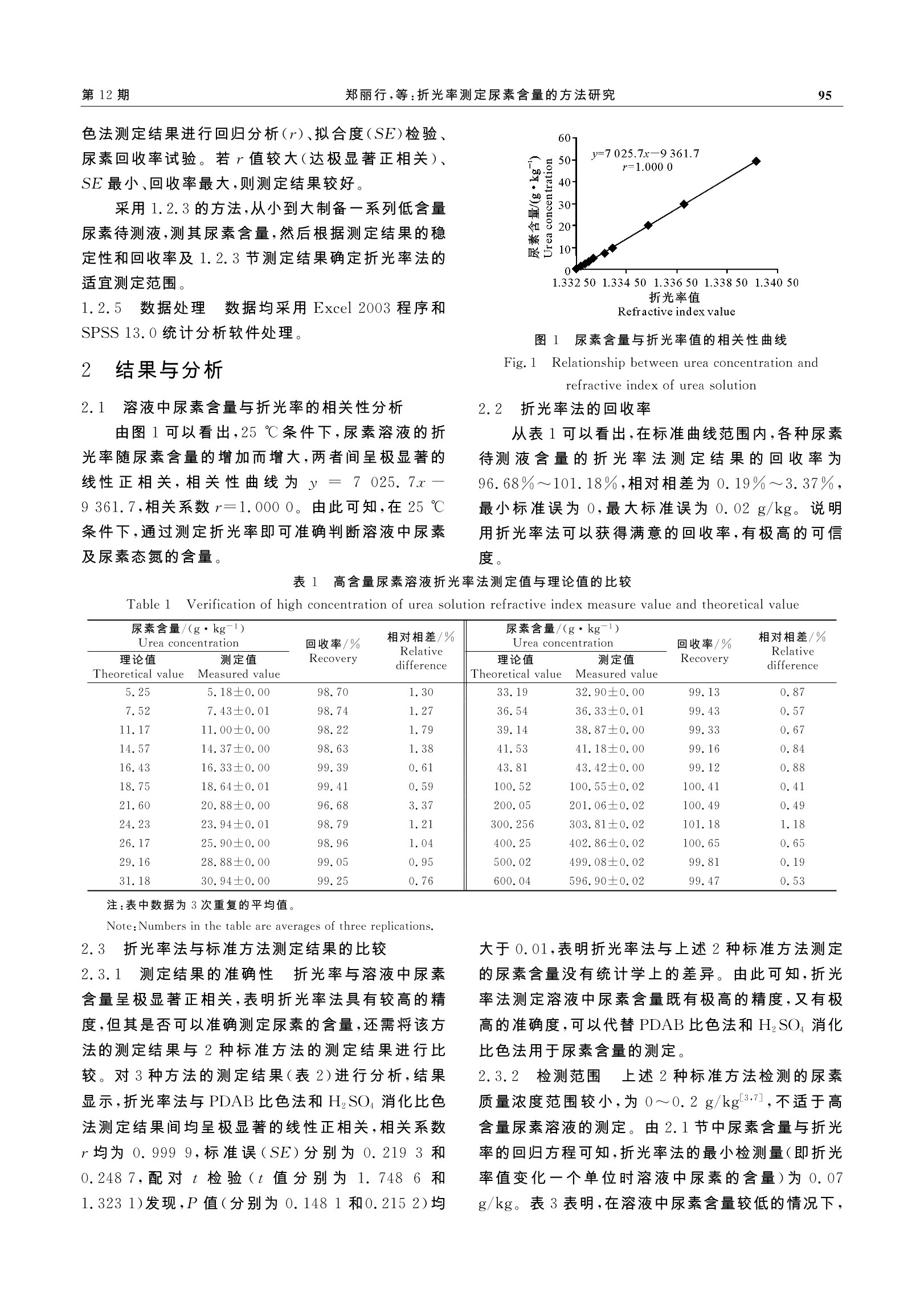
适用于专业人员的QC检测和非专业人员的现场快速检测,无须特殊实验条件,在中国的加油站、汽车生产厂、终端用户技术部、质量部、防冻液、车用尿素溶液经销商快速检测尿素浓度产品部分指标的一种工具。
目前,在中国加油站可以非常方便地帮助汽车厂家、公交公司、大型车队等终端用户检测车用尿素溶液产品的浓度及折光率是否合格.
方案详情

Vol.38No.12Dec. 2010西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版)Journal of Northwest A&F University(Nat. Sci. Ed.)第38卷第12期2010年12月 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版)第38卷94 折光率测定尿素含量的方法研究 郑丽行,樊小林,刘 刚,杨 2 (1华南农业大学资源环境学院,广东广州510642;2上海化工院国家化肥检测中心,上海200062) [摘 要] 【目的】建立简便、快速、准角、可靠的尿素含量测定方法。【方法】参照折光率仪的工作原理,建立测定溶液中尿素含量的折光率法,并将其与2种标准方法(对二甲氨基苯甲醛(PDAB)比色法和HzSO4消化比色法)的测定结果进行比较,通过对比分析、相关分析和校验研究,评价25℃恒温条件下折光率法测定溶液中尿素含量的准确性和可靠性。【结果】折光率与溶液中尿素含量呈量显著线性正相关,相关系数达0.999 9以上。折光率法与PD-AB比色法、HSO4 消化比色法则定结果均呈极显著线性正相关(r值均在0.9999以上,标准误分别为0.2193和0.248 7),测定结果无统计学差异(t值分别为1.7486和1.3231)。折光率法测定尿素的平均回收率为96.68%~101.18%,最小检测限为0.5 g/kg,最大检测限为600 g/kg,测定的尿素浓度范围远大于 PDAB 比色法和 HzSO4 消化比色法。【结论】用折光率法可直接测定溶液中尿素的含量,且该方法具有分析速度快、测定效率高、检测尿素浓度范围广、不需任何化学试剂和无污染等优点,可以替代 PDAB 比色法和 HzSO消化比色法,适用于尿素或包膜尿素企业及教学科研部门批量分析测定溶液中的尿素含量。 [关键词] 尿素;尿素态氮;折光率;相关分析;回收率;折光率法 [中图分类号] TQ441.41 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1671-9387(2010)12-0093-06 Study on refractive index method for determinationof urea concentration ZHENG Li-xing,FAN Xiao-lin,LIU Gang,YANG Yi' (1 College of Resources and Environmental, South China Agricultural University,Guangzhou,Guangdong 510642,China;2 Shanghai Research Institute of Chemical Industry,Shanghai 200062,China) Abstract:【Objective】The purpose of the study is to establish a simple,rapid,accurate and reliablemethod to determine urea concentration.【Method】 Referred to operating principle of refractive index,thecontrast and correlation analysis as well as verification method were applied to evaluate the accuracy andreliability of refractive index method (RIM) to determine urea concentration in solution under the conditionof 25℃ by taking paradimethylaminobenzal dehydedmaba (PDAB) colorimetric and HSOdigestive color-imetric method as standard.【Result】 There was a significantly and positive correlation between refractiveindex value (RIV) and urea concentration in the solution,and the linear correlation coefficient was morethan 0.999 9. Urea content tested by use of the RIM,i. e. the urea concentration measured by RIV regres-sion equations (standard curve) of urea standard solution, was significantly linearly positive correlated tothe urea concentration measured by PDAB colorimetric method and H SO digestive colorimetric one re-spectively (r value being more than 0. 999 9,SE less than 0. 219 3 and 0.248 7 separately). There was nostatistic difference between measurement results by RIM and the two standard methods respectively (t val-ue less than 1. 748 6 and 1.323 1). The average recovery rate of urea was between 96.68% and 101.18%, [收稿日期] 2010-08-18[基金项目] 国家自然科学基金项目(30871594,31071857);国家科技支撑计划项目(2006BAD10B02,2008BADA03B10,2006BAD05B08) ( L 作者简介] 郑丽行(1985一 ) ,男,福建莆田人,在读硕士,主要从事控释尿素质量检测研究。E-mail:zl x 016@yahoo. com. cn ) ( [ 通信作者] 樊小林(1958一),男,陕西三原人,教授,博士生导师,主要从事新型肥料和作物营养研究。E-mail:xlfan@scau. edu. cn ) and the test range was from 0.5 g/kg to 600 g/kg by use of refractive index method,much greater than PD-AB colorimetric and H,SO digestive colorimetric method.【Conclusion】The refractive index is able to beused to measure the concentration of urea in solution directly and the method possesses advantages,such asfast analysis,high efficiency,without any chemical reagent consumption and pollution-free. Therefore,RIMis suitable for urea enterprises,coated urea enterprises,slow or controlled release urea enterprises,instituteand universities to measure the urea concentration in batch. Key words:urea;urea-nitrogen;refractive index;standard regression curve;recovery rate;refractive in-dex method 尿素是常用的氮肥品种。在尿素的生产和使用中,均要求能快速、准确地测定尿素的含量。目前,虽已有多种测定尿素含量的方法,但这些方法往往存在一定的局限性1-2」,如通常采用的对二甲氨基苯甲醛(PDAB)比色法L3-5和HSO消化比色法6等,这2种方法是间接测定溶液中尿素含量的方法,因测定结果准确可靠而被视为尿素溶液中尿素含量的标准测定方法,但这2种方法不能直接测定溶液中尿素含量,且样品前处理耗时费事。此外,以上2种方法的检测范围小(0~0.2g/kg)[3-5,71,只适用于低含量尿素溶液的测定,不适于直接测定尿素肥料中的尿素含量。鉴于尿素在常温常压下是稳定的有机分子,纯尿素溶液中尿素含量与溶液的折光率呈正相关,本研究首次将折光率仪引入尿素含量的检测中,建立了测定尿素含量的折光率法(简称折光率法),旨在为尿素应用、生产过程中的质量控制及包膜控释尿素的在线质量控制,提供简便、快速、准确的检测方法。 1 材料与方法 1.1 材 料 1.1.1 供试肥料 供试尿素为富岛尿素(含氮量46.52%)。 1.1.2 主要仪器 日本产 ATAGO RX-5000α3261型折光率仪、国产T6S紫外可见分光光度计、德国BRAN+LUEBBE公司制造的AA3连续流动分析仪等。 1.2 方 法 1.2.1 尿素标准溶液的配制 称取尿素和控释尿素12.50g(控释尿素按包膜内核芯尿素计),分别溶于250.00 mL高纯水中,即得尿素释放率为100%(假设1份尿素全部溶于20份水中时的相对溶出率为100%)的标准溶液,重复3次。分别吸取上述标准溶液0.00,2.00,4.00,6.00,8.00,10.00,15.00,20.00,40.00,60.00,100.00 mL于100mL容量瓶 中,用高纯水定容至刻度,即得尿素释放率分别是0,2%,4%,6%,8%,10%,15%,20%,40%,60%,100%的系列标准液,备用。 1.2.2 折光率法的建立 (1)折光率法的原理。由于光在2种不同介质中的传播速度不同,所以当光线从一种介质进入另一种介质时,若其传播方向与2种介质的界面不垂直,则光在界面处的传播方向会发生改变,这称为光的折射现象。折光率指光线在空气中的传播速度与在供试样品中的传播速度的比值,据文献报道,温度恒定时折光率与溶液中有机物质含量呈极显著的线性正相关8-14J,但是溶液的折光率随着温度的升高而降低19-12]。基于上述原理,在恒温条件下用折光率就能直接衡量尿素溶液中尿素的含量。 (2)折光率法的测定步骤。折光率法具体步骤为:在(25±0.02)℃下,分别测定上述尿素系列标准溶液的折光率,以折光率值为自变量x、溶液中尿素实际含量为因变量y,进行回归分析,得出折光率与尿素含量的回归方程;测定待测尿素溶液的折光率,将其代入上步建立的回归方程,即可求得待测液中的尿素含量。 1.2.3 折光率法的回收率试验 准确称量不同质量的尿素(精确至0.0001g)若干份,溶解后定溶至100.00 mL得到一系列高含量尿素溶液,在(25±0.02)℃下测定溶液的折光率,将其代入1.2.2节建立的方程即可算出高含量尿素容液中尿素的含量,然后按照下列公式计算折光率法测定尿素含量的回收率: 式中:c为折光率法测定的尿素含量(g/kg),v为尿素待测液的体积(mL),m 为待测尿素的质量(g)。 1.2.4 折光率法与标准方法的比较 分别采用PDAB比色法31和HzSO消化比色法612种标准方法及折光率法测定相同尿素溶液中的尿素含量,将折光率法测定结果与 PDAB 比色法、HSO消化比 色法测定结果进行回归分析(r)、拟合度(SE)检验、尿素回收率试验。若r值较大(达极显著正相关)、SE 最小、回收率最大,则测定结果较好。 采用1.2.3的方法,从小到大制备一系列低含量尿素待测液,测其尿素含量,然后根据测定结果的稳定性和回收率及1.2.3节测定结果确定折光率法的适宜测定范围。 1.2.5 数据处理 数据均采用 Excel 2003 程序和SPSS 13.0统计分析软件处理。 2 结果与分析 2.1 溶液中尿素含量与折光率的相关性分析 由图1可以看出,25℃条件下,尿素溶液的折光率随尿素含量的增加而增大,两者间呈极显著的线性正相关,相关性曲线为y=7025.7x一9361.7,相关系数r=1.0000。由此可知,在25℃条件下,通过测定折光率即可准确判断溶液中尿素及尿素态氮的含量。 图1 尿素含量与折光率值的相关性曲线 Fig. 1 Relationship between urea concentration andrefractive index of urea solution 2.2 折光率法的回收率 从表1可以看出,在标准曲线范围内,各种尿素待测液含量的折光率法测定结果的回收率为96.68%~101.18%,相对相差为0.19%~3.37%,最小标准误为0,最大标准误为0.02g/kg。说明用折光率法可以获得满意的回收率,有极高的可信度。 表1 高含量尿素溶液折光率法测定值与理论值的比较 Table 1 Verification of high concentration of urea solution refractive index measure value and theoretical value 尿素含量/(g·kg)Urea concentration 回收率/% 相对相差/% 尿素含量/(g·kg)Urea concentration 回收率/% 相对相差/% Relative Relative difference 理论值 测定值 Recovery difference 理论值 测定值 Recovery Theoretical value Measured value Theoretical value Measured value 5.25 5.18±0.00 98.70 1.30 33.19 32.90±0.00 99.13 0.87 7.52 7.43±0.01 98.74 1.27 36.54 36.33±0.01 99.43 0.57 11.17 11.00±0.00 98.22 1.79 39.14 38.87±0.00 99.33 0.67 14.57 14.37±0.00 98.63 1,38 41.53 41.18±0.00 99.16 0.84 16.43 16.33±0.00 99.39 0.61 43.81 43.42±0.00 99.12 0.88 18.75 18.64±0.01 99.41 0.59 100.52 100.55±0.02 100.41 0.41 21.60 20.88±0.00 96.68 3.37 200.05 201.06±0.02 100.49 0.49 24.23 23.94±0.01 98.79 1.21 300.256 303.81±0.02 101.18 1.18 26.17 25.90±0.00 98.96 1.04 400.25 402.86±0.02 100.65 0.65 29.16 28.88±0.00 99.05 0.95 500.02 499.08±0.02 99.81 0.19 31.18 30.94±0.00 99.25 0.76 600.04 596.90±0.02 99.47 0.53 注:表中数据为3次重复的平均值。 Note:Numbers in the table are averages of three replications. 2.3 折光率法与标准方法测定结果的比较 2.3.1 测定结果的准确性 折光率与溶液中尿素含量呈极显著正相关,表明折光率法具有较高的精度,但其是否可以准确测定尿素的含量,还需将该方法的测定结果与2种标准方法的测定结果进行比较。对3种方法的测定结果(表2)进行分析,结果显示,折光率法与 PDAB比色法和HzSO消化比色法测定结果间均呈极显著的线性正相关,相关系数r均为0.999 9,标准误(SE)分别为0.2193和0.2487,配对t检验(t值分别为1.74836和1.3231)发现,P值(分别为0.1481和0.2152)均 大于0.01,表明折光率法与上述2种标准方法测定的尿素含量没有统计学上的差异。由此可知,折光率法测定溶液中尿素含量既有极高的精度,又有极高的准确度,可以代替 PDAB 比色法和HzSO4消化比色法用于尿素含量的测定。 2.3.2 检测范围 1上述2种标准方法检测的尿素质量浓度范围较小,为0~0.2g/kg3.71,不适于高含量尿素溶液的测定。由2.1节中尿素含量与折光率的回归方程可知,折光率法的最小检测量(即折光率值变化一个单位时溶液中尿素的含量)为0.07g/kg。表3表明,在溶液中尿素含量较低的情况下, 折光率法回收率较低,相对相差较大,当溶液中尿素含量达到 0.5 g/kg以上时,折光率法可以准确测定尿素的含量。结合表1结果可见,当溶液中尿素含量为0.5~600 g/kg时,折光率法能准确测定溶液中的尿素含量,但是当尿素含量大于 600 g/kg 时,由于测定过程中有尿素晶体析出,导致测定结果不稳定,由此可以认为折光率法测定的上限为600 g/kg。结果表明,折光率法能准确、快速地测定溶液中的尿素含量,检测范围远大于上述2种标准方法,且操作简便、快捷、不需要任何其他化学试剂。在尿素生产企业中,待测液中尿素含量往往高达到几十甚至几百g/kg,这时采用折光率法便可直接而准确地测定溶液中的尿素含量。 表2 折光率法与 PDAB比色法、HSO4 消化比色法测定尿素含量结果的比较 Table 2 Comparison of urea concentration measured by use of PDAB colorimeter,H SO digestioncolorimeter and refractive index method g/kg 待测液 PDAB比色法 H2SO4消化比色法 折光率法 待测液 PDAB比色法 H2SO4消化比色法 折光率法 H2SO4 digestion Refractive H2SO4 digestion Refractive Sample PDAB colorimeter colorimeter index method Sample PDAB colorimeter colorimeter index method 1 0.00±0.00 0.00±0.00 0.00±0.00 7 7.52±0.03 7.28±0.06 7.47±0.02 2 1.07±0.01 1.16±0.02 0.94±0.02 8 10.45±0.06 9.95±0.09 10.04±0.00 3 2.10±0.01 2.19±0.02 1.90±0.04 9 19.83±0.09 19.35±0.28 20.1±0.02 4 3.02±0.02 3.05±0.05 2.93±0.02 10 31.11±0.16 28.46±0.28 30.1±0.02 5 3.91±0.03 4.12±0.02 3.91±0.02 11 52.13±0.33 47.68±0.45 49.78±0.00 6 5.17±0.01 5.234±0.03 4.92±0.00 注:方差分析采用配对t检验;数据为3次重复的平均值。 Note:Pair t test is used for variance analysis;numbers in the table are averages of three replications. 表3低含量尿素溶液折光率法测定值与理论值的比较 Table 3 Verification of low concentration of urea solution refractive index measure value and theoretical value 尿素含量/(g·kg)Urea concentration 回收率/% 相对相差/% 尿素含量/(g·kg)Urea concentration 回收率/% 相对相差/% Relative Relativedifference 理论值 测定值 Recovery difference 理论值 测定值 Recovery Theoretical value Measured value Theoretical value Measured value 0.00 0.00±0.00 0.00 0.20 0.21±0.00 105.00 4.88 0.04 0.02±0.02 56.91 54.92 0.51 0.49±0.00 99.65 3.41 0.08 0.05±0.02 60.61 49.06 1.06 1.05±0.00 99.15 0.85 0.11 0.14±0.00 123.89 21.34 2.20 2.17±0.00 98.77 1.24 注:数据为3次重复的平均值。 Note:Numbers in the table are averages of three replications. 3 讨 论 尿素是重要的工业产品,同时也是主要的农业生产资料之一。无论是在工业制造过程中,还是在农业生产中,都要随时测定尿素的含量。鉴于尿素是有机化合物,在水中溶解后呈均匀的有机分子溶液,本研究参照折光率仪的工作原理15]及其在相关领域的应用[16-20],采用精度为0.000 01的日本AT-AGO公司的 RX-5000α型折光率仪直接测定尿素溶液的折光率,通过标准溶液中尿素含量与折光率值的线性回归方程,计算溶液中尿素含量,建立了测定尿素含量的折光率法。结果表明,折光率法测定结果与 PDAB比色法、HzSO消化比色法测定结果均呈极显著线性正相关,无统计学意义上的差异,回收率为96.68%~101.18%。因此,折光率法可以替代PDAB比色法和 H2SO肖化比色法,作为溶液 中尿素含量的分析方法。 应用折光率法测定尿素含量时需注意以下几个问题。第一,在一定范围内待测液的尿素含量越高,测定结果越准确。在尿素含量较高时,折光率法能准确地测定溶液中的尿素含量,避免因稀释待测液,甚至多次稀释待测液造成的试验误差。但是用折光率法测定低含量尿素溶液时,回收率较低,相对相差较大,因此在低含量溶液中用折光率法得到的结果不如高含量尿素溶液准确。在尿素工业和农业生产中,尿素待测液的尿素含量往往偏高,所以说折光率法适用于尿素工业和农业中。第二,折光率易受溶液中无机离子及其他有机分子干扰,因此在配制尿素待测液时,所用纯水应采用二级以上纯水,同时应做空白对照,并以空白为零点校对折光率仪。第三,尿素待测液以及尿素标准液制备好后要在1个工作日内完成测定。根据本试验结果可知,pH7以下尿 素溶液中的尿素虽在25℃可转化为NH或进一步转化为NOs,但转化率在1d内可忽略不计,对尿素溶液的折光率没有影响。 本研究建立的折光率法具有检测范围广、准确度高、精度高,测定速度快、工作效率高、简单易行等特点,这扩大了折光率法的应用领域;另外,该法测定过程不需任何化学药品,在节约成本的同时,还避免了化学试剂可能造成的环境污染。鉴于上述优点,折光率法既可作为尿素企业及缓/控释尿素企业尿素释放率在线质量控制的检测方法,也可以作为教学、科研部门测定尿素含量的方法。 4 结 论 1)在恒定温度(25℃)下,溶液中尿素的含量与其折光率呈极显著线性正相关。 2)当溶液中尿素含量为0.5~600 g/kg时,折光率法测定结果与传统 PDAB 比色法、H2SO4消化比色法测定结果均呈极显著正相关,其间无统计学差异。 3)折光率法测定结果准确度高、尿素回收率高、误差小、测定范围广,且操作简单,无需化学试剂,可以代替传统 PDAB比色法和HSO消化比色法用于测定溶液中的尿素含量,适合尿素、树脂包膜尿素、硫衣尿素企业作为生产过程中的质量控制检测方法。 ( [参考文献] ) ( [ 1] 孙宝慈.国内外尿素生产及技术进步综进 [J].大氮肥,2009, 32(1):1-9. Sun B C. Overview o f a d vances o f u r e a technology a n d p r oduc-tion at home a nd a broad [ J ] . L arge S cale Nitrogenous F e rtilizer Industry,2009,32(1):1-9. (in Chinese) ) ( [ 2 ] F rancis P S, Lewis S W, Lim K F . Analytical methodology forthe determination of u rea: current p ractice and f u ture t r ends[J ] . TrAC T rends in Analytical Chemistry,2002,21(5):389-400. ) ( [ 3] 左秀锦,王祯鑫,戴小敏,等.紫外分光光度法测定控释尿素的透膜扩散速率[J].光 谱 学与光谱分析,2006,26(6):1151- 11 5 4. Zuo X J,Wang Z X,Dai X M, et al. Rate of controlled-release urea pervasion through membrane d e termined b y ul t raviolet spectrophotometry [ J] . S pectroscopy a nd S p ectral A n alysis, 2006,26(6): 1 151-1154. (in C hinese) ) ( [ 4] 刘志刚,赵庆良,孙丽欣,等.PDAB比色法直接测定液相中的常量尿素 [J ] .哈尔滨工业大学学报,2008,40(8):1214-12 1 7. Liu Z G,Zhao Q L, Sun L X,et a l . D etermination of mediumconcentration u rea i n solution b y p - dimethylam in o benzalde- ) ( h yde colorimetry [J] . J ournal o f H arbin I n stitute o f T echnolo- gy,2008,40(8):1214 - 1217.( i n C hinese) ) ( [5] 李 敏,郑长立,张 勇.对二甲氨基苯甲醛比色法测定解析废液中的微量尿素 [J] . 化工技术与开发,2005,34(3):42-43,53. LiM,Zheng C L, Z hang Y. R ecovery process of p-Chlorobenze- nesulfonic acid from w aste a c id o f d ic ofol production [J ] .Technology&D e ve l o p ment of C h emical I n dustry,2005,34(3): 4 2- 4 3,53. ( i n Chinese) ) ( [6] 鲁如坤.土壤农业化学分析方法[M].北京:科学出版社, 2000:355-356. Lu R K. A n a lytical m e thods of so i l a n d ag r icultural c h emistry [M]. B eijing: Science Press,2000:355-356. (in Chinese) ) ( [7 ] 张英利,许安民,尚浩博,等.AA3型续续流动分析仪测定土壤和植物全氮的方法研究 [ J].西北农林科技大学学报:自然科 学版,2006,34(10):128-132. Zhang Y L , Xu A M ,Shang H B, e t al. Determinati o n s t udy of total nitrogen in soi l and plan t by continuous f low a nalyticalsystem [J ]. Journal of Northwest A &F University: Nat Sc i Ed,2006,34 ( 10):128-132.(in Chinese ) ) ( [8 ] 王 彬,倪永全.聚甘油的折光率与聚合度[J].无锡轻工大学 学报,2000,19(3):273-275 . Wang B,Ni Y Q. Refractive index and polymorization d egree of t he polyglycerols [J ] .Journal of Wuxi University of Light In-dustry,2000,19(3):273-275. (in Chinese) ) ( L9 J 陈婉玉,叶卫胜.蜂王浆水分含量的快速测定 [ J ].福建农业大学学报,1995,24(4):4 6 1- 4 65. Chen W Y, Ye W S . R apid testing of the water c o ntent i n ro y al jelly [ J ] . Joural of Fujian Agriculture Universi t y,1995,24(4): 4 61- 4 65.(in C h inese ) ) ( [10] 戈 芳.双液体系折光率-组成工作曲线的绘制 [J].三明师专学报,2000(2):70-72. Ge F. R ef r active i ndex o f liquid-liquid system-composed c a li-bration curve’s drawing [J]. Journal s o f Sanming TeachersCollege,2000(2):70-7 2 . (in Chinese) ) ( [11] 童克锦,史子瑾,陈忠仁.乙丙橡胶正己烷溶液的物性研究,Ⅰ折光率、密度的测定[J].合成橡胶工业,1985,8(4):246-25 0 . T ong K J,Shi ZJ,Chen Z R . Properties of EPDM solution in H exane, I D e termination of r e f r active i ndex and d ensity [ J ].Synthetic R ubber Industry,1985, 8 (4):246-250 . (in Ch i nese) ) ( 12 ] 周锡堂,樊栓狮,梁德青.折光率法测定四氢呋喃溶液的组成LJ].中国测试技术,2007,33(1):15- 17 . Zhou X T ,Fan S S,Liang D Q. Determination of composition of THF s o lutions b y using refractive i n dex [J]. China Me a s- urement Technology,2007,33(1):15-1 7 . (in C hinese) ) ( [13] 陈志斌.以折光率法测定甘露醇含量 [ J ].现代实用医学, 2001,13(6):296.Chen Z B . D e termination the co t ent of mannitol by usi n g re-fractive index [ J]. Modern Practical Medicine,2001,13(6):296. ) ( [14] B asker D. Relationship b e tw e en ref r a c tive in d ex and spe c ific gravity of aqueous glycerol solutions [ J]. The A nalyst,1978, 103(1223):185.(in C h inese) ) ( [ 15 ] 竺美,胡亚芹,杨 平 .折光率法和电导率法测定稀土废水中氯化铵[J].环境监测管理与技术,2006,18(2):29-31. Zhu M ,Hu Y Q, Yang P. D e termination o f ammonia c hloridein rare-earth wastewater by conductometric and re f r a ctometric [ J ] .Environmental Monitoring Management and Technology, 2006,18(2):29-31. ( in C h inese) ) ( [ 16 ] 高海涛,葛 新,范玉贤,等.头孢唑啉钠溶液的折光率测定[J].黑龙江医药,1995,8(3):154-155. Gao H T ,Ge X,F a n Y X ,et al.Determination refractive in - dex o f C e fazolin solution [ J]. Heilongjiang Medical J ournal, 1995,8(3):154-155.(in Chinese) ) ( [ 17 ] 田 丰,李传枚.折光率因数法测定100 g/L (10%)水合氯醛溶液的含量 [J] . 医 药 导报,2005,24(12):1167-1168. Tian F,Li C M. Refractive index factor method determination 100 g/L (10% ) chloral hydrate c ontent [J ] . H er a ld o f M edi- cine,2005,24(12):1 16 7-1 16 8.(in Chinese) ) ( [ 18 ] 孙镇之,万世义,孙洪伟.折光率法测定煤焦油中酚类含量 ) (上接第92页) ( [ 17 ] 吴伟祥,叶庆富,闵 航.不同生长期转 Bt 基因水稻秸秆还土对淹水土壤酶活性的影响[J].生态学报,2003,23(11):2353- 2358.Wu W X, Ye Q F ,Min H. Enzy m e activ i ties variation in f l o o-ded soils amended with B t t r ansgenic r i ce straws a t d i fferent stages of plant development [ J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2003, 23( 1 1):2353-2358.(in Chinese) ) ( [ 18 ] Frankenberger W T , Dick W A. Relationships between e n - z yme a c tivities a nd m i crobial g r owth and act i vity indices insoil [ J ]. Soil Science Soci a l Americ a Journal,1983, 4 7:945- 951. ) ( [ 19 ] P oorter H . Interspecific variation in the growth r esponse o f plants to an elevated ambient CO2 c oncentration [ J ] . Plant E - cology,1993,104 / 105:77-97 ) ( [ 20] Bentson G M , Bazzaz F A. Elevated C O and the m a gnitude and s easonal d ynamics o f r o ot production a n d l o ss i n B e tula papyrifera [ J ] . P l ant and Soil, 1997,190:211-2 1 6. ) ( [ 2 1 N orby R J. I s sues a n d perspectives fo r in v estigating root re - sponses t o elevated atmospheric c a rbon d ioxide [ J ]. Plant and Soil,1994,165:9- 2 0. ) ( [ 22 ] Darrah P R . Rhizodeposition under ambient and e levated CO2 levels [J] . Plant an d Soil,1996,187:265-275. ) ( 2 3 Pregitzer K S,Zak D R, Cu r tis P S,et al. Atmospheric C O2, s oil nitrogen, and t urnover of f ine roots [ J ] . New Phytologist, 1995,129:579- 5 85. ) ( [ J].太原工业大学学报,1989,20(3):94- 98 . Sun Z Z,Wang S Y,Sun H W. Determination of p h enol c o n- tent in coal-tar by refractiv e ind e x method [ J]. Journal o f T aiyuan Unive r sity o f T e chnology,1989,20(3):94-98. (i n Chinese) ) ( [19] 张 莉,何善全,杨亮.浅析DR-45密度和折光率仪在精细化工质量控制分析中的应用[J ] .仪器仪表与分析检测,2007 ( 4) :39-40. Zhang L , He S Q , Ya n g L . Application of DR- 4 5 c ombined meter in t he f ine chemical lines [ J] . In s trument and Analysis Determination,2007(4 ) :39-40. (in C hinese) ) ( [20] 徐徐,王琳琳,陈小鹏,等.折光率法快速测定松节油主要成分的含量 [J].化学世界,2008(11):660-661,656. Xu X, Wang L L , Chen X P,e t al. Refractometric determina- tion of the content of turpentine [ J] . C h emistry World,2008 (1 1 ):660- 6 61,656. ( in Chinese) ) ( [24] Rogers H H,Runion G B, K rupa S V . Plant re s ponses to a t -mospheric CO enrichment w i th emphasis on ro o ts a n d therhizosphere [J]. Environment Pollution,1994,83:15 5 -189. ) ( [25] Van G J H ,Gorissen A , van V J A. Car b on and nitrogen allo- cation in Lolium p erenne in r esponse to elevated atmospheric CO w i th emphasis on so i l c a rbon d y namics [J]. P lant a n d Soil,1997,187:299-308. ) ( [26 ] 李伏生,康绍忠,张富仓.大气 C O 2浓度和温度升高对作物生理生态的影响 [J] . 应用生态学报,2002,13(3):1169-1173. Li F S,Kang S Z,Zhang F C. Response of plant p hysiology to elevated atmospheri c CO [J] . Chin J Appl E col, 2002, 13 (3):1169-1173.( i n Chinese) ) ( [27] 韩士杰,周玉梅,王琛瑞,等.红松幼幼苗 CO2 浓度升高的生理生态反应 [J ] .应用生态学报,2001,12(1):27-30. Han S J, Z hou Y M , Wa n g C R , et a l. Ec o physlologlcal re - sponse o f P inus k oraiensis s e e dlings to elevated CO [ J ] .Chin J Appl Ecol,2001, 1 2(1):27-30. (in Chinese) ) ( [28 ] 周玉沐,韩士杰,张军辉,等.CO2浓度升高对长白山三种树木幼苗碳水化合物和氮含量的影响 [J].应用生态学报,2002, 13(6):663-666.Zhou YM, Han S J,Zhang J H,e t al. Photosynthetic charac-teristics o f thre e tree species seedlin g s in Changba i Mountainunder diffeent CO2 concentrations [ J ] . Ch i n J A p pl Ecol, 2002,13(1 ): 663-6 6 6. (in Chinese) )
确定




还剩4页未读,是否继续阅读?
ATAGO(爱拓)中国分公司为您提供《车用尿素液中浓度检测方案(饮用酒检测仪)》,该方案主要用于汽车电子电器中理化分析检测,参考标准--,《车用尿素液中浓度检测方案(饮用酒检测仪)》用到的仪器有ATAGO(爱拓)车用尿素浓度计PAL-Urea、ATAGO(爱拓)全自动台式温控折光仪(折射仪)RX-5000i
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多