
本文介绍了戴安公司的“只加水”(淋洗液自动发生)技术与AS15阴离子分析柱结合分析高纯水中的痕量阴离子和低分子量的有机酸,大体积直接进样,不需要预浓缩柱、加样泵等附加装置,获得非常好的检出限。具体方法请见附件。
方案详情

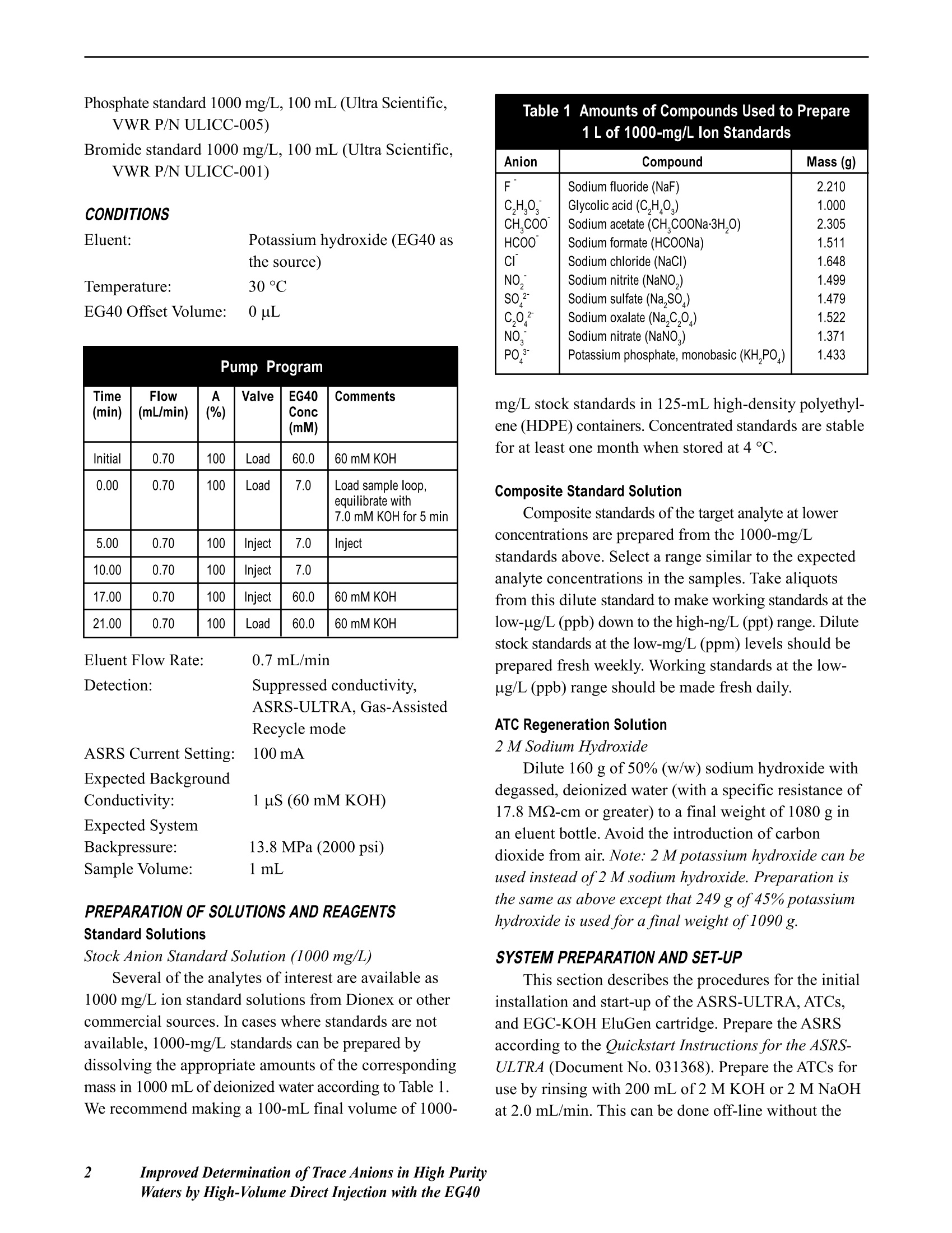
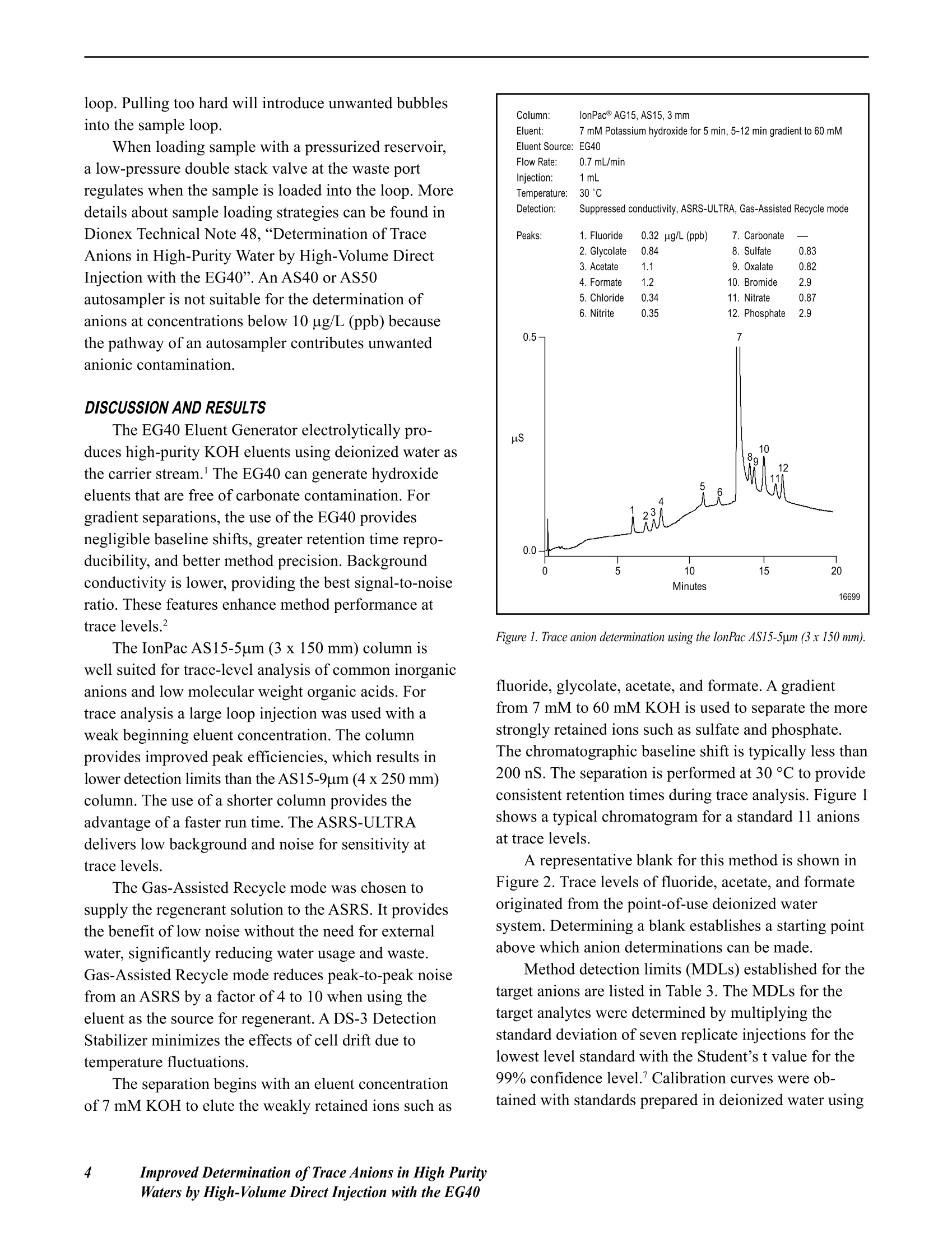
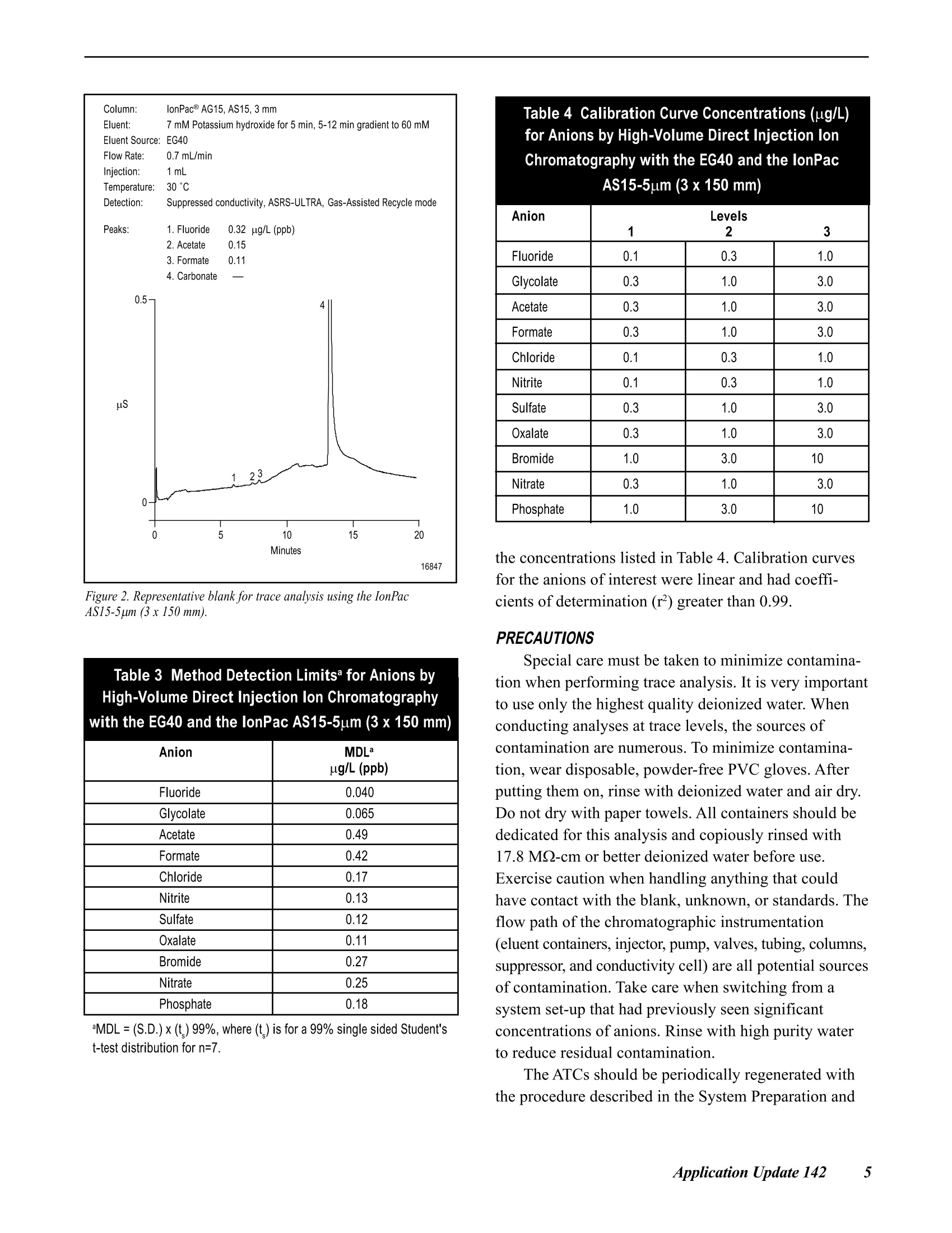
DDIONEX Application Update 142 Improved Determination of Trace Anions in HighPurity Waters by High-Volume Direct Injectionwith the EG40 INTRODUCTION This document describes the use of the EG40potassium hydroxide (KOH) eluent generator with theIonPac@ AS15-5pm (3x 150 mm) column for traceanion analysis. The EG40 generates high-purity andcarbonate-free hydroxide eluents on-line to improve themethod performance for determination of target analytesat trace levels.12 The high-volume direct injectiontechnique is used to achieve sensitive detection at lowto sub-ug/L levels without the use of a concentratorcolumn, sample loading pump, and additional valve.3-5The AS15-5um column is used to separate commoninorganic anions and low molecular weight organicacids in less than 20 minutes. This column providesimproved peak efficiencies, which results in lowerdetection limits than the AS15-9um column (4x 250mm). The analytes are detected by suppressed conduc-tivity with a 2-mm ASRS@-ULTRA operated in the Gas-Assisted Recycle mode. This Application Updateexpands on work presented in Dionex Technical Note48,“Determination of Trace Anions in High-PurityWater by High-Volume Direct Injection with theEG40”.6 EQUIPMENT Dionex DX-600 ion chromatography system consisting of:GS50 Gradient Pump CD25 Conductivity DetectorLC30 Chromatography Enclosure equipped withRheodyne Model 9126 injector PEEK, rearloading (P/N 052291)IonPac AS15-5um analytical, 3 x 150 mm Columns:(P/N 057594)IonPac AG15-5um guard, 3x 30 mm(P/N 057597) Trap Columns:ATC-1 Trap,9 x24 mm (P/N 037151)placed after pumpATC Trap, 4x 35 mm (P/N 043131)placed between the EG40 degasmodule and injector Suppressor: ASRS-ULTRA 2-mm (P/N 053947) EG40 Eluent Generator with EluGenEGC-KOHcartridge Gas-Assisted Regeneration Kit (P/N 056886) Pressurized sample vessel (P/N 037460) and low-pressure 3-way double stack valve (P/N 045009),optional 300 cm of green 0.75-mm (0.30-in.) PEEK tubing tomake a 1000-uL sample loop PeakNet@ Chromatography Workstation REAGENTS AND STANDARDS Deionized water, Type I reagent grade, 17.8 MQ-cmresistance or better Sodium and potassium salts, ACS reagent grade, forpreparing anion standards (VWRor other) Sodium hydroxide 50% w/w aqueous solution (FisherScientific) Potassium hydroxide 45% w/w aqueous solution (FisherScientific); optional instead of sodium hydroxide Fluoride standard 1000 mg/L, 100 mL (Dionex P/N037158) Chloride standard 1000 mg/L, 100 mL (Dionex P/N037159) Sulfate standard 1000 mg/L, 100 mL (Dionex P/N037160) Nitrate standard 1000 mg/L, 100 mL (Ultra Scientific,VWR P/N ULICC-004) Phosphate standard 1000 mg/L, 100 mL (Ultra Scientific,VWR P/NULICC-005) Bromide standard 1000 mg/L, 100 mL (Ultra Scientific,VWR P/N ULICC-001) CONDITIONS Eluent: Potassium hydroxide (EG40 asthe source)Temperature: 30 CEG40 Offset Volume: 0 uL Pump Program Time(min) Flow(mL/min) A(%) Valve EG40Conc(mM) Comments Initial 0.70 100 Load 60.0 60 mM KOH 0.00 0.70 100 Load 7.0 Load sample loop,equilibrate with 7.0 mM KOH for 5 min 5.00 0.70 100 Inject 7.0 Inject 10.00 0.70 100 Inject 7.0 17.00 0.70 100 Inject 60.0 60 mM KOH 21.00 0.70 100 Load 60.0 60 mM KOH Eluent Flow Rate: 0.7 mL/minDetection: Suppressed conductivity,ASRS-ULTRA, Gas-AssistedRecycle modeASRS Current Setting: 100 mAExpected BackgroundConductivity: 1 uS (60 mMKOH)Expected SystemBackpressure: 13.8 MPa (2000 psi) Sample Volume: l mL PREPARATION OF SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTSStandard Solutions Stock Anion Standard Solution (1000 mg/L) Several of the analytes of interest are available as1000 mg/L ion standard solutions from Dionex or othercommercial sources. In cases where standards are notavailable, 1000-mg/L standards can be prepared bydissolving the appropriate amounts of the correspondingmass in 1000 mL of deionized water according to Table 1.We recommend making a 100-mL final volume of 1000- Table 1 Amounts of Compounds Used to Prepare1 L of 1000-mg/L Ion Standards Anion Compound Mass (g) F Sodium fluoride (NaF) 2.210 C.HO Glycolic acid (C,HO,) 1.000 CH,COO Sodium acetate (CH,COONa·3H,0) 2.305 HCOO Sodium formate (HCOONa) 1.511 CI Sodium chloride (NaCl) 1.648 NO. Sodium nitrite (NaNO,) 1.499 SO Sodium sulfate (Na,SO) 1.479 C.0 Sodium oxalate (Na,C,0) 1.522 NO. Sodium nitrate (NaNO,) 1.371 PO Potassium phosphate,monobasic (KH,PO) 1.433 mg/L stock standards in 125-mL high-density polyethyl-ene (HDPE) containers. Concentrated standards are stablefor at least one month when stored at 4°C. Composite Standard Solution Composite standards of the target analyte at lowerconcentrations are prepared from the 1000-mg/Lstandards above. Select a range similar to the expectedanalyte concentrations in the samples. Take aliquotsfrom this dilute standard to make working standards at thelow-ug/L (ppb) down to the high-ng/L (ppt) range. Dilutestock standards at the low-mg/L (ppm) levels should beprepared fresh weekly. Working standards at the low-ug/L (ppb) range should be made fresh daily. ATC Regeneration Solution 2 M Sodium Hydroxide Dilute 160 g of 50% (w/w) sodium hydroxide withdegassed, deionized water (with a specific resistance of17.8 MQ-cm or greater) to a final weight of 1080 g inan eluent bottle. Avoid the introduction of carbondioxide from air. Note: 2M potassium hydroxide can beused instead of2 M sodium hydroxide. Preparation isthe same as above except that 249 g of 45% potassiumhydroxide is used for a final weight of 1090 g. SYSTEM PREPARATION AND SET-UP This section describes the procedures for the initialinstallation and start-up of the ASRS-ULTRA, ATCs,and EGC-KOH EluGen cartridge. Prepare the ASRSaccording to the Quickstart Instructions for the ASRS-ULTRA (DocumentNo. 031368).Prepare the ATCs foruse by rinsing with 200 mL of 2 M KOH or 2 M NaOHat 2.0 mL/min. This can be done off-line without the 2 Improved Determination ofTrace Anions in High PurityWaters by High-Volume Direct Injection with the EG40 GS50 by pressurizing an eluent bottle with helium at34.5 kPa (5 psi). Rinse the two ATCs with deionizedwater at 2.0 mL/min for 20 min. Install the EGC-OH EluGen cartridge according tothe instructions in the Operator s Manual for the EG40Eluent Generator System (Document No. 031373).Place the 4-mm ATC-1 column between the GS50 outletand the EGC-KOH cartridge inlet and the 2-mm ATCcolumn between the EG40 degas unit outlet and theinjection valve inlet, as shown in Figure 9,“EG40 FlowPath Diagram”, in the EG40 Eluent Generator SystemManual. Program the EG40 to generate the highest concen-tration of KOH (60 mM) that will be used by themethod and rinse the second ATC column and theseparation column for 30 minutes at the method flowrate. For the Gas-Assisted Recycle mode, connect theRegen In line (shorter tubing from the tee) to the SRSRegen In port. Connect the line from the Cell Out on theconductivity cell to the From Cell line (longer tubingfrom the tee). Connect a gas line to the regulator.Compressed air can be used in place of helium ornitrogen if it is purified with suitable traps to removemoisture, hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide, and otherparticulate matter. (For more information see the SRSGas-Assisted Regeneration Kit Installation and UseInstructions (Document No. 031665-02). Make a 1000-uL sample loop by cutting a 220 cmportion of the green 0.030-in. (0.75-mm) i.d. PEEKtubing. If a different loop or tubing with a differentinternal diameter is desired, refer to Table 2 to calculatethe length needed. The volume of a loop can be verifiedby measuring the weight difference between the sampleloop filled with deionized water and the empty loop.The inside diameter of tubing varies by as much as 20%(for example, 0.010±0.002 in.). Table 2 Volume per Unit Length forVarious Tubing Internal Diameters Material Color InternalDiameter EstimatedVolume (uL/cm) (inches) (millimeters) PEEK Red 0.005 0.125 0.126 PEEK Black 0.010 0.250 0.506 PEEK Orange 0.020 0.500 2.022 PEEK Green 0.030 0.750 4.550 Connect the columns and suppressor in the ICsystem by using the red 0.005-in. (0.125-mm) PEEKtubing. Keep the lengths of connecting tubing as shortas possible to minimize system void volume. This willensure efficient 3-mm column operation. Carefully use arazor blade or plastic tubing cutter to ensure that thesurfaces of the tubing cuts have straight, smoothsurfaces. Irregularity on the surface of a tubing end canresult in unwanted additional dead volume. SYSTEM OPERATION Turn on the gradient pump to begin the flow ofeluent through the system. If the system backpressure isbelow 14 MPa (2000 psi), a portion of yellow PEEK0.003-in. (0.075 mm) tubing should be added betweenthe outlet of the degas assembly in the EG40 and theinlet of the injection valve. For optimal EG40 perfor-mance, maintain a system backpressure of 15.2 to 16.6MPa (2200 to 2400 psi). Confirm that there are no leaksanywhere in the chromatographic pathway. For moreinformation see the Operator s Manual for the EG40Eluent Generator System (Document No. 031373). After stable eluent flow has been established, apply10-15 psi gas pressure to the Regen In port of theASRS. A mixture of gas and liquid will be observedexiting the Regen Out port. Turn the power on to supplycurrent to the ASRS; the gas flow rate across theregenerant chamber will be about 100 mL/min at a setpressure of 10-12 psi. Turn on the EG40 using PeakNet to deliver thehighest eluent concentration required by the method.Allow the LC30 oven to stabilize at the 30°C operatingtemperature. Assess the quality of the blank by measur-ing the short-term noise. In a representative 1-minutelevel portion of the chromatogram, a“peak-to-peak”measurement should be less than 10 nS. It will take atleast 4 hours for the system to equilibrate to a stablebackground conductivity for trace analysis. It is a goodpractice to run a system overnight to equilibrate for usethe following day. The sample is loaded with either a syringe or apressurized reservoir. When using a syringe, take carenot to introduce contamination by contact of the samplewith the syringe. The black rubber plunger in disposableplastic syringes can be a source of significant contami-nation. To avoid contamination, the syringe should beplaced at the waste port and used to pull sample into the loop. Pulling too hard will introduce unwanted bubblesinto the sample loop. When loading sample with a pressurized reservoir,a low-pressure double stack valve at the waste portregulates when the sample is loaded into the loop. Moredetails about sample loading strategies can be found inDionex Technical Note 48,“Determination of TraceAnions in High-Purity Water by High-Volume DirectInjection with the EG40”. An AS40 or AS50autosampler is not suitable for the determination ofanions at concentrations below 10 ug/L (ppb) becausethe pathway of an autosampler contributes unwantedanionic contamination. DISCUSSION AND RESULTS The EG40 Eluent Generator electrolytically pro-duces high-purity KOH eluents using deionized water asthe carrier stream. The EG40 can generate hydroxideeluents that are free of carbonate contamination. Forgradient separations, the use of the EG40 providesnegligible baseline shifts, greater retention time repro-ducibility, and better method precision. Backgroundconductivity is lower, providing the best signal-to-noiseratio. These features enhance method performance attrace levels. The IonPac AS15-5um (3 x 150 mm) column iswell suited for trace-level analysis of common inorganicanions and low molecular weight organic acids. Fortrace analysis a large loop injection was used with aweak beginning eluent concentration. The columnprovides improved peak efficiencies, which results inlower detection limits than the AS15-9um (4x250 mm)column. The use of a shorter column provides theadvantage of a faster run time. The ASRS-ULTRAdelivers low background and noise for sensitivity attrace levels. The Gas-Assisted Recycle mode was chosen tosupply the regenerant solution to the ASRS. It providesthe benefit of low noise without the need for externalwater, significantly reducing water usage and waste.Gas-Assisted Recycle mode reduces peak-to-peak noisefrom an ASRS by a factor of 4 to 10 when using theeluent as the source for regenerant. A DS-3 DetectionStabilizer minimizes the effects of cell drift due totemperature fluctuations. The separation begins with an eluent concentrationof 7 mM KOH to elute the weakly retained ions such as Figure 1.Trace anion determination using the IonPac AS15-5um (3x150mm). fluoride, glycolate, acetate,and formate. A gradientfrom 7 mM to 60 mM KOH is used to separate the morestrongly retained ions such as sulfate and phosphate.The chromatographic baseline shift is typically less than200 nS. The separation is performed at 30°C to provideconsistent retention times during trace analysis. Figure 1shows a typical chromatogram for a standard 11 anionsat trace levels. A representative blank for this method is shown inFigure 2. Trace levels of fluoride, acetate, and formateoriginated from the point-of-use deionized watersystem. Determining a blank establishes a starting pointabove which anion determinations can be made. Method detection limits (MDLs) established for thetarget anions are listed in Table 3. The MDLs for thetarget analytes were determined by multiplying thestandard deviation of seven replicate injections for thelowest level standard with the Student’s t value for the99% confidence level. Calibration curves were ob-tained with standards prepared in deionized water using Figure 2. Representative blank for trace analysis using the IonPacAS15-5um (3x150 mm). Table 3 Method Detection Limitsa for Anions by Anion MDLa ug/L (ppb) Fluoride 0.040 Glycolate 0.065 Acetate 0.49 Formate 0.42 Chloride 0.17 Nitrite 0.13 Sulfate 0.12 Oxalate 0.11 Bromide 0.27 Nitrate 0.25 Phosphate 0.18 MDL =(S.D.) x(t)99%, where (t) is for a 99% single sided Student'st-test distribution for n=7. Table 4 Calibration Curve Concentrations (ug/L)for Anions by High-Volume Direct Injection IonChromatography with the EG40 and the lonPac Anion Levels 1 2 3 Fluoride 0.1 0.3 1.0 Glycolate 0.3 1.0 3.0 Acetate 0.3 1.0 3.0 Formate 0.3 1.0 3.0 Chloride 0.1 0.3 1.0 Nitrite 0.1 0.3 1.0 Sulfate 0.3 1.0 3.0 Oxalate 0.3 1.0 3.0 Bromide 1.0 3.0 10 Nitrate 0.3 1.0 3.0 Phosphate 1.0 3.0 10 the concentrations listed in Table 4. Calibration curvesfor the anions of interest were linear and had coeffi-cients of determination (r) greater than 0.99. PRECAUTIONS Special care must be taken to minimize contamina-tion when performing trace analysis. It is very importantto use only the highest quality deionized water. Whenconducting analyses at trace levels, the sources ofcontamination are numerous. To minimize contamina-tion, wear disposable, powder-free PVC gloves. Afterputting them on, rinse with deionized water and air dry.Do not dry with paper towels. All containers should bededicated for this analysis and copiously rinsed with17.8 MQ-cm or better deionized water before use.Exercise caution when handling anything that couldhave contact with the blank, unknown, or standards. Theflow path of the chromatographic instrumentation(eluent containers, injector, pump,valves, tubing, columns,suppressor, and conductivity cell) are all potential sourcesof contamination. Take care when switching from asystem set-up that had previously seen significantconcentrations of anions. Rinse with high purity waterto reduce residual contamination. The ATCs should be periodically regenerated withthe procedure described in the System Preparation and Set-up section. Monitoring the blank for any significantincrease in anionic contamination will indicate whenregeneration is necessary. Monitoring the baseline shiftduring the EG40 hydroxide gradient will also indicatewhen regeneration is necessary. A significant increasebeyond 200 nS indicates that the ATC has exceeded itscapacity to trap ionic contaminants and should beregenerated. The frequency of regeneration depends onthe quality of the deionized water and the usage rate ofthe instrument. ( REFERENCES ) ( 1. Liu, Y.; Avdalovic.N.; P ohl, C.; Matt, R .; Dhillon,H.; Kiser. R. Am. Lab.,30(23)1998,48C-58C, ) ( 2. Liu, Y.; Kaiser, E. ; Avdalovic, N. Microchem J., 1999, 62,162-173. ) ( 3. Kaiser, E.; Riviello, J.;Rey, M . ; Statler,J.;Heberling, S. J.Chromatogr. 1 997, 7 89, 1 49-155. ) ( 4. Application Note 1 13. Dionex C orporation,Sunnyvale, CA, 1996. ) ( 5. Application Note 114. Dionex Corporation,Sunnyvale, CA, 1996. ) ( 6. Technical Note 48. Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale,CA, 1999. ) ( 7. Glaser, J.; Foerst , G. ; McKee,G.; Quave, S . ;Budde. W . Environ. Sci. Technol. 1981,15 (12) 1426. ) SUPPLIERS ( Fisher Scientific, 711 Forbes Avenue. Pittsburgh, PA15219-4785, USA. Tel: 1-800-766-7000 ) ( VWR Sc i entific, P.O. Box 7900, San F r ancisco, CA 94120, USA. Tel: 1-800-932-5000 ) Dionex Corporation Dionex Corporation Dionex U.S. Regional Offices Dionex International Subsidiaries IS0 1228 Titan Way Salt Lake City Technical Center Sunnyvale, CA (408) 737-8522 Austria (01) 616 51 25 Belgium (015) 203800 Canada (905) 844-9650 China (852) 2428 3282 Denmark (45) 36 36 90 90 P.O.Box 3603 1515 West 2200 South, Suite A Westmont, IL (630) 789-3660 France 01 39 30 01 10 Germany 06126-991-0 ltaly (06) 66 51 50 52 Japan (06) 6885-1213 The Netherlands (0161) 434303 9001 Sunnyvale, CA Salt Lake City, UT Houston, TX (281)847-5652 Switzerland (062) 205 99 66 United Kingdom (01276) 691722 94088-3603 84119-1484 Atlanta, GA (770)432-8100 *Designed, developed, and manufactured under an NSAl registered ISO 9001 Quality System. LPN 1291-015M 8/01 (408)737-0700 (801)972-9292 Marlton, NJ (856)596-0600 2001 Dionex Corporation Application Update mproved Determination of Trace Anions in High PurityWaters by High-Volume Direct Injection with the EG
确定



还剩4页未读,是否继续阅读?
赛默飞色谱与质谱为您提供《饮用水中无机阴离子检测方案 》,该方案主要用于饮用水中无机阴离子检测,参考标准--,《饮用水中无机阴离子检测方案 》用到的仪器有
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多








