
方案详情
文
Stable carbon isotope ratios are used widely for the authentication of
foodstuffs, especially for the detection of added cane sugar in fruit juices,
spirits and honey. The major deficiency of stable carbon isotope analysis is
that it cannot be used to detect the addition of beet sugar syrups to
C3 crops, as the beet plant also uses the Calvin photosynthetic pathway.
However, the addition of commercial sweeteners such as beet medium
invert syrup can be detected by isotope ratio mass spectrometry if the
abundance of deuterium in the sugars is determined.
方案详情

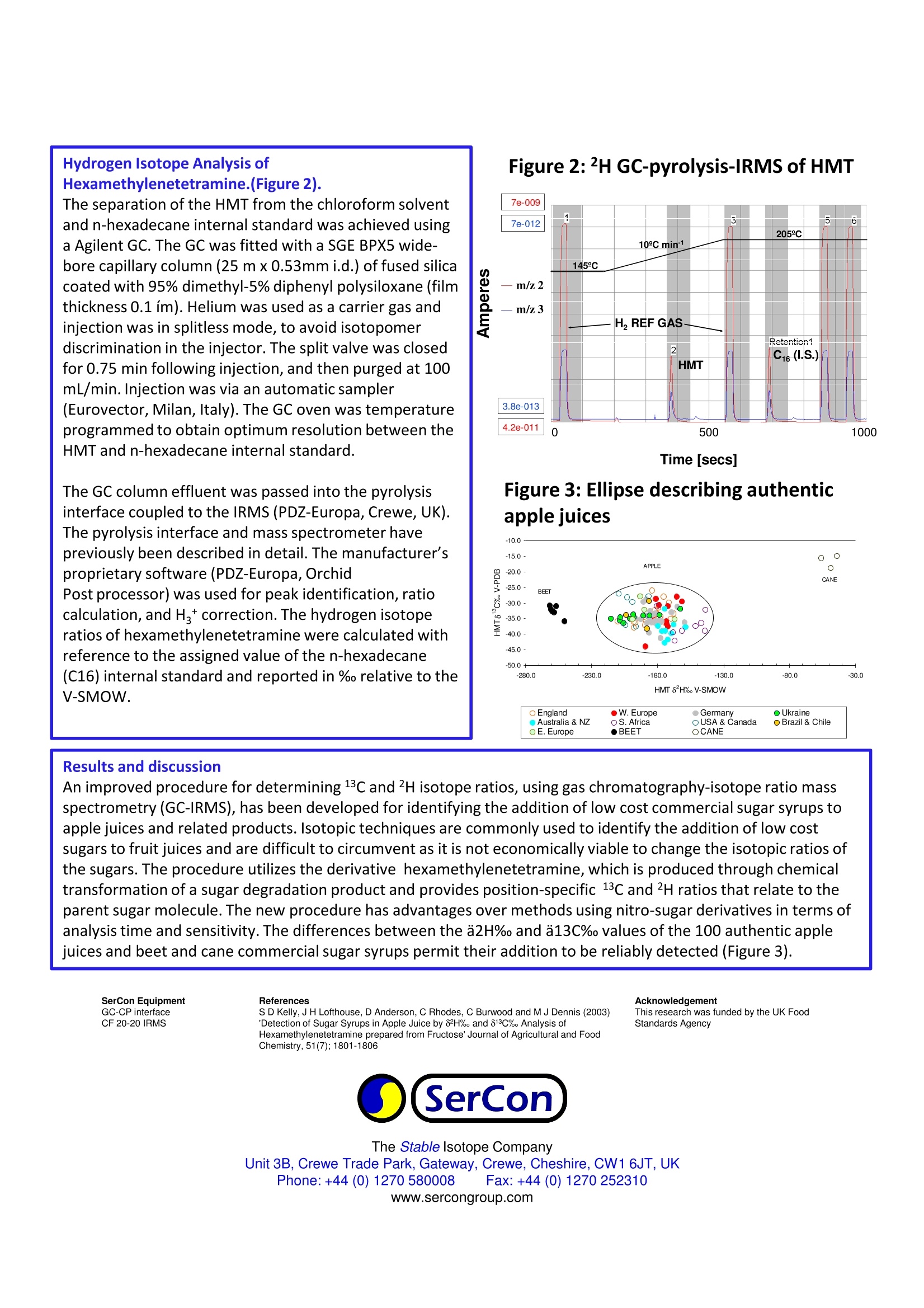
The Stable Isotope CompanyUnit 3B, Crewe Trade Park, Gateway, Crewe, Cheshire, CW1 6JT, UKPhone: +44 (0) 1270 580008 Fax: +44 (0) 1270 252310www.sercongroup.com Application Note 001 Detection of Sugar Syrups in Apple Juice by 62H% and 613C% Analysisof Hexamethylenetetramine Prepared from Fructose Simon D. Kelly# Christopher Rhodest Janice H.Lofthouse* Dominic Andersont Christine E. Burwoodt M. John Dennis* and Paul BreretonT # School of Environmental Science, University of East Anglia, Norwich, United Kingdom NR4 7TJ, t Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, Central Science Laboratory, Sand Hutton, York, United Kingdom YO41 1LZ Introduction Stable carbon isotope ratios are used widely for the authentication offoodstuffs, especially for the detection of added cane sugar in fruit juices,spirits and honey. The major deficiency of stable carbon isotope analysis isthat it cannot be used to detect the addition of beet sugar syrups toCg crops, as the beet plant also uses the Calvin photosynthetic pathway.However, the addition of commercial sweeteners such as beet mediuminvert syrup can be detected by isotope ratio mass spectrometry if theabundance of deuterium in the sugars is determined. KEYWORDS: Apple juice; authenticity;hydrogen isotope; GC-IRMS; pyrolysis Preparation of Hexamethylenetetramine from Fructose (Figure 1). Apple juice fructose was obtained by semi-preparative HPLC and dissolved in deionized water (5 mL). A solutioncontaining 8 g of potassium hydrogen carbonate dissolved in 10 mL of water was added to the fructose solutionand stirred. A 15% w/v periodic acid solution was then added slowly with stirring. After reaction for 45 min at 20℃, the fructose was quantitatively degraded to formaldehyde (C1 and C6) and formic acid (C2 to C5). A total of 5mL of a 35% w/v ammonia solution was added to the reaction mixture. After 3 h at 20℃, the reaction offormaldehyde with ammonia produced the 6:4 tricyclic complex hexamethylenetetramine (HMT). The HMT wasextracted from the reaction residue by shaking with 3 x 10 mL portions of chloroform. mL. This solution was usedfor isotopic analysis by 2H GC-Pyrolysis-IRMS. Hydrogen Isotope Analysis of Hexamethylenetetramine.(Figure2).The separation of the HMT from the chloroform solventand n-hexadecane internal standard was achieved usinga Agilent GC. The GC was fitted with a SGE BPX5 wide-bore capillary column (25 mx0.53mm i.d.)of fused silicacoated with 95% dimethyl-5% diphenyl polysiloxane (filmthickness 0.1 im). Helium was used as a carrier gas andinjection was in splitless mode, to avoid isotopomerdiscrimination in the injector. The split valve was closedfor 0.75 min following injection, and then purged at 100mL/min.Injection was via an automatic sampler(Eurovector, Milan,Italy). The GC oven was temperatureprogrammed to obtain optimum resolution between theHMTand n-hexadecane internal standard.The GC column effluent was passed into the pyrolysisinterface coupled to the IRMS (PDZ-Europa, Crewe,UK).The pyrolysis interface and mass spectrometer havepreviously been described in detail. The manufacturer'sproprietary software (PDZ-Europa,OrchidPost processor) was used for peak identification, ratiocalculation, and Ha* correction. The hydrogen isotoperatios of hexamethylenetetramine were calculated withreference to the assigned value of the n-hexadecane(C16) internal standard and reported in %o relative to theV-SMOW. Figure 2:2H GC-pyrolysis-IRMS of HMT Time [secs] Figure 3:Ellipse describing authenticapple juices Results and discussion An improved procedure for determining 13C and 2Hisotope ratios, using gas chromatography-isotope ratio massspectrometry (GC-IRMS), has been developed for identifying the addition of low cost commercial sugar syrups toapple juices and related products. Isotopic techniques are commonly used to identify the addition of low costsugars to fruit juices and are difficult to circumvent as it is not economically viable to change the isotopic ratios ofthe sugars.The procedure utilizes the derivative hexamethylenetetramine, which is produced through chemicaltransformation of a sugar degradation product and provides position-specific 13c and 2H ratios that relate to theparent sugar molecule. The new procedure has advantages over methods using nitro-sugar derivatives in terms ofanalysis time and sensitivity. The differences between the a2H% and a13C%o values of the 100 authentic applejuices and beet and cane commercial sugar syrups permit their addition to be reliably detected (Figure 3). SerCon EquipmentGC-CP interfaceCF 20-20 IRMS ReferencesS D Kelly, J H Lofthouse, D Anderson, C Rhodes, C Burwood and M J Dennis (2003)'Detection of Sugar Syrups in Apple Juice by 82H%。 and 813C%。 Analysis ofHexamethylenetetramine prepared from Fructose' Journal of Agricultural and FoodChemistry,51(7);1801-1806 AcknowledgementThis research was funded by the UK FoodStandards Agency
确定
还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
北京华沛智同科技发展有限公司为您提供《苹果汁中真伪鉴别检测方案 》,该方案主要用于果蔬汁类及其饮料中理化分析检测,参考标准--,《苹果汁中真伪鉴别检测方案 》用到的仪器有
相关方案
更多







