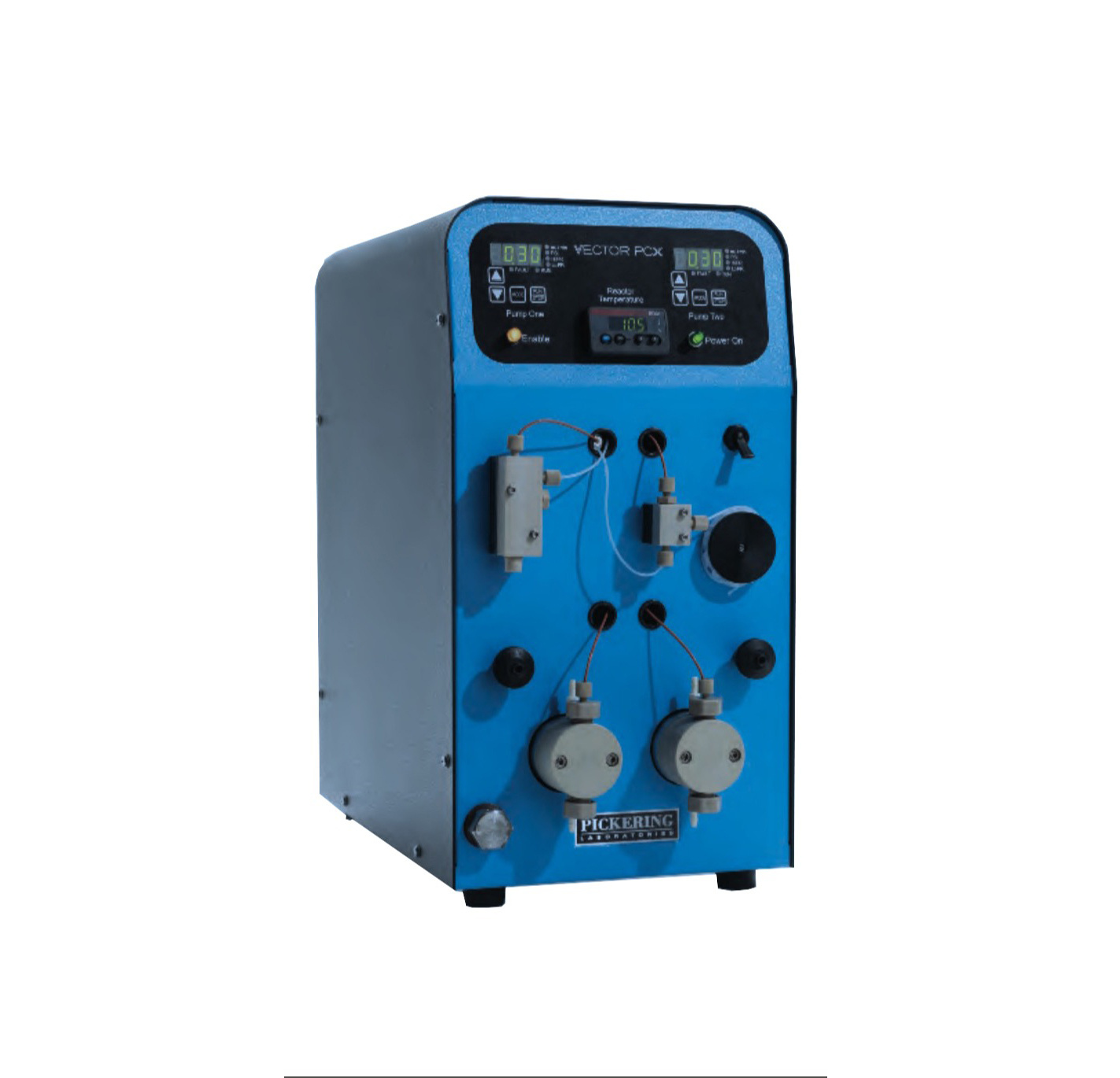
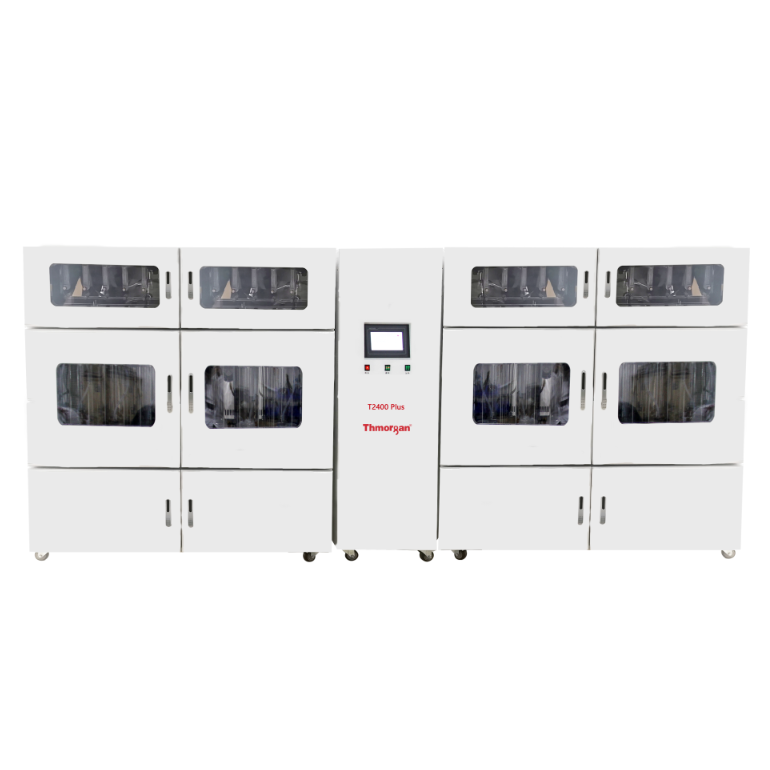
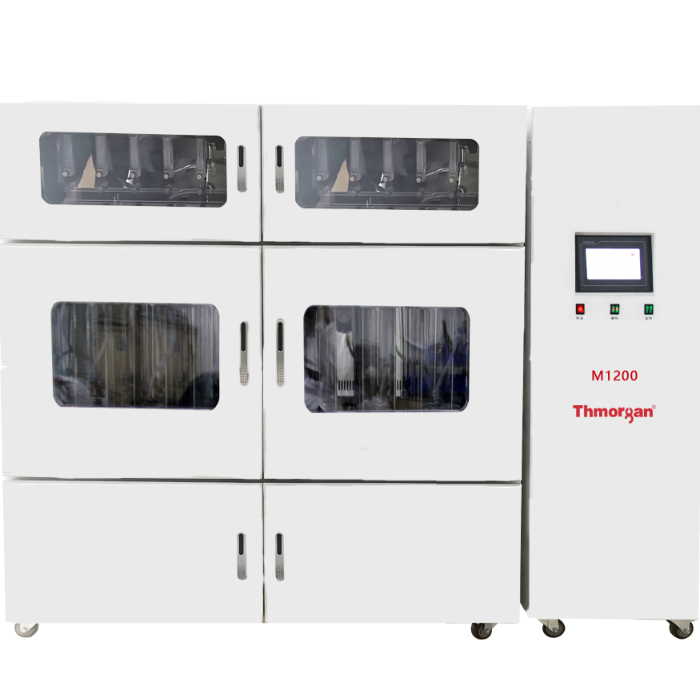
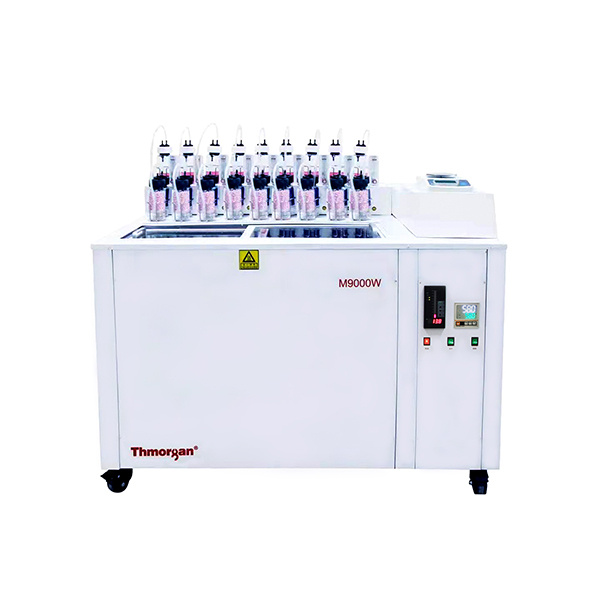
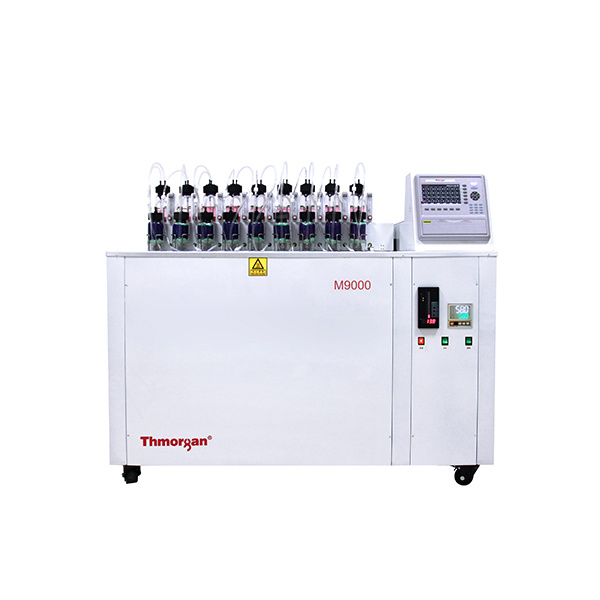
农产品,园艺产品中二氧化碳,氧气检测方案(气调保鲜)
世界贸易改变了食品零售,推动了园艺产品运输和储存技术的发展,提供全年供应的水果和蔬菜。园艺产品极易腐烂,因为水果和蔬菜继续其代谢过程,导致采后成熟和衰老,使它们最终无法进入市场。先进的采后技术对于减少食物浪费至关重要,同时保持高标准的安全和质量。与冷藏,可控气氛(CA)和气调包装(MAP)一起应用于改变农产品的内部和外部环境,降低其代谢活动和延长保质期。CA和MAP都受益于技术创新。呼吸商控制改善了传统和最近开发的CA系统的管理; 天然气清除剂使MAP更有效率; 天然添加剂的加入提高了整个供应链的食品安全性。本文回顾了新的采后技术在操纵气体环境中的应用,并突出了需要进一步研究的领域
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
理化分析
图拉扬科技有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
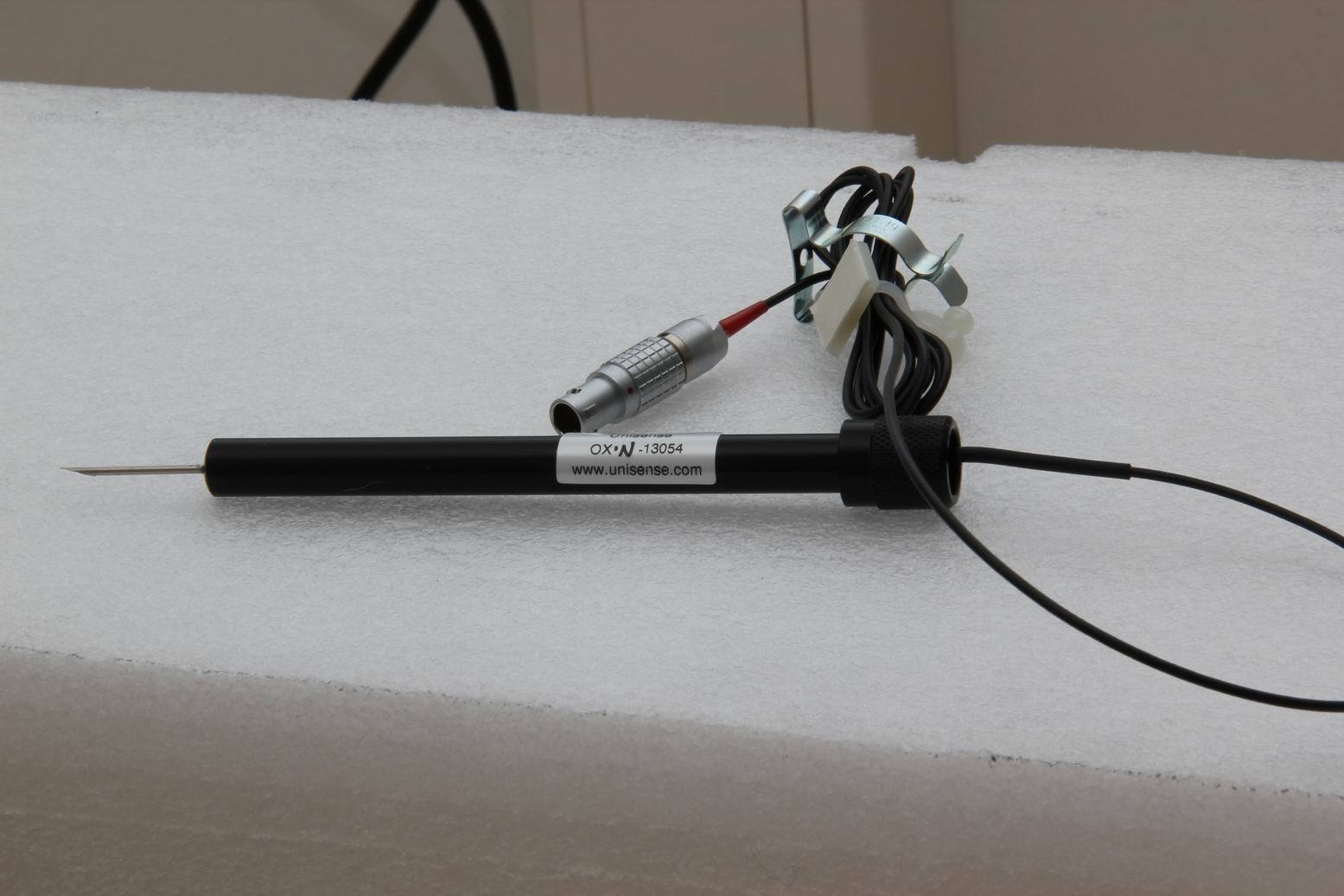
土壤碳中根系分泌物保护作用的机制检测方案(溶解氧测定仪)
主要讨论了根系分泌物对土壤中的碳的保护作用,研究过程中应用unisense氧气微电极对根际周围加入不同的渗入液(草酸、葡萄糖等)后对应的氧浓度剖面分布进行了测试,从而确定了根系分泌物对根际微区微生物呼吸速率的影响。获得的氧浓度剖面表明了草酸的加入显著降低了周围土壤微生物对O2的应用的有效性,其影响的最高深度可达5mm,而葡萄糖和乙酸的添加量则局限在1.5 mm处。草酸处理中的土壤内的微生物呼吸作用超过使用葡萄糖的效果。这也进一步了解根际碳矿化的加速(即启动效应)是否是由渗出物从保护性的矿物-有机结合中释放碳的能力所促进。并发现了一种由根、根相关的真菌和细菌产生的有机酸(草酸),具有较强的金属络合能力,对微生物的生物能利用有限。根际上述的相关实验结构,研究人员发现一种常见的根分泌物草酸会促进使有机化合物从与矿物的保护性联系中释放出来而造成的碳损失。而通过加强微生物与以前的矿物保护化合物,这种间接机制会加速碳损失的过程,该研究结果也为“启动”现象背后的生物-非生物耦合机制提供了一些见解,并挑战了关于矿物质相关的碳是受微生物保护的假设机制
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
植物生理
上海谓载科技有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
棉花栽种粘土中曝气地下灌溉用水的影响检测方案(氧分析仪)
Inadequate oxygen concentration in the root zone is a constraint to plant performance particularly in heavy, compacted and/or saline soils. Sub-surface drip irrigation (SDI) offers a means of increasing
oxygen to plant roots in such soils, provided irrigation water can be hyper-aerated or oxygenated. Hydrogen peroxide (HP) at the rate of 5 litre ha-1 at the end of each irrigation cycle was injected
through SDI tape to a field-grown zucchini (courgette) crop (Cucurbita pepo) on a saturated heavy clay soil in Queensland, Australia. Fruit yield, number and shoot weight increased by 25%, 29% and 24% respectively due to HP treatment compared to the control. Two pot experiments with vegetable soybean (Glycine max) and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) compared the effectiveness of HP and air injection using a MazzeiTM air injector (a venturi), throughout the irrigation cycle in raising crop yield in a heavy clay soil kept at saturation or just under field capacity. Fresh pod yield of vegetable soybean increased by 82-96% in aeration treatments compared with the control. The yield increase was associated
with more pods per plant and greater mean pod weight. Significantly higher above ground biomass and light interception were evident with aeration, irrespective of soil water treatment. Similarly cotton
lint yield increased by 14-28% in aeration treatments compared with the control. The higher lint yield was associated with more squares and bolls per plant which accompanied greater above ground biomass
and an increase in root mass, root length and soil respiration. Air injection and HP effected greater water use, but also brought about an enhancement of water use efficiency (WUE) for pod and lint
yield, and increased leaf photosynthetic rate in both species but had no effect on transpiration rate and stomatal conductance per unit leaf area.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
理化分析
科艺仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
菜用大豆栽种粘土中曝气地下灌溉用水的影响检测方案(氧分析仪)
Inadequate oxygen concentration in the root zone is a constraint to plant performance particularly in heavy, compacted and/or saline soils. Sub-surface drip irrigation (SDI) offers a means of increasing
oxygen to plant roots in such soils, provided irrigation water can be hyper-aerated or oxygenated. Hydrogen peroxide (HP) at the rate of 5 litre ha-1 at the end of each irrigation cycle was injected
through SDI tape to a field-grown zucchini (courgette) crop (Cucurbita pepo) on a saturated heavy clay soil in Queensland, Australia. Fruit yield, number and shoot weight increased by 25%, 29% and 24% respectively due to HP treatment compared to the control. Two pot experiments with vegetable soybean (Glycine max) and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) compared the effectiveness of HP and air injection using a MazzeiTM air injector (a venturi), throughout the irrigation cycle in raising crop yield in a heavy clay soil kept at saturation or just under field capacity. Fresh pod yield of vegetable soybean increased by 82-96% in aeration treatments compared with the control. The yield increase was associated
with more pods per plant and greater mean pod weight. Significantly higher above ground biomass and light interception were evident with aeration, irrespective of soil water treatment. Similarly cotton
lint yield increased by 14-28% in aeration treatments compared with the control. The higher lint yield was associated with more squares and bolls per plant which accompanied greater above ground biomass
and an increase in root mass, root length and soil respiration. Air injection and HP effected greater water use, but also brought about an enhancement of water use efficiency (WUE) for pod and lint
yield, and increased leaf photosynthetic rate in both species but had no effect on transpiration rate and stomatal conductance per unit leaf area.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
理化分析
科艺仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
西葫芦栽种粘土中曝气地下灌溉用水的影响检测方案(氧分析仪)
Inadequate oxygen concentration in the root zone is a constraint to plant performance particularly in heavy, compacted and/or saline soils. Sub-surface drip irrigation (SDI) offers a means of increasing
oxygen to plant roots in such soils, provided irrigation water can be hyper-aerated or oxygenated. Hydrogen peroxide (HP) at the rate of 5 litre ha-1 at the end of each irrigation cycle was injected
through SDI tape to a field-grown zucchini (courgette) crop (Cucurbita pepo) on a saturated heavy clay soil in Queensland, Australia. Fruit yield, number and shoot weight increased by 25%, 29% and 24% respectively due to HP treatment compared to the control. Two pot experiments with vegetable soybean (Glycine max) and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) compared the effectiveness of HP and air injection using a MazzeiTM air injector (a venturi), throughout the irrigation cycle in raising crop yield in a heavy clay soil kept at saturation or just under field capacity. Fresh pod yield of vegetable soybean increased by 82-96% in aeration treatments compared with the control. The yield increase was associated
with more pods per plant and greater mean pod weight. Significantly higher above ground biomass and light interception were evident with aeration, irrespective of soil water treatment. Similarly cotton
lint yield increased by 14-28% in aeration treatments compared with the control. The higher lint yield was associated with more squares and bolls per plant which accompanied greater above ground biomass
and an increase in root mass, root length and soil respiration. Air injection and HP effected greater water use, but also brought about an enhancement of water use efficiency (WUE) for pod and lint
yield, and increased leaf photosynthetic rate in both species but had no effect on transpiration rate and stomatal conductance per unit leaf area.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
理化分析
科艺仪器有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
高效液相色谱柱后衍生技术应用在农作物中草甘膦与氨甲基膦酸的分析
高效液相色谱柱后衍生技术应用在农作物中草甘膦(Glyphosate)与氨甲基膦酸(AMPA)上面的分析
─使用一种用于柱后衍生的简单且可重现的萃取与过滤方法
近年来用于农作物中草甘膦及其主要代谢产物氨甲基膦酸分析的方法往往要承受一个很昂贵和费时的过滤过程,且重现性不够理想,尽管过滤后配备的柱后衍生离子交换色谱法的分析严谨且灵敏。我们现在终于找出了新的方法来提高样品的制备,这就是AOAC的 方法。我们将展现给您这种适宜于经典的离子交换/柱后衍生法的样品制备是如何的简便。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
美瑞泰克科技——Labbuy实验室商城
查看联系电话
前往展位
【EmStat3Blue电化学应用】功能化黑磷纳米复合材料,用于芦丁超灵敏检测的便携式无线智能电化学传感器
摘要:为了建立一种便携、灵敏的黄酮类化合物浓度监测方法,本文建立了一种新的电化学传感方法。通过使用氮掺杂碳化聚合物点(N- CPDs)锚定少层黑磷烯0D-2D异质结构(N-CPDs@FLBP)和金纳米颗粒(AuNPs)作为修饰剂,以碳离子液体电极和丝网印刷电极(SPE)作为基板电极,分别构建了传统的电化学传感器和便携式无线智能电化学传感器。详细地研究了芦丁在所制备的电化学传感器上的电化学行为与分析性能。由于芦丁的电活性基团,纳米复合材料与芦丁之间的π-π堆积和阳离子-π相互作用,芦丁在AuNPs/N-CPDs@FLBP修饰电极上的电化学反应明显增强。在最佳条件下,可实现芦丁的超灵敏检测AuNPs/N-CPDs@FLBP/SPE的检测范围为1.0 nmol L−1 至220.0 μmol L−1检测限为0.33 nmol L−1(S/N = 3)。最后,用两种传感器进行了实时性测试样品并得到了满意的结果。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
芦丁
雷迪美特中国有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
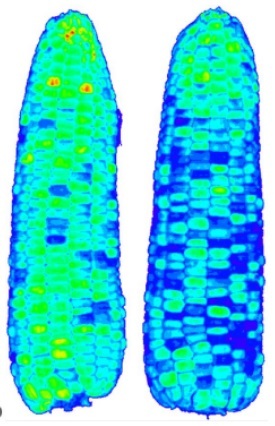
枸杞中品种品质研究检测方案(高光谱仪)
该研究使用一种新的混合卷积神经网络(New-Hybrid-CNN)架构,充分利用像素信息,将每个产地的枸杞样本划分为2500个3D斑块,并将不同产地的枸杞样本随机分为训练集(70%)和测试集(30%),随机选取训练集的20%作为验证集。再使用具有3×3×3卷积核的同构3D卷积架构从高光谱立方信息中提取光谱-空间联合信息,然后使用深度可分离卷积(DSC)来学习空间信息,结合3D卷积和DSC的优点,有效地提取了深层光谱-空间联合信息,使架构更加轻量化。并将3D-CNN、HybridSN和SVM与所提出的方法在同一参数下进行比较,发现New-Hybrid-CNN表现出了更优的分类效果(如下左图),并且所需参数数量最少、用时最短以及最稳定。
实验结果表明,充分结合了高光谱成像中光谱和空间信息的New-hybrid-CNN分类方法能够有效识别不同产地的枸杞,并且具有普适性,有助于解决食品分类和农业应用中的类似问题。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
品种品质研究
北京易科泰生态技术有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供348篇其他检测方案,可分别用于理化分析检测、营养成分检测、重金属检测、前处理检测,参考标准主要有等