方案详情
文
最新一代布鲁克timsTOF fleX使用创新的激光后电离MALDI-2技术获得了较传统MALDI 高1-3个数量级的灵敏度。MALDI-2提高了离子产率并降低了离子抑制效应。同时,MALDI-2还可对传统MALDI不能电离的药物和代谢物分子检测和成像,如甾醇、他汀类、激素、维生素、聚糖等生物分子。这种实质性的改进对于DMPK研究尤其重要。
方案详情

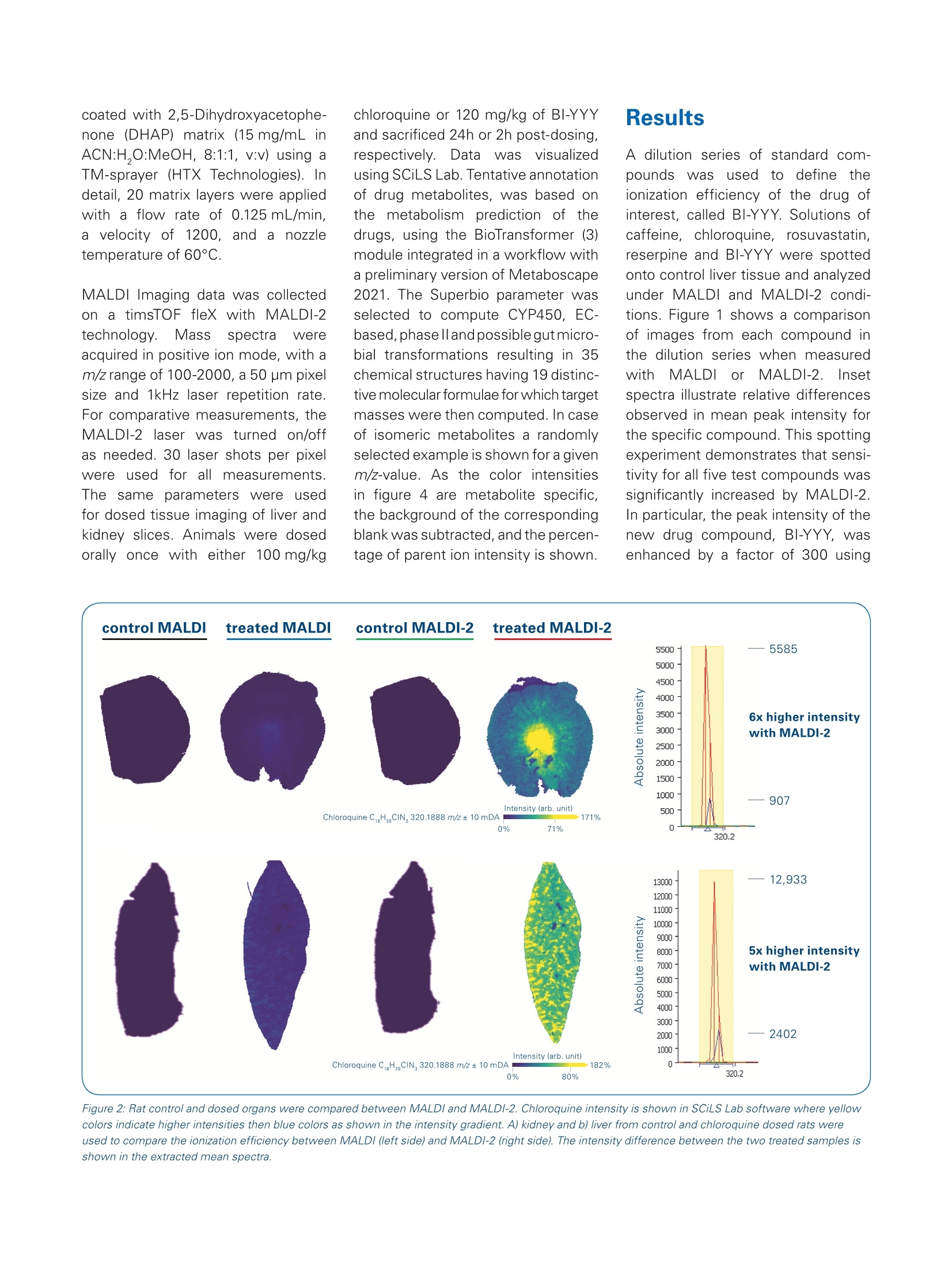
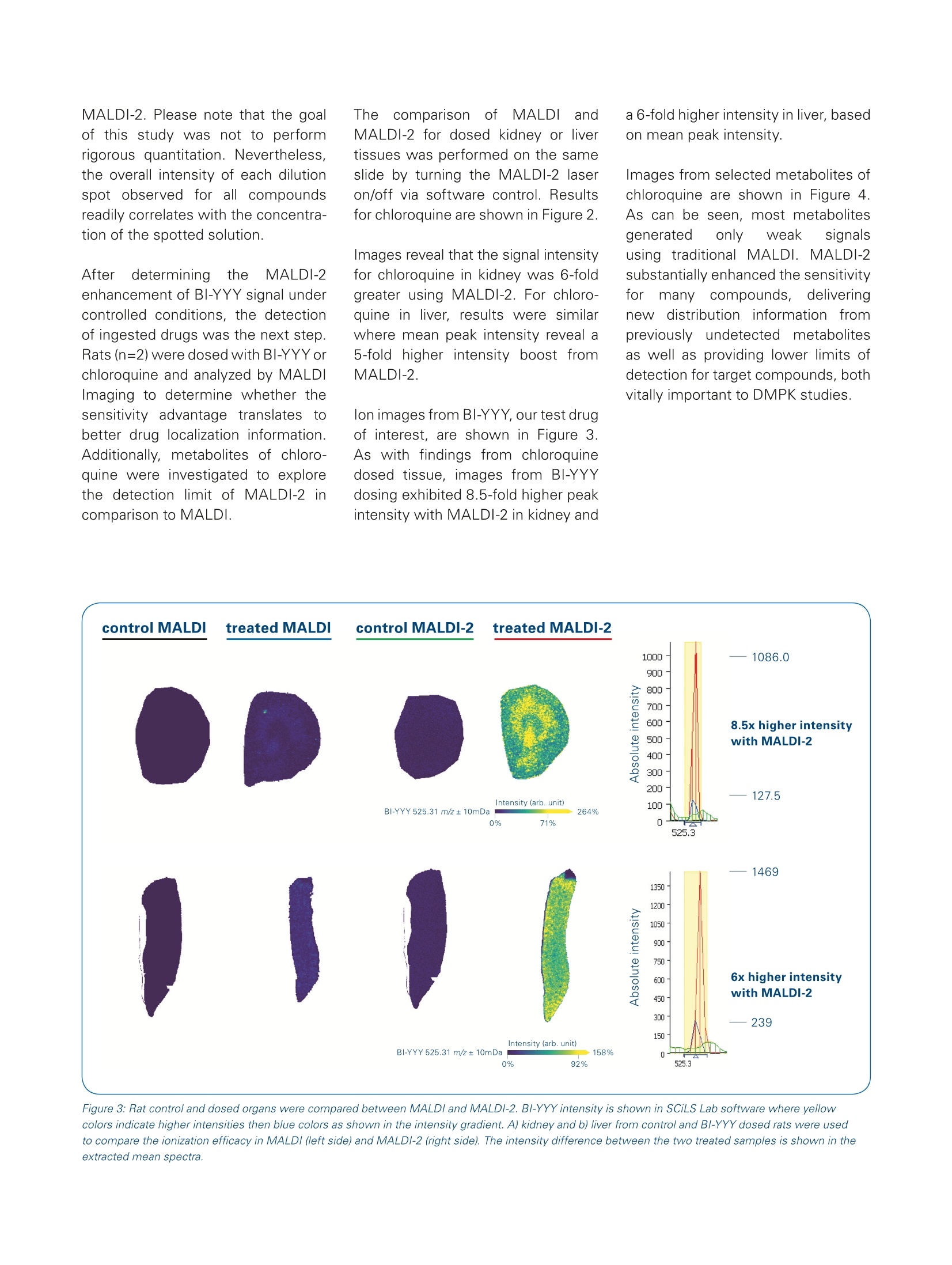
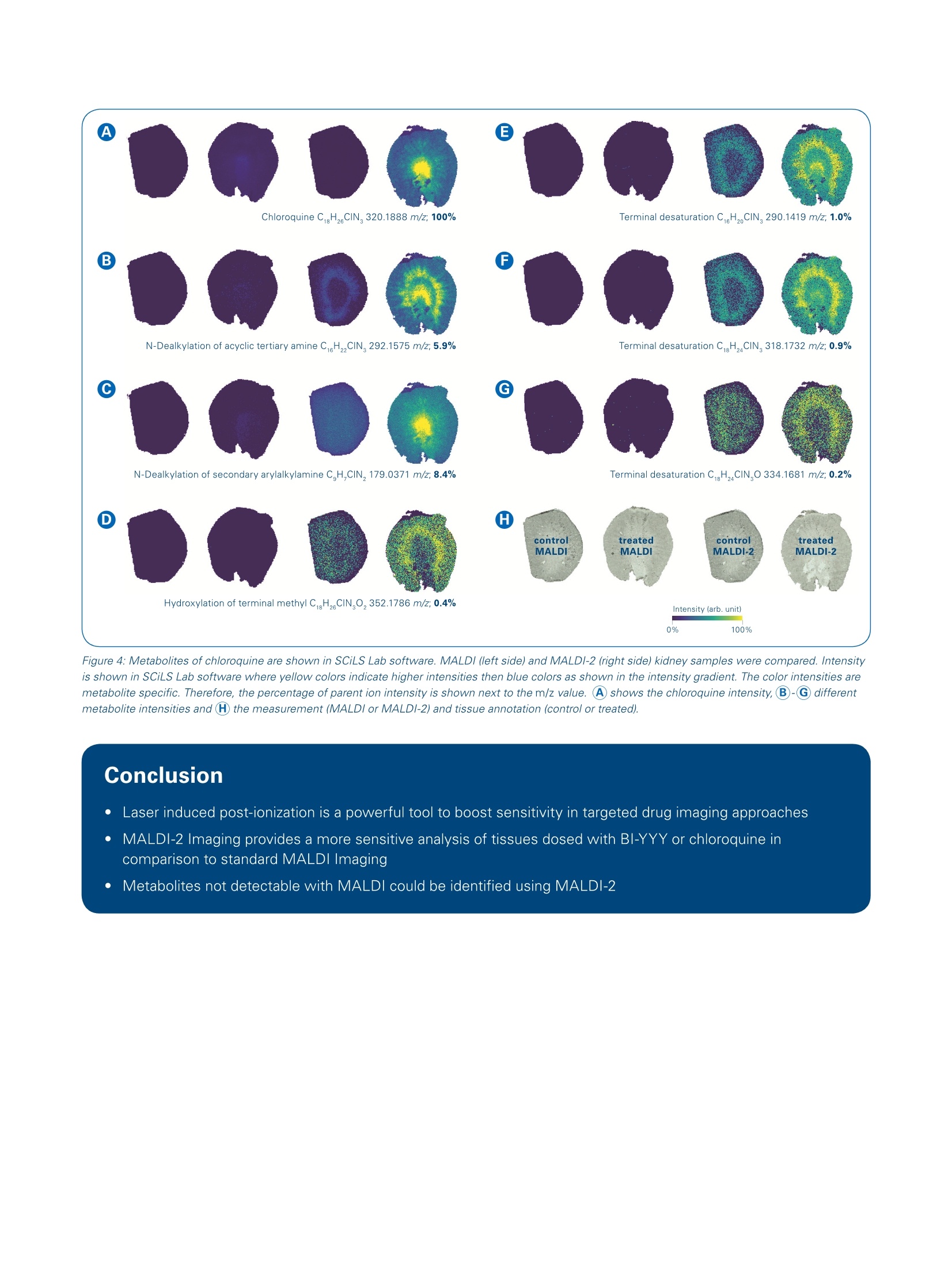
The combination of MALDI-2 and timsTOF fleXbrings targeted drug imaging to the next level Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) Imaging is a powerful toolfor DMPK studies, providing untargeted and targeted measurements that can bedeployed early in the discovery pipeline. Abstract The combination of MALDI withlaser-induced post-ionization(MALDI-2) is a recently introducedmethod that has demonstrated significant enhancement ofsensitivity in mass spectrometryimaging. n thisApplicationNote, we determine the practicalbenefit that MALDI-2 providesfor imaging drug compounds. The MALDI-2ionization(effi-ciency of the investigated drugsis established by using MALDIImaging results on a standarddilutionseries.5.FResultsshowthat MALDI-2 increases the ( A u th ors: C o r i nna Hen ke l1 , An n i ka K o c h , M i c hael Bec ke r 2 , T ob ias O rt h ? , J a n H e n d rik Kobarg' , S h a nno n Co r n e t t3 , C r i s t i na S i l v es c u , Ai k o Barsch ' , M i chae l E aste rli n g ;Bruke r Da l t o n i k Gm bH, B r e m e n , G e r ma n y;2 B o eh rin g e r In g e lheim Ph a r ma G m b H & Co. KG, B i b er ac h/ R i ss, Ge r ma n y ;3B ru ke r D alt o n ik , Bil ler i c a , MA, U SA . ) Figure 1: Spotted dilution series from 100 pM down to 1 pM concentration and blank, the complete series is shown in the first example caffeine.Additionallychloroquine, rosuvastatin, BI-YYY and reserpine are shown in MALDI (left side) and MALDI-2 (right side) mode. A table with the intensity change of the meanpeak intensity in MALDl and MALDI-2 for the whole dilution series is shown. sensitivity for all1 c(ompoundsbyorders of magnitude. Two specificdrugs of interest were further investi-gated in dosed tissue. For both targetcompounds as well as metabolites,MALDI-2 demonstrated】significantenhancement cofsensitivity.Thissubstantial improvement over tradi-tional MALDI Imaging is particularlysignificant for DMPK studies. The timsTOF fleX isthe newestMALDI Imaging instrument inthe Bruker portfolio. With its dualESI/MALDI capability, timsTOF fleXis a versatile analytical tool, rangingfrom targeted label-free molecularimaging to untargeted SpatialOMxstudies that integrate very sensitiveLC-MS/MSPASEFmeasurementswith high-resolution MALDI Imaging.The newest generation of timsTOFfleX is now available with innovative MALDI-2 technology, which resultsinhigher sensitivityfor MALDIImaging studies. MALDI-2 uses a post-ionization laserto improve the MALDI experiment.This provides access to compoundstypically not accessible by MALDl,with very high sensitivity [1,2]. Thepost-ionization leads to both a boostin ion yields and a reduction of ionsuppression effects, resulting in asensitivity boost of up to 2-3 ordersof magnitude compared to traditionalMALDI (depending on sample, matrixand analyte). For a MALDI Imagingexperiment, this increased efficiencytranslates to more than double thenumber of molecules detected perpixel -resulting in much improvedphysiological context. inadditiontoboostingddetectionsensitivitv.MALDI-2 also makes it possible todetect and image chemical classestypically not ionized by traditional MALDI. The post-ionization eventsignificantly boosts the sensitivityofanalyteslikee sterols.statins.hormones,s,vitamins, glycansandother notablebiomolecules.Thisresults in more confident identifica-tions of compounds, especially intargeted approaches. Fresh-frozen liver and kidney tissuesections were cut in 10 pm thicknessand mounted on Bruker IntelliSlides.After drying, a 0.5 ul mixture of thefollowinagssubstances were spot-ted on top of the tissue: caffeine,chloroquine,.rosuvastatin.l,BI-YYY.and reserpine. Each mixture wasspotted in a dilution range from 1 pMto 100 uM (9 spots). The slides werescanned using a Bruker TissueScoutto (obtaina grayscalee referenceimage for automated teaching of theIntelliSlides. The slides were then coated with 2,5-Dihydroxyacetophe-none (DHAP) matrix (15 mg/mL inACN:H,O:MeOH,8:1:1,v:v) using aTM-sprayer (HTX Technologies). Indetail, 20 matrix layers were appliedwith a flow rate of 0.125 mL/min,a velocity of 1200, and ainozzletemperature of 60°C. MALDI Imaging data was collectedon a timsTOF fleX with MALDI-2technology. Mass spectra wereacquired in positive ion mode, with am/z range of 100-2000, a 50 pm pixelsize and 1kHz laser repetition rate.For comparative measurements, theMALDI-2 laser was turned on/offas needed. 30 laser shots per pixelwere used for all measurements.The same parameters were usedfor dosed tissue imaging of liver andkidney slices. Animals were dosedorally once with either 100 mg/kg chloroquine or 120 mg/kg of BI-YYYand sacrificed 24h or 2h post-dosing,respectively..Data wasvisualizedusing SCiLS Lab. Tentative annotationof drug metabolites, was based onthe metabolism prediction of thedrugs, using the BioTransformer (3)module integrated in a workflow witha preliminary version of Metaboscape2021.The Superbio parameter wasselected to compute CYP450, EC-based,phasell andpossible gut micro-bial transformations resulting in 35chemical structures having 19 distinc-tive molecular formulae for which targetmasses were then computed. In caseof isomeric metabolites a randomlyselected example is shown for a givenm/z-value. As the color intensitiesin figure 4 are metabolite specific,the background of the correspondingblank was subtracted, and the percen-tage of parent ion intensity is shown. A dilution series of standard com-poundsWasusedl to define theionization efficiency of the drug ofinterest, called BI-YYY. Solutions ofcaffeine, chloroquine, rosuvastatin,reserpine and BI-YYY were spottedonto control liver tissue and analyzedunder MALDI and MALDI-2 condi-tions. Figure 1 shows a comparisonof images from each compound inthe dilution series when measuredwith MALDI or MALDI-2.liinsetspectra illustrate relative differencesobserved in mean peak intensity forthe specific compound. This spottingexperiment demonstrates that sensi-tivity for all five test compounds wassignificantly increased by MALDI-2.In particular, the peak intensity of thenew drug compound, BI-YYY, wasenhanced by a factor of 300 using Figure 2: Rat control and dosed organs were compared between MALDI and MALDI-2. Chloroquine intensity is shown in SCiLS Lab software where yellowcolors indicate higher intensities then blue colors as shown in the intensity gradient. A) kidney and b) liver from control and chloroquine dosed rats wereused to compare the ionization efficiency between MALDI (left side) and MALDI-2 (right side). The intensity difference between the two treated samples isshown in the extracted mean spectra. MALDI-2. Please note that the goalof this study was not to performrigorous quantitation. Nevertheless,the overall intensity of each dilutionspot observed for all compoundsreadily correlates with the concentra-tion of the spotted solution. Afterdetermininggtthe MALDI-2enhancement of BI-YYY signal undercontrolled conditions, the detectionof ingested drugs was the next step.Rats (n=2) were dosed with BI-YYYorchloroquine and analyzed by MALDIImaging to determine whether thesensitivity advantage translates tobetter drug localization information.Additionally, metabolites of chloro-quine were investigated to explorethe detection limit of MALDI-2 incomparison to MALDI. Theecomparison cof MALDIandMALDI-2 for dosed kidney or livertissues was performed on the sameslide by turning the MALDI-2 laseron/off via software control. Resultsfor chloroquine are shown in Figure 2. lmages reveal that the signal intensityfor chloroquine in kidney was 6-foldgreater using MALDI-2. For chloro-quine in liver, results were similarwhere mean peak intensity reveal a5-fold higher intensity boost fromMALDI-2. lon images from BI-YYY, our test drugof interest, are shown in Figure 3.As with findings from chloroquinedosed tissue, images from BI-YYYdosing exhibited 8.5-fold higher peakintensity with MALDI-2 in kidney and a 6-fold higher intensity in liver, basedon mean peak intensity. Images from selected metabolites ofchloroquine are shown in Figure 4.As can be seen, most metabolitesgenerated only weak signalsusing traditional MALDI. MALDI-2substantially enhanced the sensitivityforrmanvy compounds,i, deliveringnewdistribution information frompreviously undetectedmetabolitesas well as providing lower limits ofdetection for target compounds, bothvitally important to DMPK studies. Figure 3: Rat control and dosed organs were compared between MALDI and MALDI-2. BI-YYY intensity is shown in SCiLS Lab software where yellowcolors indicate higher intensities then blue colors as shown in the intensity gradient. A) kidney and b) liver from control and BI-YYY dosed rats were usedto compare the ionization efficacy in MALDI (left side) and MALDI-2 (right side). The intensity difference between the two treated samples is shown in theextracted mean spectra. Figure 4: Metabolites of chloroquine are shown in SCiLS Lab software. MALDI (left side) and MALDI-2 (right side) kidney samples were compared. Intensityis shown in SCiLS Lab software where yellow colors indicate higher intensities then blue colors as shown in the intensity gradient. The color intensities aremetabolite specific. Therefore, the percentage of parent ion intensity is shown next to the m/z value. A) shows the chloroquine intensity, B-G differentmetabolite intensities and (H) the measurement (MALDI or MALDI-2) and tissue annotation (control or treated). Conclusion Laser induced post-ionization is a powerful tool to boost sensitivity in targeted drug imaging approaches MALDI-2 Imaging provides a more sensitive analysis of tissues dosed with BI-YYY or chloroquine incomparison to standard MALDI Imaging Metabolites not detectable with MALDI could be identified using MALDI-2 Learn More You are looking for further Information? Check out the link or scan the QR code for more details. www.bruker.com/timstofflex References [1] Soltwisch J et al. (2015). Mass spectrometry imaging with laserinduced postionization, Science, 348, 211-215. [2]Barre FPY et al. (2019). Enhanced Sensitivity Using MALDI Imaging Coupled with Laser Postionization (MALDI-2) forPharmaceutical Research,Anal. Chem., 91, 10840-10848 [3]Djoumbou-Feunang et al. (2019). BioTransformer: a comprehensive computational tool for small molecule metabolismprediction and metabolite identification, Journal of Cheminformatics, 5;11(1):2 For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Clinical Diagnostic Procedures. Bruker Daltonik GmbH Bruker Scientific LLC Bremen· GermanyBillerica,MA·USAPhone +49(0)421-2205-0Phone +1(978) 663-3660 ms.sales.bdal@bruker.com-www.bruker.com 基质辅助激光解吸电离(MALDI)成像是DMPK研究的有力工具,它提供了药物和代谢物的特异性测量,用于早期药物筛选。timsTOF fleX是布鲁克新型的MALDI成像质谱系统,凭借ESI/MALDI双重离子源和把高灵敏的LC-MS/MS PASEF测量与高分辨率MALDI成像相结合,完成从目标分子成像到非目标SpatialOMx研究。最新一代的timsTOF fleX使用创新的激光后电离MALDI-2技术获得了较传统MALDI 高1-3个数量级的灵敏度【1-2】。MALDI-2提高了离子产率并降低了离子抑制效应。同时,MALDI-2还可对传统MALDI不能电离的药物和代谢物分子检测和成像,如甾醇、他汀类、激素、维生素、聚糖等生物分子。这种实质性的改进对于DMPK研究尤其重要。本应用报告测试了MALDI-2对添加BI-YYY药物标样组织切片灵敏度的增强,并在大鼠用氯喹或BI-YYY给药后,用MALDI-2成像分析,以确定灵敏度提高是否转变为重要的药物定位信息。此外,还研究了氯喹代谢物分布,测试MALDI-2在检出限上的提高。样品制备与实验条件实验使用大鼠新鲜肝脏和肾脏组织冷冻切片,切片安放在布鲁克IntelliSlide™自定位玻片上。在切片表面点加咖啡因、氯喹、瑞舒伐他汀、BI-YYY和利血平混合物,施加2,5-二羟苯乙酮(DHAP)基质,在1-100µM浓度范围内测试MALDI-2的灵敏度增加。随后,大鼠在分别给予氯喹或 BI-YYY药物2小时或24小时后取组织样本,在配置了MALDI-2的timsTOF fleX质谱系统上采集切片的质谱数据,像素尺寸为50µm。用SCiLS Lab软件处理得到组织切片分子图像,然后用MetaboScape® 2021软件中的BioTransformer模块预测了35个代谢产物[3],对其中19个特别代谢物做了鉴定和强度测量,并计算了相对含量。结果与讨论标准小分子药物被用来考察BI-YYY药物电离效率的增加。比较系列浓度咖啡因、氯喹、瑞舒伐他汀、利血平和BI-YYY混合物的对照肝组织的MALDI和MALDI-2分子图像(见图1),MALDI-2显著提高了所有五种受试化合物的灵敏度,其中新的药物BI-YYY的峰值强度使用MALDI-2提高了300倍。图1: 对照和氯喹或BI-YYY给药大鼠,用MALDI和MALDI-2的SCiLS Lab成像结果比较。不同颜色表示强度梯度变化,黄色比蓝色有更高的强度。动物给药后的MALDI-2成像显示肾脏和肝脏中氯喹峰强度分别高出6倍和5倍,BI-YYY的峰强度增加了8.5倍和6倍。图2显示了所选氯喹代谢物的图像。可以看出,传统MALDI对大多数代谢物的信号微弱的,而MALDI-2对许多化合物的响应显著提高,获得了以前未被检测到的代谢物的组织分布信息和更低的目标化合物的检测限,这对DMPK研究都至关重要。图2:氯喹的代谢物,用MALDI和MALDI-2用SCiLS Lab成像结果比较。不同颜色表示强度梯度变化,黄色比蓝色有更高的强度。结论结果表明,MALDI-2激光诱导后电离是提高药物成像灵敏度的有力工具,可对更多类型的化合物分子测量,得到BI-YYY或氯喹在体内代谢和组织分布更多的信息。参考文献[1] Soltwisch J. et al. Mass spectrometry imaging with laser-induced postionization, Science, 2015, 348: 211-215.[2] Barré FPY et al. Enhanced Sensitivity Using MALDI Imaging Coupled with Laser Postionization (MALDI-2) for Pharmaceutical Research, Anal. Chem., 2019, 91: 10840-10848[3] Djoumbou-Feunang et al. BioTransformer: a comprehensive computational tool for small molecule metabolism prediction and metabolite identification, Journal of Cheminformatics, 2019, 5;11(1):2
确定



还剩4页未读,是否继续阅读?
布鲁克·道尔顿(Bruker Daltonics)为您提供《大鼠新鲜肝脏和肾脏组织冷冻切片中质谱成像分析检测方案(液质联用仪)》,该方案主要用于其他中生化检验检测,参考标准--,《大鼠新鲜肝脏和肾脏组织冷冻切片中质谱成像分析检测方案(液质联用仪)》用到的仪器有布鲁克 timsTOF fleX with MALDI-2
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多
















