作为痕量证据的玻璃碎片有多种分析方法。玻璃的物理特性,如颜色、厚度、形状或纹理,可以作为di一次筛选进行直观研究。折射率(RI)也被用作将玻璃碎片与已知来源相匹配的技术。然而,单独RI不能区分某些玻璃类型。例如,浮法玻璃和容器玻璃的折射率值非常相似,尽管这两种玻璃具有非常不同的化学成分。此外,平板玻璃制造工艺的巨大改进,使得使用物理性质和RI的检测来区分非常相似的玻璃碎片的有效性降低。
在法医学调查工具箱中加入元素分析可以显著提高玻璃鉴定结果的可信度。在玻璃制造过程中会添加不同的微量元素,如改性剂、着色剂、脱色剂或精制剂。因此,以高灵敏度分析玻璃碎片中诸如Li、B、Al、Ca、Mg、K、Sr、Ti、Fe和Zr等元素的能力,是充分利用元素分析进行玻璃鉴别的关键。
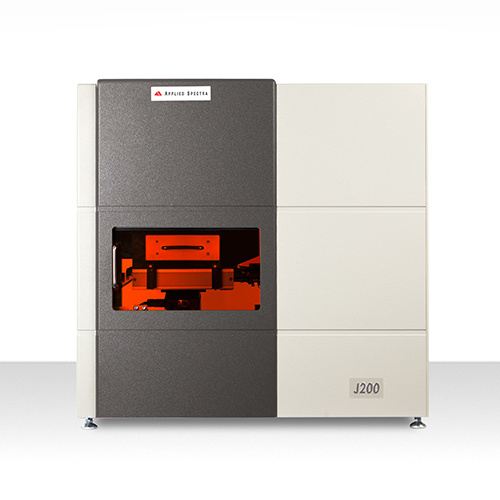
激光诱导击穿光谱(LIBS)是一种新兴的基于等离子体光发射光谱的快速元素分析技术。与XRF和SEM-EDS相比,LIBS可以提供更高的检测灵敏度和测量更轻的元素。LIBS是一种保持样品完整性的微采样技术。LIBS的检测速度也非常快,单个样品的测量持续时间不超过几秒,这使分析人员能够收集大量的比较数据,以减少类型I(假阳性)和类型II(假阴性)的错误。本应用简报将重点介绍如何利用J200 LIBS有效地分析玻璃样品。
方案详情

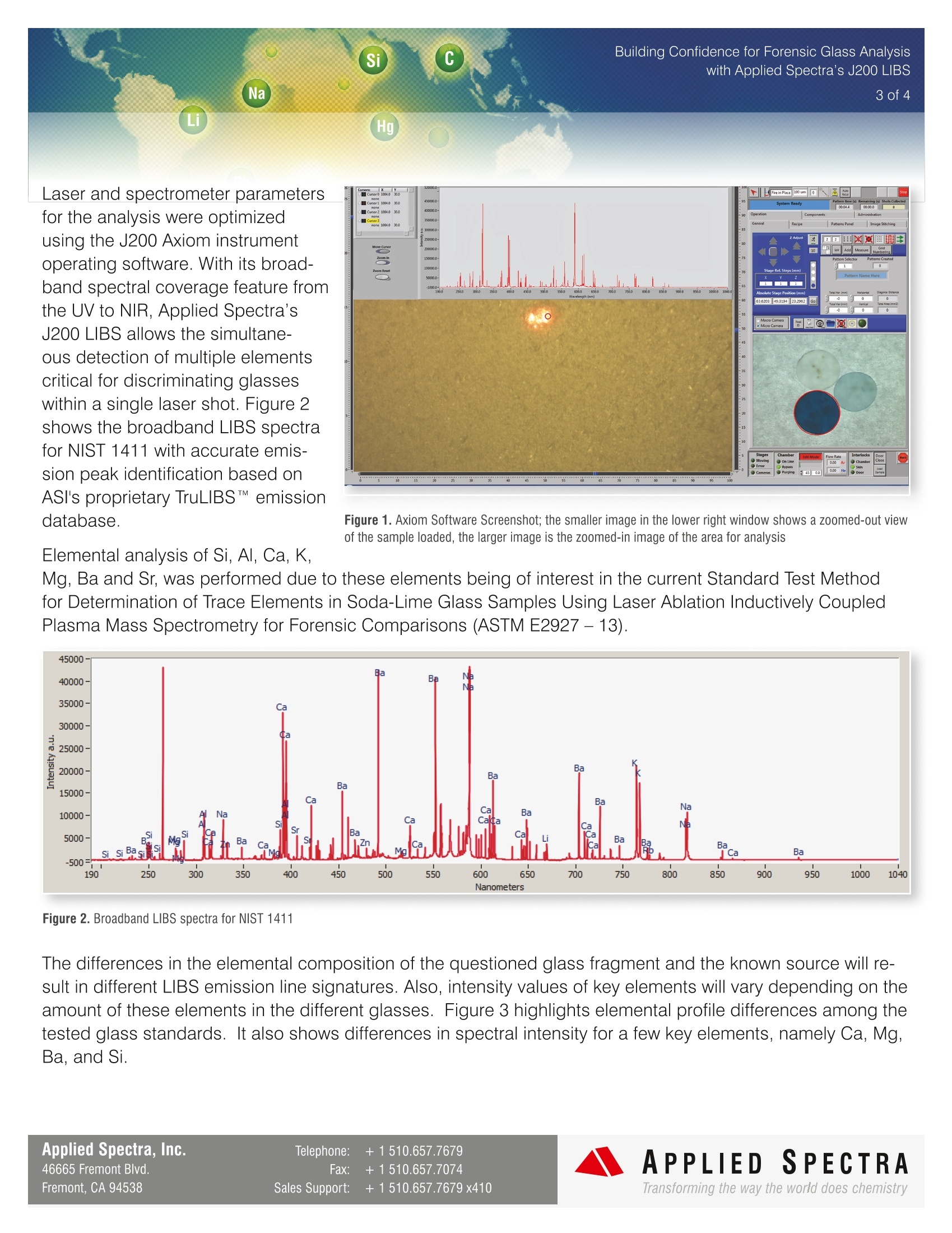
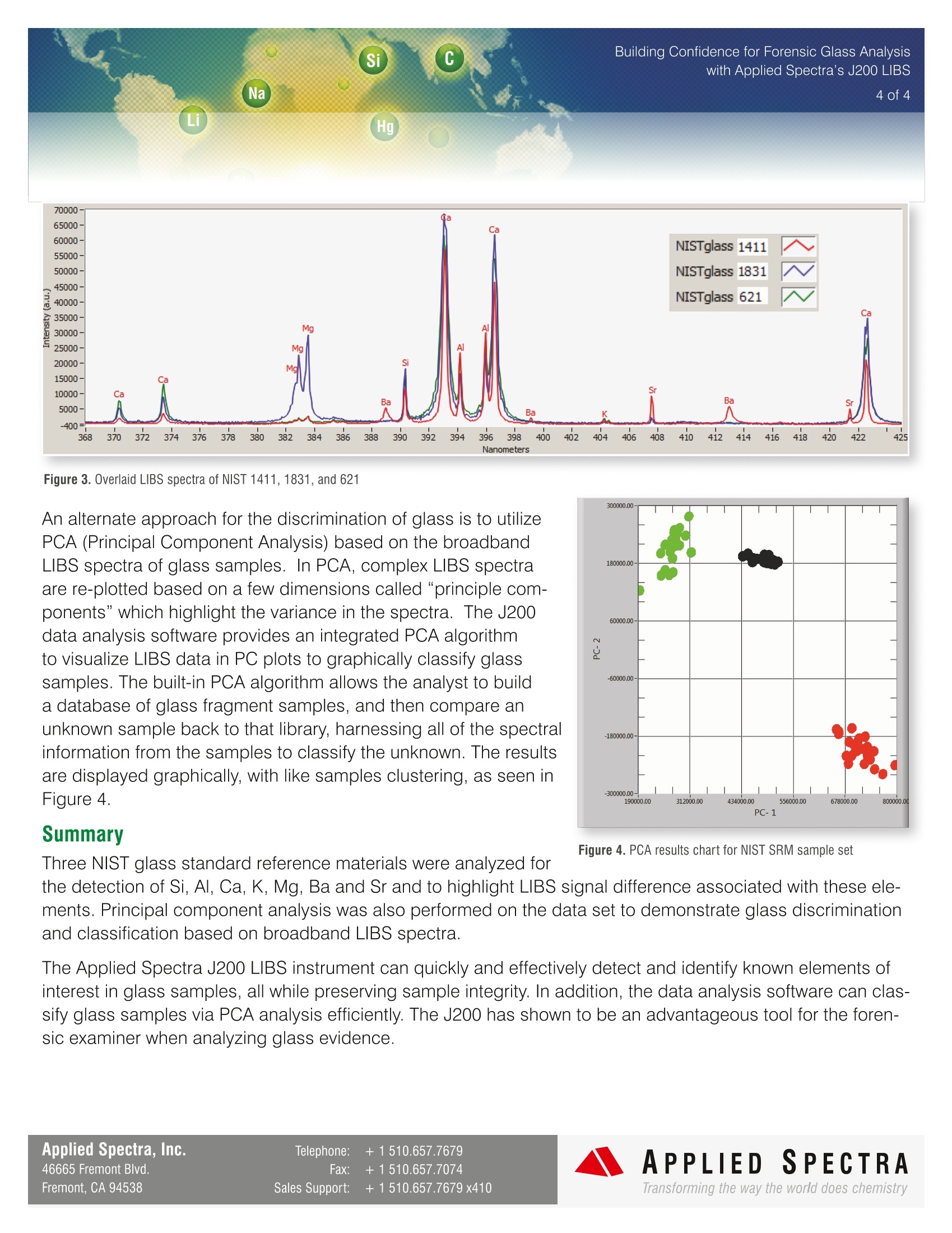
Building Confidence for Forensic Glass Analysiswith Applied Spectra's J200 LIBS2 of 4 APPLIEDSPECTRAwww.AppliedSpectra.comTransforming the way the world does chemistry Glass fragments are oneimportant type of forensic traceevidence that can help to linkan individual or vehicle tothe scene of a crime. Theforensic analyst needs a reliablemeans of matching questionedglass fragments to aKnown source. Glass fragments as traceevidence are analyzed in anumber of ways. Physical properties of glass such as color, thickness, shape, or texture can be investigated visually as a first screening. Refractive index (Rl) also has been used as a techniquefor matching glass fragments to known sources. However,Rl alone can fail to differentiate certain glass types. Forinstance, float and container glass exhibit refractive indexvalues that are extremely similar, although these twoglasses have very different chemical compositions. Also,vast improvements in sheet glass manufacturing processeshave made investigation of physical properties and Rlmeasurement less effective in differentiating very similarglass fragments for forensic purposes. Applied Spectra Inc.’s J200 LIBS Instrument Li Hg Adding elemental analysis to the forensic technician's investigational toolbox can significantly enhance theconfidence of glass discrimination results. Different elements are added during the glass manufacturingpro-cess in trace quantities as modifiers, colorants, de-colorants, or refining agents. For this reason, theability to analyze elements in glass fragments such as Li, B, Al, Ca, Mg, K, Sr, Ti, Fe, and Zr with highsensitivity is key to harnessing the full power of elemental analysis for glass discrimination. Adding elemental analysis to theforensic technician's toolbox canenhance the confidence of glassdiscrimination results. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a rap-idly emerging elemental analysis technique based onthe emission spectroscopy of the plasma light gener-ated from a focused laser beam. Compared to XRF andSEM-EDS, LIBS can offer higher detection sensitivityand measure lighter elements. LIBS is a micro-sam-pling technique which preserves sample integrity. LIBSis also extremely fast with a single measurement last- Operating Parameters ● J200 LIBS system ● 266 nm laser Broadband spectral coverage SSamples: NIST SRM 621, 1411, and 1831,see Table 1. Sample Analysis Three glass standards from NIST (NationalInstitute of Standards and Technology) wereanalyzed using Applied Spectra's J200 LIBSinstrument with broadband spectral coverage.A 266 nm wavelength laser was used for ef-ficient energy coupling for the glass sample, as Table 1. NIST SRM Information NIST 1411 NIST 621 NIST 1831 SiO2 58.04 %m/m SiO2 71.13 %m/m SiO2 73.08 %m/m Na20 10.14 %m/m Na20 12.74 %m/m Na20 13.32 %m/m AI203 5.68 %m/m AI203 2.76 %m/m AI203 1.21 %m/m K20 2.97 %m/m K20 2.01 %m/m K20 0.33 %m/m CaO 2.18 %m/m CaO 10.71 %m/m CaO 3.51 %m/m MgO 0.33 %m/m MgO 0.27 %m/m MgO 0.087 %m/m Fe203 0.05 %m/m Fe203 0.04 %m/m Fe203 0.019 %m/m TiO2 0.02 %m/m TiO2 0.014 %m/m TiO2 BaO 5 %m/m BaO 0.12 %m/m BaO SrO 0.09 %m/m SrO 0.27 %m/m SrO ZnO 3.85 %m/m ZnO ZnO B203 10.94 %m/m B203 B203 %m/m SO3 0.13 %m/m SO3 0.25 %m/m ZrO2 0.007 %m/m K20 0.33 %m/m FeO 0.025 %m/m the samples' integrity. Three glass samples were placed in the drawer-type sample chamber. Using AppliedSpectra’s Axiom operating software, the samples were visualized, specific areas were selected for analysis,and LIBS spectra were rapidly collected for elemental identification and composition comparison. Si CBuilding Confidence for Forensic Glass Analysiswith Applied Spectra's J200 LIBSNa 3 of 4LiHg Laser and spectrometer parametersfor the analysis were optimizedusing the J200 Axiom instrumentoperating software. With its broad-band spectral coverage feature fromthe UV to NIR, Applied Spectra’sJ200 LIBS allows the simultane-ous detection of multiple elementscritical for discriminating glasseswithin a single laser shot. Figure 2shows the broadband LIBS spectrafor NIST 1411 with accurate emis-sion peak identification based onASI's proprietary TruLIBSM emissiondatabase. Figure 1. Axiom Software Screenshot; the smaller image in the lower right window shows a zoomed-out viewof the sample loaded, the larger image is the zoomed-in image of the area for analysis Elemental analysis of Si, Al, Ca, K, Mg, Ba and Sr, was performed due to these elements being of interest in the current Standard Test Methodfor Determination of Trace Elements in Soda-Lime Glass Samples Using Laser Ablation Inductively CoupledPlasma Mass Spectrometry for Forensic Comparisons (ASTM E2927-13). Figure 2. Broadband LIBS spectra for NIST 1411 The differences in the elemental composition of the questioned glass fragment and the known source will re-sult in different LIBS emission line signatures. Also, intensity values of key elements will vary depending on theamount of these elements in the different glasses. Figure 3 highlights elemental profile differences among thetested glass standards. It also shows differences in spectral intensity for a few key elements, namely Ca, Mg,Ba, and Si. Applied Spectra, Inc. Telephone: +1510.657.7679 APPLIEDSPECTRATransforming the way the world does chemistry 46665 Fremont Blvd. Fax: +1510.657.7074 Fremont, CA 94538 Sales Support: +1510.657.7679 x410 Si C Na 4 of 4 Li Hg Figure 3. Overlaid LIBS spectra of NIST 1411, 1831, and 621 An alternate approach for the discrimination of glass is to utilizePCA (Principal Component Analysis) based on the broadbandLIBS spectra of glass samples. In PCA, complex LIBS spectraare re-plotted based on a few dimensions called “principle com-ponents” which highlight the variance in the spectra. The J200data analysis software provides an integrated PCA algorithmto visualize LIBS data in PC plots to graphically classify glasssamples. The built-in PCA algorithm allows the analyst to builda database of glass fragment samples, and then compare anunknown sample back to that library, harnessing all of the spectralinformation from the samples to classify the unknown. The resultsare displayed graphically, with like samples clustering, as seen inFigure 4. 可疑玻璃碎片和已知来源玻璃的元素组成的差异将导致不同的LIBS发射线特征。同样,关键元素的光谱强度值也会随着不同玻璃中这些元素的含量而变化。图3突出显示了被测玻璃标准之间的元素差异。它还显示了几个关键元素的光谱强度差异,即Ca、Mg、Ba和Si。 图3 NIST 1411、1831和621的叠加LIBS谱另一种鉴别玻璃的方法是利用基于玻璃样品宽带LIBS光谱的主成分分析(PCA)。在主成分分析中,复杂的LIBS光谱是基于几个称为“主成分”的维度重新绘制的,这些维度强调了光谱的差异。J200数据分析软件提供了一个集成的主成分分析算法来使LIBS数据可视化,以图形化分类玻璃样品。内置的PCA算法允许分析人员建立一个玻璃碎片样本的数据库,然后将一个未知样本与该库进行比较,利用样本中的所有光谱信息对未知进行分类。结果以图形化方式显示,具有相似的样本聚类,如图4。图4 NIST SRM样本集的主成分分析结果图
确定


还剩2页未读,是否继续阅读?
北京富尔邦科技发展有限责任公司为您提供《玻璃中多元素检测方案(激光诱导击穿)》,该方案主要用于建筑玻璃中多元素检测,参考标准--,《玻璃中多元素检测方案(激光诱导击穿)》用到的仪器有美国ASI 激光诱导击穿光谱仪(LIBS)
推荐专场
相关方案
更多














