方案详情
文
环氧树脂是现成的载体;没有强制的活化步骤。然而再开始固定程序前,可以使用具有所需缓冲液的步骤清洗。
由于环氧基团倍蛋白石/酶基团的亲和攻击打开,所以会发生固定化。环氧开环将在载体与蛋白/酶亲核基团之间形成共价键。
蛋白质/酶固定化试验通常是分批进行的,用搅拌或轨道振动筛(不要使用磁棒搅拌器),以保持树脂悬浮状态,避免产生泡沫,这通常是蛋白质变性的结果。
所提供的建议必须作为一般准则加以考虑,并不是针对所有具体的固定案例都详尽无遗。
方案详情

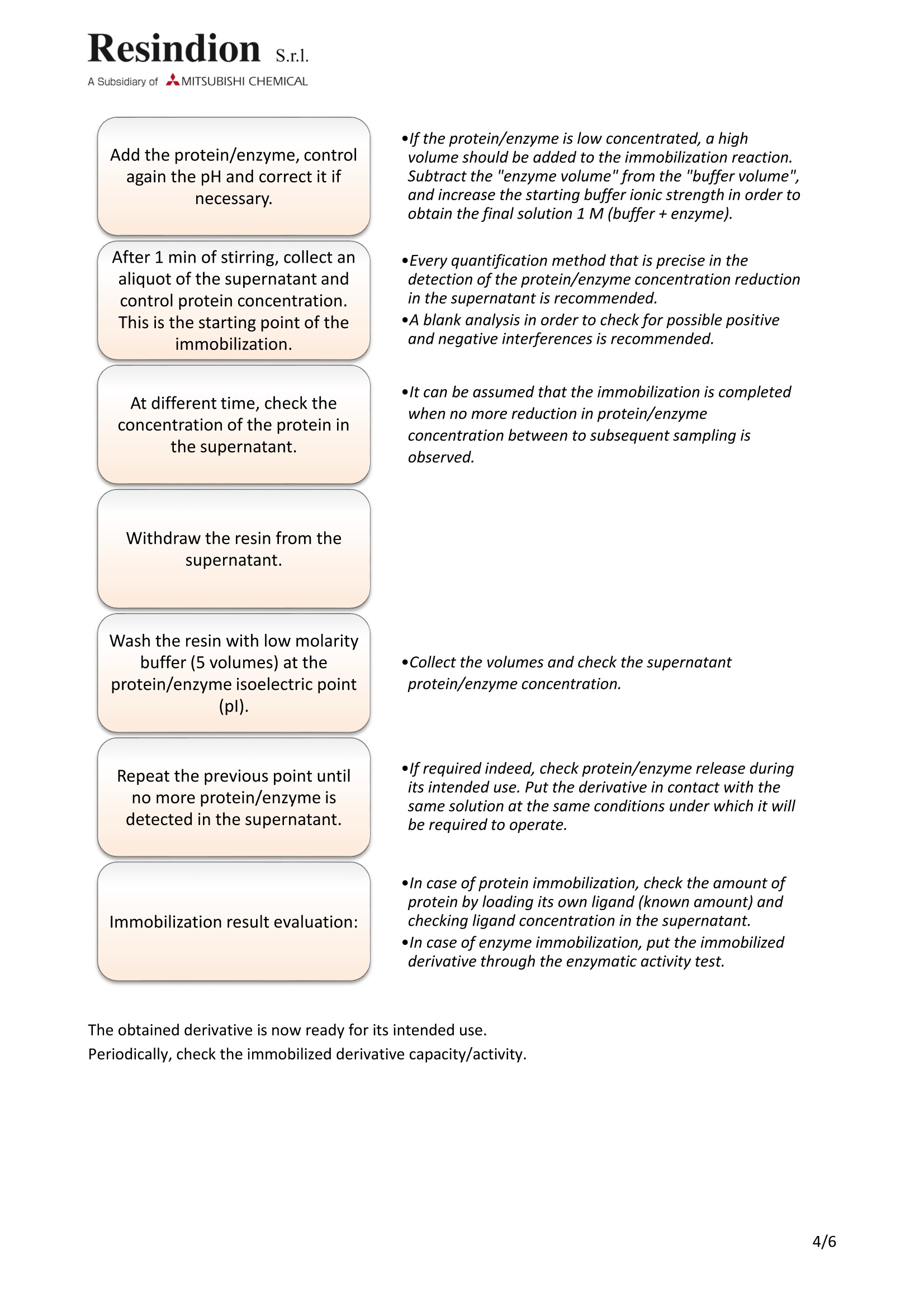
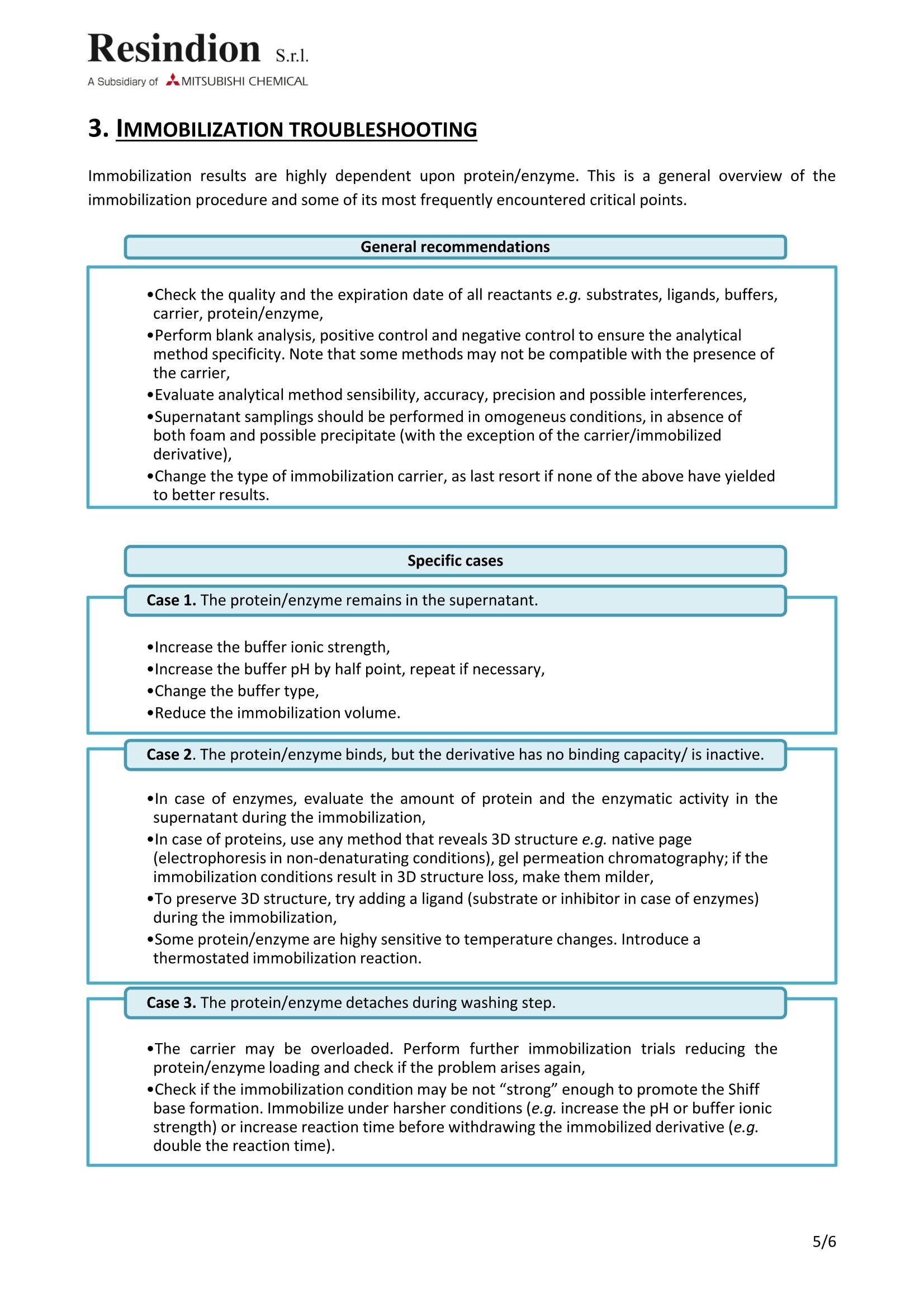
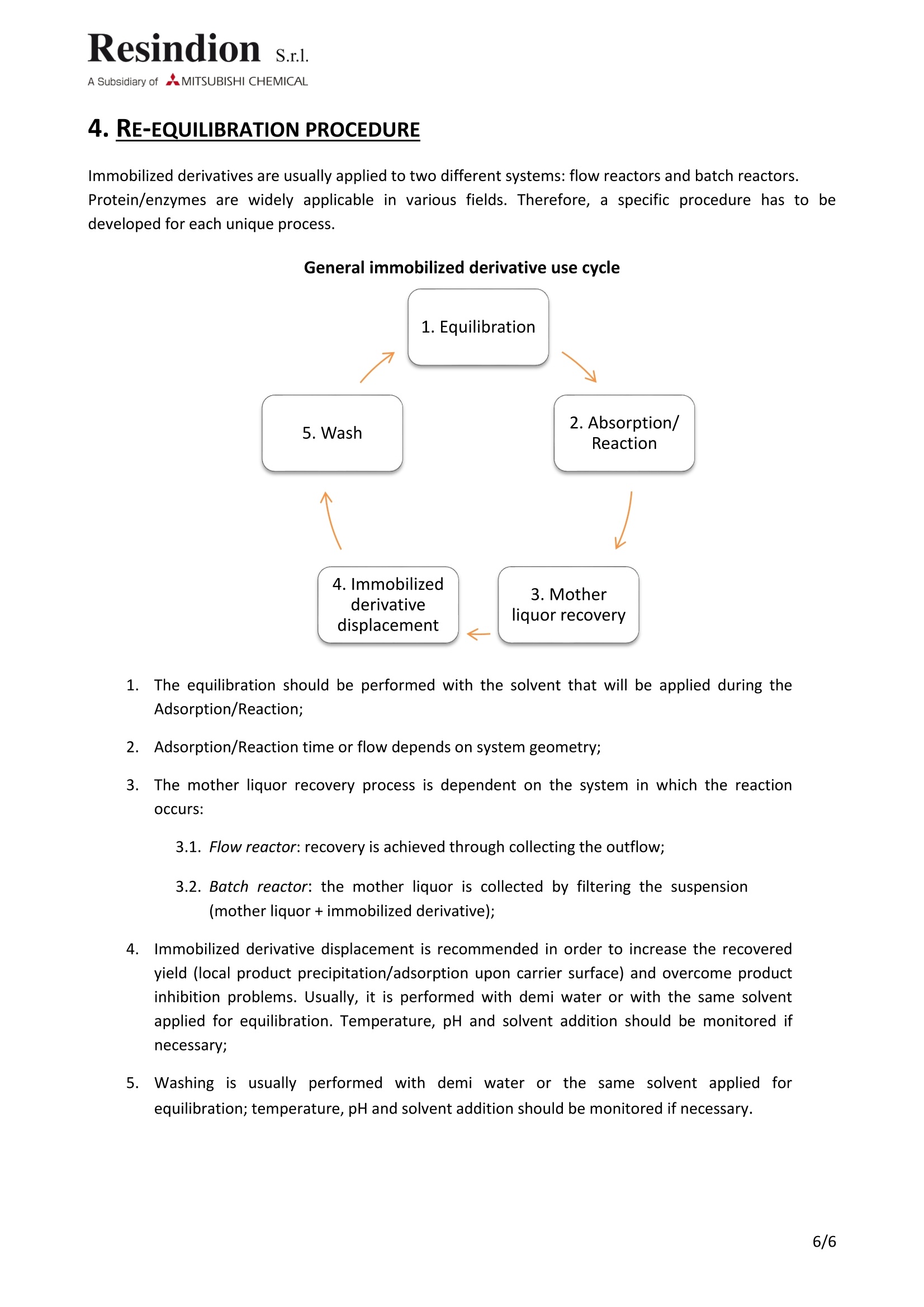
Resindion. S.r.l.A Subsidiary of AMITSUBISHI CHEMICAL Documentation: Guideline |D Number: GL-0058Subject: Protein/enzyme immobilizationRevision Date: 31st July, 2017 Revision: 001procedure on epoxy carrier GUIDELINE ID Number GL-0058 Revision Date Effective date Revision 31st July, 2017 001 3rd July, 2017 Subject Protein/enzyme immobilization procedure on epoxycarrier SUMMARY Summary...... .2 Glossary......... .2 1. Background.......... ..3 1.1. Pre-treatment ....... .3 2. Immobilization....... .3 3. Immobilization troubleshooting ........ 5 4. Re-equilibration procedure ....... .6 GLOSSARY 1 volume: the amount of carrier multiplied by its density. ●Target: protein/enzyme that is to be immobilized. Carrier/solid support: resin that will be bound to the protein/enzyme. Denaturation: process through which the protein/enzyme loses its 3D structure and, therefore,its activity. ●Supernatant: the liquid lying above a sediment or settled precipitate. In this case the precipitateis the carrier. Immobilized derivative: the protein/enzyme bound to the carrier. Mother liquor: solution in which the reaction has occurred. Specificity: the ability to assess unequivocally the analyte in the presence of components, which areexpected to be present. These might include impurities, degradants, matrix, etc. Lack of specificity of anindividual analytical procedure may be compensated by other supporting analytical procedure(s).(Extracted from ICH Q2(R1), pag. 4) Accuracy: of an analytical procedure expresses the closeness of agreement between the value which isaccepted either as a conventional true value or an accepted reference value and the value found. This issometimes termed trueness. (Extracted from ICH Q2(R1), pag.4) Precision: of an analytical procedure expresses the closeness of agreement (degree of scatter) betweena series of measurements obtained from multiple sampling of the same homogeneous sample under theprescribed conditions. (Extracted from ICH Q2(R1), pag.4)’ ( 1 Web site: http://www.ich.org/products/guidelines/quality/article/quality-guidelines.html ) 1.BACKGROUND Each protein/enzyme has its unique characteristics. Therefore, each immobilization procedure must betuned to the target and to its intended use. The immobilization steps are listed in Section 2. Details are omitted, since the aim is to provide suggestionsand highlight critical points. This document will not be exhaustive for all specific immobilization cases, but itcan be used as guide for most common immobilization procedures. 1.1. PRE-TREATMENT Epoxy resins are ready-to-use carriers; no activation step is mandatory. Nevertheless, a washing step with the desired buffer may be applied before starting the immobilizationprocedure (Section 2 of the present document). 2.IMMOBILIZATION The immobilization will occur thanks to epoxy groups that are opened by nucleophile attack made byprotein/enzyme groups. The epoxy ring opening will form covalent bonds between the carrier and theprotein/enzyme nucleophilic groups. Protein/enzyme immobilization trials are usually executed in batches with overhead stirring or orbitalshakers (do not use magnetic bar stirrer) in order to maintain the resin in suspension and avoid foamproduction, which is, usually, a result of protein denaturation. The provided suggestions have to be considered as general guidelines and will not be exhaustive for allspecific immobilization cases. Weigh the carrier and transferit into a vessel, which allows forcontrolled stirring.Add 9 volumes of high ionicstrength buffer, usually 1 M, atpH7.50-8.50.Check the pH of the suspension(carrier+ buffer) and correct itwith the respective counter ion, ·Choose the buffer type with respect to protein/enzymestability. lf the protein/enzyme is unstable in high molarbuffer, use NaC/ to increase the ionic strength and reducethe buffer molarity (NaCl molarity+buffer molarity ~1M). opHmust be checked and controlled carefully. pH changesmay modify immobilization result. The range is givensince the highest tolerated pH depends upon protein/enzyme characteristics. if available. Add the protein/enzyme,controlagain the pH and correct it ifnecessary. After 1 min of stirring, collect analiquot of the supernatant andcontrol protein concentration.This is the starting point of theimmobilization. At different time, check theconcentration of the protein inthe supernatant. Withdraw the resin from thesupernatant. Wash the resin with low molaritybuffer (5 volumes) at theprotein/enzyme isoelectric point(pl). Repeat the previous point until no more protein/enzyme is detected in the supernatant. Immobilization result evaluation: ·lf the protein/enzyme is low concentrated, a highvolume should be added to the immobilization reaction.Subtract the "enzyme volume" from the "buffer volume",and increase the starting buffer ionic strength in order toobtain the final solution 1 M (buffer+enzyme). ·Every quantification method that is precise in thedetection of the protein/enzyme concentration reductionin the supernatant is recommended.A blank analysis in order to check for possible positiveand negative interferences is recommended. ·lt can be assumed that the immobilization is completedwhen no more reduction in protein/enzymeconcentration between to subsequent sampling isobserved. ·Collect the volumes and check the supernatantprotein/enzyme concentration. lfrequired indeed, check protein/enzyme release duringits intended use. Put the derivative in contact with thesame solution at the same conditions under which it willbe required to operate. ·In case of protein immobilization, check the amount ofprotein by loading its own ligand (known amount) andchecking ligand concentration in the supernatant. ·In case ofenzyme immobilization, put the immobilizedderivative through the enzymatic activity test. The obtained derivative is now ready for its intended use. Periodically, check the immobilized derivative capacity/activity. 3.IMMOBILIZATION TROUBLESHOOTING Immobilization results are highly dependent upon protein/enzyme. This is a general overview of theimmobilization procedure and some of its most frequently encountered critical points. General recommendations ·Check the quality and the expiration date of all reactants e.g. substrates, ligands, buffers, carrier, protein/enzyme, ·Perform blank analysis, positive control and negative control to ensure the analytical method specificity. Note that some methods may not be compatible with the presence of the carrier. ·Evaluate analytical method sensibility,accuracy, precision and possible interferences, ·Supernatant samplings should be performed in omogeneus conditions, in absence of both foam and possible precipitate (with the exception of the carrier/immobilized derivative), ·Change the type of immobilization carrier, as last resort if none of the above have yielded to better results. Specific cases Case 1. The protein/enzyme remains in the supernatant. ·Increase the buffer ionic strength, Increase the buffer pH by half point, repeat if necessary, ·Change the buffer type, ·Reduce the immobilization volume. Case 2. The protein/enzyme binds, but the derivative has no binding capacity/ is inactive. oIn case of enzymes, evaluate the amount of protein and the enzymatic activity in thesupernatant during the immobilization, ·In case of proteins, use any method that reveals 3D structure e.g. native page(electrophoresis in non-denaturating conditions), gel permeation chromatography; if theimmobilization conditions result in 3D structure loss, make them milder, ·To preserve 3D structure, try adding a ligand (substrate or inhibitor in case of enzymes)during the immobilization, ·Some protein/enzyme are highy sensitive to temperature changes. Introduce athermostatedimmobilization reaction. Case 3. The protein/enzyme detaches during washing step. ·The carrier may be overloaded. Perform further immobilization trials reducing theprotein/enzyme loading and check if the problem arises again,·Check if the immobilization condition may be not “strong"enough to promote the Shiffbase formation. Immobilize under harsher conditions (e.g. increase the pH or buffer ionicstrength) or increase reaction time before withdrawing the immobilized derivative (e.g.double the reaction time). 4. RE-EQUILIBRATION PROCEDURE Immobilized derivatives are usually applied to two different systems: flow reactors and batch reactors.Protein/enzymes are widely applicable in various fields. Therefore, a specific procedure has to bedeveloped for each unique process. General immobilized derivative use cycle 1.The equilibration should be performed with the solvent that will be applied during theAdsorption/Reaction; 2./Adsorption/Reaction time or flow depends on system geometry; 3. The mother liquor recovery process is dependent on the system in which the reactionOccurs: 3.1. Flow reactor: recovery is achieved through collecting the outflow; 3.2. Batch reactor: the mother liquor is collected by filtering the suspension(mother liquor +immobilized derivative); 4.Immobilized derivative displacement is recommended in order to increase the recoveredyield (local product precipitation/adsorption upon carrier surface) and overcome productinhibition problems. Usually, it is performed with demi water or with the same solventapplied for equilibration. Temperature, pH and solvent addition should be monitored ifnecessary; 5. Washing is usually performed with demi water or the same solvent applied forequilibration; temperature, pH and solvent addition should be monitored if necessary. 环氧树脂是现成的载体;没有强制的活化步骤。然而再开始固定程序前,可以使用具有所需缓冲液的步骤清洗。由于环氧基团倍蛋白石/酶基团的亲和攻击打开,所以会发生固定化。环氧开环将在载体与蛋白/酶亲核基团之间形成共价键。 蛋白质/酶固定化试验通常是分批进行的,用搅拌或轨道振动筛(不要使用磁棒搅拌器),以保持树脂悬浮状态,避免产生泡沫,这通常是蛋白质变性的结果。所提供的建议必须作为一般准则加以考虑,并不是针对所有具体的固定案例都详尽无遗。
确定



还剩4页未读,是否继续阅读?
苏州汇通色谱分离纯化有限公司为您提供《氧化还原酶、水解酶、裂解酶中酶载体检测方案(液相色谱配件)》,该方案主要用于其他中酶载体检测,参考标准--,《氧化还原酶、水解酶、裂解酶中酶载体检测方案(液相色谱配件)》用到的仪器有
相关方案
更多









