
The cultivation of Helianthus annuus suspension cultures in single‐use bioreactors of different culture volume should be adapted and established by determining
process parameters. A comparison with the cultivation attempts conducted by the TU Dresden (Geipel, Werner) should point out the advantages and
disadvantages of the culture systems concerning growth rate and foam generation.
方案详情

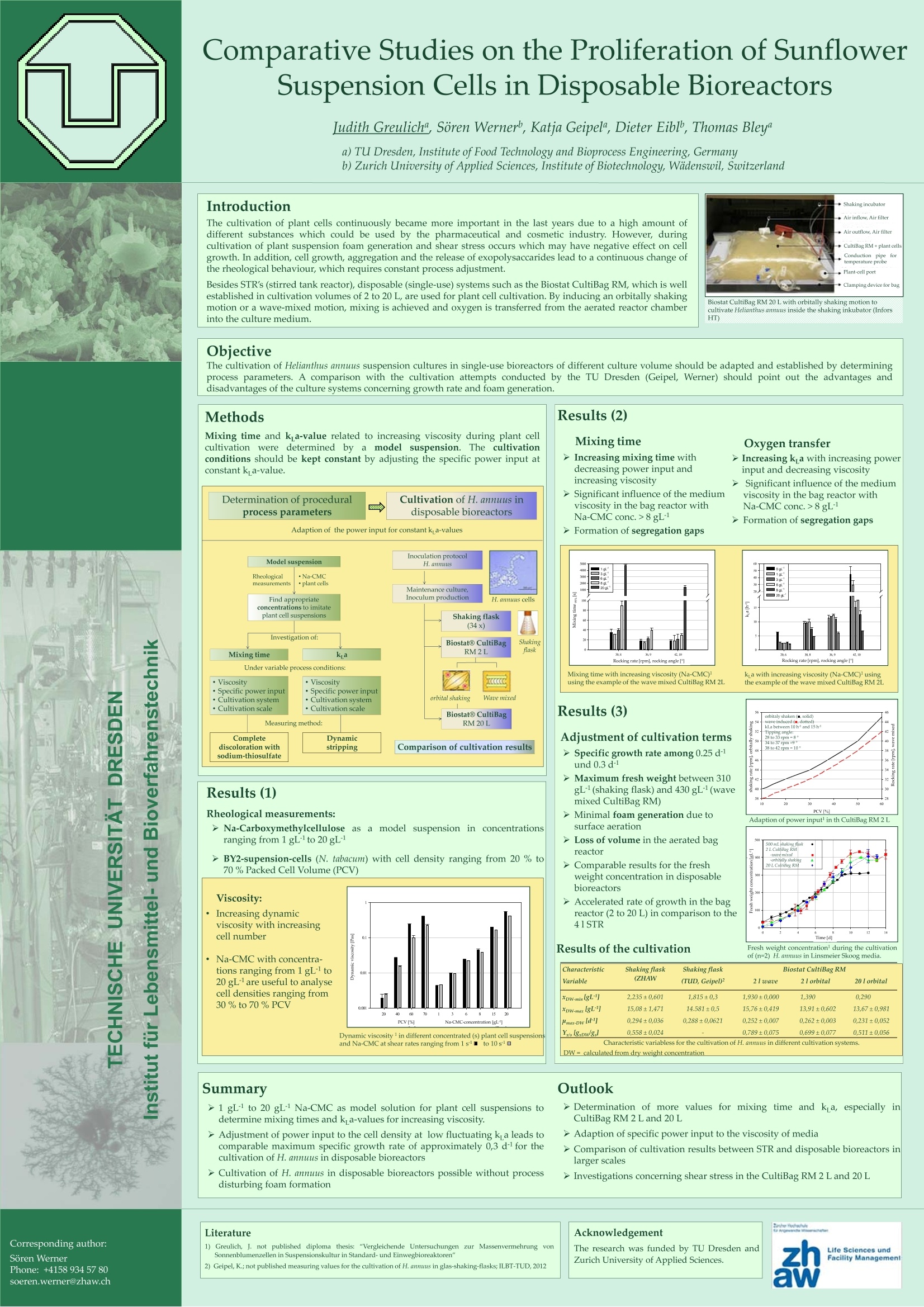
Comparative Studies on the Proliferation of SunflowerSuspension Cells in Disposable Bioreactors Judith Greuliche, Soren Werner, Katja Geipel", Dieter Eibl, Thomas Bleya a)TU Dresden, Institute of Food Technology and Bioprocess Engineering, Germany b) Zurich University of Applied Sciences, Institute of Biotechnology, Wadenswil, Switzerland Introduction The cultivation of plant cells continuously became more important in the last years due to a high amount ofdifferent substances which could be used by the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry. However, duringcultivation of plant suspension foam generation and shear stress occurs which may have negative effect on cellgrowth. In addition, cell growth, aggregation and the release of exopolysaccarides lead to a continuous change ofthe rheological behaviour, which requires constant process adjustment. Besides STR's (stirred tank reactor), disposable (single-use) systems such as the Biostat CultiBag RM, which is wellestablished in cultivation volumes of 2 to 20 L, are used for plant cell cultivation. By inducing an orbitally shakingmotion or a wave-mixed motion, mixing is achieved and oxygen is transferred from the aerated reactor chamberinto the culture medium. Biostat CultiBag RM 20 L with orbitally shaking motion tocultivate Helianthus annuus inside the shaking inkubator (Infors HT) Objective The cultivation of Helianthus annuus suspension cultures in single-use bioreactors of different culture volume should be adapted and established by determiningprocess parameters. A comparison with the cultivation attempts conducted by the TU Dresden (Geipel, Werner) should point out the advantages anddisadvantages of the culture systems concerning growth rate and foam generation. Results (2) Mixing time Oxygen transfer > Increasing mixing time withdecreasing power input andincreasing viscosity > Increasing k a with increasing power input and decreasing viscosity >Significant influence of the mediumviscosity in the bag reactor with > Significant influence of the mediumviscosity in the bag reactor withNa-CMC conc.>8gL Na-CMC conc.>8gL >Formation of segregation gaps >Formation of segregation gaps Mixing time with increasing viscosity (Na-CMC)using the example of the wave mixed CultiBag RM 2L ka with increasing viscosity (Na-CMC) usingthe example of the wave mixed CultiBag RM 2L Results (3) orbitaly shaken(m,solid) re induced fm, dotted) kLa betwi 10h and 15h Adjustment of cultivation terms> Specific growth rate among 0.25 d rpm-89 PI rpm-10 und 0.3 d- >Maximum fresh weight between 310gL(shaking flask) and 430 gL(wave mixed CultiBag RM) 20 30 40 50 > Minimal foam generation due to PCV[%] Adaption of power input in th CultiBag RM 2L surface aeration > Loss of volume in the aerated bag 500mL shaking flask reactor 2L CultiBag RM -orbitally shaki248 >Comparable results for the freshweight concentration in disposablebioreactors 20 L CaltiBag RM >Accelerated rate of growth in the bagreactor (2 to 20 L) in comparison to the41STR Time [d] Results of the cultivation Fresh weight concentration during the cultivation Characteristic Shaking flask Shaking flask Biostat CultiBag RM Variable (ZHAW (TUD,Geipel) 2I wave 2lorbital 20lorbital xDW-minlgL4 2,235±0.601 1,815±0.3 1.930±0.000 1.390 0.290 xpw-maxlgL4 15,08±1,471 14.581±0,5 15,76±0,419 13,91±0,602 13,67±0,981 Hmax-Dwld 0,294±0,036 0,288±0,0621 0,252±0,007 0,262±0,003 0,231±0,052 0,558±0.024 0.789±0.075 0,699±0,077 0.511±0.056 Characteristic variabless for the cultivation of H.annuus in different cultivation systems. DW= calculated from dry weight concentration Outlook >Determination of more values for mixing time and k a, especially inCultiBag RM 2 L and 20 L >Adaption of specific power input to the viscosity of media >Comparison of cultivation results between STR and disposable bioreactors inlarger scales >Investigations concerning shear stress in the CultiBag RM 2 L and 20 L The cultivation of plant cells continuously became more important in the last years due to a high amount of different substances which could be used by the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry. However, during cultivation of plant suspension foam generation and shear stress occurs which may have negative effect on cellgrowth. In addition, cell growth, aggregation and the release of exopolysaccarides lead to a continuous change of the rheological behaviour, which requires constant process adjustment.Besides STR’s (stirred tank reactor), disposable (single‐use) systems such as the Biostat CultiBag RM, which is well established in cultivation volumes of 2 to 20 L, are used for plant cell cultivation. By inducing an orbitally shaking motion or a wave‐mixed motion, mixing is achieved and oxygen is transferred from the aerated reactor chamber into the culture medium.
确定
还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
维根技术(北京)有限公司(WIGGENS)为您提供《向日葵中悬浮培养检测方案(发酵罐)》,该方案主要用于其他中悬浮培养检测,参考标准--,《向日葵中悬浮培养检测方案(发酵罐)》用到的仪器有
相关方案
更多








