方案详情
文
纤维先被加工成纱线,继而编织成纺织品,其有效加工取决于表面摩擦系数和静电荷等属性。这些性能的控制是通过严格控制纤维表面油基涂层来实现的。相对于传统溶剂萃取法和市场上其他仪器,MQC+ 台式核磁共振分析仪在测量油基涂料方面有诸多优点。
方案详情

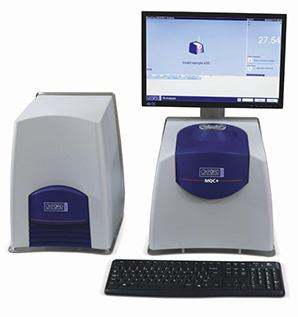
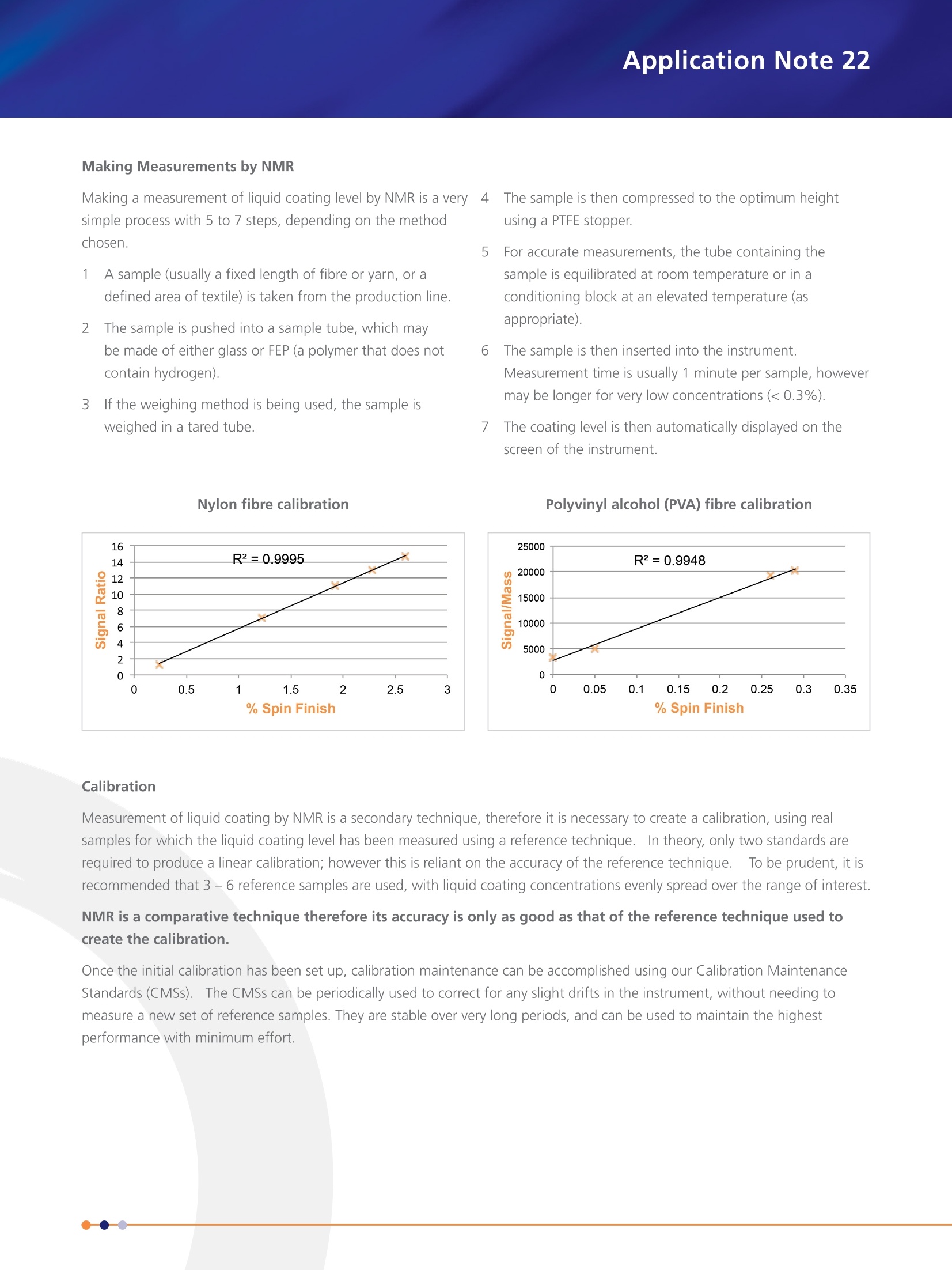
Liquid Coatings on Fibres & Fabrics Application Note 22 Conversely, too little coating leads to problems fromexcessive friction, likely to cause yarn breakage, excessivestatic charge build-up, causing erratic fibre behaviour, anduncontrolled performance in downstream processes. For these reasons, constant attention to ensuring theapplication of the correct amount of liquid coating isessential to efficient and profitable fibre,yarn, and fabricprocessing.This constant attention means that in a busymanufacturing facility, many tens or hundreds of samplesshould be measured each dav. Measurement Approaches The amount of liquid coating on fibres, yarns, and fabrics hasbeen measured for many years.S.The traditional method hasbeen to take a set length or weight of sample, and to carryout a chemical extraction using an organic solvent, eitherat room temperature or an elevated temperature. This isassumed to remove all of the liquid coating from the fibres,transferring it into the solvent.Subsequently, the quantity ofliquid coating is determined after evaporation of the solventor indirectly from the loss in mass of the fibres due to theextraction. Solvent extraction has a number of features thatmake it unattractive in an industrial environment: ● It is time consuming ● It requires skilled operators . It uses flammable and hazardous solvents It needs to be conducted in a fumecupboard / fume hood The consistency of results depends uponthe skill of the operator . Environmentally acceptable disposalof solvents is costly The use of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) for themeasurement of liquid coatings on fibres, yarns and fabricsaddresses all of these issues: No solvent extraction is required Measurement can be carried out by process operatorswith minimal training . Results are consistent and operator-independent ● The instrument needs only a benchtop in a reasonablyclean and stable-temperature environment; no fumecupboard is required Measurement is fast, allowing hundreds of samples tobe measured each day In addition, NMR has other advantages: . NMR is a bulk measurement technique; it measuresthe whole sample equally, and is not affected by airvoids NMR is generally insensitive to colour . NMR measurement is non-destructive, someasurements can be easily repeated NMR is stable over long periods, and has minimalrecalibration requirements The advantages of using NMR for measuring liquid coatingon fibres, yarns, and fabrics are widely accepted in the textileindustry, and NMR is the method of choice in hundreds orthousands of textile manufacturing plants all over the world. NMR Methods The NMR instrument can distinguish between the hydrogensignal from solids (such as fibre, yarn, textile or nonwovenfabric) and liquids (such as an oil-based coating). The sameinstrument can (with a different probe) also measure fluorinebased liquid coatings. .Two variants of the NMR technique are available: ·TThe weighing method TThe non-weighing method The choice of which is more appropriate depends upona number of factors,including the level of liquid coatingapplied, the accuracy of results required, and the samplethroughput needed. All samples can be measured by the weighing method.1.lnthis method, the liquid signal from the NMR is ratioed againstthe total mass of solid (fibre) and liquid (coating) obtainedby weighing the sample.2.The weighing method is the mostaccurate method, and is also most suitable where low levelsof liquid coating are applied (for example<0.3 %) The non-weighing method also uses the liquid signal fromthe NMR measurement, but in this case the liquid NMRmeasurement is ratioed against the total NMR signal (fromboth solid and liquid).This avoids the need to weigh thesample, and, whilst not quite as accurate as the weighingmethod, it is faster (no weighing is required), and sufficientlyaccurate for most applications.5.The Oxford InstrumentsMQC+ instrument can be used with either the weighing ornon-weighing measurement. An enormous and ever-expanding range of fibre types areavailable.The main types can be broadly categorised intothree classes, and several subclasses; Natural Fibres Cotton . Wool . Linen . Silk Reconstituted Fibres . Rayon (Viscose) ●CCellulose Acetate Cellulose Triacetate Synthetic Fibres ● Polyester FPolyEthylene Terephthalate (PET) PolyButylene Terephthalate (PBT) . Polyamide (Nylon, Tactel, Cordura) Polypropylene (PP) PolyAcryloNitrile (PAN, Acrylic, Dralon, Orlon, Acrilan) ● Elastane (Spandex, Lycra, Polyurethane-PolyureaCopolymer) PolyVinyl Alcohol (PVA, PVOH) Aramid (Kevlar, Twaron, Nomex) Carbon A similarly broad range of liquid coatings has been developed,each tailored for use with particular fibres, and oftenspecifically developed to optimise the fibre properties for aparticular use or application. NMR measurements are commonly used for syntheticand reconstituted fibres, such as polyesters, polyamides,polypropylene, elastanes, rayons, cellulose acetates, andaramids. Making a measurement of liquid coating level by NMR is a verysimple process with 5 to 7 steps, depending on the methodchosen. A sample (usually a fixed length of fibre or yarn, or adefined area of textile) is taken from the production line. 2The sample is pushed into a sample tube, which maybe made of either glass or FEP (a polymer that does notcontain hydrogen). 3 If the weighing method is being used, the sample isweighed in a tared tube. Nylon fibre calibration 5 For accurate measurements, the tube containing thesample is equilibrated at room temperature or in aconditioning block at an elevated temperature (asappropriate). 6 The sample is then inserted into the instrument.Measurement time is usually 1 minute per sample, howevermay be longer for very low concentrations (<0.3%). 7 The coating level is then automatically displayed on thescreen of the instrument. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibre calibration Calibration Measurement of liquid coating by NMR is a secondary technique, therefore it is necessary to create a calibration, using realsamples for which the liquid coating level has been measured using a reference technique. IIn theory, only two standards arerequired to produce a linear calibration; however this is reliant on the accuracy of the reference technique. To be prudent, it isrecommended that 3 -6 reference samples are used, with liquid coating concentrations evenly spread over the range of interest. NMR is a comparative technique therefore its accuracy is only as good as that of the reference technique used tocreate the calibration. Once the initial calibration has been set up, calibration maintenance can be accomplished using our Calibration MaintenanceStandards (CMSs). The CMSs can be periodically used to correct for any slight drifts in the instrument, without needing tomeasure a new set of reference samples. They are stable over very long periods, and can be used to maintain the highestperformance with minimum effort. Conclusion NMR is an attractive, accurate, fast, reliable and easy-to-use technique for the measurement of liquid coating levelsin the textile industry. It is widely accepted, and makes ameaningful contribution to the most efficient operation of atextile plant. Complete Packages Oxford Instruments offers two packages especially tailored tothe measurement of liquid coatings on textile fibres. The Standard package is: ●Oxford Instruments MQC+23 NMR Analyser ● 0.55 Tesla (23 MHz) high homogeneity magnet ● Probe for 18 mm diameter sample tubes (7 ml samplevolume) Integrated system controller (no external PC required) ● Integrated flat-screen display MultiQuant software including RI Calibration,Rl Analysis, and the EasyCal 'Spin Finish'application,including both weighing and non-weighing methodcapability 18 mm glass tubes or 18 mm FEP tubes ●PTFE tube stoppers (to fix the sample height) Stopper insertion/removal tool ● Instrument tuning sample User manual For larger samples, we recommend the Advanced package which consists of: Oxford Instruments MQC+23 NMR Analyser 0.55 Tesla (23 MHz) high homogeneity magnet Probe for 26 mm diameter sample tubes (14 ml sample volume) Integrated system controller (no external PC required) IIrntegrated flat-screen display ● MultiQuant software including RI Calibration, RI Analysis, and the EasyCal'SpinFinish' application, including both weighing and non-weighing method capability C26 mm glass tubes or 26 mm FEP tubes PTFE tube stoppers (to fix the sample height) Stopper insertion/removal tool ●Instrument tuning sample User manual Method sheet Optional items are: ●A dry block heater with holes for sample conditioning at 40℃ (18 mm or 26 mm) A precision balance (only required for weighing method) A set of four Calibration Maintenance Standards for Spin Finish visit www.oxinst.com/mqc for more information or email: magres@oxinst.com This publication is the copyright of Oxford Instruments and provides outline information only which (unless agreed by the company inwriting) may not be used, applied or reproduced for any purpose or form part of any order or contract or be regarded as a representationrelating to the products or services concerned. Oxford Instruments' policy is one of continued improvement. The company reserves theright to alter, without notice, the specification, design or conditions of supply of any product or service. Oxford Instruments acknowledgesall trademarks and registrations.@ Oxford Instruments plc, 2018. All rights reserved. Ref.LCT-09-18 The Business ofScience Summaryi●Up to 250 times faster than wet chemistry methodsNo hazardous solvents required; nohazardous waste produced● Easiest, most reliable technique available- suitable for unskilled personnelReliable measurements down to low concentrationsIdeal for high sample throughput Introduction The textile industry is one of the largest industries in globalcommerce. With many hundreds of years of technologicaldevelopment, today's industry provides an almost unlimitedvariety of products, many of which are carefully optimisedfor specific applications. Even high-volume commodityproducts use a sophisticated understanding of the propertiesand behaviour of fibres to provide the performance andfunctionality that is required. The Role of Liquid Coatings in the Textile Industry One aspect of the technology routinely utilised is the use ofliquid coatings to control and modify the behaviour of fibres.These liquid coatings are applied at a variety of stages in themanufacturing process, sometimes as early as fibre extrusionin synthetic fibre manufacture, but sometimes as late asapplication to woven or non-woven fabrics.Liquid coatingsare known by a variety of names, such as: Spin Finish (SF) .Coning Oil ●Finish on Fibre (FoF)Finish on Yarn (FoY)Oil Pick-Up (OPU)●Lubricant on●Carding LubricantThread (LoT)Carding OilYarn Lubricant (LY)Staple Fibre Finish (SFF)Needle OilTexturising OilAgents d'Avivage Avivagen The name used depends partly on application, and partly ongeography.lTo encompass all these variants, the term liquidcoating will be used here. Whatever name is preferred, these liquid coatings are carefullyformulated products, often combining many components.Liquid coatings may be oil- or aqueous-based, and mayinclude many substances, such as oils, soaps, surfactants,waxes, anti-statics, and others. They may be true liquids, emulsions, or suspensions.TThevare designed to perform a number of functions, particularlycontrol of inter-fibre friction, static charge, inter-fibrecohesion, heat generation and heat dissipation. TThey mayalso be used to control appearance, feel, and texture. Application of the correct amount of liquid coating is criticalfor both performance and economic reasons.Too muchcoating can lead to insufficient inter-fibre cohesion, build-up on downstream machinery, uncontrolled fibre behaviour,problems with downstream processes such as dyeing, and, ofcourse, too much coating is an unnecessary increase in cost ina very cost-sensitive industry. 纤维先被加工成纱线,继而编织成纺织品,其有效加工取决于表面摩擦系数和静电荷等属性。这些性能的控制是通过严格控制纤维表面油基涂层来实现的。相对于传统溶剂萃取法和市场上其他仪器,MQC+ 台式核磁共振分析仪在测量油基涂料方面有诸多优点。
确定





还剩4页未读,是否继续阅读?
牛津仪器科技(上海)有限公司为您提供《纤维和织物中液体涂层检测方案(核磁共振)》,该方案主要用于纺织品/服装/帽中化学成分检测,参考标准--,《纤维和织物中液体涂层检测方案(核磁共振)》用到的仪器有牛津仪器MQC+台式磁共振分析仪
推荐专场
相关方案
更多