
方案详情
文
本文综述了液相色谱- 质谱联用(LC /MS)技术的分类、发展,以及近年来国内、外利用此技术分析环境污染物的应用,为我国环保监测部门开展此方面的工作提供参考。
方案详情

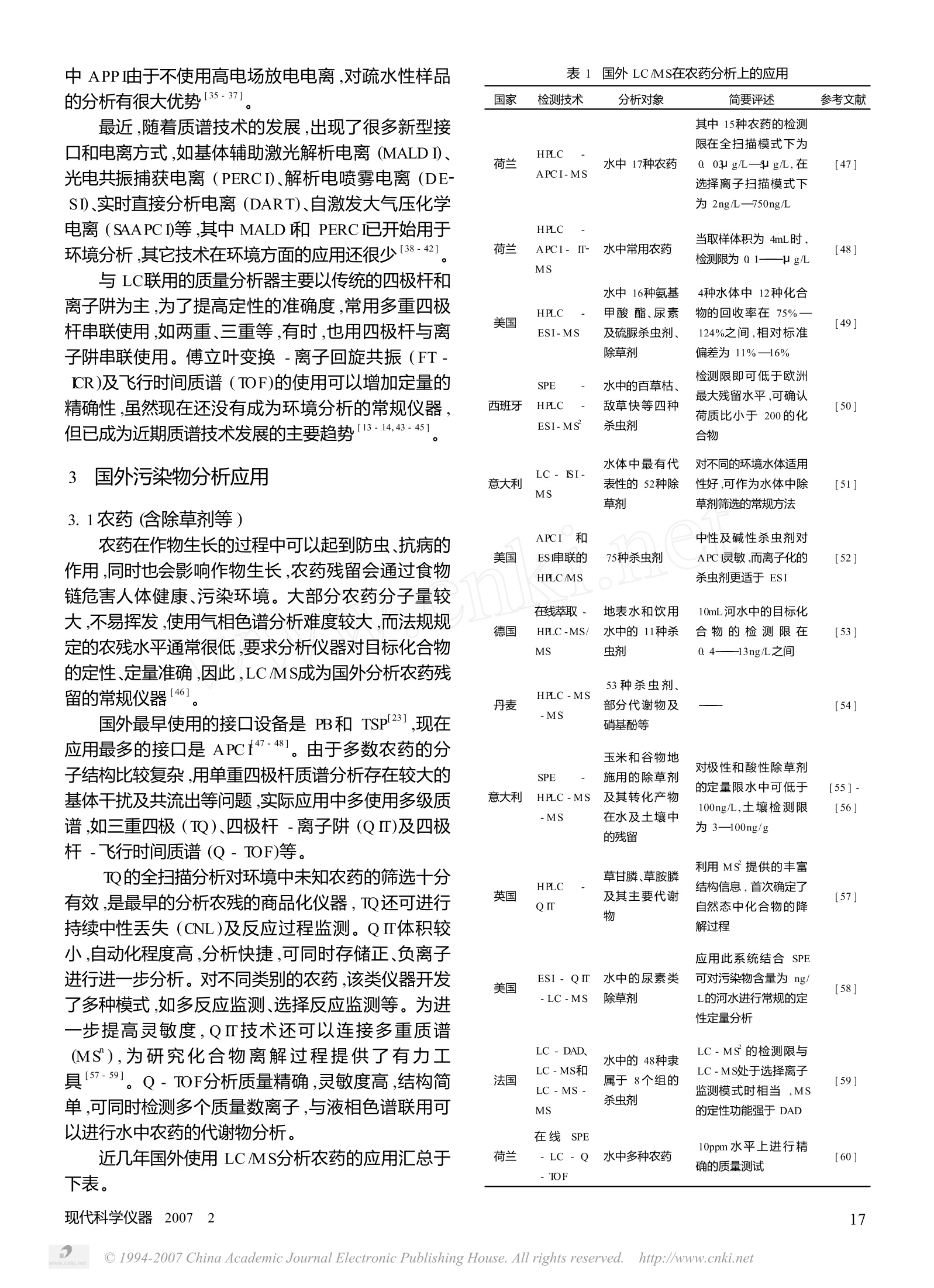
液相色谱/质谱(LC/MS)联用技术在环境污染物分析中的应用 赵起越 (北京市环境保护监测中心 北京 100044) Email: Qiyuezhao6@homail com 摘 要 本文综述了液相色谱-质谱联用(LC/MS)技术的分类、发展,以及近年来国内、外利用此技术分析环境污染物的应用,为我国环保监测部门开展此方面的工作提供参考。 关键词 液质联用;环境污染物;分析和应用 中图分类号 0657 The Applica tion of L iqu id Chroma tography - Mass Spectrometryn the Field of Env ironm en tal Pollution Ana lysis Zhao Qiyue (Beijing Municipal EnvironmentalMonitoring Center, Beijing 100044, China) AbstractThis paper reviewed the category and development of liquid chromatography- mass spectrometry(LC/MS) and its application in analysis of various environmental pollutants, offering references for environmentalmonitoring departments in our country to make use of this technique Key words Liquid Chromatography - mass Spectrometry (LC/MS);eenvironmental pollution; analysisand app lication 引 言 色谱和质谱联用技术是对复杂样品进行定性、定量分析的有力工具,其中气相色谱/质谱联用技术发展较早,已广泛用于痕量有机物的定性和定量分析1,10],但对极性较大、热稳定性强、难挥发性的样品使用液相色谱/质谱联用技术 (LCMS)分析效果更好。目前,这一技术已突破了色谱、质谱连接的难题,多种商品化的接口相继问世,各领域的分析工作活跃地开展起来1-17] 2 液相色谱与质谱联用接口技术与检测器种类 液相色谱的流动相为液体,流速较大,而质谱需要在真空的环境下工作,因此,两者的连接成为LC/MS技术的关键。几十年来,各国开发了很多种LC/MS接口,主要有移动带(MB)、直接液体引入(DLI)、热喷雾(TSP)、快原子碰撞(FAB)、颗粒束(PB)、大气压(APl接口等。MB、DLI TSP和 FAB接口出现较 ( 收稿日期:2006-11-26 ) ( 作者简介:赵起越(1968-),教授级高工,从事环境保护工作。 ) 早,在技术和工艺上存在较大问题,使用量逐渐减少。由于以PB连接 HPLC与四极杆质量分析器的分析结果可以与标准谱库的谱图进行对照,因此此接口在一定范围内还有应用118-24]。而现在 LCMS使用最广的接口设备是大气压接口[25-29] 大气压接口按照不同的电离方式分为电喷雾电离、大气压化学电离和大气压光电离等。 电喷雾电离(Electro sp ray bnization,简 ESI适于分析分子量较大的极性化合物,这种电离较温和,易形成多电荷分子碎片,但要获得较满意的分析效果,流动相的流速不能太大(通常<1.0mL/min)。对此种技术进行改进,形成离子喷雾电离(nspray bni-zation,简称ISI),流动相的流速可达到1. 0mL /m in,分析灵敏度和检测限均有很大改善[30-34]。 大气压化学电离(Amospheric pressure chemicalionization, 简称APCI和大气压光电离(A tmosphericpressure photoionization, 简称 APPI对分子量不大的弱极性化合物的定性、定量比较准确。这种离子源进行的分析不易形成多电荷分子碎片,谱图较简单。其 中APPI由于不使用高电场放电电离,对疏水性样品的分析有很大优势[35-37] 最近,随着质谱技术的发展,出现了很多新型接口和电离方式,如基体辅助激光解析电离(MALDI、光电共振捕获电离(PERCI)、解析电喷雾电离(DE-SI、实时直接分析电离(DART)、自激发大气压化学电离(SAAPCI等,其中 MALDI和 PERCI已开始用于环境分析,其它技术在环境方面的应用还很少[38-42] 与LC联用的质量分析器主要以传统的四极杆和离子阱为主,为了提高定性的准确度,常用多重四极杆串联使用,如两重三重等,有时,也用四极杆与离子阱串联使用。傅立叶变换-离子回旋共振(FT-IR)及飞行时间质谱(TOF)的使用可以增加定量的精确性,虽然现在还没有成为环境分析的常规仪器,但已成为近期质谱技术发展的主要趋势13-14,43-45] 3 国外污染物分析应用 3.1农药(含除草剂等) 农药在作物生长的过程中可以起到防虫、抗病的作用,同时也会影响作物生长,农药残留会通过食物链危害人体健康、污染环境。大部分农药分子量较大,不易挥发,使用气相色谱分析难度较大,而法规规定的农残水平通常很低,要求分析仪器对目标化合物的定性、定量准确,因此,LC/MS成为国外分析农药残留的常规仪器46] 国外最早使用的接口设备是 PB 和 TSP[231,现在应用最多的接口是 APCf47-48]。由于多数农药的分子结构比较复杂,用单重四极杆质谱分析存在较大的基体干扰及共流出等问题,实际应用中多使用多级质谱,如三重四极(TQ)、四极杆-离子阱(QIT)及四极杆-飞行时间质谱(Q-TOF)等。 TQ的全扫描分析对环境中未知农药的筛选十分有效,是最早的分析农残的商品化仪器,TQ还可进行持续中性丢失(CNL)及反应过程监测。QI体积较小,自动化程度高,分析快捷,可同时存储正、负离子进行进一步分析。对不同类别的农药,该类仪器开发了多种模式,如多反应监测、选择反应监测等。为进一步提高灵敏度,QⅡ技术还可以连接多重质谱MS),为研究化合物离解过程提供了有力工具137-591。Q-TOF分析质量精确,灵敏度高,结构简单,可同时检测多个质量数离子,与液相色谱联用可以进行水中农药的代谢物分析。 近几年国外使用LC/MS分析农药的应用汇总于下表。 使用MS和MSMS的 荷兰 Q-TOF 水中农残 自动切换扩大了分析 [61] 物的质量范围 使用全扫描模式计算 SPE - LC 地中海流域水 西班牙 了化合物的精确质量 [62] -QTOMMS 中农药 数和可能的元素组成 目前,国外LCMS在农残上的应用以分析苯脲、三嗪、氨基甲酸酯、氯苯氧酸及硝基酚为主[53-55,58-63]。分析仪器主要使用TQ和QI。定量分析使用 SM.不同的农药分析需要选取不同的检测模式。 一般说来,中性及碱性农药,如三嗪、氨基甲酸酯、有机磷、季胺盐农药、苯脲使用正离子(PI检测,而酸性农药,如苯氧酸_磺酰脲使用负离子(ND检测。有时两种模式同时使用。除了分析水体中的农药外,LC/MS技术还可以进行农药在土、水、动物体中代谢研究.[64] 3.2多环芳烃类化合物(含硝基多环芳烃、氧化多环芳烃等) 多环芳烃(PAHs)及其硝基衍生物是一大类环境污染物。它们即使在很低的浓度水平也会威胁人体健康,污染环境[65-67]。过去,这类物质主要采用HPLC或 GCMS衍生进行分析。由于这类物质分子量通常较大,溶、沸点较高,使用上述两种仪器分析难于达到很满意的效果68-71]。。LC-MS是分析此类化合物较理想的方法,早在30年前就有应用报道。如美国 Carll等应用API源HPLC-MS分析了气体中的多环芳烃,实验与Ni离子源直接进样紫外(UV)检测进行了比较。该方法为环境空气中 PAHs的分析创造了条件1721。德国的Schauer等应用 HPLC-在线衰减-荧光检测技术、大气压化学源-飞行时间质谱 (APCI-TOF-MS)对环境空气、汽车尾气和实验室制备气中的硝基 PAHs进行了测定,并测出了氧化PAHs及 PAHs化合物,其中 APCI-TOF-MS作为HPLC-在线减减-荧光检测技术的补充,对分析大气颗粒物中 PAHs与 NO、O;发生杂化反应提供了有力工具。该研究首次提出了 PAHs与大气光化学物质(NO,、Os等)反应形成硝基苯醌的试验证据 3.3有机金属化合物分析 环境中某些金属及其化合物与人类生存关系紧密。其中金属价态不同,化合物的毒性相差很大.传统的分析仪器只能分析出该金属总含量水平,不能区别各种存在形态。近几十年来,用高效液相色谱通过电感耦合(CPMS)相联可以进行金属元素的形态 确认和进行定量分析41。如美国的 BHymer等使用HPLC-ICP-MS对环境和生物体中的As的各种化合物进行了分析测定,实验针对不同基体不同价态的As化合物采取了不同的前处理,通过优化选择仪器分析条件,对目标化合物进行了准确定量1731.德国的Nischwitz等使用在线LC-ICP-MS对道路扬尘中的 Pt(II)及 Pt(Ⅳ)的氯化物进行了测试,该实验创建了一种修正HO干扰的数字模式,其检测限约比 LC-UV低10倍76]。Chatterjee通过高能N,微波诱导等离子质谱(MIPMS)-LC超声雾化(UN)及氰化物发生(HG)系统进行了硒化合物的优化测定。该系统可进行在线形态分析,硒酸盐、亚硒酸盐、三甲基硒油、硒代蛋氨酸及硒代硫氨基酪酸的检测限均可低于0.15g/L”。 3.4激素类物质的分析 环境中存在的激素类物质有天然的,有人工合成的,目前最受关注的是雌激素类物质,它们通常分子量较大,极性较强,需要使用 HPLCMS进行分析78-79]。意大利 Lagana 等使用新型基体固相扩散一 SPE-HPLC-MSMS分析了彩虹鳝鱼的肝和肌肉组织中雌激素毒枝菌素玉米烯酮的代谢物,实验利用湍流离子喷雾-串联质谱测试了玉米烯酮及其主要的代谢物——α-玉米烯酮,上述污染物在鳟鱼服入0148h后在肝脏和肌肉组织中仍有检出[80]。意大利的Pojana等以 HPLC-ESI-IT-MS系统分析了海边泻湖水中天然及合成的雌激素,方法可对天然与合成激素同时进行分析,大部分物质使用负离子检测,检测限为0.1-26ug/L。用该方法对威尼斯泻湖湖水中的几种目标化合物进行分析,其浓度为28-33ng/L[81]。英国的 Gomes等使用 SPE-LCMS法分析了水体中9种天然、合成类固醇激素及它们的结合体。Gomes等建立的方法的主要优点是类固醇类结合体与单体同步分析,无须衍生反应。他们用这个方法分析了不同的环境水体,实验结果表明:湖水及饮用水中没有检出游离态类固醇,工业污水处理厂中仅发现一种,市政污水处理厂水中的具有生物活性的游离态类固醇类物质种类最多182]。 另外,藻类毒素也可使用LCMS分析,美国Maizels等使用反相 LC-ESI-TOFMS测定了不同水体中氰菌毒素,但这种方法目前还没有用于常规分析〔83] 3.5其它污染物分析 这部分工作主要集中在染料、表面活性剂、树脂等工业产品的分解产物上。具体应用见下表。 表2国外使用LC-MS分析其它环境污染物的应用 国家 污染物 基体 应用特点 文献 瑞典 有机酸酐和异 空气 目标化合物与尿素衍生,正、 [84] 氰酸盐 负离子同步检测 使用 SPE及 APPI电离源,河 日本 8个2-苯基苯 并三唑化合物 河水 [85] 水中此类污染物的检测水平 达到ng/L以下 波兰 包括单体、添加 医用棉花 实验结果与分析对象、萃取溶 剂及浸提时间等因素有关 [86] 物及降解产物 在内的有机物 首次区别检测了直链和支链 乙氧基聚合物,回收率为51一 109%,检测限为1—5ug/kg 西班牙 阴离子及非离 子表面活性剂 海底淤泥 [[87] 美国 全氟辛酸和全 不同基体 PFOA和PFOS的检测限可达 [88] 氟辛烷磺酸盐 ppb,甚至 ppt水平 高氯酸盐及消 毒副产物 美国 水 [89-91] 4 国内污染物分析应用 国内环境监测部门中 LCMS分析技术还不普及,该领域的应用报道不多,主要集中在农残分析方面。金军等使用API-CD-MS对三嗪类、磺酰脲类除草剂及有机磷农药进行了碎片谱的研究,并与 Ban-oub等使用 ESI-MS-MS所做的结果进行了比较2。另外,他们还研究了磺酰脲类除草剂的HPLC/ESMS分析,比较了绿磺隆、胺苯磺隆 ESMS正负离子谱图并认为它们的负离子谱有较好的响应,最小检测限可达 0.1ng。潘元海等用短柱 HPLC-APCI进行了6种有机磷农药的快速分析,一次分析仅需10min,与 HPLC-UV方法相比,在SM模式下大部分目标化合物的检出限小于 5ng941。潘元海等对三嗪类除草剂及有机磷农药进行了碰撞诱导解离.(CD)碎片谱的研究。他们选择了适当的锥体电位,同时得到了待测化合物的分子量和结构信息,作者认为APCI/CDMS的灵敏度虽然不很高,但在迁移区产生的CD谱具有与串联质谱所得CD谱相似的信息,因此该技术在鉴定复杂混合物中未知成分时有一定价值。任晋等使用SPE-HPLC-MS技术在线分析了水中7种农药,整个过程仅需45m in,检测限低于欧共体所要求的饮用水质量标准196]。祁彦等使用LCMS的 SR同时测定了大豆中10种磺酰脲类除草剂的残留。10种中质的加标回收率在72.1—98.8%之间,相对标准偏差为0.90—7.74%,可满足出口大豆中多种农药残留的检测需要。吴晓东等使用LCMS对宜城市广德县水体中的豆磺隆进行了检测。 在检测的8个样品中有6个检出豆磺隆,其浓度范围在 5.5-22. 3mg/L之间98]。Si you - bin 等使用HPLC-MSMS研了了除草剂甲基乙氨硫的水解反应,实验证明该水解反应为一级反应,反应速率与 pH有关。研究确认了甲基乙氨硫的11种水解产物,探讨了形成途径和反应机理 5 小 结 使用LC/MS分析的环境污染物大部分属于内分泌干扰物质(Endocrine Disrupting Chem icals,简称EDC),它们会干扰生物体内分泌系统的正常机能,对人体产生多方面的影响,属于持久性有机污染物(POPs)。目前国外使用这一技术开展的环境分析工作范围较广,发展较快 17,40]。TQ和QI早已成为常规性的环境监测仪器,QTOFMS的使用正在普及。而我国使用LCMS进行的环境分析还仅限于农药类,并且仪器的普及率很低,开展的工作在深度和广度上与国外有很大差距。 随着色谱技术的发展,小型或微型色谱柱和有效、科学的流动相组成及洗脱方式等都大大提高了HPLC的分离效果,接口技术的改进和完善、MS谱库识别技术的发展使 LCMS分析的检测限大大降低,灵敏度有很大提高。随着LCMS技术的日益成熟,其在环境领域的应用也会越来越多。 ( 参考文献 ) ( [1] H amer T, Bzp l eman T, Oct a n o 1 - A ir Partition Coef f icient for Descri-bing Particle /Gas Partitioning of A romatic C ompounds in U rban A i r , En vi - ron Sci Techno1 1998,32,1494-1502 ) ( [2]Oh J. E , ChoiJ. S , Chang Y. S , G as/Particle Partitioning of PCDD & PCDF i n A tmosphere E valuation of Predicting Models , Amos Envimn , 2001, 35 , 4125-4134 ) ( [3]朱利中,松下秀鹤,空气中多环芳烃的研究现状,环境科学进展,1997,5 (5),18-29 ) ( [4] P olkow ska Z , k o tA. , W ie g owskiM., e t a l, Org a nic Pollutants in Pr e -cip itation Dete m ination of Pestici d es & PAH s in Gdansk, Poland, A mosE n vimon, 2 000,34,1233- 1 245 ) ( [5]祁士华,盛国英,傅家谟等,澳门大气溶溶胶中多环芳烃的源解析尝 试,中国环境科学,2002,22(2),118- 122 ) ( [6]L i M. A. , Ba u gh P. J. , Py r ethroid So il Extraction, Pr operties ofM ixed Solvents and Tme Profiles U sing GC/ M S -NIIAnalysis, Intemn J. Envi- ion Anal Chem., 83(11), 9 09-923 ) ( [7]吴建伟,张萃民,气相色谱、质谱(GCMS)联用在我国环境监测中的应 用,中国环境监测,1999,15 ( 4),53-59 ) ( [8]E i ceman G A. , T o rresdey J . G, O verton E , et a l, Gas Chromatogra- phy, Anal Chem., 2 004, 7 6,3387-3394 ) ( [9] Menzelaar H. L. C , Dworzanski J . P., AnoldN. S , et a l ,Advances inField Portable Mobile G C /MS In s trumentation, F i e l d Analytical C h em istry & Technology, 2000 , 4(1),3- 1 3 ) ( [10]李娟,丁曦宁,胡冠九,等,微波萃取-气相色谱、质谱法测定土壤中的有机氯农药,中国环境监测,2005,21(4),49-51 ) ( [ 1 1] ParrisN. A. , I n strumentalL iquid Chromatography, a practical manual onhigh -perfomance li q uid c h iomatographic methods, s e cond, c o mpletelyrevised edito r , V . , P. O . Box 21 1 , 1000 AE Am sterdam, The Netherlands, 1984, E l sevier Science Publishers B . ,120- 1 21 ) ( [12]刘祥东,梁琼麟,罗国安,等,液质联用技术在医药领域中的应用,药 物分析杂志,2005,25,110-116 ) ( [13]K o ester C. J , M o ulik A . , Tr e nds in Environmental Analysis, A nal Chem., 2 005, 7 7,3737- 3 754 ) ( [14] R ichardson S D., E n vironmentalMass Spectrometry: Emer g ing Contam i- nants and Current Issu e s, A n al Chem. ,200 4 ,76,333 7 - 3 364 ) ( [ 1 5] K oester C.J. , Smonich S L. E s ser, B . K , Environmental Analysis, A- nal Chem. 2003, 75,2813-2828 ) ( [ 1 6]L inscheidM., W e stmoreland D. G, An a l ytical Techniques for T rac e Organic Compounds - V I Application o f Liquid C hromatography - M assSpectrometr y , Pure & Ap p l Chem . ,1994,66,1913- 1 930 ) ( [17]任晋,蒋可,内分泌干扰剂的研究进展,化学进展,2001,13,135-14 4 ) ( [ 1 8 ] W i nkler P. C, Pe rkins D. D. , W i l liam s W. K, et a l , P e rfommance ofan m piovalMonodisperse A ero sol Generation Int e rface for L iquid Chioma-tography /Mass Spectrometry, Anal Ch e m . ,1988,60,489-493 ) ( [ 1 9 ] W illoughby B. C . , B raoner R . F . , Monodisperse Aeroso1 Generation In- t erface for Combining L iqui d Chromatography with Spectroscope, AnalChem.,1 9 84, 56,2626 - 2631 ) ( [20]Ho J . S , B e hymer T D. , Budde W. L . , et t a l,M a ss Transport a ndCalibration in L iquid Chromatography Particle B eam M a ss Spectrometry,J . Am. Soc M ass Spectrom. , 1 992, 3,662-6 7 1 ) ( [21] C a p p iello A. , Fam iglini G , Capillary - Scale Particl e - Beam L i quidChromatography - M ass Spectrometry Int e rface; C an Ele c tron bo n izationSusta i n the Competitio n , J . Am. Soc Mass S pectrom. , 1998,9 , 99 3 -1001 ) ( [ 2 2 ] Bellar T A., B ehymer T D . , Bu d de W. L., Inve st igation of E nh a ncedbn Abundances from a Carrier P rocess in High - Perfomance L i quidChromatography P article Beam M ass S p ectrometry, J. Am . Soc Mass Spectrom., 1990,1,92-98 ) ( [23] BetowskiL. D. , Pace C M. , RobyM. R ., E vidence f or ThemmalDecom-position Contribution to the Mass Spectra of Chlorinated Phenoxyacid Herbicides Obtained by Particle Beam L iquid ChromatographyMass Spectrom-etry, J . Am . Soc Mass Spectrom. ,1992 , 3,823-830 ) ( [ 2 4] B ehymerTD. , Be l lar T A. , B u dde W. L. , L iquid C h romatography /Particle Beam Mass Spectrometry of Polar Compounds of EnvironmentalInteres t , Ana l Chem., 1990, 62,1686-1 6 90 ) ( [ 2 5] G a skellS J., E l e c tro sp ray: Principles and Practice, J. M a ss Spectrom., 1997,32,677-688 ) ( [ 2 6] A vian J., T h e co u p ling of Gas a n d L i quid C h romatography with MassSpectrometry, J . Mass Spectr o m . ,1999,34,157- 1 68 ) ( [27] R eem tsma T , T h e use o f liquid chromatography- a t mospheric pressureionization - mass s p ectrometry i n w a ter analysis - Pa r t Il : O b stacles,trends , 2001 , 20,533-542 ) ( [28] McEwen C. N.,Mckay R. G , A c ombination A tmospheric Pressure LC/MS: G C/MS bn Source: A dvantages ofDual AP- L CMS: GC / MS In-strumentation, J . Am . So c Mass Spectrom., 2005, 16,1730- 1 738 ) ( [29] Homing E C , CarrllD. I , Dzidic I , et al , Liquid ch i omatograph - m ass spectrometer -c o mputer analytical s y stem s, A c o ntinuous -flow system based on a mosphere pressure i o nization mass spectrometry, J. Chromatography, 1 974, 9 9, 1 3 - 2 1 ) ( [30] Shaffer S A. , Prior D . C , Anderso n G A . , et al, An b n Funnel I n-terface for mproved I o n Focusing and Sensitivity, U sing Electro spray bni-zation Mass Spectrometry, Anal Chem., 1998 , 70, 4111-4119 ) ( [ 3 1] N iessen W . M . A. , Ti nke A. P . , L i q u id c h romatography -m a s s spec- t rometry G eneral principles a n d instrumentation, J. C h i omatogr A. 1995, 703,37-57 ) ( [ 3 2] C appiello A. , Fam iglini G , ManganiF.,et a l, Ne w tre n ds in the ap-plication of electron ionizatio n to liquid chromatography-mass spectrome-try interfacin g , Mass Spectrometr y Reviews , 2001, 20,88-1 0 4 ) ( [33] L opez- He r rera J. M . , B arreno A. , Boucard A. , An Experimental Study of the E lectro sp raying of W ater in A ir at A mospheric P ressure, J . A m . Soc Mass Spectrom . , 2004 , 15,25 3 -259 ) ( [34] M annM.,MengC K, Fe n nJ . B . , In t e rpr etingMass Spectra ofMultip lyCharged bns, Anal Chem., 1 989, 61,1702-1708 ) ( [35] Cai S S , Sya ge J. A . , C o mparison of A tmospheric Pressure Ph o toioniza- tion, A tmo spheri c Pressure Chemical bnization, and E lectrosp ray bniza- tion M ass Spectrometry fo r A nalysis of L ip ids, Anal Ch em., 2 0 06, 78,1191- 1 199 ) ( [36] H oming E C, CarmllD. I, Dzidic I, et al , A m ospheric pressure i- o nization mass spectrometry studies of negative ion fommation for detectionand q uantification puiposes , J . Chromatography, 1977, 142,481- 4 95 ) ( [ 37] Syaze J. A. , Mechanism of [M +H ]+ Fo m ation in P ho toionizationM a ssSpectrometry , J . Am. Soc Mass Spectrom., 2004 , 15,152 1 - 1 533 ) ( [ 3 8] Z hang X, Marcisse D. A., Mu rray K K, O n- line S ingle D rop letDep-osition for MALD I Mass Spectrometry, J. Am. Soc M a ss Sp e ctrom. , 2004, 15,147 1 -1477 ) ( [39] LaFranchiB. W., P e t r ucci G A . , Pho t oelectron Resonance Cap ture bni - zation (PERCI A N ovel Technique for t he Soft - b n iz a tion of O rganicCompounds, J. Am. S oc M ass Spectrom., 2004,15, 4 24-430 ) ( [40] Takats Z, W iseman J . M., Gologan B., e t al, M a s s Spectrometry S amp ling Under Ambient Con d itions with Desoip tion E l ectro sp ray bniza- tion , Scienc e , 200 4 ,306,47 1 -473 ) ( [ 4 1] C ody R . B. , L aramee J . A . , Durst H. D., Versatile New b n Source forthe Analysis ofMaterials i n Open A ir under Ambient Conditions, A nal Chem., 2005,77,2297- 2 302 ) ( [42] A sano K G , FordM. J., Tom k ins B. A. , et al, S el f - asp i r ating At-mospheric Pressure Chem ical bonization Source forD irect Samp lingofAna- l ytes on Surface s an d i n L iqui d Solutions, Rapid Commun Mass Spec- trom.,2005,19,2305- 2 312 ) ( [43] BelovM. E , Anderson G A., W ingerd M. A., et a l , An AutomatedHigh P erfoimance Ca p illary Liquid Chromatography - F ourier T ransfommbn C yclotion Resonance Mass Spectrometer for High- Th r oughput Pro-teom ics, J . Am . Soc Mass Spectrom. , 2004, 1 5,212-232 ) ( [44 ] B ristow A . W . T, W ebbK S, I nter c omparison stud y on accurate mas sm easurement of s mall molecules in mass spectrometry, J. Am. Soc Mass Spectrom. ,2003 , 14,1086- 1 098 ) ( [45] E ichhom P . , A g a D. S , I d entification o f a P h otoxygenation P r oduct o f Chlortetracycline in Ho g Lagoons U sing LC/ E S I - b n Trap -MS andL C /ESI-T i me - of- F l ight - MS, Anal Chem., 2004, 76,60 0 2-6011 ) ( [46] P ico Y ., B l asco C . , F ont G , E n v i ronmental and Food Applications of Modemn S c ientific I nstruments 2007 2 ) ( LC - T a ndem Mass Spectrometry in Pesticide- R esidue Analysis a n O-verview, Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2004, 23,45 - 85 ) ( [47] H ogenboom A . C , Slobodnik J. , VreulsJ.J, et a l, Si n gle short col-umn liquid chromatograp hy with amo spheri c pressur e che m ica l - ioniza-tion - ( tandem) mass - s p e c trometric dete c tion for trace environmentalanalysis , Chromatographia , 1996,42,506 - 514 ) ( [48] H ogenboom A. C. , Niessen W. M. A . , B r inkman U. A. T, R a p i d target analysis of microcontam inants in water by on - l ine s ingle- s h ort - co l -umn liquid chromatography c ombined with atmospheric pressure c hemicalionizatio n io n - trap mass spectrometr y , J . ChromatogrA . , 1998b, 794,201-210 ) ( [49] WangN., B u dde W., Detemm ination of Carbamate, Urea a nd ThioureaPesticides and Herbicides in Wate r , Ana l Chem., 2001, 73,997-1 0 06 ) ( [ 5 0] C astro R. , Moyano E , G alceranM. T , D etemmination o f quatemary am-monium pesticides by li q uid chromatography - e l e c tro sp ray tandem mas s spectrometry, J . Chromato g r A, 2001b, 914,111-121 ) ( [51] C urini R. , G e ntili A . , Marchese S , et al , So l id - p h ase extractionfollowed by high - perfomance li q uid chromatography- ionsp ray interface - m ass spectrometry f o r monitoring of herbicides in environmentalwater, J . Chromatogr A, 2000, 874,187-198 ) ( [52] T humman E M . , F e rrer I, B a rcelo D., C h oosing between amosphericchem ical i onization a nd electrosp ray ionization interfaces for the HPLC MSanalysis of pesticides, A n al Chem. 2001, 73, 5441-5449 ) ( [ 5 3] A sperger A. , EferJ., KoalT, e t al, Tra c e detemination of priority7pesticides in water by means of hig h - speed on - line soli d - phase e x-traction - l iquid chromatography- t andem m a ss sp e ctrometry using turbulent - flow c hromatography c olumns for e nrichment, J . C hromatogr A, 2002,960,109-119 ) ( [ 5 4] B ossi R ., Vejrup K V., M ogensen B. B. ,e t al , An a l ysis of polar pes-ticides i n rainwater i n Denmar k by liquid chromatography- tandem massspectrometry, J . Chromato g r A, 2002 , 957,27-36 ) ( [55]Lagana A. , BacaloniA., Leva I D ., e t al , Occurrence and detemi-nation of herbicides and theirmajor transfomation products in environmen-tal water s , Ana l Chim . Act a , 2002b, 462,187 - 198 ) ( [ 5 6] L agana A. , B acaloni A . , L e va I D. , et a l , Detemm ination of maize and grain herbicides and their transfo mation pioducts in so i l by use of so i l column extraction t hen liquid c hromatography with tandem ma s s spe c trom-etry, Chromatographia, 2002a, 56, 3 37-343 ) ( [ 5 7] G oodw in L . , Startin J . R. , Gooda l lD. M., et al, Ta ndem mass sp e c-trometric analysis of glyphosate, g lufosinate , a am inomethylphosphonic acid, and methyl- p hosphinicop rop ino i c aci d , Rapid Commun M ass Spectrom., 2003,17,963 - 969 ) ( [58] D raper W. M . , E l e c trospray liq u id ch r omatography quadrupole ion t rapmass s p ectrometry detemm ination of phenylurea herbicides in water, J. A gric Food Chem, 2001,49,2746- 2 755 ) ( [ 5 9] J eannot R., Sabik H., S a uvard E, e t al, A ppl i cation of liquid chro - m atography with mass spectrometry combined with photodiode array detec- t ion and t andem mass spectrometry for monitoring pesticides i n surface waters , J . Chromatogr A, 2000 , 879,51-71 ) ( [ 6 0] H ogenboom A . C . , N i essen W. M . A . , Little D. ,Accurate mass detemi-nation f or the confimation and i d entification of organic miciocontam inantsin surface water u sing on- l i ne solid - p ha se extraction liq u id chromatog-raphy electro sp r a y orthogon al - acceleration time - of - f l i ght massspectrometr y , Rap id Comm u n Mass Spectrom.,1999,13,125 - 133 ) ( [61] B obeldijk I , Vissers J. P. C , Keamey G, e t a l, Sc r e e ning and iden - ) ( t ification o f unknown contam i n ants in water w i th l i q uid c h romatography and quadrupole -o r thogonal acceleration- time - of - f li g ht tandem mass s pectrometry , J . Chromatogr A, 2001 , 929,63-74 ) ( [62] I lbanezM., S a nchoJ.V. , P o z o O. J, et al , U s e of quadrupole time-of- f light mass spectrometry i n t h e e l ucidation o f unknown co m poundspresent in environmental water, Rap id Commun M a ss Spectrom., 2 0 0 5 ,19.169-178 ) ( [ 6 3] C alza P., B andino S , A igotti R. , et al , Hi g h - pe rfomance liqui d chromatographic/tandem mass spe c trometric ide n tification of th e ph o to-transfomation pioducts of t ebuconazole o n t itanium d ioxide, J . Ma ssSpectrom. , 2002, 37,566- 5 76 ) ( [64] B eeson M. D., D r iskellW. J. , Ba r r D. B. , I so tope dilution - high -perfomance liquid chromatography- tandem ma s s sp e ctrometry method f or quantifying urinary metabolites of atrazine , malathion , and 2, 4 - d i-chlorophenoxyaceti c ac i d , An al Chem., 1999, 71,3526-3530 ) ( [65] K avonras I G, Lawrence J., Koutrakis P., e t a l , Measurement ofparticulate aliphatic and polynuclear a r omatic hydiocarbons in S an t iago deChile: s ource reconciliation a n d ev a luation of samp ling art i facts, A t mos Envimn ,1999,33,4977-4986 ) ( [66]金祖亮,董淑萍,何宇联,等.大气飘尘中硝基多环芳烃的高效液相色 谱分析,环境科学,1985,4(4),25-29 ) ( [67] Yang H. H, HsiehL. T, L i n H C, e t al , Polycyclic armatic hydro-carbon emissions fr o m motorcycles, Am o s Envimon ,2005,39,17-25 ) ( [ 68] Kuo C. T , Ch en H. W ., Lin S T, Tra c e detem ination of nitrated poly-cyclic aromatic hydrocarbons u sing liquid chromatography with on - lineelectrochem i cal reduction and fluorescence detection, Anal Ch im. Ac t a, 2003,482,219- 2 28 ) ( [69] Dugek B. , H a jglova J., K o c ourek V., De te m ination of nitrated polycy- c lic aromatic hydrocarbons a n d th e ir pr e cursors in b iotic mat r ices, J.Chromatogr A, 2002, 98(1),127- 1 43 ) ( [70] P yle S M., B e twskiL. D. , Marcus A. B., et a l, Ana l ysis of Polycy-clic A romati c Hydrocarbons by bn T rap T andem Mass Spectrometry, J.Am. S oc M ass Spectrom., 1997, 8,183- 1 90 ) ( [ 7 1] N ourse B . D. , CoxK A . , M orand K L. , e t al , Collisional Activationof Pyrene and Anthracene i n and bn- T r ap Mass Spectrometer, J . A m. Chem. S oc , 1992, 1 14,2010-2 0 16 ) ( [72] CarollD. I , Dzidic I , S tillell R. N. , et al, A mospheric Pressurebnization Mass Spectrometry: C o rona D i scharge bn Source for U se inLiq-uid Chromatography-Ma s s Spectrometer- Com p uter A nalytical Sys t em, Anal C hem., 1 975, 47,2369-2373 ) ( [ 7 3] Schauer C , Ni essner R. , P oschlU. , A nalysis of nitrated p o lycyclic aro- m atic hydrocarbons b y l iquid chromatography with f luorescence and mass s pectrometry detection, a i r particulate m a tter, s oo t, an d reaction productstudies , Ana l B ioan a l Chem . ,2004, 3 78,725 -7 3 6 ) ( [74]黄志勇,吴熙鸿,胡广林,等.高效液相色谱、电感耦合等离子体质谱 联用技术用于元素形态分析的研究进展,分析化学,2002,30,1387- 1393 ) ( [ 7 5] BHymerC, Car u s o J. A., A rse n ic and it s speciation analy s is using high- p erfomance liquid chromatography and i n ductively coupled p lasamass spectrometry , J . Chromatogr A , 2004 , 1045, 1 -13 ) ( [76] N ischwitz V. , M ichalke B. , K ettrup A. , Speciation of Pt( I I) a nd P t(Ⅳ) in sp iked e x tracts firom r oad dust using on- l i ne l iquid chromatogra-phy- inductively c o up led plasma m ass spectrometry, J. Chiomatogr A , 2003, 1016,223- 2 34 ) ( [ 7 7] C hatterjee A. , Shibat a Y. , Tao H., et a l, H igh- p e r fomance liq u id ) ( chromatography-u l t r a sonic n e bulizer high -p o wer nitrogen m i c rowave - induced p lasma mass spectrometry, re a l- tim e on- li n e c oup ling for sele- nium speciation analysi s , J . Chromatogr A, 2004, 1042,99 - 106 ) ( [ 7 8]D i az - CruzM. S , L o pez de A ldaM. J . , LopezR. , e t a l , Detem in a -tion of estrogens and progestogens by mass spectrometric techniques (GC/MS, L C /MS andLC/MSMS), J. Mass Spectrom., 2003, 3 8,917-9 2 3 ) ( [ 7 9] Koch H. M . , R o ssbach B. , D r exlerH. , e t al, Inter n al exposure of thegeneral population to DEHP and o t her phthalates- d e t eim ination of s e c-ondary and primary p h thalate m o noester metabolites in ur i ne, Env i ron Res ,2003,93(2),177- 1 85 ) ( [ 8 0] L agana A., F a beri A. , Fa go G , e t al , A p p l ication of and innovativematrix s olid - phase dispersion - solid - phase tandem mass spectrometryanalytical methodo logy to the study ofthe metabolism of the estrogenic my-cotoxin zearalenone in rainbow tout l iver and muscular tissue, I ntem JEnviion Anal Chem. 2004, 8 4,1009-1 0 16 ) ( [ 8 1] P ljana G, B onfa A. , BusettiF, et a l, D e t em ination of natural and synthetic estrogenic compounds i n coastal lagoon waters by HPLC-E l e c - trosp r a y- mass spectromet r y , ntem J. Envirn A nal Chem., 2004, 84,717-727 ) ( [ 8 2] G omes R . L . , B irkett J. W . , Scrim shaw M. D., e t al , S imultaneousdetemm ination o f n atural and synthetic st e roid es t rogens and the i r conju-gates in aqueous matrices by l iquid chromatography/mass s pectrometry,Intem J . Enviin Anal Chem . ,2004,85,1- 1 4 ) ( [ 8 3]M a izelsM., Bu d de W. L., A LC / MSMethod for t h e Detemm ination ofCy-anobacteria Toxins in Wat e r, A n al Chem.,76,1342- 1 351 ) ( [ 8 4 ] Dahlin J. , K arisson D., S k arp ing G, et al , De t emm ination of airbomeanhydrides using LC -MS monitoring negative ions of d i - n- butylam inederivative s , J . Envi i on Moni t , 200 4 ,6,624-629 ) ( [85] Moriwaki H. , Harino H , Yoshikura T , et al,Smultaneous detemi- nation of2- phenylbenzotriazole - type mutagens, PB TA - 1 thr o ugh - 8 , in r iver water by liqui d chromatograph y - t andem m ass spectrome- try , J. Envirn Monit , 2004, 6 ,897-902 ) ( [86] Rogalewicz R . , B atko K , V o e lkel A., Ide nt ification of organic extract-ables from commercial r esin - modified glass - i onomers using HPLC - MS, J . Environ Monit ,2004, 8, 7 50-7 5 8 ) ( [87] Martin P. A. L. , Parra A . G, Mazo E G, P r e ssured li q uid e x traction f ollowed by l iquid chromatography - m a s s spectrometry for the detemina-tion o f major surfactants in marine sedimen t s, nt e m J . Enviro n Anal Chem.,2005, 85,293- 3 03 ) ( [ 8 8] SchultzM. M . , B a rofsky D. F., F i e ld J. A . , F l u orinated A lkyl Surfac- tants, Environmental Engineering Science, 2003, 20,487- 5 0 1 ) ( [89] SnyderS A. , Vanderford B. J., Re x i ngD. J., Tra c e analy s is of bromate,chlorate, iodat e , Envir n Sci Techno 1 , 200 5 ,39,4586-4593 ) ( [901 EPA Document#: 8 15-R-05-007Method331. 0 Detemm ination of Perchborate i n D rinking Water by L iquid Chromatography Electrospray bniza- t ion Mass Spectrometry R e vision 1 . 0, J a nuary 2005 ) ( [91 ] W inkler P., M inteerM., W illey J., A n alysis of Perchlorate inW ater andSoil by Electro sp rayLC/MSMS, An a l Chem.,76,469-473 ) ( [92]周同惠主编,生物医药色谱新进展,北京,化工出版社,1996,105 ) ( [93]陈耀祖主编,有机分析方法研究和应用,西安,陕西师范大学出版社, 1996,189 ) ( [94]潘海海,金军,蒋可.高效液相色谱、大气压化学电离质谱快速分析水中痕量有机磷农药,分析化学,2000,28,666-671 ) ( [95]潘元海,金军,蒋可.源内碰撞诱导解离谱谱技术在农药残留分析中 的应用,分析试验室,2000,19,77-80 ) ( [96]任晋,黄翠玲,赵国等,等.固相萃取-高效液相色谱-质谱联机在线 分析水中痕量除草剂,分析化学,2001,29,876-880 ) ( [97]祁彦,李淑娟,占春瑞,等.高效液相色谱-质谱法测定大豆中磺酰脲 类除草剂多残留量的研究,分析化学,2004,32,1421-1425 ) ( [98]吴晓东,王志举,周新欣.液相色谱-质谱联用法测定水中豆磺隆的 研究,安徽化工,2005,137,55-56 ) ( [ 9 9] S i Y.B. , Z h angL., Ta k agi K , Application of coup led liquid chro m atog-raphy- m ass spectrometry in hydrolysis stu d ies of the he r bicide ethametsulfuron - methyl, Inter n J . Envim n Ana l Chem., 2005, 85,7 3 -88 ) <试剂网》入试运行 北京中协联合试剂技术有限公司、中国分析测试协会共同建设的《试剂网》(域名:www. unireagent com),目前已进入试运行阶段。该网站作为中国分析测试协会指定的专业网站,意在建立一个试剂专业信息平台,为广大分析测试事业工作者提供服务。为此,衷心希望大家与我们进行全方位的合作,共同为促进分析测试事业的发展做出贡献。 ( 中国分析测试协会实业部 2007年4月10日 ) odem Scientific InstrumentsChina Academic Journal Electronic Publishing House. All rights reserved. http://www.cnki.net
确定






还剩5页未读,是否继续阅读?
上海力晶科学仪器有限公司为您提供《环境污染物中液相色谱/质谱检测方案 》,该方案主要用于其他中其他检测,参考标准--,《环境污染物中液相色谱/质谱检测方案 》用到的仪器有
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多








