方案详情
文
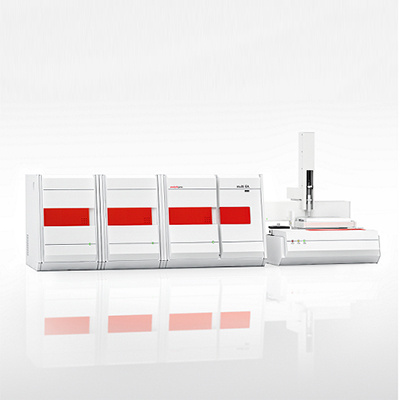
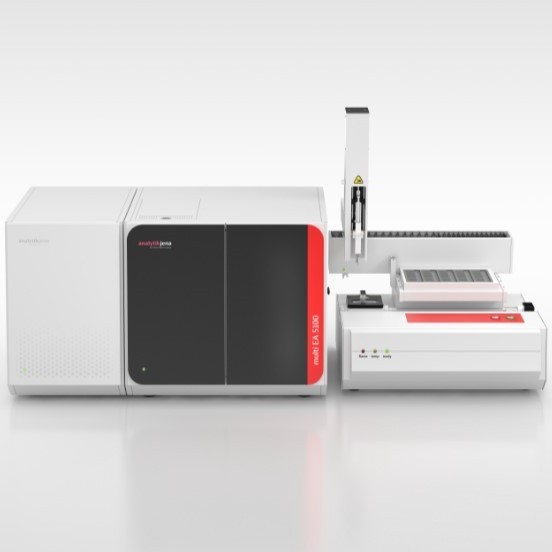
multi EA 4000 集多个检测模块于一身,可用来检测固体,液体,粘稠性物体中的硫,碳,氯含量,由于它的革新技术,multi EA4000 仪器有很宽的应用范围,并且具有很强的适用性和灵活性,是各行业高效的检测工具。
方案详情

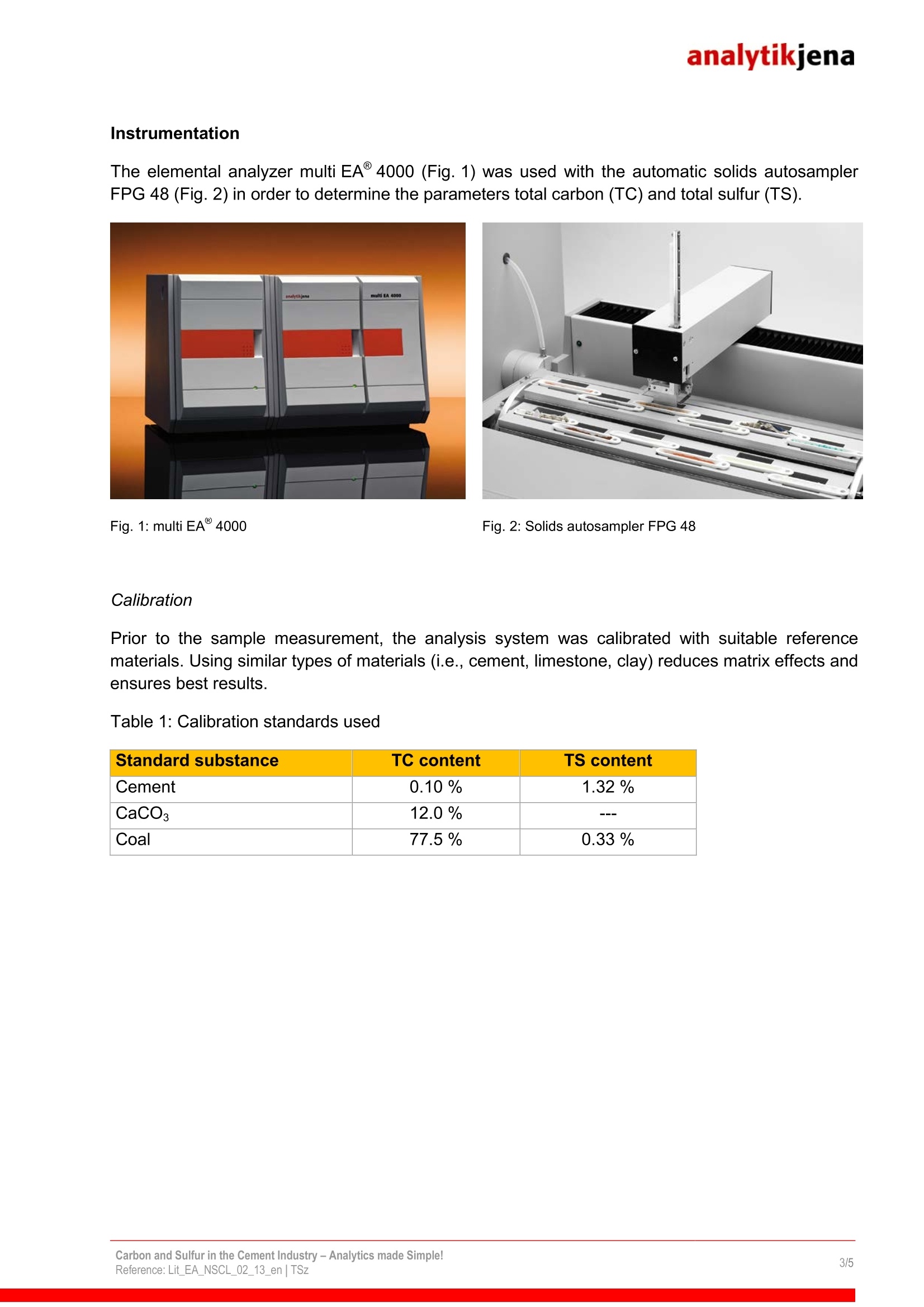
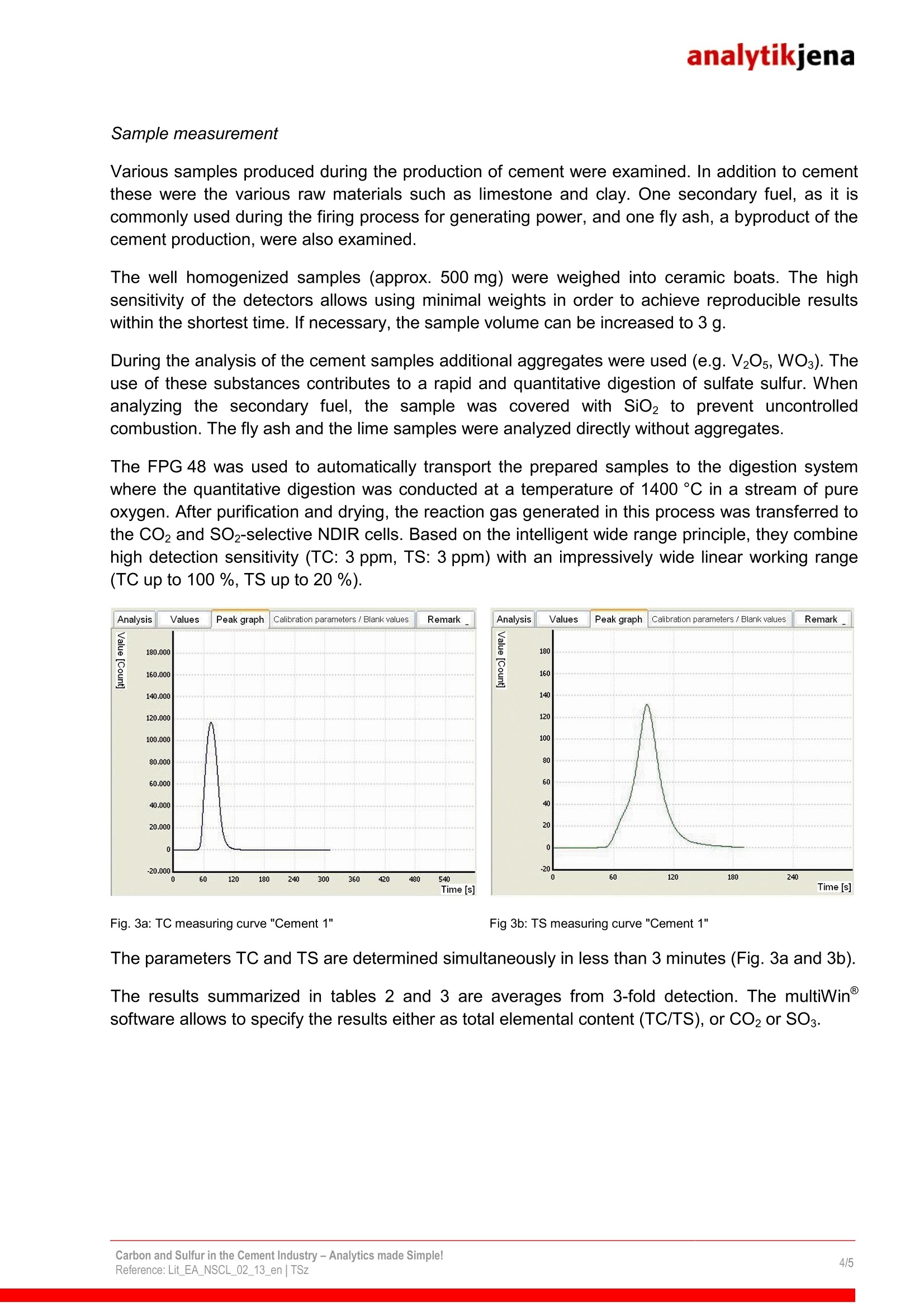
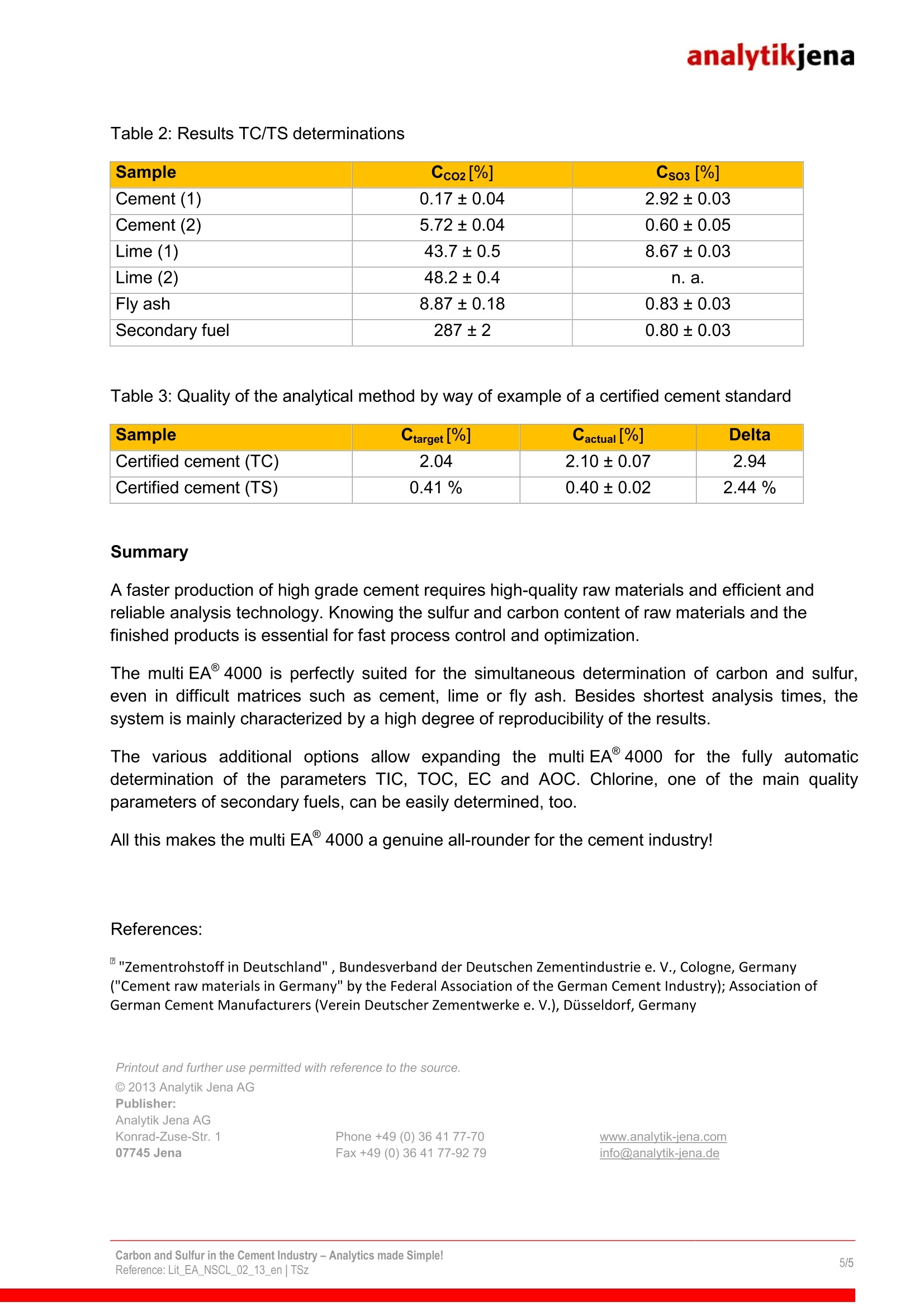
analytikjena Field of Application/Industrialsector: Chemistry/Polymer Industry Clinical Chemistry/Medicine/Hygiene/Health Care Electronics ■Semiconductor Technology Energy Environment/Water/Waste Geology/Mining Nutrition/Agriculture Metallurgy/Electroplating Refineries/Petrochemistry Pharmacy Cosmetics Material Analysis Other Carbon and Sulfur in the Cement Industry-Analytics made Simple! Dr. Tony Szuppa, Product Specialist, Elemental Analysis, Analytik Jena AG, Konrad-Zuse-Str. 1, 07745 Jena, Germany The elements carbon and sulfur play a key role in the production and quality assurance of cementand are therefore subject to strict controls. If due to an incomplete firing process the carboncontent is too high, this has a negative effect on the quality of the cement. High levels of sulfur inthe raw materials result in increased SO2 emissions during the sintering process. If sulfur levels inthe final product are too high, however, this can lead to corrosive effects and can cause theconcrete to age prematurely. To prevent this, it is vital to determine the sulfur and carbonconcentrations in a fast and reliable way. And this is the key feature of the multi EA 4000. The industrial production of cement started in 1850. The quantity produced worldwide hasincreased to 1.5 billion tons per year today. Limestone and clay are the main raw materials usedin the process. Depending on the quality of those materials, iron ore or sand may need to beadded. The homogenized material mixture is fired at 1450°℃ in order to remove the unwantedcarbon. The raw materials also contain different types of sulfur compounds (sulfides, sulfates).When fired they produce SO2 which is detrimental to the environment and must be removed fromthe exhaust gases with suitable filters. The required capacity of the filter units can only beestimated if the content of sulfur is known. After firing, the cement is ground and mixed with sulfates. This is done to enhance the bindingproperties of the cement. Carbon and sulfur also still play an important role in the final product. Only small amounts ofcarbon should be left after a complete firing process, since the cement would otherwise lose itscapacity to bind after it gets mixed with water. A high carbon content is an indication of anincomplete process and/or ingress of foreign matter during the milling of the firing material. If sulfurlevels are too high, this will lead to the formation of sulfuric compounds which will make the setconcrete corrode from the inside and reduce its stability. Powerful analysis technology is needed if the quality requirements for raw materials and thefinished product are to be met. It must guarantee a complete digestion even of challengingmatrices such as cement and rock. Short analysis times, easy operation and low maintenancerequirements are of particularimportance. To meet these requirements, Analytik Jena has developed the multi EA 4000, a fully automatedanalyzer for determining the elements carbon, sulfur and chlorine. Instrumentation The elemental analyzer multi EA 4000 (Fig. 1) was used with the automatic solids autosamplerFPG 48 (Fig.2) in order to determine the parameters total carbon (TC) and total sulfur (TS). Fig. 1: multi EA 4000 Fig.2: Solids autosampler FPG 48 Calibration Prior to the sample measurement, the analysis system was calibrated with suitable referencematerials. Using similar types of materials (i.e., cement, limestone, clay) reduces matrix effects andensures best results. Table 1: Calibration standards used Standard substance TC content TS content Cement 0.10% 1.32% CaCOs 12.0% Coal 77.5% 0.33% Sample measurement Various samples produced during the production of cement were examined. In addition to cementthese were the various raw materials such as limestone and clay. One secondary fuel, as it iscommonly used during the firing process for generating power, and one fly ash, a byproduct of thecement production, were also examined. The well homogenized samples (approx. 500 mg) were weighed into ceramic boats. The highsensitivity of the detectors allows using minimal weights in order to achieve reproducible resultswithin the shortest time. If necessary, the sample volume can be increased to 3 g. During the analysis of the cement samples additional aggregates were used (e.g. V20s, WOs). Theuse of these substances contributes to a rapid and quantitative digestion of sulfate sulfur. Whenanalyzing the secondary fuel, the sample was covered with SiO2 to prevent uncontrolledcombustion. The fly ash and the lime samples were analyzed directly without aggregates. The FPG 48 was used to automatically transport the prepared samples to the digestion systemwhere the quantitative digestion was conducted at a temperature of 1400°C in a stream of pureoxygen. After purification and drying, the reaction gas generated in this process was transferred tothe CO2 and SO2-selective NDIR cells. Based on the intelligent wide range principle, they combinehigh detection sensitivity (TC: 3 ppm, TS: 3 ppm) with an impressively wide linear working range(TC up to 100 %, TS up to 20 %). Fig. 3a: TC measuring curve "Cement 1" Fig 3b:TS measuring curve "Cement 1" The parameters TC and TS are determined simultaneously in less than 3 minutes (Fig. 3a and 3b). The results summarized in tables 2 and 3 are averages from 3-fold detection. The multiWinsoftware allows to specify the results either as total elemental content (TC/TS), or CO2 or SO3. Table 2: Results TC/TS determinations Sample Cco2[%] Cso3 [%] Cement (1) 0.17±0.04 2.92±0.03 Cement (2) 5.72±0.04 0.60±0.05 Lime (1) 43.7±0.5 8.67±0.03 Lime (2) 48.2±0.4 n.a. Fly ash 8.87±0.18 0.83±0.03 Secondary fuel 287±2 0.80±0.03 Table 3: Quality of the analytical method by way of example of a certified cement standard Sample Ctarget[%] Cactual[[%] Delta Certified cement (TC) 2.04 2.10±0.07 2.94 Certified cement (TS) 0.41% 0.40±0.02 2.44% Summary A faster production of high grade cement requires high-quality raw materials and efficient andreliable analysis technology. Knowing the sulfur and carbon content of raw materials and thefinished products is essential for fast process control and optimization. The multi EA 4000 is perfectly suited for the simultaneous determination of carbon and sulfur,even in difficult matrices such as cement, lime or fly ash. Besides shortest analysis times, thesystem is mainly characterized by a high degree of reproducibility of the results. The various additional options allow expanding the multi EA 4000 for the fully automaticdetermination of the parameters TIC, TOC, EC and AOC. Chlorine, one of the main qualityparameters of secondary fuels, can be easily determined, too. All this makes the multi EA 4000 a genuine all-rounder for the cement industry! References: "Zementrohstoff in Deutschland",Bundesverband der Deutschen Zementindustrie e. V., ColColognnee,Germany("Cement raw materials in Germany" by the Federal Association of the German Cement Industry); Association ofGerman Cement Manufacturers (Verein Deutscher Zementwerke e. V.), Dusseldorf, Germany Printout and further use permitted with reference to the source. C 2013 Analytik Jena AGPublisher:Analytik Jena AGKonrad-Zuse-Str. 1 Phone +49 (0) 36 41 77-70 www.analytik-jena.com07745 Jena Fax +49 (0) 36 41 77-92 79 info@analytik-jena.de Carbon and Sulfur in the Cement Industry - Analytics made Simple!Reference: Lit EA NSCL en | TSz/
确定


还剩3页未读,是否继续阅读?
耶拿分析仪器(北京)有限公司为您提供《水泥工业中碳和硫的快速测量》,该方案主要用于水泥/混凝土中--检测,参考标准--,《水泥工业中碳和硫的快速测量》用到的仪器有multi EA® 5000碳、氮、硫、氯 元素分析仪
推荐专场
相关方案
更多















