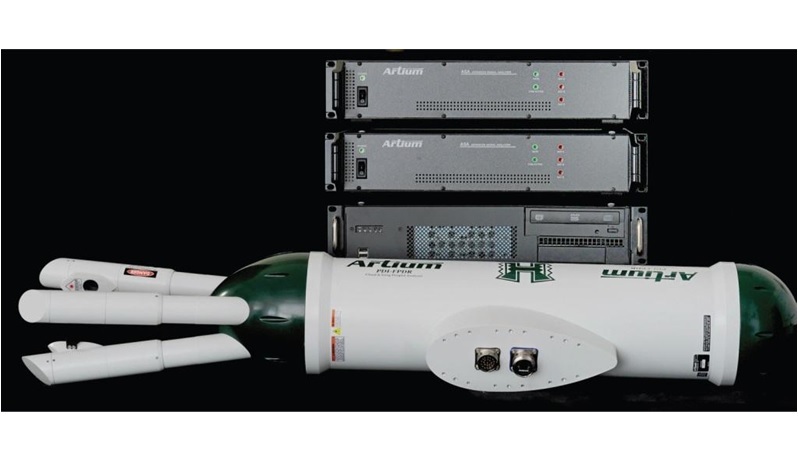
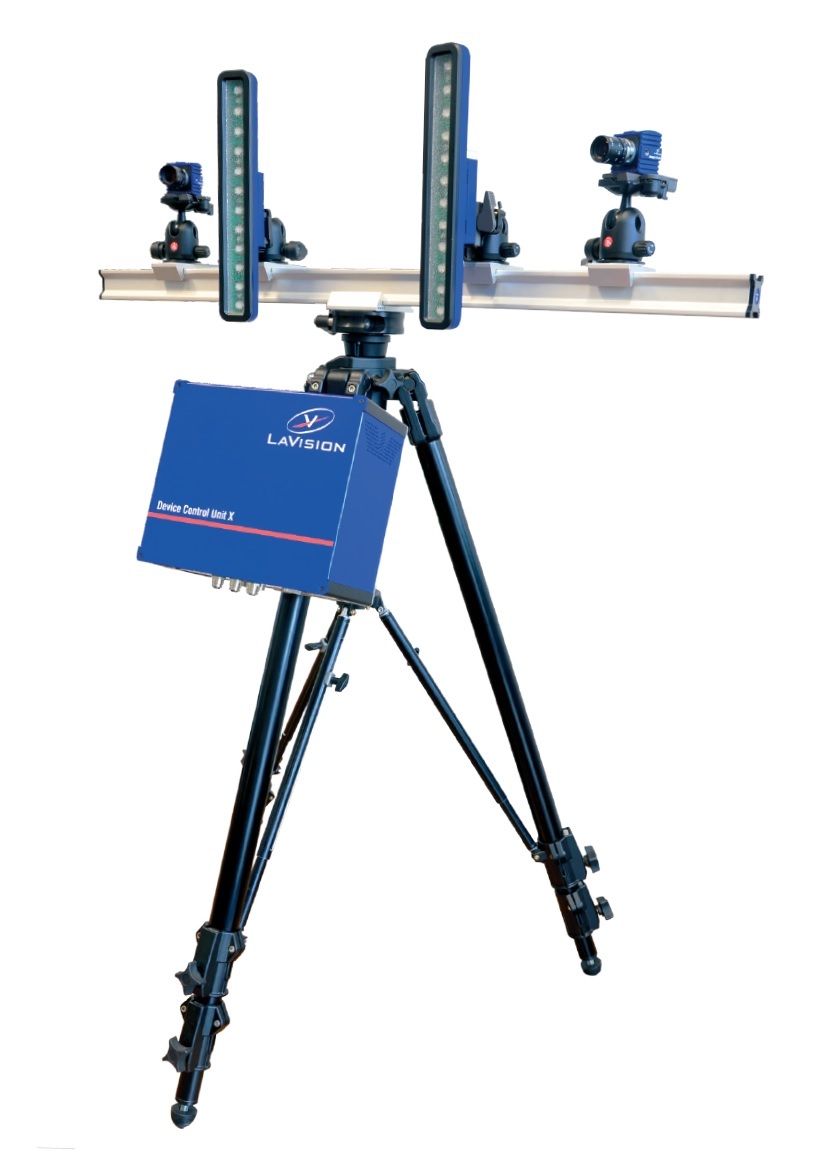
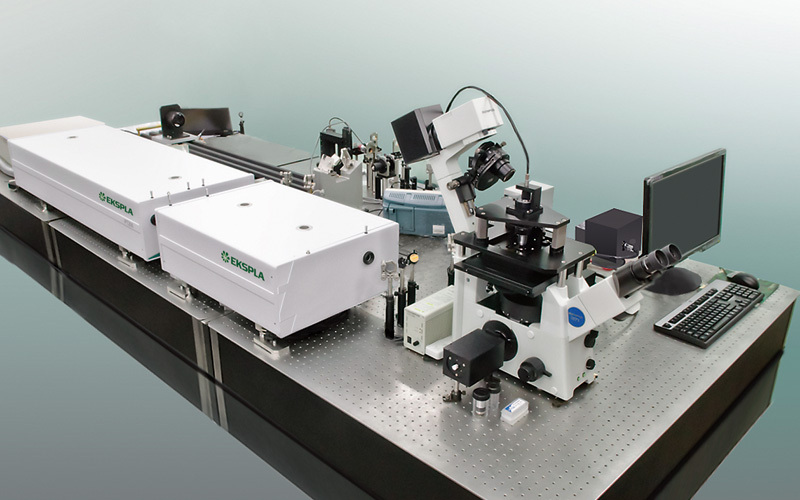
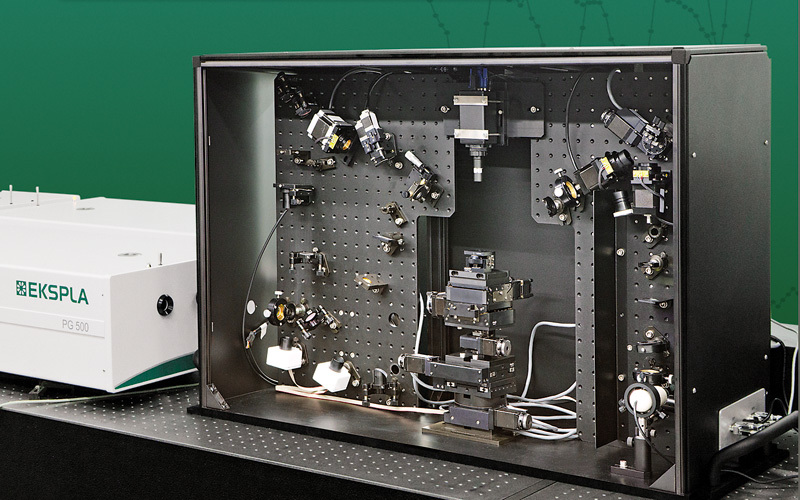
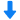
水洗喷嘴中液滴粒径,液滴速度,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(干涉仪)
Crude Unit Column Overhead – Corrosion
Water is usually injected in the
overhead piping to:
• Help quench and scrub the
overhead vapors
• Dilute acids formed
• Prevent any salts or acids from
forming in the system
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
液滴粒径,液滴速度,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案
Turbulence of the round jet has been assessed using invariants
of the velocity gradient tensor. Experimental data, obtained
using Tomographic Particle Image Velocimetry (Tomo-PIV),
using four PCO-4000 cameras with 11 megapixel resolution,
is presented for a seeded free air jet, operating in the turbulent
regime and the Re number based on the diameter of the nozzle
is 10000. Using the acquired 3-D velocity fields, the local
statistical and geometrical structure of three-dimensional
turbulent flow can be described by properties of the velocity
gradient tensor. The invariants of the velocity gradient (R and
Q), rate-of-strain ( Rs andQs ), and rate-of-rotation (Qw )
tensors are analyzed across the turbulent expanding regions at
different distances from the nozzle outlet. More specifically,
the JPDF of invariants is computed, which allows a detailed
statistical characterization of the dynamics, geometry and
topology of the flow during the entrainment process. It should
be noted that the results obtained are indicative of the
preliminary work in this area.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
l流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The motion tracking enhancement technique
(MTE) is a recently introduced method to improve the
accuracy of tomographic PIV measurements at seeding
density higher than currently practiced. The working
principle is based on the fact that the particle field and its
projections are correlated between the two exposures.
Therefore, information from subsequent exposures can be
shared within the tomographic reconstruction process of a
single object, which largely reduces the energy lost into
ghost particles. The study follows a previous work based
on synthetic particle images, showing that the MTE technique
has an effect similar to that of increasing the number
of cameras. In the present analysis, MTE is applied to
Tomographic PIV data from two time-resolved experiments
on turbulent shear flows: a round jet at Re = 5,000
(facq = 1,000 Hz) and a turbulent boundary layer at the
trailing edge of an airfoil (Rec = 370,000) measured at
12,000 Hz. The application of MTE is extended to the case
of more than two recordings. The performance is assessed
comparing the results from a lowered number of cameras
with respect to the full tomographic imaging system. The
analysis of the jet flow agrees with the findings of
numerical simulations provided the results are scaled taking
into account the concept of MTE efficiency based on
the volume fraction where ghost-pairs (Elsinga et al.
2010a) are produced.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中3D3C速度矢量场,速度场,速度矢量场,体视速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
To apply Tomographic PIV to industrial flow, ex. flow around rain gutter, 50 mm volume
thickness and 0.1 ppp particle density, at least, are necessary. In such experimental conditions, signal to
ghost ratio of object images and accuracy of vectors are problems. To tackle these problems, influence
of number of cameras, image pre-processing and vector post-processing to the accuracy of Tomographic
PIV are experimentally investigated at different measurement volume thickness and particle densities.
This investigation reveals that time-series minimum subtraction at each pixel without any spatial filter is
suitable for image pre-processing for such conditions. Although this filter results in lower signal to ghost
ratio, better vector field without less spurious vectors than a traditional one. This signal to ghost ratio is
improved linearly by increasing the number of camera up to 8 and accuracy of velocity vectors also
increasing up to 8 at any particle density and volume thickness conditions. This improvement by
increasing the number of camera is experimentally proved as a first time. Obtained velocity vectors are
filtered by spatial filter in physical domain and frequency domain to reduce measurement noise. Filtered
velocity profile of thick volume measurable domain, 135 x 230 x 50 mm3 in air, is well coincident with
previous experiments even in velocity fluctuation and Reynolds stress. To resolve turbulent fine scale
vortex and large scale vortex simultaneously, more than 6-camera are needed for the case of 0.12 ppp
particle density and 50 mm volume thickness. For the case of 0.45 ppp and 50 mm volume thickness
with 8-camera has also enough accuracy to access velocity fluctuation and Reynolds stress. This paper
achieves the large measurable domain, 160 x 220 x 80 mm3, at the particle density of 0.53 ppp.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
3D3C速度矢量场,速度场,速度矢量场,体视速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流场中速度场,速度矢量场,气动声学性能检测方案(粒子图像测速)
One of the major environmental problems facing the aviation industry is that of aircraft noise. The work
presented in this paper, done as part of the EU’s OPENAIR Project, looks at reducing spoiler noise whilst
maintaining aerodynamic performance, through means of large-scale fractal porosity. It is hypothesised that
the highly turbulent flow generated by fractal grids from the way the multiple-length-scales are organised in
space, would reduce the impact of the re-circulation region and with it, the low frequency noise it generates.
In its place, a higher frequency noise is introduced which is more susceptible to atmospheric attenuation and
is less offensive to the human ear. A total of nine laboratory scaled spoilers were looked at, seven of which
had a fractal design, one with a regular grid design and one solid for reference. The spoilers were inclined at
an angle of 30. Force, acoustic and flow visualisation experiments on a flat plate were carried out and it was
found that the present fractal spoilers reduce the low frequency noise by 2.5dB. Results show that it is possible
to improve the acoustic performance by modifying a number of parameters defining the fractal spoiler, some
of them very sensitively. From these experiments, two fractal spoilers were chosen for a detailed aero-acoustic
study on a three-element wing system, where it was found that the fractal spoilers had a reduction of up to 4dB
in the sound pressure level while maintaining similar aerodynamic performances as conventional solid spoilers
on the measured wing system.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场,气动声学性能
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Particle image velocimetry (PIV) experiments have been carried out to study the correlation between the high-
Reynolds number turbulent flow and wall heat transfer characteristics in a two-pass square channel with a smooth wall
and a 90 rib-roughened wall. Detailed averaged velocity distributions and turbulent kinetic energy for both the main
and the secondary flows are given for a representative Reynolds number (Re) of 30,000. The PIV measurement results
were compared with the heat transfer experimental data of Ekkad and Han [International Journal of Heat Mass
Transfer 40 (11) (1997) 2525–2537]. The result shows that the flow impingement is the primary factor for the two-pass
square channel heat transfer enhancement rather than the flow turbulence level itself. The characteristics of the secondary
flow,for example,vortex’s shape, strength,rotating-direction and positions, are closely correlated with the wall
heat transfer enhancements for both smooth and ribbed wall two-pass square channels. The rib-induced flow turbulence
increases the heat transfer mainly because of the enhanced local flow impingement near the rib.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
空气流体中速度场检测方案
The flow at Reynolds number 100k around an inflexible, two-dimensional flapping airfoil is investigated using the stereoscopic Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) technique. The typical phenomenon of a moving laminar separation bubble during one flapping cycle is identified. The measurement data is compared with URANS computations.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
granular matter,颗粒流,粒子流,颗粒体中流动场,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The paper presents results of strain measurements in cohesionless sand in two different
boundary value problems, namely quasi-static pull-out test of a steel wall and
confined granular flow in a rectangular model silo using a non-destructive method
called Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) which is a technique for measuring surface
displacements from digital images. Advantages and disadvantages of the method are
outlined.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流动场,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中PLIF,平面激光诱导荧光,浓度场,速度场检测方案(流量计)
A concept for dynamic mixture formation
investigations of fuel/air mixtures is presented which can
equally be applied to several other laser induced fluorescence
(LIF) applications. Double-pulse LIF imaging was
used to gain insight into dynamic mixture formation processes.
The setup consists of a modified standard PIV setup.
The ‘‘fuel/air ratio measurement by laser induced fluorescence
(FARLIF)’’ approach is used for a quantification of the
LIF images in order to obtain pairs of 2D fuel/air ratio maps.
Two different evaluation concepts for LIF double pulse
images are discussed. The first is based on the calculation of
the temporal derivative field of the fuel/air ratio distribution.
The result gives insight into the dynamic mixing process,
showing where and how the mixture is changing locally. The
second concept uses optical flow methods in order to estimate
the motion of fluorescence (i.e., mixture) structures to
gain insight into the dynamics, showing the distortion and
the motion of the inhomogeneous mixture field.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
PLIF,平面激光诱导荧光,浓度场,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The active control of laminar and turbulent flows with dynamic actuators is of
great scientific and technological interest in nearly all fields of fluid mechanics.
Today, most of the well established actuator concepts are based on pneumatic and
micro-mechanic bases. However, owing to their limited dynamic range, their potential
seems to be limited from the present point of view [1]. Recently it was successfully
demonstrated that a boundary layer flow can be efficiently controlled by
using an optical actuator concept, which allows non-intrusive excitation of the flow
with nearly any pulse-width and repetition-rate by heating the surface of a model
with a short-focused laser pulse [2]. The drawback of the proposed and examined
method was the gradual ablation of the model surface. To avoid this problem the
excitation was performed above the surface in this investigation [3]. By using the
phased locked stereoscopic PIV and Schlieren technique the dynamic effect of the
laser induced plasma on a boundary layer flow could be examined in detail. In this
contribution the main results will be summarized and the perspective of this actuation
method for fundamental and applied fluid mechanics will be outlined.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The active control of laminar and turbulent flows with dynamical actuators is of great scientific and
technological interest in nearly any field of fluid mechanics. On on hand it becomes possible to generate artifical
flow structures whose properties and significance for the turbulent mixing, or their interaction with other flow
structures, can be examined. On the other hand, these devices suppress flow separation on profiles or increase the
performance of flow engines. Today, most of the well established actuator concepts are based on pneumatic and
micro-mechanic basis. However, owing to their limited dynamic range their potential seems to be limited from the
present point of view, see Gad-el-Hak (2001), and also their technical implementation is sometimes difficult. In
the following an optical actuator concept is proposed and examined that allows to excite the flow non-intrusively
with nearly any pulse-width and repetition-rate.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
We report particle image velocimetry measurements of the collision of a vortex ring with a heated
wall kept at constant temperature. We consider the case when both the vortex ring and the thermal
boundary layer generated by the vertical heated wall are stable and laminar prior to any interaction.
The impingement process can be divided into two parts. sid A ring-driven stage, where the vortex
ring grows in diameter while approaching the wall and therefore it sweeps progressively an
increased surface on the wall. siid A boundary layer-driven stage, where the vortex ring moves
upward due to the thermal convective motion generated by the heated wall. In some cases, the
head-on collision triggers the ring’s azimuthal instability as revealed by the formation of vortical
structures arranged on a wavy starlike pattern and confirmed by flow visualizations. A single
collision generates important velocity gradients and shear stresses along the wall accompanied with
the creation of local vorticity normal to the vertical heated wall. Peak wall shear stresses occur near
the point of impact of the vortex ring core.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Simultaneous local jitter, 2-D wavefronts and accelerometer measurements were performed in the flow over a flat-window turret at Mach numbers between 0.3 and 0.4 along a centerplane with a viewing angle varying between 90 and 118 degrees. Both local and global jitter imposed on a small- and large-aperture laser beams were measured using position-sensing devices and a high-speed 2-D wavefront sensor. A linear stochastic estimation technique was applied to separate the mechanically-related component of the jitter from the aero-optical component. Spectra of aero-optical jitter for different elevation angles and speeds were calculated and useful scaling laws were proposed. It was shown that aero-optical jitter was due to the presence of both the stationary and traveling aero-optical components. Detailed analysis of the global and the local jitter spectra and the spectral cross-correlation between them at different speeds and viewing angles is presented and discussed in details. Additionally, PIV system was used to measure the flow field over the flat window, simultaneously with the aero-optical jitter measurements.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度矢量场,跨音速, 二氧化碳,CO2检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Particle image velocimetry (PIV) is utilized with solid carbon dioxide (CO2)
seeding material to conduct boundary layer measurements in the test section of the Air
Force Research Laboratory’s Trisonic Gas-dynamics Facility (TGF), which has a 24 inch
by 24 inch cross-section. Freestream velocity was set at Mach 0.3, Mach 0.5, or Mach
0.8 while stagnation pressure ranged from 500 to 2400 pounds per square foot (psf). High
pressure liquid CO2 was directed through expansion nozzles into shroud tubes which led
to solidified particles in the wind tunnel stagnation chamber. Two different sets of
shroud tubes were used to modify the size of dry ice particles produced and the particle
number density. Shroud tubes with an inside diameter (ID) of 0.824 inches provided
good particle count and coverage for stagnation pressures between 500 and 1500 psf,
while 0.364 inch ID shroud tubes demonstrated good particle count and coverage for
stagnation pressures over 1000 psf. Overall, the PIV results produced freestream velocity
measurements and boundary layer profiles which compared well with expected values.
After initial processing, turbulence data closely followed trends expected within
boundary layer, but levels were somewhat higher than anticipated. When the PIV data
was processed using elliptical interrogation regions, elongated in the streamwise
direction, resulting turbulence levels were much closer to expectations.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场,跨音速, 二氧化碳,CO2
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中相关的几何学的剪切区模拟检测方案(其它无损检测仪器/设备)
The geometry of ductile strain localization phenomena is related to the rheology of the deformed rocks. Both qualitative and quantitative
rheological properties of natural rocks have been estimated from finite field structures such as folds and shear zones. We apply physical modelling
to investigate the relationship between rheology and the temporal evolution of the width and transversal strain distribution in shear zones,
both of which have been used previously as rheological proxies. Geologically relevant materials with well-characterized rheological properties
(Newtonian, strain hardening, strain softening, MohreCoulomb) are deformed in a shear box and observed with Particle Imaging Velocimetry
(PIV). It is shown that the width and strain distribution histories in model shear zones display characteristic finite responses related to material
properties as predicted by previous studies. Application of the results to natural shear zones in the field is discussed. An investigation of the
impact of 3D boundary conditions in the experiments demonstrates that quantitative methods for estimating rheology from finite natural structures
must take these into account carefully.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
相关的几何学的剪切区模拟
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
燃烧,火焰,分层火焰,涡流中速度场,流场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Stereoscopic Planar Image Velocimetry (SPIV) has been applied to obtain the three
components of the instantaneous velocity vectors on a vertical plane above the burner
outlet where the flames propagate. The instantaneous temperature fields have been
determined through Laser Induced Rayleigh (LIRay) scattering. Planar Laser Induced
Fluorescence (PLIF) on acetone has been used to calculate the average equivalence ratio
distributions. Instantaneous turbulent burning velocities have been extracted from SPIV
results, while flame curvature and flame thermal thickness values have been calculated
using the instantaneous temperature fields. The probability distributions of these
quantities have been compared considering the separate influence of equivalence ratio
stratification and turbulence. It has been observed that increased levels of turbulence
determine higher turbulent burning velocities and flame front wrinkling. Flames
characterized by stronger fuel stratification showed higher values in turbulent burning
velocities. From the curvature analysis emerged that increased fuel concentration
gradients favour flame wrinkling, especially when associated with positive small radius
of curvature. This determines an increased surface area available for reaction that
promotes a faster propagation of the flame front in the oncoming combustible mixtures.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,流场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中3D3C速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Over the past twelve years, two-dimensional and stereoscopic particle image velocimetry (PIV)
techniques have been used to obtain detailed measurements of the thermal and transport properties
of the microparticle component of dusty plasma systems. This letter reports on an extension of these
techniques to obtain a volumetric, three-dimensional velocity vector measurement using
tomographic PIV. Initial measurements using the tomographic PIV diagnostic are presented.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
3D3C速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
发动机中流场,速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
1.The HARVEST Project
2.2D-2C PIV Measurements
3.NumericalComputation
4.Results
1.ComparisonsPIV / CFD
2.Characterizationof dynamicstall
5.Conclusions
----------------------------------------------------------
Objective:Convertcineticenergyof riversor of tidal flow
Specificity:Vertical axis turbine, radial flux, new generationof Darrieusand Gorlovturbine
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流场,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度矢量场,速度场,体视速度场,3D3C速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) denotes a prevailing technique for
imaging turbulent fluids with high-speed cameras. Corresponding image
sequences provide the basis for estimating such flows and related flow
patterns through image processing. While so far this technique has been
applied in two dimensions (2D) in terms of an illuminated plane intersecting
the volume, recent research focuses on imaging fluids directly in
3D. This paper provides a synopsis of the state-of-the-art and its connections
to previous research work on image restoration. We address
the basic problems involved and point out promising research directions
for reconstructing scalar-valued particle functions from few tomographical
measurements. Solutions to these problems will provide an essential
processing step prior to the estimation of 3D flows from reconstructed
volume functions.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场,速度场,体视速度场,3D3C速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中3D3C速度矢量场,速度场,体视速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
This paper describes the principles of a
novel 3D PIV system based on the illumination,
recording and reconstruction of tracer particles within
a 3D measurement volume. The technique makes use
of several simultaneous views of the illuminated particles
and their 3D reconstruction as a light intensity
distribution by means of optical tomography. The
technique is therefore referred to as tomographic
particle image velocimetry (tomographic-PIV). The
reconstruction is performed with the MART algorithm,
yielding a 3D array of light intensity discretized
over voxels. The reconstructed tomogram pair is then
analyzed by means of 3D cross-correlation with an
iterative multigrid volume deformation technique,
returning the three-component velocity vector distribution
over the measurement volume. The principles
and details of the tomographic algorithm are discussed
and a parametric study is carried out by means of a
computer-simulated tomographic-PIV procedure. The
study focuses on the accuracy of the light intensity field
reconstruction process. The simulation also identifies
the most important parameters governing the experimental
method and the tomographic algorithm
parameters, showing their effect on the reconstruction
accuracy. A computer simulated experiment of a 3D
particle motion field describing a vortex ring demonstrates
the capability and potential of the proposed
system with four cameras. The capability of the technique
in real experimental conditions is assessed with
the measurement of the turbulent flow in the near
wake of a circular cylinder at Reynolds 2,700.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
3D3C速度矢量场,速度场,体视速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中3D3C速度矢量场,3D3C速度场,速度场,速度矢量场,体视速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The wakes of wall mounted circular cylinders of very low
aspect ratio have been investigated in a wind tunnel. Besides
planar PIV, also high resolution tomographic PIV was used
to capture the flow phenomena downstream of the cylinder.
By changing the velocity U¥ and the cylinder height h at a
constant aspect ratio L = h=D, a wide database of different
flow conditions was obtained. The resulting relative height of
the boundary layer thickness d was 0:6 h=d 2:5, while the
Reynolds number based on the length l between leading edge
and cylinder centre Rel was 57;000 Rel 188; 000. A pair of
counter-rotating vortices was found in the wake of the cylinder.
The rotation sense is such, that in the center of the wake a
positive vertical velocity component results. Also horseshoe
vortices were found next to these trailing vortices. The relative
height of the incoming boundary layer has a large impact on the
development, strength and dissipation of the vortex system.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
3D3C速度矢量场,3D3C速度场,速度场,速度矢量场,体视速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中3D3C速度场检测方案
A novel technique to increase the accuracy of multiplicative algebraic reconstruction
technique (MART) reconstruction from tomographic particle image velocimetry (PIV)
recordings at higher seeding density than currently possible is presented. The motion tracking
enhancement (MTE) method is based on the combined utilization of images from two or more
exposures to enhance the reconstruction of individual intensity fields. The working principle is
first introduced qualitatively, and the mathematical background is given that explains how the
MART reconstruction can be improved on the basis of an improved first guess object obtained
from the combination of non-simultaneous views reduced to the same time instant deforming
the 3D objects by an estimate of the particle motion field. The performances of MTE are
quantitatively evaluated by numerical simulation of the imaging, reconstruction and image
correlation processes. The cases of two or more exposures obtained from time-resolved
experiments are considered. The iterative application of MTE appears to significantly improve
the reconstruction quality, first by decreasing the intensity of the ghost images and second, by
increasing the intensity and the reconstruction precision for the actual particles. Based on
computer simulations, the maximum imaged seeding density that can be dealt with is tripled
with respect to the MART analysis applied to a single exposure.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
3D3C速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
MAVDelFlyII型扑翼机,扑翼机中力,流场,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Recent years have seen an increasing interest in Micro Air Vehicles (MAVs). MAVs are small
(micro sized) aircraft and find their application in a multitude of commercial, industrial and
military purposes. To perform their missions MAVs should be small sized, have good
manoeuvrability, be well controllable and have a broad flight envelope. When flying in small
confinements, the ability to fly at low airspeed and to have good manoeuvrability is critical. One
type of MAVs, the flapping-wing MAV, particularly has attractive characteristics for flight in
confined spaces.
DelFly is a biplane flapping-wing MAV designed and built at Delft University of Technology.
DelFly is able to hover and has an onboard camera for observation and vision-based control. For
the DelFly project a top-down approach is followed, where from the study of a relative large
model experience and theoretical insights can be gained, that can assist to create smaller,
functional versions of the DelFly. The ultimate aim of the DelFly project is to improve the
design to a very small full autonomous aircraft.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
力,流场,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
通用襟翼模型中冷喷射漩涡的相互作用检测方案(粒子图像测速)
As part of the FARWAKE project, subtask 2.1.1, wake vortex flow experiments are performed using the PIV measurement technique in a water tank. The wake generating model consists of a simple wing/flap model that can be equipped with water jets to simulate propulsion effects. The model was tested at a speed of 3m/s and two angles of attack: 0and 6. Chord Reynolds number of approximately 225.000 and Vortex Reynolds numbers of approximately 150.000 and
220.000 were obtained during the tests.
The main objective of the present study is to investigate the influence of a jet on the flap end vortex and the wake vortex formation. The investigation focuses on the direct influence of
the jet on the flap end vortex and the (merged) vortex characteristics in the near to mid field.
The main vortex characteristics addressed in this report are: the vortex trajectory, the maximum tangential velocity, the peak vorticity and the vortex core radius.
The vortex information is obtained from Stereo-PIV experiments performed in a fixed plane perpendicular to the towing direction. The measurements return the 3 components of the velocity in that plane and the streamwise component of the wake vorticity. A submergible
moving camera system is used in order to keep the moving vortex in the field of view during the vortex downward motion.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
冷喷射漩涡的相互作用
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
圆柱体中圆柱体振动,拖曳阻力,运动幅度,速度场,速度矢量场,PIV,粒子成像测速检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Reducing the deleterious effect of Vortex Induced Vibrations (VIV) in marine risers is an
important task for ocean engineers; and many competing factors exist in the design of
VIV suppression devices. This thesis explores the experimental minimization of the drag
force and the disruption of v0l1ex formation by utilizing VIV suppression devices.
Two series of tests are conducted-both utilizing separate testing designs. The first tests
are the flexible cylinder experiments, detailed in Chapter 2, which determine the drag
force and vibration amplitude of numerous, original testing configurations. The second
series of tests are the rigid cylinder, PIV experiments, detailed in Chapter 3. These tests
measure both the drag force on the cylinder and the oscillating component of the lift
force, the latter of which is a good indication of v011ex formation. The Chapter 3 tests
also image the test section wake-providing helpful insight into the physical process of
vortex formation.
In brief, this thesis presents a detailed description and results of the two series of original
VIV suppression tests. Many original configurations are tested, and the results are
contained herein.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
圆柱体振动,拖曳阻力,运动幅度,速度场,速度矢量场,PIV,粒子成像测速
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Turbulent jets have been always present in fluid-mechanic researches due to the
large number of applications they have and to the presence of all the turbulence features
on them. Thanks to the use of relative new non-intrusive techniques–such as PIV
(Particle Image Velocimetry)-, the knowledge of turbulence in general, and turbulent
jets in particular has increased.
This work is focused on the assessment of both, the main characteristics of the
turbulent jet and, at the same time, some significant PIV features. For that aim two
experiments are proposed:
-The first one, denominated “Spatial Resolution in PIV”, tries to determine the
best position to place the digital camera that films the movement of the particles
present in the jet, taking into account that we are interested on studying not only
the microscales of the turbulent flow, but also the velocity field and the
recovering of isotropy by evaluating the turbulent parameters (skewness,
kurtosis, square mean derivative ratios,…).
-In the second one, called “Effect of the Reynolds Number in Turbulence”,
starting from the results of the first experiment, the behavior of the jet depending
on the relationship between the inertia forces and the viscous ones is analyzed.
To do this, three different zones along the jet and eight different Reynolds
numbers are to be studied.
This report is structured in four different chapters. The first one corresponds to a
theoretical introduction to turbulence. In the second one the experimental setup is
described after introducing the PIV measurement technique. The third one presents the
results and carries out a deep analysis of them. Finally, in chapter four, the results are
summarized obtaining some important conclusions and considering as well future
challenges of the present work.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
俯冲地震周期的模拟模型;地震构造中弧前演化检测方案(其它无损检测仪器/设备)
We introduce and test an experimental approach to simulate elastoplastic megathrust
earthquake cycles using an analogue model and apply it to study the seismotectonic
evolution of subduction zones. The quasi-two-dimensional analogue model features
rate- and state-dependent elastic-frictional plastic and viscoelastic material properties and
is scaled for gravity, inertia, elasticity, friction, and viscosity. The experiments are
monitored with a high-resolution strain analysis tool based on digital image correlation
(particle imaging velocimetry, PIV), providing deformation time series comparable to
seismologic, geodetic, and geologic observations. In order to separate elastic and
nonelastic effects inherent the experimental deformation patterns, we integrate elastic
dislocation modeling (EDM) into a hybrid approach: we use the analogue earthquake slip
and interseismic locking distribution as EDM dislocation input and forward model the
coseismic and interseismic elastic response. The residual, which remains when the EDM
prediction is subtracted from the experimental deformation pattern, highlights the
accumulation of permanent deformation in the model. The setup generates analogue
earthquake sequences with realistic source mechanisms and elastic forearc response and
recurrence patterns and reproduces principal earthquake scaling relations. By applying
the model to an accretionary-type plate margin, we demonstrate how strain localization at
the rupture peripheries may lead to a seismotectonically segmented forearc, including a
tectonically stable shelf and coastal high (<20% plate convergence accommodated by
internal shortening) overlying the area of large megathrust earthquake slip. Fifty to 75% of
plate convergence is accommodated by internal shortening in the slope region where
earthquake slip tapers out toward the trench. The inner forearc region remains undeformed
and represents a basin.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
弧前演化
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
燃料,喷雾,液滴中粒径,速度,形状检测方案(激光粒度仪)
In the present work the process of a transient fuel injection in a constant high-pressure atmosphere is investigated experimentally. As fuel, dimethyl ether (DME) is used. The goal is to receive new information about the charac-teristics referring to the droplet size, the droplet velocity and the droplet shape in the jet. The high-pressure chamber has a constant pressure of 2 MPa and the fuel spray is injected with a pressure of 6 MPa, 7 MPa and 8 MPa. The spray is analysed by a Shadow-Sizing-technique and digital image analysis with temporal and spatial resolution, which even allows investigating non-spherical droplets. The correlations of d
velocity and droplet shape are presented as Joint Probability Density Functions (JPDF). The conclusion of the investigation shows that little increase of the injection pressure has a remarkable effect on the droplet size. Furthermore, the centricity is widely influenced by the injection pressure. With lower injection pressure the droplet velocity decreases. Moreover, the droplets mean diameter shows a significant decrease with increasing time after the injection
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
粒径,速度,形状
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中数字成像和PIV方法用于多相流检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Multiphase flows in process industry- project (ProMoni) was a by Tekes and Finnish industry funded three year research project. Five Finnish universities and research units were working in the project in different applications of multiphase flows. All the results are reported in the projects final report1.
The aim of this report is to give detailed insight to the work which was made by TUT:s Experimental fluid dynamics group. In the project were developed methods for dispersed phase characterization, for turbulence measurements in multiphase flows and for turbulence characterization. Digital Imaging and Particle Image Velocimetry were the used measurement methods.
In institute of Energy and Process Engineering at TUT has been developed Experimental Fluid Mechanics knowledge based on optical and digital imaging measurement methods. The work has been continued several years with support of TEKES and various industrial partners. At this ProMoni-project has been reached a level, which enables research of new key tasks in multiphase fluid mechanics. The project has enabled the research of interaction of dispersed phase and turbulence and this leads to many new inventions industrial applications. This is the main motivation to publish this separate report.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
数字成像和PIV方法用于多相流
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
雾沫中雾化形成在静电旋转钟镀膜中的应用检测方案(激光粒度仪)
Electrostatic, rotating bell (ESRB) application is one of the most important coating application techniques
for industries with demanding specifications for optical attractiveness of coatings, such as automotive. The
ESRB process involves production of droplets using a high-speed rotating bell, which are subsequently
transported to the substrate being coated via shaping air [1-3]. An electrical potential is applied between the
bell and the substrate which further helps droplet atomization and transport. This research investigates the
effects of inertia, centrifugal force, drag force, and electrostatic force on the atomization mechanism and
particle size distribution using an automotive OEM base coat formulation. Coating flow rate (CFR), shaping
air flow rate (SAFR), bell speed (BS), and electrostatic potential (EP) were used as primary parameters to
create various atomization conditions and particle size distributions. The atomization mechanism, ligament
formation, and particle size distribution were measured using high-speed laser shadowography and image
processing. The effects of governing forces and particle size generated on efficiency of droplet transfer to the
substrate and optical appearance of the coatings were studied to generate operating windows for optimum
process efficiency and appearance.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
雾化形成在静电旋转钟镀膜中的应用
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2271篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等