确定用于清洗验证和纯化水应用的最佳TOC分析仪,通常会有两种常用检测技术的比较:,NDIR检测和膜电导率。本研究中,在药物的应用上,通过使用几种不同的基质和分析物,分析比较这两种分析检测技术。
方案详情

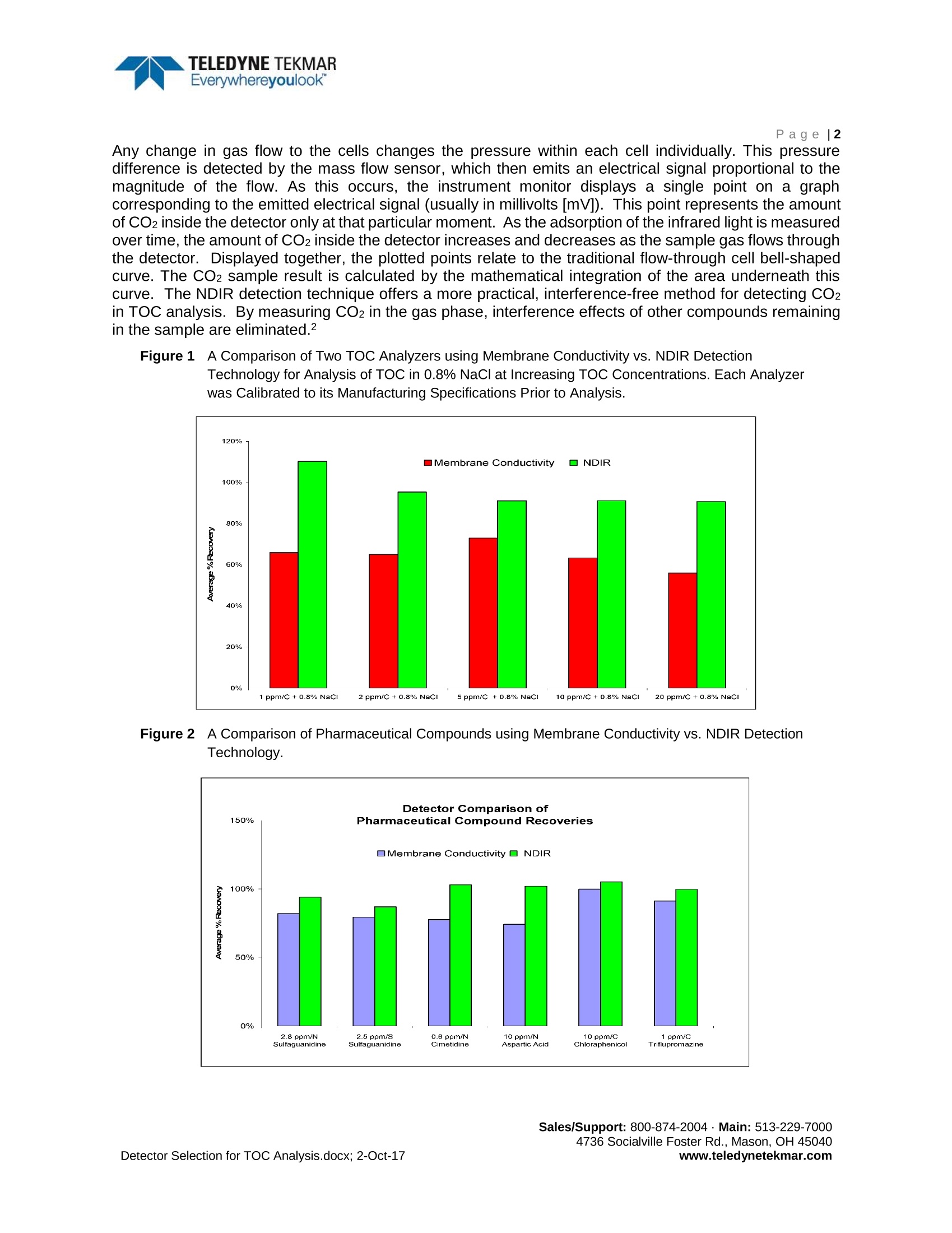
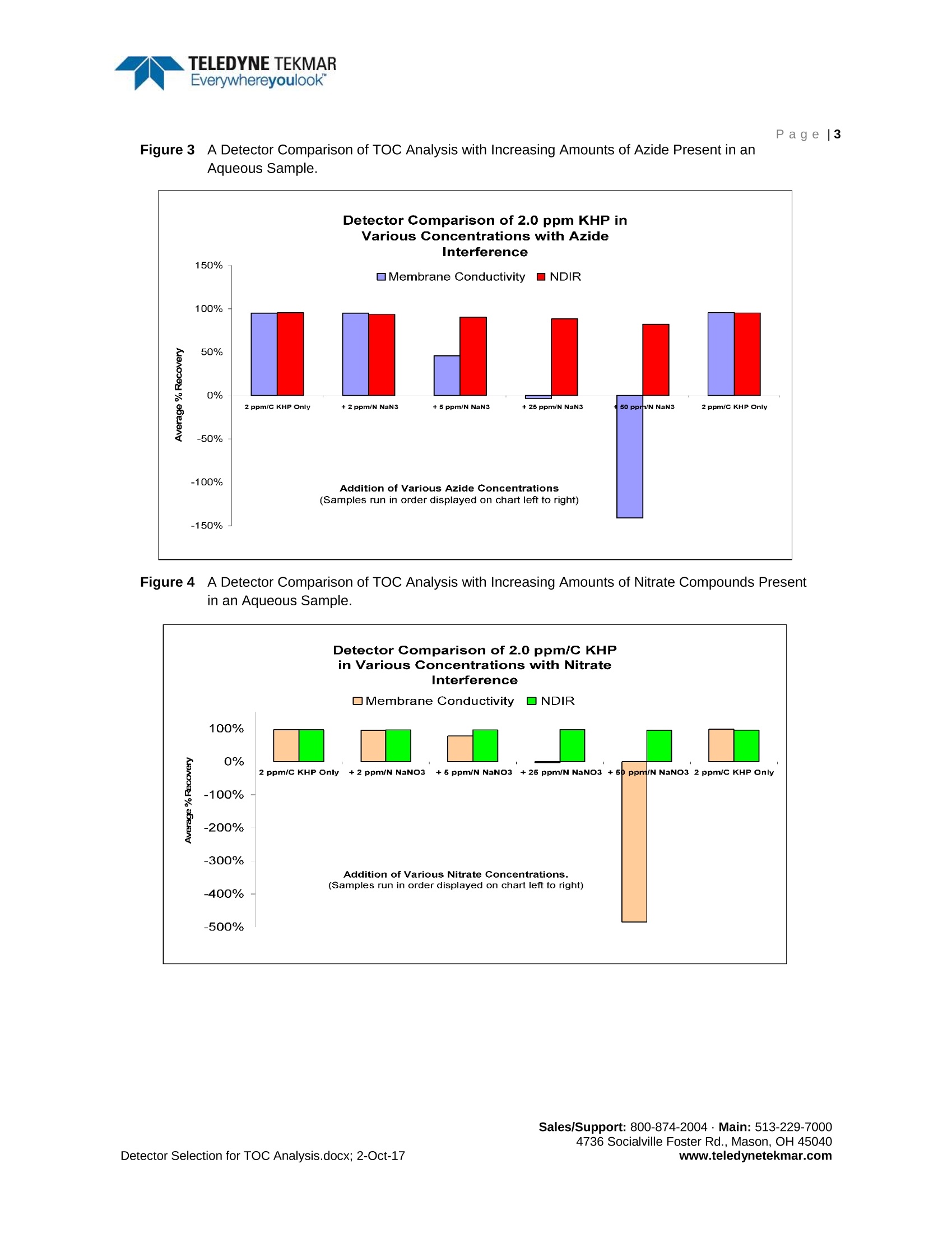
TELEDYNE TEKMAREverywhereyoulook"An Analytical DetectorComparison for TOC Analysis inCleaning Validation and WaterPurification Applications TELEDYNE TEKMAREverywhereyoulookPage |2 Product White Paper Page|1 Determining the best TOC analyzer for cleaning validation and purified water applications often results in acomparison of the two commonly used detection techniques: NDIR detection and membrane conductivity.In this study, an analytical comparison of these detection techniques was conducted using several differentmatrices and analytes in a pharmaceutical application. Background Conductivity TOC analyzers that employ direct conductivity detectors offer the simplest and most compact designavailable. The conductivity method (including direct and membrane conductivity) measures the conductivityof the sample before and after it is oxidized. The resulting differential measurement is attributed to the TOCcontent of the sample. During the sample oxidization phase, Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and other gases areformed. The dissolved CO2 forms a weak acid,thereby changing the conductivity of the original sample inproportion to the TOC content. The success of the technique relies on the assumption that only CO2 ispresent in the sample matrix. In the event that other chemical species are present in the sample, theirindividual products of oxidation may present either a positive or a negative interference to the actual TOCvalue, resulting in commensurate analytical error. Additionally, measurements over 50 ppmC are notuniformly proportional to the TOC of the sample and therefore not achievable.1 Lastly, the conductivitycompensation errors related to temperature and pH, can also be of significant importance. Membrane Conductivity A different approach to improving the accuracy of TOC analysis using conductivity incorporates the use ofhydrophobic gas permeation membranes.These membranes allow a more “selective” passage of thedissolved CO2 gas to the“zero” water used for conductivity analysis. While this approach has solved certainproblems, membranes often have their own particular limitations. Potential problems often include clogging,true selectivity, micro leaks, flow problems, dead spots, and microbial growth (blockage). Of greatestconcern is the membrane's tendency to become a location for secondary chemical reactions that promote"false negatives,”a condition far more severe than "false positives”, in critical applications. Because falsenegatives can lead to an erroneous conclusion of meeting cleaning validation criteria, they are of thegreatest consumer safety concerns. Other concerns include the inability of membrane methods to recover their operational performance afteran overload condition arises that over-ranges the instrument. Recovery can often take hours beforereturning to reliable service and recalibration. Small changes in pH are also a well-known contributor toinaccuracy, leading to incomplete oxidation of organics and consequently CO2 detection interference. NDIR Detection NDIR detectors use Infrared (IR) energy to detect the presence of CO2. An IR beam is transmitted throughthe sample chamber as the sample gas containing CO2 fills the chamber. Pressurized front and rear cellsconnected by a mass flow sensor are located within the detector. An optical filter allows only light of apredetermined wavelength to reach the detector cells from the IR source. When IR energy passes throughCO2 gas, it creates a unique adsorption spectrum making CO2 distinguishable from other gases.Tocollimate the IR light through the sample chamber and to increase optical efficiency, the light source issurrounded by a parabolic reflector assembly, which is typically gold lined. Any change in gas flow to the cells changes the pressure within each cell individually. This pressuredifference is detected by the mass flow sensor, which then emits an electrical signal proportional to themagnitude of the flow. As this occurs, the instrument monitor displays a single point on a graphcorresponding to the emitted electrical signal (usually in millivolts [mV]). This point represents the amountof CO2 inside the detector only at that particular moment. As the adsorption of the infrared light is measuredover time, the amount of CO2 inside the detector increases and decreases as the sample gas flows throughthe detector. Displayed together, the plotted points relate to the traditional flow-through cell bell-shapedcurve. The CO2 sample result is calculated by the mathematical integration of the area underneath thiscurve. The NDIR detection technique offers a more practical, interference-free method for detecting CO2in TOC analysis. By measuring CO2 in the gas phase, interference effects of other compounds remainingin the sample are eliminated.2 Figure1 1A Comparison of Two TOC Analyzers using Membrane Conductivity vs. NDIR DetectionTechnology for Analysis of TOC in 0.8% NaCl at Increasing TOC Concentrations. Each Analyzerwas Calibrated to its Manufacturing Specifications Prior to Analysis. Figuire 2 A Comparison of Pharmaceutical Compounds using Membrane Conductivity vs. NDIR DetectionTechnology. Figure 33A Detector Comparison of TOC Analysis with Increasing Amounts of Azide Present in anAqueous Sample. Figure 4 A Detector Comparison of TOC Analysis with Increasing Amounts of Nitrate Compounds Presentin an Aqueous Sample. www.teledynetekmar.com Conclusion A comparison of brine sample analysis at a concentration of 0.8% sodium chloride shown in Figure 1,demonstrates the superiority of NDIR detection. NDIR detection far surpasses the ability of membraneconductivity detection to analyze brines. A comparison of hard to oxidize pharmaceutical compounds (dueto their complex molecular structure and varying levels of nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon) is shown in Figure2. As illustrated, the membrane conductivity detector did not effectively recover these compounds incomparison to the NDIR detector. Figure 3 and Figure 4 demonstrate the nitrogen chemical species in thesample (and their individual oxidation products) interfering negatively with the membrane conductivity TOCrecovery, as the nitrogen concentration increases. NDIR detection technology achieved superior recoveryand accuracy over membrane conductivity for all compounds analyzed, as well as a wide range of samplewater matrices. References 1..Light, T.S.; Kingman, E.A.; Bevilacqua A.C. The Conductivity of Low Concentrations of CO2 Dissolvedin Ultrapure Water From 0-100℃; Paper presented at the 209th American Chemical Society NationalMeeting, Anaheim, CA, April 2-6, 1995. [Online] http://www.gatewayequipment.com/cond CO2.pdf(accessed Sept 28,2017). 2.Wallace, B.; Stevens, R. Evaluating Oxidationn andd Detection Technologies,PharmaceuticalFormulation. March/April 2004, 76-77. www.teledynetekmar.com Sales/Support: Main: Socialville Foster Rd., Mason, OH etector Selection for TOC Analysis.docx; -Oct-ww.teledynetekmar.com 确定用于清洗验证和纯化水应用的最佳TOC分析仪,通常会有两种常用检测技术的比较:,NDIR检测和膜电导率。本研究中,在药物的应用上,通过使用几种不同的基质和分析物,分析比较这两种分析检测技术。背景电导率TOC分析仪采用直接的电导率检测器,提供最简单和最紧凑的设计应用。电导率法(包括直接电导法和膜电导法)测量样品氧化前后的电导率。结果的差异测量归因于样品的TOC含量。在样品氧化阶段,形成二氧化碳(CO2)和其他气体,溶解的二氧化碳形成一种弱酸,从而改变原始样品的电导率,它与TOC的含量成一定比例。该技术的成功依赖于样品基体中只存在二氧化碳的假设,如果样品中存在其他化学物质,它们单独的氧化产物可能对实际TOC值产生正干扰或负干扰,从而导致相应的分析误差。此外,超过50 ppmC的测量值与样品的TOC并不是均匀成比例的,因此无法实现。最后,电导率补偿误差与温度和pH值有关,这也是非常重要的。膜电导率另一种利用电导率提高TOC分析准确性的方法是使用疏水气体渗透膜。这些膜可以让溶解的二氧化碳气体有更大的“选择性”通过,到达用于电导率分析的“零级”水。虽然这种方法解决了某些问题,但膜往往有其自身的局限性。潜在的问题通常包括堵塞、真正的选择性、微泄漏、流动问题、死点和微生物生长(堵塞)。最令人担忧的是,在关键应用中,膜容易发生二次化学反应,导致“假阴性”,这种情况比“假阳性”严重得多。因为假阴性可能导致符合清洁验证标准的错误结论,它们是消费者最大的安全问题。其他的担忧包括一旦发生超负荷的条件,超过仪器的范围,膜法无法恢复他们的操作性能,恢复通常需要数小时才能恢复到可靠的服务和重新校准。pH值的微小变化也是导致不准确的一个众所周知的因素,它会导致有机物的不完全氧化,从而干扰CO2检测。NDIR检测器NDIR探测器使用红外(IR)能量来检测二氧化碳的存在。当含有二氧化碳的样品气体充满样品室时,红外光束通过样品室传输。通过位于检测器内质量流量传感器连接的前后加压的池子,光学滤光片只允许预定波长的光从红外源到达探测器单元,当红外能量穿过二氧化碳气体时,会产生独特的吸收光谱,使二氧化碳有别于其他气体,为了校准通过样品室的红外光并提高光学效率,光源被一个特别的金质内衬的抛物面反射器组件包裹。流向检测池的气体的任何变化都会单独改变每个池内的压力。这种压力差由质量流量传感器检测,然后发出与流量大小成比例的电信号。当这种情况发生时,仪表监测器在与发出的电信号对应的图形上显示一个单点(通常以毫伏[mV]为单位)。这个点表示检测器内的二氧化碳在特定时刻的量。随着时间的推移,测量红外光的吸附量,样品气体流经检测器时,检测器内的二氧化碳量会增加或减少。集合在一起后发现,绘制的点与传统的流通池钟形曲线有关。二氧化碳样品的结果是通过曲线下面积的数学积分计算出来的。NDIR检测技术为TOC分析中CO2的检测提供了一种更实用、无干扰的方法。通过测量气相中的二氧化碳,消除了残留在样品中的其他化合物的干扰效应。Figure 1 在0.8% NaCl条件下,随着TOC浓度的增加,两台分别采用膜电导率和NDIR检测技术的TOC分析仪的比较。在分析之前,每个分析仪都根据其制造规格进行校准Figure 2利用膜电导率与NDIR检测技术对比药物化合物的回收率Figure 3 随着水样中叠氮化物量的增加,TOC分析检测器的比较Figure 4 随着水样中硝酸盐量的增加,TOC分析检测器的比较结论 对比图1中0.8%氯化钠浓度下的卤水样品,可以看出NDIR检测的优越性。NDIR检测器远远超过膜电导率检测分析盐水的能力。图2显示,难以氧化的药物化合物 (由于它们复杂的分子结构和不同的氮、硫和碳含量) 的比较。如所示,与NDIR检测器相比,膜电导率检测器不能有效地回收这些化合物。图3和图4表明,随着氮浓度的增加,样品中的氮化学物质(及其各自的氧化产物) 对膜的电导率TOC回收率有负影响。相比膜电导率技术,NDIR检测技术在所有的化合物分析以及广泛的水样品基质分析中,表现出优越的回收率和精度。参考文献1. Light, T.S.; Kingman, E.A.; Bevilacqua A.C. TheConductivity of Low Concentrations of CO2 Dissolved in Ultrapure Water From0-100 °C; Paper presented at the 209th American Chemical Society NationalMeeting, Anaheim, CA, April 2-6, 1995. [Online] http://www.gatewayequipment.com/cond_CO2.pdf(accessed Sept 28, 2017).2. Wallace, B.;Stevens, R. Evaluating Oxidation and Detection Technologies, PharmaceuticalFormulation. March/April 2004, 76 – 77.
确定


还剩2页未读,是否继续阅读?
培安有限公司为您提供《水中TOC检测方案(TOC分析仪)》,该方案主要用于环境水(除海水)中有机物综合指标检测,参考标准--,《水中TOC检测方案(TOC分析仪)》用到的仪器有Tekmar 总有机碳TOC分析仪 UV紫外线/过硫酸盐法
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多