方案详情
文
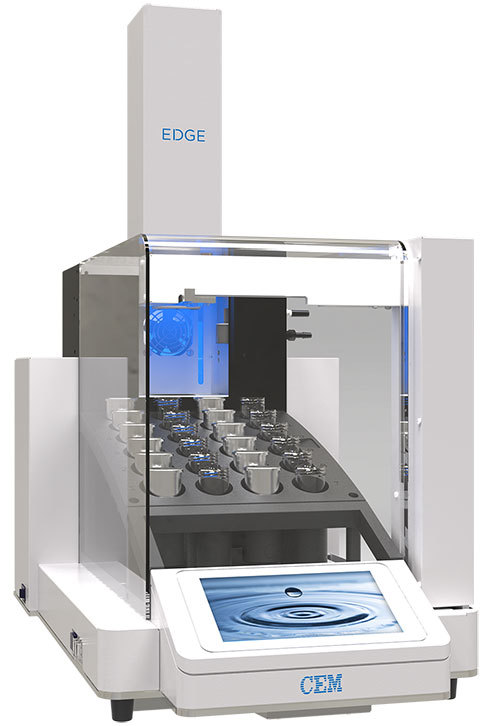
美国CEM公司发明的新型快速溶剂萃取EDGE技术,应用首创的动态化压力震荡萃取方式,搭配超长冷凝管设计,实现只用40mL溶剂,萃取7min,即获得自动冷却至室温的样品液,即刻开始后续操作,为科研节约宝贵时间。
方案详情

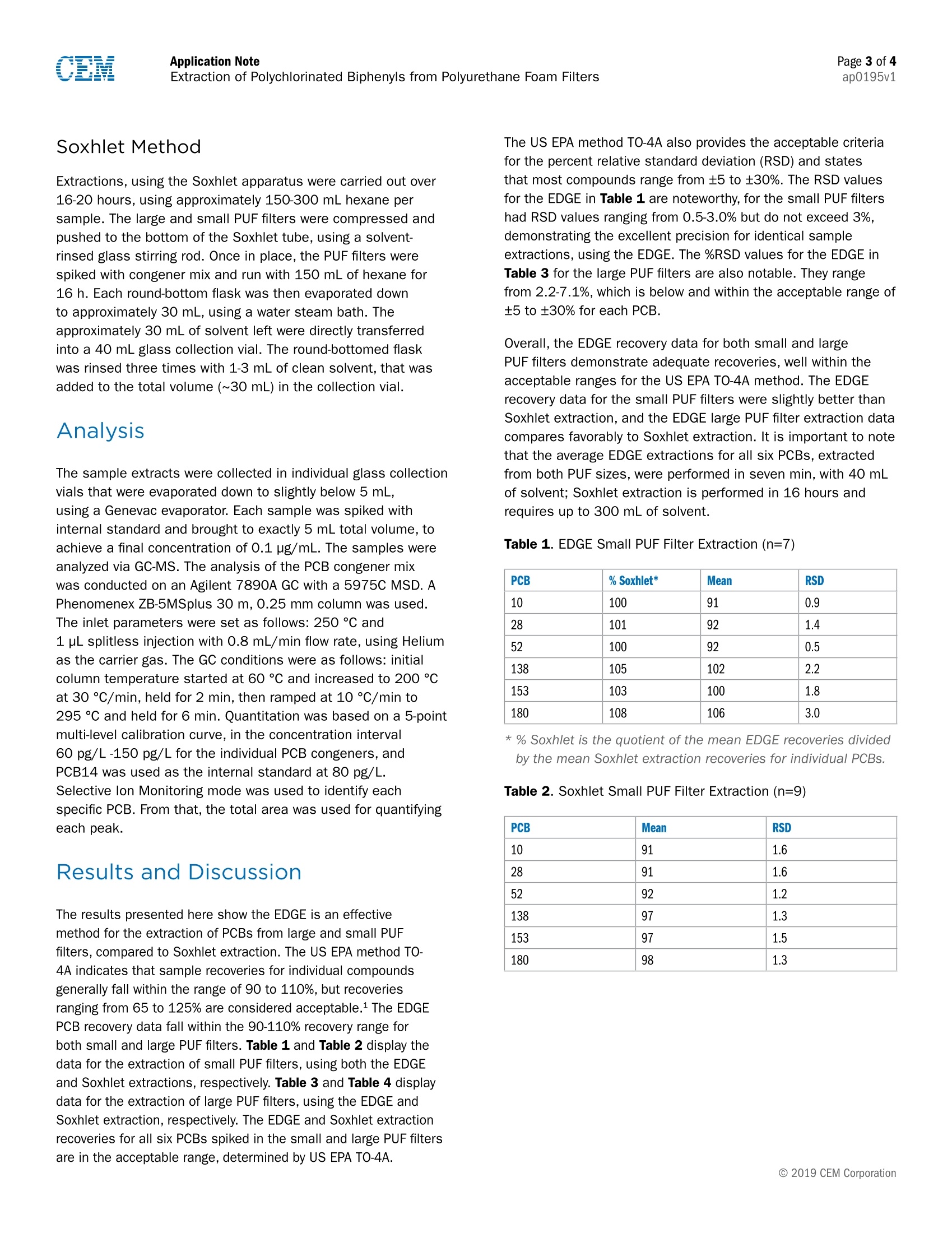
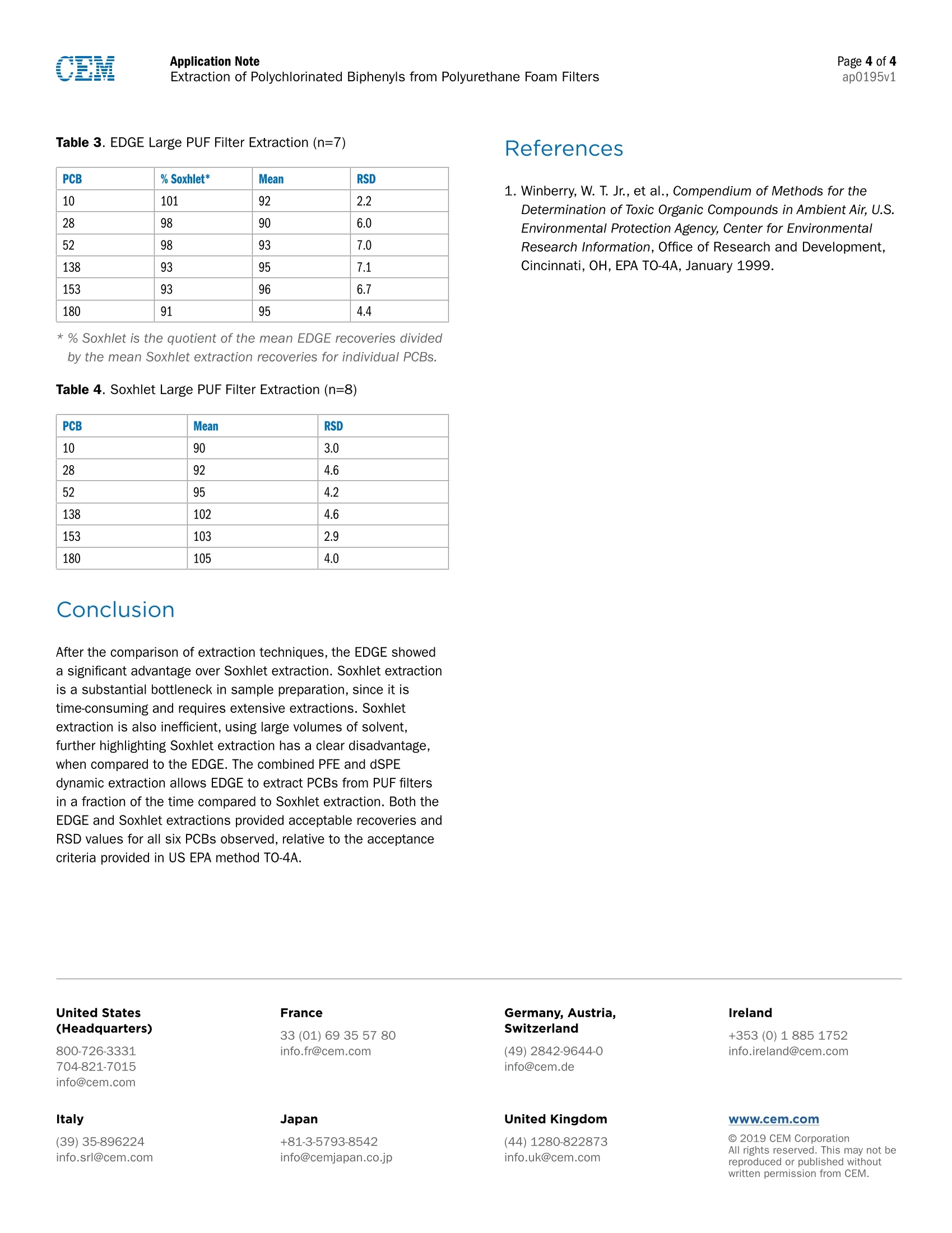
Page 1 of 4ap0195v1Application NoteExtraction of Polychlorinated Biphenyls from Polyurethane Foam Filters Extraction of Polychlorinated Biphenyls from PolyurethaneFoam Filters The EDGE offers a reliable, quick, and efficient samplepreparation method for any sample type, including the extractionof polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) from polyurethane foam(PUF) filters. It utilizes a combination of pressurized fluidextraction and dispersive solid phase extraction to drasticallyreduce the sample preparation time, solvent usage, and potentialfor human error by unprecedented levels. EDGE recovery resultsare comparable to the traditional extraction method, Soxhlet,for the small and large PUF filters. The extractions performedwith the EDGE use less solvent, last seven minutes, and do notrequire post extraction clean-up or volume transfer. The Soxhletextraction apparatus took 16 hours, 300 mL of solvent, andmultiple vessel transfers, further highlighting the extractionefficiency of the EDGE. In this application note, the EDGE is compared to Soxhletextraction as a method for the extraction of PCBs from PUF filters.The U.S. EPA TO-4A Compendium of Methods for the Determinationof Toxic Organic Compounds in Ambient Air refers to Soxhletextraction as the primary extraction method used to accuratelyquantify PCBs extracted from Polyurethane foam (PUF) filters.1 PUFis the primary material used to filter and capture persistent organicpollutants (POPs), including PCBs for air monitoring, as describedin US EPA TO-4A. PUF filters are used in high-volume air samplingsystems, or as passive air samplers (PAS), because of their abilityto trap PCBs. As a PAS, PUF filters are economical and do notrequire electricity, like high-volume air samplers. The importance of monitoring ambient air for PCBs is relatedto their negative impact on human health and the environment.PCBs are man-made chlorinated organic compounds containinga biphenyl nucleus on which a combination of one to all ten ofthe hydrogen atoms are substituted with chlorine. Their usewas very popular in the electronics and automotive industries,until the US EPA banned them in 1979. Because of theirchemical and physical stability, PCBs do not regularly breakdown in the environment and are, therefore, still present insoil, air,and water sources. Inhalation of PCBs is connectedto a variety of adverse health effects, including cancer. Risk ofinhalation exposure is greater in industrial and urban areas,where PCB-contaminated equipment is likely still present.The volatilization of PCBs from spills, landfills, road oils, andother sources, results in measurable atmospheric emissions.Atmospheric transport is the primary mode of the globaldistribution of PCBs. This further highlights the importance ofmonitoring the presence of PCBs in ambient air and extractingthem for accurate quantification at variable concentrations ofcontamination. The efficiencies for the extraction of PCBs from PUF filtersobtained with the EDGE are comparable to Soxhlet extraction.A typical Soxhlet extraction takes 16 hours, up to 300 mL ofsolvent and multiple vessel transfers.In contrast, extractionon the EDGE takes seven minutes, uses less than 50 mL ofsolvent, and does not require a vessel transfer. Application Note Materials and Methods Reagents 100 pL of 5 pg/mL congener spike mix was used throughoutthe study to spike both large and small PUF filters (0.5 pg ofPCB mix/PUF filter). Six PCBs, IUPAC Nos. 10,28,52,138,153, and 180 in a PCB congener mix, were used as the spikemix, which was purchased from Supelco Sigma-Aldrich. Theinternal standard used was PCB No. 14 (3,5-Dichlorophenyl),purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, to provide quantitative results.ACS Reagent Grade hexane, mixture of isomers, was purchasedfrom Sigma-Aldrich. The small, pre-cleaned PUF filters (22 mmOD x 760 mm L) were obtained from Supelco with certificationsof cleanliness. The large, uncleaned PUF filters (6.0 cm OD x2.5 cm L) were obtained from Supelco and cleaned with theEDGE, using a process developed prior to spiking. Sample Preparation Small and large PUF filters were positioned accordingly in theQ-Cup in order to optimize solvent penetration and extractionefficiency. Prior to sample insertion,the Q-Cups were rinsedwith hexane to prevent any cross-contamination and eliminatebackground noise during analysis.A C9+G1+C9 Q-Disc@sandwich was placed in the bottom cap of the Q-Cup to allowfor inline filtration. To insert the large PUF filter into the Q-Cup,the outer circumference was compressed horizontally into thetop of the Q-Cup opening. Once inserted from the top, thecompressed PUF filter was pushed to the base of the Q-Cup ina way such that it was equally pressed against all sides of theinterior wall. See lmage 1. The small PUF filter was insertedfrom the base of the Q-Cup, where the cap is removed. Thesmall PUF filter was handled by both ends and folded togetherin an“S,"so that it supported itself horizontally against theinterior wall. See Image 2. The base of the Q-Cup containingthe Q-Disc was then secured onto the body of the Q-Cup. EDGE Method Small PUF Filters Q-Disc: C9+G1+C9 Solvent: Hexane Top Add: 15 mL Bottom Add: 0 mL Rinse: 15 mL Temperature: 100°℃ Hold Time: 10 s Wash 1: 10 mL Hexane Wash 2: 10 mL Hexane Image 1: Insertion of large PUF filter into a Q-Cup Image 2: Insertion of small PUF filter into a Q-Cup EDGE Method Large PUF Filters Q-Disc: C9+G1+C9 Solvent: Hexane Top Add:20 mL Bottom Add: 5 mL Rinse: 15 mL Temperature: 115℃ Hold Time: 3 min Wash 1: 10 mL Hexane Wash 2: 10 mL Hexane Soxhlet Method Extractions, using the Soxhlet apparatus were carried out over16-20 hours, using approximately 150-300 mL hexane persample. The large and small PUF filters were compressed andpushed to the bottom of the Soxhlet tube, using a solvent-rinsed glass stirring rod. Once in place, the PUF filters werespiked with congener mix and run with 150 mL of hexane for16 h. Each round-bottom flask was then evaporated downto approximately 30 mL,using a water steam bath. Theapproximately 30 mL of solvent left were directly transferredinto a 40 mL glass collection vial. The round-bottomed flaskwas rinsed three times with 1-3 mL of clean solvent, that wasadded to the total volume (~30 mL) in the collection vial. The sample extracts were collected in individual glass collectionvials that were evaporated down to slightly below 5 mL,using a Genevac evaporator. Each sample was spiked withinternal standard and brought to exactly 5 mL total volume, toachieve a final concentration of 0.1 pg/mL. The samples wereanalyzed via GC-MS. The analysis of the PCB congener mixwas conducted on an Agilent 7890A GC with a 5975C MSD. APhenomenex ZB-5MSplus 30 m, 0.25 mm column was used.The inlet parameters were set as follows: 250 °℃ and1 pL splitless injection with 0.8 mL/min flow rate, using Heliumas the carrier gas. The GC conditions were as follows: initialcolumn temperature started at 60 C and increased to 200 °℃at 30 °℃/min, held for 2 min, then ramped at 10 °C/min to295℃ and held for 6 min. Quantitation was based on a 5-pointmulti-level calibration curve, in the concentration interval60 pg/L-150 pg/L for the individual PCB congeners, andPCB14 was used as the internal standard at 80 pg/L.Selective Ion Monitoring mode was used to identify eachspecific PCB. From that, the total area was used for quantifyingeach peak. Results and Discussion The results presented here show the EDGE is an effectivemethod for the extraction of PCBs from large and small PUFfilters, compared to Soxhlet extraction. The US EPA method TO-4A indicates that sample recoveries for individual compoundsgenerally fall within the range of 90 to 110%, but recoveriesranging from 65 to 125% are considered acceptable.1 The EDGEPCB recovery data fall within the 90-110% recovery range forboth small and large PUF filters. Table 1 and Table 2 display thedata for the extraction of small PUF filters, using both the EDGEand Soxhlet extractions, respectively. Table 3 and Table 4 displaydata for the extraction of large PUF filters, using the EDGE andSoxhlet extraction, respectively. The EDGE and Soxhlet extractionrecoveries for all six PCBs spiked in the small and large PUF filtersare in the acceptable range, determined by US EPA TO-4A. The US EPA method TO-4A also provides the acceptable criteriafor the percent relative standard deviation (RSD) and statesthat most compounds range from ±5 to ±30%. The RSD valuesfor the EDGE in Table 1 are noteworthy, for the small PUF filtershad RSD values ranging from 0.5-3.0% but do not exceed 3%,demonstrating the excellent precision for identical sampleextractions, using the EDGE. The %RSD values for the EDGE inTable 3 for the large PUF filters are also notable. They rangefrom 2.2-7.1%, which is below and within the acceptable range of±5 to ±30% for each PCB. Overall, the EDGE recovery data for both small and largePUF filters demonstrate adequate recoveries, well within theacceptable ranges for the US EPA TO-4A method. The EDGErecovery data for the small PUF filters were slightly better thanSoxhlet extraction, and the EDGE large PUF filter extraction datacompares favorably to Soxhlet extraction. It is important to notethat the average EDGE extractions for all six PCBs, extractedfrom both PUF sizes, were performed in seven min, with 40 mLof solvent; Soxhlet extraction is performed in 16 hours andrequires up to 300 mL of solvent. Table 1. EDGE Small PUF Filter Extraction (n=7) PCB % Soxhlet* Mean RSD 10 100 91 0.9 28 101 92 1.4 52 100 92 0.5 138 105 102 2.2 153 103 100 1.8 180 108 106 3.0 * % Soxhlet is the quotient of the mean EDGE recoveries dividedby the mean Soxhlet extraction recoveries for individual PCBs. Table 2. Soxhlet Small PUF Filter Extraction (n=9) PCB Mean RSD 10 91 1.6 28 91 1.6 52 92 1.2 138 97 1.3 153 97 1.5 180 98 1.3 Table 3. EDGE Large PUF Filter Extraction (n=7) References PCB % Soxhlet* Mean RSD 10 101 92 2.2 28 98 90 6.0 52 98 93 7.0 138 93 95 7.1 153 93 96 6.7 180 91 95 4.4 1. Winberry, W. T. Jr., et al.,Compendium of Methods for theDetermination of Toxic Organic Compounds in Ambient Air, U.S.Environmental Protection Agency, Center for EnvironmentalResearch Information, Office of Research and Development,Cincinnati,OH, EPA TO-4A, January 1999. * % Soxhlet is the quotient of the mean EDGE recoveries dividedby the mean Soxhlet extraction recoveries for individual PCBs. Table 4. Soxhlet Large PUF Filter Extraction (n=8) PCB Mean RSD 10 90 3.0 28 92 4.6 52 95 4.2 138 102 4.6 153 103 2.9 180 105 4.0 Conclusion After the comparison of extraction techniques,the EDGE showeda significant advantage over Soxhlet extraction. Soxhlet extractionis a substantial bottleneck in sample preparation, since it istime-consuming and requires extensive extractions. Soxhletextraction is also inefficient, using large volumes of solvent,further highlighting Soxhlet extraction has a clear disadvantage,when compared to the EDGE. The combined PFE and dSPEdynamic extraction allows EDGE to extract PCBs from PUF filtersin a fraction of the time compared to Soxhlet extraction. Both theEDGE and Soxhlet extractions provided acceptable recoveries andRSD values for all six PCBs observed, relative to the acceptancecriteria provided in US EPA method TO-4A. C CEM Corporation CEM公司EDGE快速溶剂萃取仪7min快速提取环境空气中的多氯联苯(PCBs) 应用传统的索氏提取法提取空气滤膜(PUF)中的多氯联苯(PCBs),需耗费300mL-500mL溶剂,回流提取16h以上,再经放置,待提取液冷却至室温后,才能继续下一步操作。耗费时间长,溶剂用量大。与之相比,美国CEM公司发明的新型快速溶剂萃取EDGE技术,应用首创的动态化压力震荡萃取方式,搭配超长冷凝管设计,实现只用40mL溶剂,萃取7min,即获得自动冷却至室温的样品液,即刻开始后续操作,为科研节约宝贵时间。专利的Q-Cup 开放式萃取池设计,使得不同尺寸的空气滤膜(PUF)均可轻松载入。 内置one-touch功能,可轻松编辑提取方法,一键操作,无需看管。 首创双向进液系统,实现动态化萃取过程,大幅提高萃取效率。 结果显示用EDGE提取空气滤膜(PUF)中的多氯联苯(PCBs)的,无论PUF大小,提取效果均与传统索氏提取法相当,且平行性良好。值得强调的是,要做到这一切,用EDGE只需要40mL溶剂,萃取7min。
确定


还剩2页未读,是否继续阅读?
培安有限公司为您提供《空气滤膜中PCB105检测方案(快速溶剂萃取)》,该方案主要用于空气滤膜中PCB105检测,参考标准《HJ 903-2017 环境空气 多氯联苯的测定 气相色谱法》,《空气滤膜中PCB105检测方案(快速溶剂萃取)》用到的仪器有EDGE全自动快速溶剂萃取仪
推荐专场
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多