







If you shed tears when you miss the sun, you also miss the stars.


第二十届北京分析测试学术报告会暨展览会(BCEIA 2023) 将于2023年9月6-8日在北京· 中国国际展览中心(顺义馆)召开。作为中国分析与生化技术交流与展示的“峰会”,BCEIA2023将营造浓郁的学术会展氛围,同期举办大会报告、分会报告、高峰论坛、同期会议、墙报展等精彩学术活动,面向世界科技最前沿,邀请国内外顶尖学者分享最具前瞻性的研究进展。
2023年9月7-8日,BCEIA2023学术报告会——色谱学分会将如期举行,聚焦“分离分析谱写健康未来”主题,围绕样品制备方法、高效分离方法、高灵敏检测方法、色谱应用等几个专题方向,邀请到20位国内色谱领域资深科学家及青年才俊带来精彩报告。
特邀报告人

报告摘要
抗体药物在治疗以肿瘤为主的人类多种疾病方面起着重要作用,具有巨大的市场前景。然而,抗体表达的复杂性以及对医用抗体的高品质要求,抗体纯化已成为整个生产过程的关键步骤,约占抗体生产成本的50-80%。蛋白A亲和层析是目前公认的抗体分离纯化技术,但因其成本高,配体易脱落、酸性洗脱易造成抗体聚集等缺陷,一定程度上限制了蛋白A亲和层析规模化应用。目前基于功能小分子的混合模式色谱和短肽仿生亲和色谱在抗体分离方面具有良好的应用潜力,但仍存在吸附容量低、采用酸性洗脱等问题,仍无法满足上游产能提升对下游抗体分离纯化的要求。
本研究以4-巯乙基吡啶(MEP)为配体,以硅胶为基质,以温敏树枝状聚合物PAMAM-PNIPAM为间隔臂,制备了高容量的温敏仿生亲和色谱固定相,构建一种用于抗体分离纯化的高容量、绿色环保的温敏仿生亲和色谱。该方法以纯水为流动相,仅通过改变温度实现对抗体的一步分离纯化,对抗体蛋白的吸附量提高了2倍。通过对模型蛋白BSA和g-球蛋白分离条件的优化,结果表明采用温敏仿生亲和色谱技术,上样温度为40°C,洗脱温度为5°C条件下可一步实现对二者的完全分离。将其应用于人血清中IgG和蛋黄中IgY的分离纯化,一步纯化后IgG和IgY的纯度为99%,质量回收率大于90%。该技术洗脱条件温和,绿色环保,解决了当前混合模式色谱和仿生亲和色谱吸附容量第、酸性洗脱使抗体变性失活的难题,对抗体的分离纯化及工业化生产具有重要的应用价值。
专家简介
白泉,教授,博士导师,任职于西北大学化学与材料科学学院,现任陕西省现代分离科学重点实验室主任,中国化学会色谱专业委员会委员,Biomedical Chromatography、《色谱》和《分析测试技术与仪器》杂志编委。2006年10月至2007年9月在法国波尔多第一大学做访问学者。主要从事现代分离科学理论和生物大分子的分离纯化的研究和教学工作。
主持国家发改委重大产业化项目“重组蛋白药物示范生产线及关键设备的开发生产”二级子课题1项、国家“863”项目1项、国家自然科学基金3项、陕西省自然科学基金重点项目2项,其他各类省部级项目10余项。发表论文100余篇,授权国家发明专利6项。获得“陕西省科技进步壹等奖”两项,教育部高等学校科学研究自然科学奖二等奖一项,“中国科协期刊优秀论文奖”1项,出版专著1部。

报告摘要
Imaging using charged molecules or their fragments as pixels is now achieved through mass spectrometry (MS), commonly known as MS imaging or MSi. This enables the study of their spatial distribution, correlation and related function to determine the health status of our body. However, MSi is suffering from high technological barriers, expensive equipment, and high usage costs. In addition, MSi cannot image substances with the same m/z or difficulty in desorption and/or ionization. In order to reduce technological barriers and imaging costs, and expand the imaging range, our laboratory began attempting to use capillary electrophoresis (CE) instead of MS for imaging in 2009. In theory, CE imaging or CEi can be performed in roughly the same way as MSi, as both separate ions. In addition, CE can not only separate ions (even with the same m/z), but also neutral ions. Therefore, CEi is not limited to ions, and neutral components can also be imaged, with a size of up to one cell; CEi can reach high-speed imaging under high separation voltage or through the use of capillary arrays; And it has the ability to image biogenic substances directly from fresh and moist tissues or tissue slices. Unfortunately, its exploration did not go smoothly and was once blocked due to its inability to correctly recognize the separated peaks from various practical samples. Unlike MS, CE will change the position of the same peak under different operating conditions. This instability makes CEi practically unusable. To address these issues, we have designed and established a new version of CE called highly reproducible CE (HRCE) 1. We further utilized capillary arrays to construct a new method for HRCE imaging, which is suitable for imaging rat brain tissue sections 2. At a spatial resolution of around hundreds of micrometers, the obtained images allow for global research on the spatial distribution and correlated functions of the imaged molecules. The present CEi can also directly image some exposed living skins. This indicates that CEi is very promising and worth further exploration.
专家简介
陈义博士现为中科院化学所研究员(返聘)、淮阴工学院特聘教授,兼高端矿盐功能材料智能制备国际合作联合实验室主任、矿盐资源深度利用技术国家地方联合工程研究中心主任,任Electrophoresis、分析化学、色谱 期刊副主编,是J. Chromatogr. A、J. Chromatogr. B、Talanta、Analytical Methods、Biosensors、Exploration of Foods and Foodomics等杂志编委/顾问编委。主要从事毛细管电泳(CE,1984-现在)、表面等离子体共振成像(SPRi,1997-现在)、分子量测量(2004-现在)新方法、新装置、新技术与新应用研究。2000年启动活体分析研究,2009年建立活体分析化学中国科学院重点实验室。已发表研究论文350多篇,出书4部+15章节,获批专利40多件。曾3次入选Analytical Scientist的Power List,获中国化学会“青年化学奖”、香港求实科技基金会“杰出青年学者奖”、中国科学院“青年科学家奖”等。

报告摘要
In recent years, how to inject trace samples with minimal loss into a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) system has become one of the major challenges. We developed an integrated Falcon probe which can realize the integration of four functions of in-situ micro-area-sampling, sample injection, chromatographic separation and MS electrospray formation. We used the probe pressing micro-amount in-situ (PPMI) injection method to realize the in-situ lossless injection of trace samples on a sampling chip. The LC-MS analysis system based on the Falcon probe could obtain good repeatability and high separation efficiency and we applied it to the single-cell proteomic analysis of single 293 cells.
专家简介
方群,浙江大学求是特聘教授,博士生导师,化学系微分析系统研究所所长,浙江大学杭州国际科创中心分子智造研究所所长,国家杰出青年基金获得者。自1998年开始从事微流控芯片分析的研究工作。目前研究方向包括微流控液滴分析和筛选,微流控液相色谱、质谱和毛细管电泳分析,微型化分析系统研制,人工智能+微流控系统,以及微流控系统在单细胞多组学分析、微量生化分析、药物筛选和现场分析中的应用。发表研究论文140余篇。在微流控分析领域有32项国家发明专利获得授权。曾主持承担国家基金委重大项目课题、国家杰出青年基金、国家基金重点项目、科学仪器研制专项和面上项目,以及国家科技部重点研发计划项目课题等科研项目。

报告摘要
外泌体是异质性的,体积大小不同的每个亚型都可能在生物学功能中发挥自己的作用,因此,如果能将外泌体根据尺寸大小不同分离出不同亚型,有助于揭示其异质性,揭示其生物学功能。为了解决上述问题,我们开发了一系列从人类尿液和血浆中分离内源性外泌体及其亚型的技术。首先,我们发展了二维体积排阻液相色谱(2D-SEC)分离策略,用于解构不同尺寸尿液外泌体亚群的异质性。使用2D-SEC,将人尿液中的外泌体分离为大外泌体、中外泌体和小外泌体。然后,对尿液外泌体的大小依赖性亚蛋白质组分析进行了研究。采用液相色谱-串联质谱法(LC-MS/MS)结合数据库检索对蛋白质和翻译后修饰蛋白(PTM)进行了表征。我们发现,这些大小不同的的外泌体的蛋白质组及其PTM存在差异。此外,我们还进一步结合Mini-SEC(填充Sepharose颗粒)和高效液相尺寸排除色谱(HPL-SEC),开发了顺序尺寸排阻色谱法(SSEC),用于从血浆中分离外泌体,并利用外泌物的质谱指纹图谱结合人工神经网络来区分不同的癌症类型。SSEC方法进一步应用于从人血浆中高速、高纯度分离外泌体,从总共220份临床血浆样本中分离出外泌体,包括健康对照组、乳腺癌症患者和胰腺癌症患者。并且,通过基质辅助激光解吸/电离飞行时间质谱(MALDI-TOF MS)对它们的质谱指纹图谱进行了很好的分析。经过MS数据预处理和特征选择,提取的MS特征峰被利用。在MS数据预处理和特征选择之后,提取的MS特征峰值被用作构建多分类器人工神经网络(表示为Exo-ANN)模型的输入。优化模型实现了80.0%的诊断准确率,整个组的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.91,这意味着Exo-ANN具有在临床上进行癌症液体活检的潜力。
专家简介
高明霞,女,籍贯山东烟台,复旦大学化学系分析化学专业,教授,博士生导师。分别于2007年和2018年先后在德国环境与健康国家研究中心和美国圣母大学做访问学者。所在团队一直在蛋白质组学领域从事多维液相色谱分离的新技术新方法开发,建立了一系列高效高通量的色谱分离分析平台,成功用于完整蛋白质、蛋白质复合物等复杂生物样品的分离分析,近几年,团队利用体积排阻色谱针对外泌体开展了一系列分离分析方法的研究。发表了一系列有影响力的学术论文,在国际和国内蛋白质组学分离分析技术研究领域有一定影响力。截止2023年6月,发表研究论文90多篇,主要文章发表在 Analytical Chemistry,Journal of Chromatography A, Nanoscale,ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,Analytica Chimica Acta等期刊上,获得授权专利11项。先后主持国家自然科学基金面上项目3项,参与国家重点研发计划子课题一项,国家重点基础研究发展计划(973计划)一项。

报告摘要
高选择性捕获和操控复杂系统中的生物活性物质对于生命过程的研究具有重要意义。金属有机框架(MOF)由于具有高孔隙率、可调孔结构和丰富的表面化学性质,是构建集分离、检测和调控等多功能的理想平台。设计并构建了一种基于MOF工程化纳米复合物,具有光驱动的级联响应性质,用于复杂生物体系中蛋白质抑制剂的可控释放。利用MOF规整的孔道结构,原位沉积了分散良好的金属纳米颗粒作为光捕获模块;进一步构建了链构象可切换的聚合物壳作为次级响应单元。针对重要伴侣蛋白HSP90,在亲水作用和氢键等非共价键的驱动下,实现了抑制剂分子的高效吸附和捕获。在复杂的活细胞和活体内,利用光作为响应开关,触发级联光热转换和聚合物从构象转变,可在短时内快速、时空可控地释放抑制剂,实现了伴侣蛋白及其生物活性的高选择性分析,为伴侣蛋白的分离、检测和活性调节提供了新材料和新方法。
专家简介
2004年本科毕业于武汉大学,2009年于中国科学院化学研究所获博士学位,之后留所工作。2017.2-2018.6,赴美国德州农工大学进行访问研究。主要从事基于多肽识别的高选择性分离分析研究,发展复杂生命体系中蛋白质特异性分离新材料与分析新方法。在Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Chem. Sci., Anal. Chem.等期刊发表论文60余篇;获授权中国发明专利7项。入选2015年度中国科学院青年创新促进会会员。2021年获国家自然科学基金委优秀青年基金项目资助。担任《色谱》青年编委,《分析仪器》编委。

报告摘要
Growing life science researchers have discovered that the drug’s mechanisms of actions are much more complex than we expected.[1] In most cases, a drug often interacts with multiple targets; while the same target can be modulated by different kinds of compounds, and interactions with the unexpected cellular proteins (off-targets) often relate to the adverse drug reactions.[2] Therefore, unraveling drug-protein interactions (DPIs) is critical for understanding the mechanism action and predicting the potential side effects in the early stage of drug discovery, hence reduce the high attrition in drug development.[1]
Profiling drug-protein interactions is critical for understanding the drug’s mechanism of actions and predicting the possible adverse side effects. However, to comprehensively profile drug-protein interactions remain a challenge. To address this issue, we proposed a strategy by integrating multiple mass spectrometry-based omics analysis to provided global drug-protein interactions including physical interactions and functional interactions with rapamycin (Rap) as a model. Chemoproteomics profiling reveals 47 Rap binding proteins including the known target protein FKBP12 with the high confidence. Gen Ontology enrichment analysis suggested that the Rap binding proteins are implicated in several important cellular processes, such as the DNA replication, immunity, autophagy, programmed cell death, aging, transcription modulation, vesicle-mediated transport, membrane organization, carbohydrate and nucleobase metabolic process. The phosphoproteomics profiling revealed 255 down-regulated and 150 up-regulated phosphoproteins responding to Rap stimulation, they mainly involve in the PI3K-Akt-mTORC1 signalling axis. Untargeted metabolomic profiling revealed 22 down-regulated metabolites and 75 up-regulated metabolites responding to Rap stimulation, they are mainly associated with the synthesis processes of pyrimidine and purine. The integrative multi-omics data analysis provides us a deep insight into the drug-protein interactions and reveals a complicated Rap’s mechanism of action.
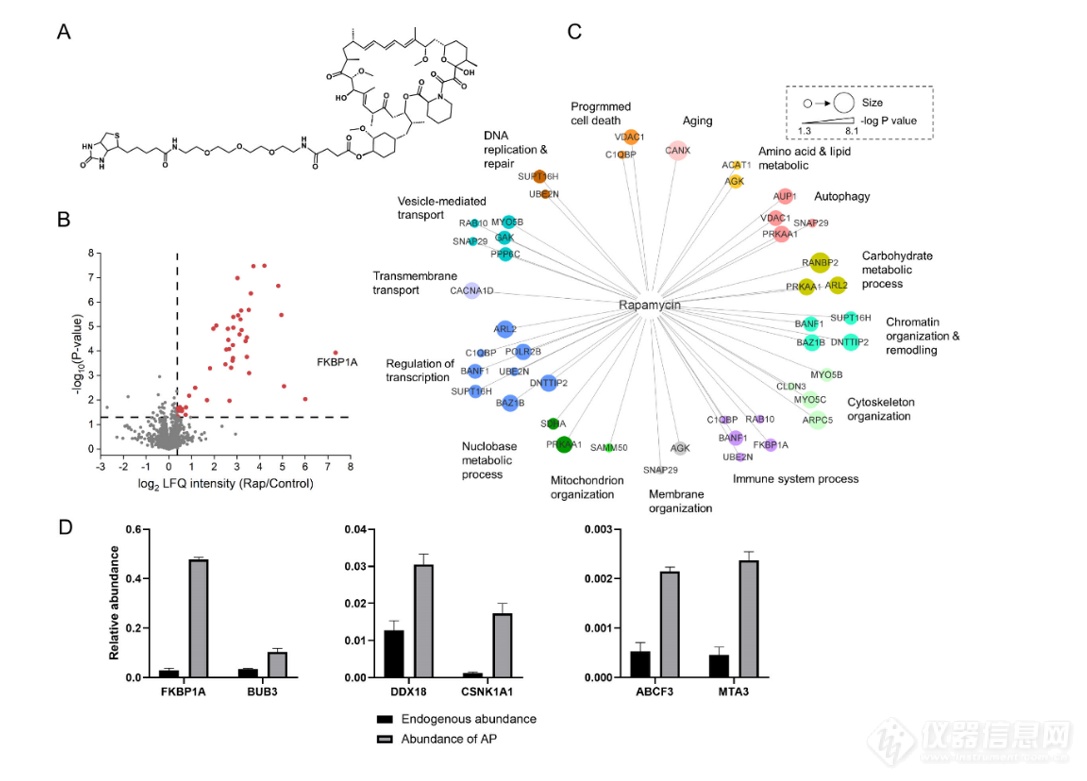
Figure 1. Profiling of Rap interacting proteins by chemoproteomics
The chemical structure of biotin-tagged Rap; (B) Volcano plot for distinguishing the Rap interaction proteins from the background; (C) The identified interacting proteins of Rap were clustered according to the involved biological process; (D) The evaluation of the affinity purification (AP) efficiency of biotin-tagged Rap by comparing the measured abundances of 6 endogenous proteins before and after affinity enrichment.
专家简介
康经武,1990年毕业于陕西师范大学,1990-1996年中科院兰州化学物理研究所攻读分析化学硕士和博士研究生,获得分析化学博士学位。1997-1999, 中国科学院兰州化学物理研究所羰基合成国家重点实验室从事博士后研究,1999年到2000年在鲁汶大学药学院做博士后研究,2000至2003年在图宾根大学有机化学研究所从事博士后研究。2003-2008年,回到上海有机化学研究所任研究员,课题组长,2009-2015年任分析化学研究室主任,研究员,博士生导师。2015-至今:任中科院上海有机化学研究所生命有机国家重点实验室课题组长。主要从事药物分析,生物分析,手性分离,药物筛选和靶标鉴定新技术研究。担任《色谱》杂志副主编,Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,《有机化学》,《分析实验室》,《分析测试技术与仪器》等杂志的编委。

报告摘要
Mass spectrometry, as a powerful detection tool, has many characteristic advantages, such as fast speed, high sensitivity, high accuracy, and a wide range of applications. It is widely used in research on chemical composition, tissue imaging, and other aspects of food, environment, materials, medicine, and bioscience. However, the mass spectrometry ionization inhibition effect between complex components is one of the key scientific issues to be solved in the development and application of mass spectrometry detection technique in these research fields. Chromatographic separation has solved the problem of complex sample separation and purification, and the combination of mass spectrometry has led to a leap in the development of mass spectrometry-based complex sample analysis. Unfortunately, compared to rapid detection by mass spectrometry, current chromatographic separation techniques require a relatively slow and lengthy separation time, which greatly affects the widespread application of the techniques in real-time and high-throughput detection.
Based on the ion evaporation principle of spray ionization and the modifiable characteristics of carbon fibers, a two-dimensional carbon fiber separation system coupled with electrospray mass spectrometry was constructed. The analytes of interest in complex samples are simply and quickly separated into three fractions, i.e., strong polar (carboxyl), medium polar (phenolic hydroxyl) and weak polar (carbonyl) using two-dimensional carbon fiber separation columns. And afterward directly injected into the electrospray ionization source. Research has shown that this method significantly improves the ionization efficiency of the tested substance and significantly shortens the full analysis time of complex samples. Using this technology, a rapid online analysis method for drug and pesticide impurities has been achieved, and a mass spectrometry database of more than 1000 medicinal plants in Changbai Mountain was also established.
专家简介
李东浩,二级教授,博士生导师,延边大学化学学科带头人,延边大学学术委员会常务副主任兼秘书长。吉林省首批“长白山学者”特聘教授、吉林省“高级专家”、吉林省第一层次拔尖创新人才、省有突出贡献中青年专业技术人才。
分析科学学报、分析测试技术与仪器、Current Analysis on Chemistry、Current Organic Chemistry等编委,中国化学会色谱专业委员会委员、中国环境科学学会专业委员会委员、中国仪器仪表学会分析仪器分会样品制备专业委员会委员、中国化工学会日用化学品专业委员会委员。
主持承担过“863计划”、自然基金仪器专项等多项科研项目。授权了发明专利11项、实用新型专利23项,开发了“微液萃取仪”和“二维碳纤维分离仪”等样品前处理仪器设备,在Gut, Analytical Chemistry, Lab on a Chip,Food Chemistry,TrAC trends in Analytical Chemistry 等杂志上发表学术论文110余篇,大会报告和邀请报告共计60余次。
主要从事于微分离技术以及生物功能分子分析相关研究工作。1)碳纳米纤维液相纳(微)萃取;2)微纳尺度物质(外泌体、单细胞等)的场流分离;3)芯片电泳分离;4)中药物质基础及协同作用研究;5)环境检测与污水处理。

报告摘要
液相色谱-质谱联用技术(LC-MS)在生命科学中的应用非常广泛,在临床实验室也发挥着越来越重要的作用。近年来,临床MS成为LC-MS的前沿热点,但MS和LC-MS真正成为临床诊断的标准方法,还有一些问题必须考虑。本文主要讨论LC-MS和MS在临床诊断中的应用所面临的问题,并提出一些个人的见解,供专家和学者参考。
专家简介
刘虎威,1990年获得北京理工大学应用化学博士学位后加盟北京大学,历任讲师、副教授、教授、博士生导师。2019年9月退休。主要从事气相色谱、液相色谱、毛细管电泳、表面等离子共振,以及与质谱的联用技术方面的科研及教学工作,研究方向是生物药物分离与检测,包括色谱(毛细管电泳)-质谱联用技术、敞开式离子化质谱技术和仪器、表面等离子共振方法。迄今发表有关论文300余篇,获得专利授权8件,著作3部,为多部英文著作撰写了12个章节,参与编写词典等工具书3部,教材3部。
中国化学会理事,美国化学会会员;中国分析测试协会理事、副秘书长。现任北京理化分析测试技术学会副理事长;中国仪器仪表学会分析仪器分会常务理事。《Journal of Separation Science》、《Journal of Analysis and Testing》副主编,《分析仪器》编委会副主任,《色谱》执行副主编;以及《化学通报 》、《中国药学. 英文版》、《分析试验室》、《分析科学学报》、《分析测试学报》、《现代科学仪器》、《现代仪器与医疗》、《岩矿测试》、《中国测试》和《食品安全质量检测学报》编委。

报告摘要
手性在生命过程中起着重要作用,因此,手性识别及手性分离研究具有十分深远的意义及实用价值。目前所面临的巨大挑战是有限的手性选择剂种类与尚待深入探究的手性识别机理。
本报告将聚焦于手性识别及手性CEC技术,开发新型寡肽配体-聚合物毛细管涂层和寡肽-纳米材料并构建系列手性识别和手性配体交换CEC(CLE-CEC)新体系;从调控分子间作用力(氢键,π-π作用及亲疏水相互作用)角度来探讨其机理并开展面向生物活体的应用研究。
专家简介
中国科学院化学研究所研究员,兼中国科学院大学岗位教授。以新型聚合物合成制备为基础,致力于生物色谱的研究及应用,面向活体分析化学的关键科学问题,开展了长期系统的研究工作,并取得了系列创新成果。入选北京市科学技术研究院“萌芽”人才计划;应邀担任国际期刊“Journal of Analytical Science and Technology”编委;在Anal. Chem., Biosen. Bioelectron., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces等核心期刊发表通讯作者SCI学术论文100余篇,获中国发明专利9项;获2012年及2016年中国分析测试协会科学技术奖一等奖各一项(第一完成人)。

报告摘要
外泌体具有重要的诊断和治疗价值。然而,外泌体的高通量、高效率和高纯度分离仍然是其临床应用的重要限制步骤。本论文开展了基于anti-Tim4功能化磁性金属有机框架材料的研究,成功研制了Fe3O4@SiO2-ILI-01@Tim4新材料。基于所研制材料基质的杰出亲水性和强磁性特征,所研制Fe3O4@SiO2-ILI-01@Tim4材料具有低的非特异性吸附,并可实现外泌体的快速和方便分离(<1 min),其对外泌体的捕获效率可达90.3±0.5%,回收率可达93.0±6.1%,所捕获外泌体同时显示了良好的完整性和生物学活性。基于所发展Fe3O4@SiO2-ILI-01@Tim4材料的良好性能,实现了人血浆样品中低丰度外泌体PD-L1的原位、高灵敏检测和精准定量分析。所发展的基于Fe3O4@SiO2-ILI-01@Tim4的策略可用于基于PD-L1的免疫治疗响应预测,特别适用于CPS测试假阴性病人的临床诊断分析,具有良好的应用前景。
专家简介
乔晓强,河北大学教授,药学院副院长,河北省杰出青年基金获得者,河北省青年拔尖人才,河北省高校百名优秀创新人才。2011年3月于中国科学院大连化学物理研究所获博士学位。2011年6月进入河北大学药学院工作。2016-2018年先后在美国德州大学阿灵顿分校和密西根州立大学进行博士后研究。迄今为止,在Analytical Chemistry、ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces、TrAC-Trends in Analytical Chemistry等权威期刊发表SCI论文60余篇,授权发明专利5项。2016年和2022年两次获河北省科技进步二等奖。目前担任期刊《Chinese Chemical Letters》和《Journal of Analysis and Testing》青年编委。

报告摘要
毛细管电泳是高效的核酸适配体筛选方法。针对不同尺度的靶标(蛋白质、小分子、外泌体)建立多种筛选模式可以进一步提高筛选效率。
我们在高效筛选蛋白质适体方面取得了重要进展,建立了多种筛选模式。由于核酸和具有核酸复合物的小分子的迁移率相似,毛细管电泳难以将核酸与具有核酸复合体的小分子分离。因此传统的毛细管电泳方法无法分离它们,也无法直接筛选它们的适体。我们建立了一个新的动态竞争结合模型,并针对小分子肽进行了适体筛选方法,能够分离出肽3、4、5、9、11和16的适体复合物,表明毛细管电泳可以高效筛选小分子和小分子肽。
此外,首次提出了一种基于毛细管电泳(CE)的新的三步进化增强策略-SELEX,用于外泌体囊泡的高效适配体选择。所提出的策略具有增强的选择亲和力和特异性,为外泌体囊泡的识别元件选择开辟了一条新的途径。
毛细管电泳用于小分子肽和外泌体的适配体筛选,进一步拓展了毛细管电泳在多尺度靶标的适配体筛选中的应用。
专家简介
1997年博士毕业于北京大学化学与分子工程学院。1998-2000年在香港中文大学和美国Southern Methodist university 从事博士后研究工作。研究领域是毛细管电泳生物医学分析,从事多尺度靶标(蛋白质,外泌体,小分子肽靶标以及样品基质靶标)的核酸适配体高效筛选机理和方法研究17年, 建立了多种高效筛选模式,发表相关论文百余篇。

报告摘要
To address the problems ‘non-specific interference at the recognition interface’ towards complicated physiological systems, we concentrate on the high-selectivity measurements based on recognition peptides. A mechanism called ‘hydrogen-bond-mediated synergistic recognition’ has been proposed to guide the peptide design and peptide library synthesis, which reduces the non-specific interference and improves the affinity, specificity and stability of recognition peptides. A new peptide screening method on high-content microfluidic chips has been established, though which the screening efficiency of peptide library is 100 times higher than conventional methods. Based on the above mechanism and method, a series of novel recognition peptides have been obtained. High-selectivity recognition applications have been developed towards the targets such as cancer-related proteins. Additionally, in vivo molecular classification has been realized in clinical test.
专家简介
王蔚芝,北京理工大学研究员,博士生导师,课题组长。2006年获得北京理工大学应用化学学士学位,2011年获得中国科学院化学研究所博士学位。2011-2019年在国家纳米科学中心工作。2019年加入北京理工大学化学与化工学院。主要研究方向为微流控高内涵筛选与多肽分子识别及分析。
近年来在Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.、Adv.Mater.、Anal. Chem. 、ACS Nano,等期刊上发表论文50余篇。授权10项发明专利。担任《Journal of Analysis and Testing》青年编委,北京色谱学会理事等。曾获得中国分析测试协会科学技术(CAIA)奖 (2020年)。

报告摘要
通用型手性分离材料体系是对映体分离领域研究人员一直的追求目标。本工作提出了准双手性通道(QDCC)对映分离平台的概念,其中表面顺序接枝的奎宁(QN)和功能环糊精(CD)可以在不相互干扰的情况下模拟两个独立的手性通道,通过差异化相互作用,以实现广谱手性拆分。手性分离结果与分子对接模拟相结合表明,QN与功能CD层的不同相互作用模式使QDCC具有较宽的分离能力。这项工作为多功能对映分离材料的合理设计提供了有效思路。
专家简介
天津大学理学院副院长,国家重点研发计划项目首席(基础研究类),国自然优秀青年基金项目获得者。在Nat. Protcls., Angew. Chem., Anal. Chem.,ACS sens., J. Chromatogr. A等期刊发表论文七十余篇,申请/授权国家发明专利近二十项。

报告摘要
高分辨率质谱(HRMS)可从生物样本的非靶向代谢组学分析中获取丰富的代谢组学信息,但仅1.8~20%的代谢特征可被注释。亟待开发大规模、自动化的注释新方法。
本研究提出了一种分子结构关联网络策略(SGMNS),对基于超高效液相色谱-高分辨率质谱(UHPLC-HRMS)的非靶向代谢组学数据进行深度注释。与基于反应网络的代谢物注释方法不同,我们通过数据库中化学结构的分子指纹相似性构建全局连通性分子网络(GCMN)进行注释。仅仅使用10个已知代谢物作为种子,SGMNS分别从细胞、粪便、血浆(NIST SRM 1950)、组织、尿液及其它们的混合样本中注释701、1557、1147、1095、1237和2041个代谢物,注释准确率大于83%,RSD小于2%。该方法将在代谢物结构注释中发挥重要作用。
专家简介
许国旺: 博士,研究员。中国科学院大连化学物理研究所生物技术部常务副主任,中国科学院分离分析化学重点实验室主任,代谢组学研究中心主任。2004年获国家自然科学基金委杰出青年基金资助。现任中国化学会色谱专业委员会主任等。
正在担任TrAC-Trends Anal Chem的特约编辑, Metabolites的副主编及Anal Chem(2021-2022), Anal Chim Acta,J Proteome Res等10多个杂志编委。HPLC国际会议科学委员会常委。
已在PNAS, Nat Protoc, Nat Commun, Hepatology, Adv Sci, Diabetes Care, Cancer Res, Clin Chem, Anal Chem等国际著名杂志发表多篇高水平文章,H-指数: 73(Web of Science Core Collection)、92 (Google)。申请发明专利超百件(其中90多项已授权)。
主要研究方向:复杂样品分离分析方法的创新性研究;代谢组学、暴露组学分析技术平台及其在疾病、中药、植物表型、食品安全等方面应用的研究。

报告摘要
Sleep deprivation (SD) is a widespread issue that disrupts the lives of millions of people. These effects initiate as changes within neurons, specifically at the DNA and RNA level, leading to disruptions in neuronal plasticity and the dysregulation of various cognitive functions, such as learning and memory. Nucleic acid epigenetic modifications that could regulate gene expression have been reported to play crucial roles in this process. However, there is a lack of comprehensive research on the correlation of SD with nucleic acid epigenetic modifications. In the current study, we aimed to systematically investigate the landscape of modifications in DNA as well as in small RNA molecules across multiple tissues, including the heart, liver, kidney, lung, hippocampus, and spleen, in response to chronic sleep deprivation (CSD). Using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis, we characterized the dynamic changes in DNA and RNA modification profiles in different tissues under CSD stress (Figure 1). Through optimization of the chromatographic separation conditions, we successfully achieved simultaneous detection of 47 RNA modifications and 2 DNA modifications. These significantly altered modifications in DNA and small RNA molecules under CSD stress have the potential to contribute to the development of diseases. Our study sheds light on the role of DNA and RNA modifications as important epigenetic marks in the context of CSD stress and highlights their potential implications in disease pathogenesis.
专家简介
袁必锋,武汉大学公共卫生学院教授、博士生导师。主要研究方向为核酸表观遗传学、代谢组学、卫生毒理学,开展了基于色谱质谱技术和测序技术的核酸表观遗传修饰分析和功能研究;建立了多种代谢组学分析方法,开展了基于代谢组的临床疾病标志物分析。主持国家自然科学基金优秀青年基金、面上项目、青年基金;参与国家自然科学基金创新群体、重点项目、科技部重点研发计划等。担任Chinese Chemical Letters副主编、Chemical Research in Toxicology顾问编委、Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry顾问编委、《癌变·畸变·突变》编委、中国生物物理学会代谢组学分会委员、中国化学会质谱分析专业委员会委员、中国环境诱变剂学会致突变专委会委员。以通讯作者在 J Am Chem Soc、Nucleic Acids Research、Chemical Science 等学术刊物上发表了100余篇SCI收录论文,论文引用九千余次。

报告摘要
针对新药研发亟需模拟药靶蛋白生理状态,建立简便精准分析方法的迫切需求,本研究以G-蛋白α亚基、β2-肾上腺素受体(β2-AR)和环形卤代烷烃脱卤素酶标签为例,通过头尾相连组装方式设计了一种三元信号传导生物智能界面。采用大肠杆菌系统成功表达了目标蛋白,并通过受体和Gαs进行了确证。通过蛋白标签与6-氯己酸修饰硅胶微球间特异性生物正交反应,制备了固定化β2AR-Gαs生物智能界面。以其为色谱固定相,建立了配体筛选与下游信号传导活性同步评价方法,为其他信号传导生物智能界面的构筑提供了借鉴,有望复杂体系高内在活性药物成分的筛选提供新途径。
专家简介
赵新锋,教授,博士生导师。中国药学会药物分析专业委员会委员,陕西省中药生物科技研究会副会长,《Chinese Medicine》等杂志编委。主要从事药物分析新方法的建立及应用研究。主持国家及省部级科研项目12项,获中国发明专利授权5项(3项已转化);出版教材和专著各1部,在Science、JACS、Chem. Sci.、Biosens. Bioelectron.、Anal. Chem.和J. Med. Chem.等杂志发表论文70余篇;获省部级科学技术奖一等奖等奖项5项。

报告摘要
The recycling and reuse of difficult-to-degrade cross-linked polymers like tires has always been a challenging issue in the industry. One important application direction is the production of pyrolysis oil through their thermal decomposition. In addition, there is extensive interest in the study of pyrolysis oil from green and sustainable biomass. However, biomass pyrolysis oil often contains a high content of oxygenated compounds, which can lead to problems such as corrosion and instability.In this study, co-pyrolysis experiments were conducted using tire powder recovered from scrap tire plants and biomass represented by moso bamboo. By employing methods such as TG-FTIR-MS and TG-GC/MS, the behavior and kinetic processes of the co-pyrolysis between waste tires and biomass were investigated, along with the exploration of the synergistic effects resulting from co-pyrolysis. The main research findings are as follows: (1) Co-pyrolysis of tires and moso bamboo did not affect the type of co-pyrolysis products and inhibited the generation of oxygen-containing compounds such as acids and alcohols. (2) Catalysts, such as Na2CO3 and MgO, were found to promote sample decomposition but increase coke formation. Na2CO3 reduced tar yield while improving the quality of co-pyrolysis tar, whereas MgO was not suitable for catalytic co-pyrolysis to produce pyrolysis oil. (3) Co-pyrolysis and catalysts significantly lowered the activation energy of tire pyrolysis. The co-pyrolysis technology improved the hydrogen-to-carbon ratio of pyrolysis oil by co-pyrolyzing polymers with biomass, thereby enhancing the quality of the pyrolysis oil. Therefore, selecting appropriate catalysts and utilizing co-pyrolysis technology can optimize the pyrolysis process for waste tires and biomass, leading to improved quality of the pyrolysis oil. This work offers new opportunities for the recycling and reuse of waste tires.
专家简介
邓楠,高级工程师,博士生导师,主要从事多维联用仪器分离分析新方法开发,包括GC-MS/MS、LC-MS/MS、STA-FTIR-MS等,并将其应用于生命科学、能源、环境和烟草等领域。主持完成国家自然基金青年基金1项,参与多项国家自然科学基金项目、企业项目,获得中国分析测试协会高校分析测试分会优秀青年人才二等奖, 中国烟草总公司科技进步二等奖1项,三等奖2项,发表SCI论文10余篇,授权专利9件。

专家简介
邱洪灯,国家优青,中科院“百人计划”(A类),甘肃省杰青,甘肃省领军人才(第二层次),现任中国科学院兰州化学物理研究所研究员,实验室副主任,手性分离与微纳分析课题组组长。获甘肃省自然科学奖二等奖、中国分析测试协会科学技术奖一等奖等奖项。目前已在Anal. Chem., Adv. Funct. Mater., J. Chromatogr. A等重要学术期刊上发表论文210余篇。现任《Chinese Chemical Letters》主编及多个期刊编委,中国化学会高级会员(2021),中国化学会色谱专业委员会委员,中国分析测试协会青年学术委员会委员,甘肃省化学会色谱专业委员会秘书长,中国化工学会离子液体专业委员会委员。

报告摘要
遗传信息载体 DNA 由 4 种碱基组成。其中,胞嘧啶和腺嘌呤可发生由酶催化产生的甲基化,是重要的表观遗传标记。胞嘧啶甲基化可发生在 C5 位和 N4 位,分别形成 5-甲基胞嘧啶 (5mC) 和 4-甲基胞嘧啶 (4mC);腺嘌呤甲基化发生在 N6 位,形成 N6-甲基腺嘌呤 (6mA)。5mC 广泛存在于真核生物基因组,而 6mA 和 4mC 则主要存在于原核生物 DNA。我们发展出独特的前处理去干扰、离子化增强质谱信号的技术,建立了多种DNA修饰的精准定量分析方法以及测序方法,包括DNA 5mC、6mA以及去甲基化中间体(5hmC、5fC)。利用所建立的DNA修饰精准分析方法,我们鉴定出多种生物活性小分子可调控胞嘧啶去甲基化。结合基因编辑、分子相互作用与深度测序等现代技术,阐明了其调控的分子机制。利用所建立的DNA腺嘌呤甲基化高精准分析技术,我们发现了高等生物基因组中存在DNA腺嘌呤甲基化修饰。另外,我们鉴定出哺乳动物基因组中存在由DNA聚合酶复制引入的掺入型DNA 6mA,并发现严格限制其在细胞内形成的检查点。我们进一步研究表明,掺入型DNA 6mA是一种潜在的疾病诊断标志物。
专家简介
汪海林,中科院生态环境研究中心研究员,杰青,基金委创新群体负责人。主要从事高灵敏DNA修饰分析以及DNA甲基化研究。发现高等生物的N6-甲基腺嘌呤(Cell, 2015, Cover),是表观遗传领域的原创性突破。已发表SCI 论文260 篇,包括Cell、Cell Res、JACS.、PNAS、Cell Discovery、Nucleic Acids Res 等。先后获得中科院院长特别奖(1997),中国分析测试协会科学技术奖特等奖(2015、2020),中科院“优秀研究生导师奖”(2012,2013)。

报告摘要
Protein methylation is receiving more and more attention due to its essential role in diverse biological processes. Large-scale analysis of protein methylation requires the efficient identification of methylated peptides at proteome level; unfortunately, a significant number of methylated peptides are highly hydrophilic and hardly retained during reversed-phase chromatography, making it difficult to be identified by conventional approaches. Herein, we report the development of a novel strategy by combining hydrophobic derivatization and high pH strong cation exchange enrichment, which significantly expand the identification coverage of the methylproteome. Noteworthily, the total number of identified methylated short peptides was improved by more than two-fold. By this strategy, we identified 492 methylation sites from NCI-H460 cells, compared to only 356 sites identified in native forms. The identification of methylation sites between before and after derivatization were highly complementary. Approximately two fold the methylation sites were obtained by combing the results identified in both approaches (native and derivatized) as compared with the only analysis in native forms. Therefore, this novel chemical derivatization strategy is a promising approach for comprehensive identification of protein methylation by improving the identification of methylated peptides of short-chain.
专家简介
Dr. Mingliang Ye obtained his Ph D under the supervision of Prof. Hanfa Zou at the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP), Chinese Academy of Science (CAS), in 2001, and worked as postdoctoral fellows under supervision of Prof. Norman Dovichi at the University of Washington, USA (2001.11-2003.3), and Prof. Reudi Aebersold at the Institute for System Biology, USA (2003.3-2004.10). In November of 2004, he came back to China and now he is a full professor in DICP and deputy director of CAS Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry. He published more than 200 peer-reviewed papers in SCI journals. He won Excellent Young Scientist Funding awarded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China in 2015. Currently his research interesting is mainly focused on developing new methods for the analysis of protein post-translational modifications and for the identification of target proteins of diverse ligands.
以上报告内容由BCEIA2023组委会提供

欢迎扫码报名参加BCEIA2023
[来源:仪器信息网] 未经授权不得转载
 钢板微观组织及性能在线预测
钢板微观组织及性能在线预测
BCEIA 2023 双碳战略下的可持续科学与技术高峰论坛即将召开
2023.08.18

相聚北京BCEIA2023 共探近红外光谱如何拥抱智能化生产和生活
2023.08.17

2024.07.30

2024.07.30

2024.07.30

2024.07.29
版权与免责声明:
① 凡本网注明"来源:仪器信息网"的所有作品,版权均属于仪器信息网,未经本网授权不得转载、摘编或利用其它方式使用。已获本网授权的作品,应在授权范围内使用,并注明"来源:仪器信息网"。违者本网将追究相关法律责任。
② 本网凡注明"来源:xxx(非本网)"的作品,均转载自其它媒体,转载目的在于传递更多信息,并不代表本网赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,且不承担此类作品侵权行为的直接责任及连带责任。如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网下载使用,必须保留本网注明的"稿件来源",并自负版权等法律责任。
③ 如涉及作品内容、版权等问题,请在作品发表之日起两周内与本网联系,否则视为默认仪器信息网有权转载。
![]() 谢谢您的赞赏,您的鼓励是我前进的动力~
谢谢您的赞赏,您的鼓励是我前进的动力~
打赏失败了~
评论成功+4积分
评论成功,积分获取达到限制
![]() 投票成功~
投票成功~
投票失败了~