ANDA申请中递交的外用药物产品的体外渗透(IVPT)研究
ANDA申请中递交的外用药物产品的体外渗透(IVPT)研究
Comments and suggestions regarding this draft document should be submitted within 60 days of publication in the Federal Register of the notice announcing the availability of the draft guidance. Submit electronic comments to https://www.regulations.gov. Submit written comments to the Dockets Management Staff (HFA-305), Food and Drug Administration, 5630 Fishers Lane, Rm. 1061, Rockville, MD 20852. All comments should be identified with the docket number listed in the notice of availability that publishes in the Federal Register.
For questions regarding this draft document, contact (CDER) Susan Levine at 240-402-7936.
Generic Drugs 仿制药
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/guidance-compliance-regulatory-information/guidances-drugs
In Vitro Permeation Test Studies for Topical Drug Products Submitted in ANDAs
ANDA申请中递交的外用药物产品的体外渗透(IVPT)研究
Guidance for Industry(注释1:指南由食品药品管理局(FDA)的医药审评与研究中心( CDER)仿制药办公室( OGD)起草制订。)
This draft guidance, when finalized, will represent the current thinking of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA or Agency) on this topic. It does not establish any rights for any person and is not binding on FDA or the public. You can use an alternative approach if it satisfies the requirements of the applicable statutes and regulations. To discuss an alternative approach, contact the FDA staff responsible for this guidance as listed on the title page. 该指南代表了 FDA 对该主题目前的看法。它并不会赋予任何人任何权利,也不会约束 FDA 或公众,如果有替代的方法能够满足法律法规的要求,可以使用替代的方法。如果想探讨替代的方法,请联系该指南首页中 FDA负责执行该指南的工作人员。 |
I. Introduction 绪论
This guidance is intended to assist applicants who are submitting abbreviated new drug applications (ANDAs) for liquid-based and/or other semisolid products applied to the skin, including integumentary and mucosal (e.g., vaginal) membranes, which are hereinafter called “topical products.”(注释2)Because of the complex route of delivery associated with these products, which are typically locally acting, and the potential complexity of certain formulations, topical products (other than topical solutions) are classified as complex products.(注释3)This guidance provides recommendations for in vitro permeation test (IVPT) studies comparing a proposed generic (test) topical product and its reference standard (RS) for the purpose of supporting a demonstration of bioequivalence (BE) to the reference listed drug (RLD). The reference standard ordinarily is the RLD.(注释4)
本文不是讨论适用于该指南范围的特定外用制剂产品的指南。FDA建议申请人,在进行IVPT研究的设计和实施时,查阅特定产品开发指南(PSGs)(注释5)和其他行业指南(注释6),同时结合其他必要的研究,以支持拟申请的仿制药与RLD的生物等效性。此外,FDA建议申请人定期查阅FDA指南网站,及时获取最新的相关指南,以促进仿制药的开发。
In general, FDA’s guidance documents do not establish legally enforceable responsibilities. Instead, guidances describe the Agency’s current thinking on a topic and should be viewed only as recommendations, unless specific regulatory or statutory requirements are cited. The use of the word should in Agency guidance means that something is suggested or recommended, but not required.
本指南已发展为FDA“药品竞争行动计划”(注释7)的一部分,配合GDUFA(注释8)项目和其他FDA举措,旨在促进处方药市场的竞争,促进优质和实惠的药品进入市场,提高公众医疗水平。
注释7:See FDA Drug Competition Action Plan (describing the FDA’s Drug Competition Action Plan, implemented in 2017 and designed to, among other things, further encourage robust and timely market competition for generic drugs), available at https://www.fda.gov/drugs/guidance-compliance-regulatory-information/fda-drug-competitionaction-plan.
注释8:In this guidance, GDUFA refers to the generic drug user fee program codified in the Generic Drug User Fee Amendments of 2012, Title III, Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act (Public Law 112-144), the Generic Drug User Fee Amendments of 2017, Title III, FDA Reauthorization Act of 2017 (Public Law 115-52), and the Generic Drug User Fee Amendments of 2022, Title III of Division F (the FDA User Fee Reauthorization Act of 2022) of the Continuing Appropriations and Ukraine Supplemental Appropriations Act, 2023 (Public Law 117-180).
《联邦食品、药品和化妆品法案》(FD&C法案)要求ANDA申请中应包含合适的信息,说明:1)仿制药与RLD相比,具有相同的活性成分、使用条件、给药途径、剂型、规格和说明书(允许存在一些差异);2)与RLD生物等效。(注释9)因此,如果ANDA中提交的信息不足以证明自制制剂与RLD具有生物等效性,则ANDA将不予批准(注释10)。
注释9:See sections 505(j)(2)(A), (j)(2)(C), and (j)(4) of the FD&C Act (21 U.S.C. 355(j)(2)(A), (j)(2)(C), (j)(4)); see also 21 CFR 314.94.
注释10:21 CFR 314.127(a)(4), (6).
An IVPT study may be used to assess the rate and extent to which a drug (i.e., an active ingredient) from a topical product becomes available at or near a site of action in the skin, and may be used to characterize and compare the rate and extent of bioavailability for a drug from a test topical product and RS. The IVPT flux profiles resemble pharmacokinetic profiles and can be analyzed using unique IVPT endpoints that are somewhat analogous to the pharmacokinetic endpoints of maximum concentration (Cmax) and the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC). Yet, IVPT studies characterize the rate and extent of absorption, not the distribution, metabolism and excretion that occurs in vivo. Therefore, while it is relevant to characterize the kinetics of topical drug bioavailability monitored by IVPT studies, the use in this guidance of the term “cutaneous pharmacokinetics” should not be construed to embody all aspects of pharmacokinetics—only those related to the absorption component that directly controls the rate and extent to which a topically applied drug becomes available locally at the site of action. This guidance focuses on general considerations and recommendations for the method development, method validation, and conduct of IVPT studies that are submitted in ANDAs and intended to support a demonstration of BE.(注释11)
IVPT研究可用于评估外用药物产品中药物(即活性成分)到达皮肤作用部位或附近的速率和程度,表征和评估自研外用制剂与对照制剂(RS)中药物的生物利用度和程度。IVPT通量曲线类似于药代动力学曲线,可以使用独特的IVPT终点进行分析,该终点与最大浓度(Cmax)的药代动力学终点和浓度-时间曲线下面积(AUC)相似。然而,IVPT研究表征的是药物吸收的速率和程度,而不是体内的分布、代谢和排泄。因此,IVPT研究虽然可用于外用药物制剂中活性成分生物利用度的动力学表征,但本指南中的俗语“皮肤药代动力学”不应被解释为药代动力学的所有方面,其表征的仅仅是“外用制剂中活性成分达到作用部位的速率和程度”。本指南旨在说明,在ANDA申请中提交、拟用于BE论证的IVPT研究的方法开发和验证的一般考虑和建议。(注释11)
注释11:A demonstration of no significant difference in the rate and extent of drug permeation into and through the skin of the test topical product and RS using an appropriately validated IVPT method can be used to support a demonstration of BE along with other data in the application (which may be specified in a PSG), as part of a comparative product characterization-based approach.在ANDA申请中,通过采用合适且经过验证的IVPT方法,说明自研外用制剂与对照制剂(RS)中药物的渗透速率和通过皮肤的量无明显差异,作为产品特性比较方法的一部分,并结合其他数据用于支持BE的论证(可能在“特定产品开发指南”中有规定)。
III. IVPT method developmen IVPT方法开发
The development of an IVPT method that is suitable to support a demonstration of BE for a specific topical product routinely involves a systematic series of exploratory studies. Inappropriate or insufficient efforts to develop an IVPT method that is suitable for its intended purpose increases the likelihood that the subsequent IVPT validation, pilot, and pivotal studies will ultimately be inadequate to support a demonstration of BE. By contrast, appropriate and systematic IVPT method development studies help to identify IVPT study designs and protocol (method) parameters which reliably produce flux profiles that can facilitate a comparison of the cutaneous pharmacokinetics of a drug delivered topically to the skin from test topical products and RSs.
适用于支持特定外用制剂BE论证的IVPT方法的开发,通常需要进行一系列系统的探索性研究。不合适或不充分的IVPT方法开发可能会导致,后续的IVPT验证、初步和正式研究不足于支持BE论证。相反,合理且系统的IVPT方法开发研究,有助于明确IVPT研究设计和方案(方法)参数,产生可靠的通量曲线,以便于自研制剂和RSs的皮肤药代动力学比较。
A detailed and well-organized IVPT method development report should be submitted in an ANDA to show how the IVPT method was optimized, and to support a demonstration that the method parameters selected for the IVPT are appropriate or necessary, particularly in situations where the method parameters are different from the methods recommended in this guidance). The Agency’s interest in reviewing the method development report is to understand why specific IVPT method parameters were selected and whether the resulting IVPT method is suitably sensitive and reproducible. This method development report should clearly indicate/distinguish the method parameters used for each set of data, illustrate the efforts made to optimize the IVPT method, and demonstrate that the method parameters selected for the IVPT are appropriate.
应在ANDA中提交详细且结构清晰的IVPT方法开发报告,说明IVPT方法是如何优化的,所选择的IVPT方法参数是合理性或必要的,尤其是方法参数与本指南中建议的方法不同时。监管机构在审核IVPT方法开发的过程中,比较关注IVPT方法参数选择的合理性,以及确定的IVPT方法是否具有合适的灵敏度和重现性,因此,需要说明在IVPT方法优化过程中所作的努力,并证明所选择的IVPT方法参数是合适的。
Applicants are encouraged to use the recommendations in this guidance, and if an applicant elects to use methods that are different from those recommended in this guidance, the IVPT method development report should demonstrate why it is scientifically justified to use an alternative approach than what is recommended in this guidance to optimize the IVPT method.(注释12)Some examples of recommended procedures are described in subsequent sections, to help applicants identify circumstances when information should be submitted in the ANDA to explain why a different procedure was utilized.
鼓励申请人采用本指南中推荐的方法,如果申请人选择其他方法,应在IVPT方法开发报告中说明,采用替代的方法优化IVPT方法的科学合理性(注释12)。以下部分描述了本指南中推荐方法的一些示例,以帮助申请人识别在ANDA申请中何时需要递交相关信息,解释为什么采用了不同的方法。
注释12:Applicants may choose to use an approach different from the approach recommended in this guidance. However, the alternative approach must comply with relevant statutes and regulations. See 21 CFR 10.115(d). 申请人可以采用指南中没有描述的其它方法。然而,所选用的替代方法必须遵守相关法律法规要求。
A. IVPT Method Parameters IVPT方法参数
All relevant parameters of the final IVPT method should be summarized (e.g., in a table) and submitted in the ANDA. Also, information should be provided to briefly explain the choice of the final IVPT method parameters like the equipment (e.g., a vertical diffusion cell (VDC)), skin source (e.g., cadaver), skin type (e.g., posterior torso), skin preparation (e.g., dermatomed), skin barrier integrity test (e.g., trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL) measurement), skin barrier integrity test acceptance criteria (e.g., < 15 grams/meter2/hour (g/m2/hr)), topical product dose amount (e.g., 15 milligrams/centimeter2 (mg/cm2)), dose duration (e.g., 6 hours), study duration (e.g., 24 hours, 48 hours, etc.), receptor solution sampling times (e.g., 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 20, and 24 hours), etc.
B. IVPT Method Considerations IVPT方法考虑因素
The choice of some IVPT method parameters like the equipment, skin source, skin type, skin preparation, and skin barrier integrity test procedures may be based upon investigator experience or convenience, like the availability of specific equipment or instrumentation in a laboratory, established tissue supply agreements, or other logistical considerations. However, if the chosen IVPT method parameters do not appear to be well-suited for a specific IVPT method, it is the applicant’s responsibility to systematically evaluate alternative method parameters, and ultimately, to validate that the IVPT method parameters chosen are suitable for the intended purpose. The recommended procedures for IVPT method validation are detailed in section IV of this guidance.
The choice of other IVPT method parameters like the topical product dose amount, dose duration, study duration (which may be longer than the dose duration), sampling schedule, sampling procedures, receptor solution composition, and sample analytical method may be different for each IVPT method, and such parameters of IVPT methods should be systematically developed, optimized, and/or validated for the relevant topical product, as appropriate. The IVPT method development studies should characterize how differences in these method parameters influence the resulting IVPT flux profile so that optimal study conditions can be objectively selected from among those evaluated.
The selection of the dose amount used in the study should be assessed for each IVPT method based upon studies performed during IVPT method development. Different dose amounts may be compared in parallel on replicate skin sections from the same set of donors to optimize the dose amount for the IVPT study. Considerations for selecting an optimal dose amount may include (1) the consistency with which the dose can be applied (potentially using different dispensing and/or spreading techniques), (2) the reproducibility of the flux profiles, (3) the influence of dose amount and dose duration on the shape of the flux profile, and (4) the approximate range of drug concentrations in receptor solution samples at different time points (relative to the sample analytical method limits of quantification).
The selected sampling schedule and study duration should be sufficient to characterize the cutaneous pharmacokinetics of the drug, which ideally includes a sufficiently complete flux profile to identify the maximum (peak) flux and a decline in the flux thereafter across multiple subsequent time points. A dose that remains on the skin for the duration of the study may continue to deliver the drug for a sustained period and may not necessarily exhibit a suitable decline in the flux at later time points. In such instances, it may be appropriate to develop an IVPT method that involves wiping off the applied dose after a suitable duration on the skin and continuing to monitor the receptor solution for an extended period thereafter, during which the decline in the flux profile can be characterized. The sampling frequency should be selected to provide a suitable resolution for the flux profile, and a minimum of eight non-zero sampling time points is recommended across the study duration (e.g., 48 hours).
所选择的取样计划(即:取样时间点)和研究持续时间应足以表征药物的皮肤药代动力学,理想情况下应包括一个足够完整的通量分布,以识别最大(峰值)通量和此后多个时间点的通量下降情况。在研究期间,如果药品持续保留在皮肤上面,其可能会持续递送药物,在最大(峰值)通量之后时间点可能不会通量下降的现象。此时,在IVPT方法开发时,可在上样一段时间后将样品擦去,然后持续监控接收液一定时间,使之呈现出通量下降的情况。所选的取样频率应足以为通量曲线提供合适的分辨率,在整个研究期间(如,48小时),推荐至少采用8个非零取样点。
C. IVPT Method Procedures and Controls IVPT方法程序和控制
Suitable technical procedures and control parameters should be established during method development. These may include procedures for preparing and mounting the skin on the diffusion cell in a consistent manner, determining the instrument settings that regulate the skin surface temperature within the specified range, performing the barrier integrity test appropriately, controlling the accuracy and precision of the dose amount dispensed on each skin section.
在方法开发过程中,应制定合适的技术规程和控制参数,包括:采用一致的方式准备皮肤并将其安装到扩散池上;确定仪器参数设置,使皮肤表面温度在既定的范围内;进行合适的屏障完整性测试;控制皮肤切片上上样量的准确度和精密度。
D. IVPT Skin Barrier Integrity Testing: Common Methods IVPT皮肤屏障完整性测试:常用方法
The technical procedures for the skin barrier integrity test should be established during IVPT method development. Three types of barrier integrity tests are common, however, there are currently no applicable compendial standard protocols or acceptance criteria for any of these three types of human skin barrier integrity tests. Nonetheless, recommended parameters for the three common types of barrier integrity tests are discussed below.
应在IVPT方法开发期间建立皮肤屏障完整性测试方法。常用的皮肤屏障完整性测试方法有三种,但还没有相应的药典收载或法定可接受标准。尽管如此,下面讨论三种常见类型屏障完整性测试的推荐参数。
1. Trans-Epidermal Water Loss Skin Barrier Integrity Test 经皮水分散失法测试皮肤屏障完整性
A TEWL skin barrier integrity test involves a measurement near the outer surface of the skin of the rate at which water (vapor) is fluxing through the skin barrier from the underside of the skin section. For the test, the skin section is mounted in a diffusion cell (e.g., clamped in place between the donor and receptor compartments), with the underside of the skin in contact with the receptor solution in the receptor compartment (e.g., phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4), and equilibrated to a skin surface temperature of 32°C ± 1°C. If skin sections are cut large enough to cover the flange of the diffusion cell in which they are mounted, then after they have equilibrated for several hours at a skin surface temperature of 32°C ± 1°C, it may be feasible to gently remove the donor compartment without disrupting a skin section’s adherence to the lower flange of the diffusion cell, thereby allowing the TEWL probe to be placed directly on the skin surface, instead of being placed atop the donor compartment. Typically, a minimum of three replicate measurements are made on each skin section, which are recorded after the measurements have stabilized.
TEWL皮肤屏障完整性测试是通过测定皮肤外表面附近的水分(蒸汽),评估水分从皮肤下侧通过皮肤屏障的速率。在测定时,将皮肤安装到扩散池中(如,夹在供给室和接收室之间),使皮肤下侧与接收室中的接收介质(如PBS,pH7.4)接触,然后将皮肤表面温度平衡至32℃±1℃。如果皮肤切片切割的足够大,能覆盖皮肤安装位点的扩散池法兰,可在皮肤表面温度平衡至32℃±1℃几小时后,在不破坏皮肤切片与其下部的扩散池法兰粘附的情况下,将供给室轻轻移去,此时可将TEWL探针直接放置在皮肤表面,而不用放置在供给室的顶部。通常,在测试结果稳定后,每个皮肤切片需至少重复测定三次,并记录相关结果。
对于人体躯干或大腿皮肤,采用TEWL屏障完整性测试法,合理的皮肤屏障完整性接受(截止)标准是每小时每平方米不大于约15g水(即,≤15g/m2/hr);如果选择其作为截止标准,TEWL大于15g/m2/hr的皮肤,则不具有皮肤完整性。未通过皮肤完整性测试的皮肤切片不应进行上样操作,但可用作为无剂量空白对照皮肤切片。但是,如果通过实验数据表明,所选的接受标准可以适当地区分屏障完整性受损的皮肤切片与屏障完整性合格的皮肤切片,也可以采用更高的截止标准(如,≤20g/m2/hr)。
然而,具有合格屏障完整性皮肤的TEWL测量值,可能会因TEWL测试设备、操作方式和环境条件的不同而变化(如,较高的环境湿度或距离皮肤表面较远的距离可能会降低TEWL的测量值)。对环境和设备/操作因素的精确控制可将TEWL测量的可变性将至最低。因此,在IVPT方法开发过程中应对TEWL的测定方法进行优化(或基于实验室之前进行该测试的优化结果)。此外,应对TEWL测试设备进行适当的校准(由生产商进行;对于某些设备,在每次实验前都需要进行校准)。申请人可提供生产商制定的相关校准程序信息,与IVPT方法开发报告一起在ANDA中递交,用于支持申请人为TEWL测量制定的技术程序的合理性。在IVPT方法开发、初步研究、验证和/或正式研究的整个研究阶段,进行TEWL屏障完整性测试时,均应监测和报告实验室的环境温度和湿度。
2. Tritiated Water Skin Barrier Integrity Test 氚化水渗透法测试皮肤屏障完整性
An example of a recommended approach to a tritiated water skin barrier integrity test would be to mount the skin in a diffusion cell (e.g., clamped in place between the donor and receptor compartments) and allow it to equilibrate to a skin surface temperature of 32°C ± 1°C with the stratum corneum exposed to the air in the donor compartment and the underside of the skin in contact with the receptor solution (e.g., phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4).
氚化水渗透法测试皮肤屏障完整性的一个推荐方法是,将皮肤安装到扩散池中(如,夹在供给室和接收室之间),使皮肤的角质层暴露在空气中(即,朝向供给室),皮肤下侧与接收液(如PBS,pH7.4)接触,然后将皮肤表面温度平衡至32°C ± 1°C。
3. Electrical Based Skin Barrier Integrity Tests 电阻/电导值法测试皮肤屏障完整性
TEER皮肤屏障完整性测试的结果,可能因LCR仪表设置(如,频率)和所用的测试技术方法不同,产生很大变化。电阻/电导值法测试皮肤屏障完整性接受标准的合理性,可通过试验数据证明,即:所选的接受标准应当可以适当地区分屏障完整性受损的皮肤切片与屏障完整性合格的皮肤切片。
E. IVPT Skin Barrier Integrity Testing: General Considerations IVPT皮肤完整性测试:注意事项
The technical procedures should not irreversibly alter the skin barrier. It may be acceptable to temporarily alter the hydration state of the stratum corneum by briefly depositing an aqueous solution on the surface of the skin, as long as sufficient time is afforded for the hydration of the stratum corneum to normalize before dosing of the topical product. The procedure described above for a brief (e.g., 5-minute) exposure of the skin surface to tritiated water followed by a 30-minute duration during which the hydration state of the stratum corneum is re-equilibrating would likely be appropriate. By contrast, a 30-minute exposure of the skin surface to an aqueous solution for an electrical-based test method, followed within 5 minutes by dosing of the topical product, may not be appropriate without further characterization of the influence of the hydration state of the stratum corneum on the discrimination sensitivity of the skin to differences in topical bioavailability. Similarly, if a portable lamp were placed close to the skin to improve visibility while study procedures were being performed, the heat from the lamp may alter the local (micro)environment of the skin in a manner that is not representative of the ambient environmental conditions in the laboratory; this should be avoided.
测定方法不应不可逆的改变皮肤完整性。可以接受将水溶液上样到皮肤表面后,短暂的改变角质层水合状态的情况,但在外用制剂上样前,经过足够长的时间后,角质层应可以恢复到正常的水合状态。如前面描述的情况,将皮肤表面短暂的暴露于氚化水一段时间(如,5分钟)后移除,经过30分钟的重新平衡,角质层的水合状态可以恢复到合适水平。相比之下,对于电阻/电导值测试法,将皮肤暴露于水溶液中30分钟后移除,而后,在5分钟后上样是不合适的,因为没有进一步评估皮肤角质层水合状态对不同外用制剂生物利用度区分灵敏度的影响。类似情况是,在测试过程中,如果将携带式手提灯放置在皮肤附近以提高能见度,从灯中散发出的热可能会改变皮肤的局部(微)环境,并不能代表实验室中的环境条件,应当避免。
The acceptance criterion should be a cutoff value for the test result, at which a skin section fails the test. Skin sections that fail a barrier integrity test should not be dosed but may serve as non-dosed control skin sections. Skin sections with a passing barrier integrity test result may be considered to have a competent barrier integrity and may be dosed. This acceptance criterion should be selected based upon an understanding of the distribution of test results (among multiple replicate skin sections from multiple donors) for the specific barrier integrity test procedure performed with the specific type and preparation of skin under conditions relevant to the IVPT pivotal studies submitted in the ANDA. The intention of the barrier integrity test is to identify (and exclude) skin sections whose barrier integrity (intactness) is compromised. The intent is not to reduce the inherent variability in barrier function (permeability) in human skin that is representative of real variation in the human population. Also, the relative permeability of the skin to a drug from a topical product may not necessarily correlate with the permeability of the skin to water, and therefore, constraining the variability of the skin permeability to water (using a stricter acceptance criterion that excludes a larger number of skin sections) may not necessarily reduce the variability in the IVPT study results.
接受标准应是皮肤未通过屏障完整性测试的截止值。未通过皮肤完整性测试的皮肤切片不应进行上样操作,但可作为无剂量空白对照皮肤切片。通过皮肤完整性测试的皮肤切片,可被视为具有合格的屏障完整性,可以进行上样试验。接受标准的选择可以依据,在ANDA申请中递交的IVPT正式研究中,采用特定类型和制备工艺皮肤进行的屏障完整性测试,对获得的测试结果(采用多个供体的多个重复皮肤切片进行)分布的理解进行选择。皮肤屏障完整性测试的目的是识别(和排除)屏障完整性(完整无缺)受损的皮肤切片。其目的并不是减少人体皮肤屏障功能(渗透性)的内在变异性,人体皮肤的内在变异性是其固有的特性。此外,皮肤对外用制剂中药物的相对渗透性,可能与皮肤对水分的渗透性无关;因此,限制皮肤对水分渗透的可变性(使用更严格的接受标准,排除更多的皮肤切片)可能不一定会减少IVPT研究结果的可变性。
The acceptance criterion should be able to discriminate skin sections with a compromised barrier integrity. This may be demonstrated by measuring the barrier integrity of skin sections mounted and equilibrated in a diffusion cell before and after deliberately compromising the skin barrier (e.g., by repeatedly using adhesive tape to strip away increasing amounts of the stratum corneum, piercing the skin several times with a 30 gauge needle, or using other physical or chemical insults to damage the skin barrier). Based upon the acceptance criterion selected, the test result for skin sections that pass the test before being damaged should fail the test after the damage.
接受标准应能够区分屏障完整性受损的皮肤切片。对于接受标准的论证,可通过“在特意破坏皮肤屏障的前后(如,通过反复使用胶布剥离越来越多的角质层、用30号针多次刺穿皮肤,或使用其他物理或化学手段破坏皮肤屏障)”,将其分别安装到扩散池并平衡后,根据屏障完整性的测定结果来评估。根据选择的接受标准,在破坏前通过测试的皮肤切片,对其破坏后应不能通过测试。
F. Differences Between IVPT Method Development and Validation IVPT方法开发和验证的区别
1. Optimization of an IVPT Method Prior to Advancing to IVPT Method Validation 在IVPT方法验证前进行IVPT方法的优化
2. Use of a Validated Sample Analytical Method for IVPT Method Validation 采用已验证的分析方法进行IVPT方法验证
The IVPT method development studies, being exploratory in nature, are often performed using a sample analytical method that is not validated (e.g., an HPLC or ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) method, often involving mass spectrometry (MS)); also, IVPT method development studies are often conducted in a manner that is not compatible with a quality management system which would otherwise make the evidence generated suitable to support valid conclusions. Such method development studies would not be suitable to demonstrate the validity of an IVPT method, or associated results. Therefore, although it may appear to be redundant, certain experiments performed during IVRT method development may need to be repeated during IVPT method validation, using appropriate controls, like a validated analytical method and procedures that are compatible with a suitable quality management system.
IVPT方法开发研究,本质上具有探索性,通常是采用未经验证的样品分析方法(如,HPLC或UPLC,通常需要进行质谱分析(MS))进行的;此外,IVPT方法开发研究通常与质量管理体系不兼容,产生的数据不足以支撑可靠的结论。因此,方法开发研究不足以支撑IVPT方法验证或相关的结果。尽管看起来似乎是多余的,但在IVPT方法开发期间进行某些试验可能需要在IVPT方法验证期间重复进行考察,进行适当的控制,如与适当的质量管理体系相兼容的已验证的分析方法和程序。
It is important to clearly segregate and consistently identify those experiments and results that were part of IVPT method development separately from those that were part of IVPT method validation. It is also important to consistently identify all relevant method parameters and experimental conditions/controls for each set of IVPT results. Information in the method development report should clearly identify/distinguish when the results for apparently similar sets of experiments may have been obtained using different method parameters. Method development reports should clarify which sets of diffusion cells were run in parallel or separately (e.g., on separate days). In addition, the sample analytical method parameters used to analyze the samples from each set of IVPT experiments should be specified, and the report should indicate whether or not the sample analytical method was validated (either at the time of sample analysis or subsequently).
需要注意的是,应将IVPT方法开发和IVPT方法验证的试验结果分开来看,并采用一致的评价标准;对于每组IVPT结果,所有相关的方法参数和试验条件/对照都应保持一致,这点非常重要。当采用不同的方法参数可以获得明显相似的试验结果时,应在方法开发报告中清楚的说明。在方法开发报告中,也应阐明扩散池是平行还是单独运行(如,在不同的日期)的。此外,应说明在IVPT试验中,用于样品分析的具体方法参数,并说明分析方法是否经过了验证(在样品分析时或样品分析后)。
IV. IVPT method validation IVPT方法验证
When all the relevant parameters of the IVPT method have been established, a pilot study should be performed using the final IVPT method and using a validated sample analytical method. The purpose of the pilot study is to validate the suitability of the selected IVPT method parameters by demonstrating that the performance characteristics of the IVPT method are appropriate to compare the cutaneous pharmacokinetics of a drug delivered topically from a test product and RS. The results from the pilot study, thereby, support the systematic validation of the IVPT method, which proceeds as a distinct study phase following IVPT method development.
在所有相关的IVPT方法参数确定之后,应采用最终确定的IVPT方法和已验证的样品分析方法进行初始研究。初步研究的目的是,通过论证IVPT方法的性能特性适用于自研制剂和对照制剂(RS)中药物的皮肤药代动力学比较,确认所选IVPT方法参数的适用性。因此,初步研究的结果支持IVPT方法的系统验证,这是IVPT方法开发之后的一个特有的研究阶段。
The results from this IVPT pilot study can help to estimate the number of donors that may be needed to adequately power the IVPT pivotal study. In addition to the test topical product and RS evaluated in the pilot study, a parallel assessment should be performed with a third topical product or formulation that is known or designed to be different from the RS, to validate the selectivity of the IVPT method to discriminate differences in bioavailability. The IVPT pilot study results should be plotted with error bars, comparing the permeation profiles for the three treatment groups in the pilot study. Separate plots should be prepared for average flux results and average cumulative permeation results. These data can be used to support specific IVPT method validation parameters (e.g., permeation profile and range).
IVPT的初步研究结果有助于评估在IVPT正式研究中所需的供体数量。在IVPT的初步研究中,除了对自研外用制剂和对照制剂(RS)评估外,还应对已知或设计与RS不同的另一种外用产品或配方进行平行评估,以确认IVPT方法在区分生物利用度差异方面的选择性。应用误差线绘制IVPT的初步研究结果,对三个试验组的渗透曲线进行比较。这些数据可用于支持特定的IVPT方法验证参数(如,渗透概况和范围)。
A pilot IVPT study performed with multiple skin donors (e.g., 4–6 skin donors) and a minimum of four replicate skin sections per donor per treatment group is recommended. As skin from an increasing number of donors is evaluated in the pilot study, the accuracy of the estimated number of donors needed to adequately power the IVPT pivotal study may improve. While skin from the same donors evaluated in the pilot study may also be used in the IVPT pivotal study, the results from the pilot study should not be combined with the results from the IVPT pivotal study for the purpose of statistical analysis.
在IVPT初步研究中,建议采用多个皮肤供体(如,4~6个皮肤供体),且每个试验组的每个供体至少4个重复皮肤切片。随着IVPT初步研究中评估的供体数量的增加,可逐步提高IVPT正式研究中所需的供体数量准确性。虽然在IVPT初步研究评估中用的相同供体皮肤也可用于IVPT正式研究,但初步研究的结果不能与IVPT正式研究中获得的结果合并进行统计分析。
The equipment, methodologies, and study conditions used in the IVPT pilot study (and the eventual IVPT pivotal study) should be appropriately validated or qualified. If an applicant elects to use equipment, methodologies, or study conditions that are different from those recommended in this guidance, the applicant should demonstrate why it was necessary and scientifically justified to do so. Detailed protocols and well-controlled study procedures are recommended to ensure the precise control of dosing, sampling, and other IVPT study parameters, as well as potential sources of experimental bias.
IVPT初步研究(和最终的IVPT正式研究)中所用的设备、方法和研究条件应进行合适的验证或确认。如果申请人使用的设备、方法或研究条件与本指南中推荐的不一致,申请人应说明这种选择的必要性,并证明其科学合理性。建议建立详细的方案和良好的研究控制程序,以精确控制上样、取样和其它IVPT研究参数,以及潜在的试验偏差来源。
The validation of the IVPT method should incorporate specific qualifications and controls (described below), performed using a validated sample analytical method, as applicable. The qualification of an IVPT method parameter refers to the process of defining what attributes make it suitable to perform its function in the IVPT method. For example, when repeated measurements of the temperature at the surface of skin mounted in a diffusion cell demonstrate that an IVPT equipment can maintain the skin surface temperature in the range of 32°C ± 1°C, the results can support a demonstration that the equipment is qualified to perform its function in an IVPT method for which a method parameter is the control of skin surface temperature in the range of 32°C ± 1°C across the relevant study duration.
IVPT方法验证应包括下述的确认和控制内容,如适用,使用已验证样品分析方法。IVPT方法参数确认是表征IVPT方法的属性是否适合于执行其功能的过程。例如,当重复测定安装在扩散池中的皮肤表面温度时,IVPT设备可以维持皮肤表面温度在32℃±1℃范围内,这个结果可以用于证明,在整个IVPT方法研究期间,该设备可以执行其功能,将皮肤表面温度控制在32℃±1℃范围内。
A. Equipment Qualification 设备确认
可用于IVPT方法的设备有VDCs(立式扩散池)和流通池。每种类型设备的操作原理和相关测定方法不同;可根据生产商提供的相关规程进行安装、操作和性能确认。各种型号的扩散池确认至少包括:1)测定供给室和接收室之间皮肤安装位置的孔口扩散面积;2)测量VDC接收室的容积,或流通池输出管的长度;3)在整个研究期间(如,48小时),测定皮肤表面温度(如,32℃±1℃)的稳定性;和4)如适用,测定VDC的搅拌速率,或流通池的流速。
如果可以从生产商处获取每个扩散池的孔口扩散面积和接收室的容积信息,除了提供实验室进行IVPT研究时测定的相关结果,还应提供生产商提供的信息。设备应可以控制扩散池的温度,确保在上样前,皮肤表面温度稳定(如,通过校准的红外温度计测定在32℃±1℃范围内);并在整个试验期间通过重复测定,连接到相同的水浴或温度调节系统、与上样剂量组平行运行的非剂量控制组的皮肤表面温度进行定期监测。
建议采用离体人类皮肤作为IVPT研究用膜。应采用合适的方法评估角质层的屏障完整性,以对上样用皮肤切片的有效性进行验证。可接受的屏障完整性测试方法包括氚化水渗透、TEWL或电阻/电导值法。研究期间所用皮肤屏障完整性测试的参数和可接受标准,应根据所用的方法和仪器,说明其合理性。研究中所用的供体皮肤应采用相同的方式进行处理,且皮肤厚度应相对一致,以满足研究方案中拟定的限度要求。如适用,应将供体皮肤的重复皮肤切片随机分配给每个试验组。可以根据研究方案中规定的程序来平衡每个试验组(自研外用制剂和RS)的皮肤厚度分布。
C. Receptor Solution Qualification 接收介质确认
IVPT研究中所用接收介质的组成和pH应根据其与皮肤的兼容性以及药物在接收介质中的稳定性和溶解度进行确认。药物在接收介质中的稳定性应作为接收液中样品分析方法验证的一部分。药物在接收介质中的溶解度,应经过三次重复检测经验确定,确保其超过IVPT正式研究中最高样品浓度,理想情况下是一个数量级。在IVPT方法验证期间的灵敏度评估中,药物在接收介质中的溶解度应足以表征,增加药物递送条件时药物渗透的最高量。
对于疏水性药物,推荐在基于生理缓冲盐的接收介质中添加0.1%(w/v)聚氧乙烯20油醚(别名Oleth-20, Volpo-20, or Brij-20;CAS:9004-98-2)提高溶解度。如有必要,可在接收介质中略微增加聚氧乙烯20油醚的浓度[例如,从0.1%(w/v)到0.2%(w/v)],通常足以满足大多数疏水药物溶解度的要求,但不应超过6%。其他改善药物在接收介质中溶解度的策略可能会改变皮肤的渗透性(例如,在接收介质中加入有机溶剂和醇),使IVPT方法失效,不建议使用。
无论研究时间的长短,建议在接收介质中加入一种抗微生物剂(例如,~0.1%叠氮化钠或~0.01%硫酸庆大霉素),以减轻在整个研究期间扩散池中细菌对真皮和/或表皮的潜在分解。如果采用其它抗微生物剂,应在ANDA中阐述选择的理由(以及使用的浓度)。
D. Receptor Solution Sampling Qualification 接收液取样确认
The accuracy and precision of receptor solution sample collection at each time point should be appropriately qualified. Evidence to qualify a sampling procedure should illustrate that the sampling technique can reliably collect a consistent volume of the sample from the well-mixed volume of the receptor compartment at each sampling event, and that no artifacts are likely to be created by the sampling technique. Information should be included describing the equipment manufacturer’s specification for the accuracy and precision of receptor solution sampling, when available.
应对接收液中每个时间点取样的准确性和精密度进行适当的确认。在取样程序的确认过程中应证明,所用取样技术可以从混合良好的接收室中始终一致的收集到相同体积的接收液,且不会因取样技术的原因引起误差。如适用,应描述设备生产商关于接收液取样准确度和精密度的规范信息。
For IVPT studies using a flow-through diffusion cell, it may be appropriate to qualify the lengths of tubing, and their associated dead volumes, to accurately calculate the lag time before a sample elutes through the tubing and is collected. For IVPT studies using a VDC, removal of the entire receptor solution volume and full volume replacement of the receptor solution at each time point may provide optimal solubility sink conditions. The sampling of small aliquots of the receptor solution for an IVPT study may introduce anomalous measurements of apparently negative flux in certain regions of the IVPT study and produce flux profiles that are difficult to interpret.
Ambient laboratory temperature and humidity during the study should be monitored and reported. An environmentally controlled temperature range of 21°C ± 2°C is recommended, and a humidity range of 50% ± 20% relative humidity is recommended, if feasible.
在研究期间,应监控和报告实验室环境的温度和湿度。如适用,建议将温度控制在21℃±2℃、湿度控制在50%RH±20%RH之间。
F. Permeation Profile and Range 渗透曲线和范围
The flux profile and cumulative permeation profile for the IVPT pilot study should be plotted across a range of sampling times, which corresponds to the IVPT pivotal study duration. The calculation of flux and cumulative total permeation is discussed in more detail below. The results of the IVPT pilot study should validate that the selected study parameters are suitable to adequately characterize the permeation profile (the cutaneous pharmacokinetics) of the drug within the selected study duration (the range of sampling time points).
在IVPT初步研究和正式研究中,应在整个取样时间范围内分别绘制通量分布曲线和累积渗透分布曲线。下文有关于通量和累积渗透量计算方式的详细讨论。应根据IVPT初步研究的结果确认,在所选择的研究期间(取样时间点范围内),所选择的研究参数是否足以表征渗透概况(皮肤药代动力学)。
A sufficiently complete flux profile should be adequate to identify the maximum (peak) flux and a decline in the flux thereafter across multiple subsequent time points in the IVPT pilot study. The results of the IVPT pilot study should also validate that the sampling frequency provides suitable resolution to adequately characterize the permeation profile (particularly the flux profile).
在IVPT初步研究中,一个充分完整的通量分布应足以识别出最大(峰值)通量和此后多个时间点的通量下降情况。应根据IVPT初步研究结果,确定取样频率,确保为表征渗透分布(特别是通量分布)提供合适的分辨率。
G. Precision and Reproducibility 精密度和重现性
The flux and cumulative permeation results from the IVPT pilot study (and the eventual IVPT pivotal study) should be calculated, tabulated, and reported for each diffusion cell at each time point, with summary statistics to describe the intra-donor average, standard deviation, and percent coefficient of variation (%CV) among replicates, as well as the inter-donor average, standard error, and %CV. Complete results for all data values used in the calculations should be reported in a clear and organized manner, to facilitate the reconstruction of the flux and cumulative permeation results. The design of the study should be detailed and clear, and data values should be clearly associated with specific donors, replicates, treatment groups, time points, etc.
在IVPT初步研究(和最终的IVPT正式研究)中,应计算和报告各扩散池在每个时间点的通量和累计渗透结果,并以表格的形式汇总统计以下信息:重复测定的批内均值、标准偏差和变异系数(%CV);以及批间均值、标准偏差和变异系数。计算中所用数据的完整结果应以清晰和有组织的方式进行报告,以便通量和累计渗透结果的重现。研究设计应是详细和清晰,将数据结果与相关供体、重复数、试验组和时间点等相关联。
H. Dose Depletion 剂量消耗
The recovery of permeated drug in the receptor solution should be characterized in each diffusion cell as the cumulative total permeation of the drug in the receptor solution over the IVPT duration. This may be expressed as a percentage of the nominal amount of drug in the applied dose (which may be estimated based upon the nominal strength of the drug in the topical product and the approximate mass of topical product dosed on the skin).
For example, if 10 mg of a topical product containing 5% drug was dosed on the membrane, the amount of drug in the applied dose may be estimated to be 0.5 mg (or 500 μg). If a cumulative total of 10 μg of drug diffused into the receptor solution across a 48-hour duration of the IVPT, it would be possible to estimate that the 500 μg dose would have been depleted by approximately 10 μg, amounting to an approximately 2% dose depletion. The average percentage dose depletion may thereby be estimated (not accounting for skin content) and should be reported.
例如,如果含有5% 药物的外用制剂上样为10mg,则在上样中药物的量大约为0.5mg(或500μg)。如果在IVPT研究的整个48小时内,药物渗透进入接收液的总量为10μg,则估计500μg的剂量消耗为10μg,相当于约2%的剂量消耗。应估算和报告平均剂量消耗百分比(不考虑皮肤含量)。
I. Discrimination Sensitivity and Selectivity 区分力—灵敏度和选择性
The discrimination ability of the IVPT method may be described using two concepts: sensitivity and selectivity. The IVPT sensitivity studies are necessarily performed during IVPT method development to establish IVPT method parameters like the dose amount, dose duration, study duration, etc. However, the analysis of the results from these studies is qualitative in nature, and they need not be repeated during the IVPT method validation phase.
The IVPT sensitivity studies are typically performed toward the end of the IVPT method development phase, and a key purpose of these studies is to incorporate the final IVPT method parameters for the target dose and dose duration to be used in the pivotal study so that the IVPT sensitivity studies can support a demonstration of the validity of the final IVPT method. Therefore, IVPT sensitivity studies are described within this section of the guidance in the context of IVPT validation (rather than method development) to avoid dissociating the discussions of IVPT sensitivity (which is performed to establish the suitability of the final IVPT method parameters) and IVPT selectivity (which is performed once the final IVPT method parameters are established, and which is based upon the IVPT pilot study that is performed as part of the IVPT method validation). With the exception of the alternative dose amounts or dose durations used in the IVPT sensitivity study, it is important that the IVPT method parameters are consistent across the IVPT sensitivity, pilot, and pivotal studies (including the anatomical region specified in the study protocol (e.g., posterior torso), the skin source, and skin preparation).
IVPT灵敏度研究通常在IVPT方法开发阶段末进行,这些研究的一个关键目的是为了确定“在正式研究中所用的最终IVPT方法参数”,包括目标上样量和剂量维持时间,因此,IVPT灵敏度研究可以为最终IVPT方法的有效性提供合理性证明。因此,本文在IVPT方法验证(而非“方法开发”)模块描述IVPT灵敏度研究,是为了避免将IVPT灵敏度(以确定最终IVPT方法参数的适用性)和IVPT选择性(基于IVPT初步研究,在最终IVPT方法参数确定之后进行,是IVPT方法验证的一部分)分开讨论。除了在IVPT灵敏度研究中的上样量或剂量维持时间不同外,在IVPT灵敏度、初步研究和正式研究的所有阶段,IVPT方法参数均应保持一致(包括:研究方案中指定的解剖区域(如,背部躯干)、皮肤来源和处理方法)。
1. IVPT Sensitivit 灵敏度
IVPT sensitivity is the ability of the IVPT method to detect changes in the cutaneous pharmacokinetics of the drug as a function of differences in drug delivery. If the IVPT method consistently demonstrates higher and lower flux profiles (i.e., higher and lower values for IVPT endpoints) in response to increased and decreased drug delivery, respectively (or in response to other conditions expected to increase and decrease drug delivery, respectively), the IVPT method may be considered sensitive.
There are a few potential approaches by which to produce the differences in drug delivery that can be differentiated by a suitably discriminating IVPT method. Regardless of the approach used, the differences in the IVPT permeation profiles are not necessarily expected to be specifically proportional to differences in the dose amount, dose duration, or product strength. For example, three-fold differences in the dose amount (even if outside the recommended target dose range) may provide distinct flux curves but may not result in three-fold differences in the IVPT endpoints because the skin barrier may be rate-limiting both in vitro and in vivo.
有几种潜在具有合适区分力的IVPT方法设计,去表征药物的不同递送行为。但无论采用何种方式,均不能期望IVPT渗透曲线的差异与药物上样量、剂量持续时间或产品规格的差异成比例关系。例如,上样量的三倍差异(即使超出了建议的目标剂量范围)可产生不同的通量曲线,但不会出现IVPT终点的三倍差异,因为皮肤屏障限制体外和体内的(渗透)速率。
换言之,如果正式IVPT研究的目标剂量是10 mg/cm2,则三倍的较低剂量为3 mg/cm2,三倍的较高剂量为30 mg/cm2;因此,可通过比较3、10和30 mg/cm2外用制剂上样量的通量曲线,确认IVPT方法的灵敏度。同理,如果正式IVPT研究的目标剂量是15 mg/cm2,则三倍的较低剂量为5 mg/cm2,三倍的较高剂量为45 mg/cm2;因此,可通过比较5、15和45 mg/cm2外用制剂上样量的通量曲线,确认IVPT方法的灵敏度。在IVPT灵敏度研究中,建议采用多个皮肤供体(如,4~6个皮肤供体),且每个试验组的每个供体至少4个重复皮肤切片。
Modulation of Dose Amount: An IVPT method development study with different dose amounts may provide supportive evidence that the IVPT methodology is sensitive to differences in drug delivery. This approach is well suited to topical products that contain volatile components that evaporate from the formulation following dose application to the skin. Modulating the dose amount for such topical products effectively alters the thickness of the applied dose. The majority of volatile components from a thinner dose will tend to evaporate more rapidly (compared to a thicker dose), and a thinner dose will tend to deliver less drug into the skin (and/or for a shorter duration) compared to a thicker dose. 调整上样量:可以采用不同的上样量进行IVPT方法开发研究,为IVPT方法对药物递送的差异具有灵敏度提供支持性证据。 该方法适用于含有挥发性成分的外用制剂,这些挥发性成分在药物制剂上样到皮肤后会挥发。调整这类制剂的上样量可以有效改变上样的厚度。采用较薄的上样量,与较厚的上样量相比,大部分挥发性成分会挥发,因此,较薄的上样量(和/或较短的维持时间)递送进入皮肤的药物量较少。
Modulating the dose amount can be an effective technique to modulate differences in drug delivery for formulations with volatile components, like gels, lotions, and many creams. However, modulating the dose amount may not necessarily produce perceptible differences in drug delivery for topical products like petrolatum-based ointments, or other types of topical products that do not evaporate on the skin, or that may not experience dose-dependent differences in metamorphosis that can alter the rate and extent of drug delivery. 对于含有挥发性组分的配方,如凝胶、洗剂和很多乳膏剂,调整上样量是改变药物递送行为的有效技术手段。然而,对于基于凡士林的软膏剂、或不会在皮肤上挥发的外用制剂、或可改变药物递送速率和程度的形变过程不具有剂量依赖性,通过改变这些制剂的上样量不一定会产生药物递送行为的明显差异。
Modulation of Dose Duration: For many topical products, it may be more effective to modulate the dose duration, instead of the dose amount, to produce differences in drug delivery and associated changes in the cutaneous pharmacokinetics of the drug. 调整剂量维持时间:对于很多外用制剂,相比于调整上样量,通过调整剂量维持时间可更有效地评估药物递送的差异和与药物皮肤药代动力学相关的变化。
An IVPT method development study with a controlled dose amount (e.g., 15 mg/cm2) dosed for different durations (e.g., 2 hours, 6 hours, and 12 hours) may be well suited to provide supportive evidence that the IVPT methodology is sensitive to differences in drug delivery from many topical products. The scenario described in this example would support an IVPT study design where a topical product dose of 15 mg/cm2 is dosed for 6 hours (the target duration for the IVPT study) and then wiped off. The applied dose may be removed with a series of cotton-tipped swabs, one or more of which may be dry and one or more of which may be moistened (e.g., with a soap solution or water). The initial (dry) swab typically removes the bulk of the dose and subsequent swabs are used to remove the residual dose (i.e., the residue of the topical product which may otherwise continue to deliver drug into the skin) and/or to rinse the skin.
在IVPT方法开发研究中,通过将一定量的外用制剂(如,15 mg/cm2)在皮肤上维持不同的时间(如,2h、6h和12h)可能是提供支持性证据的比较合适方式,以证明IVPT方法对很多外用制剂中药物递送的差异具有敏感性。本例描述了用于支持IVPT研究设计的场景,将上样量为15 mg/cm2的外用制剂在皮肤上维持6h(研究的目标维持时间),然后将其擦除。可以采用一些棉签移除样品,包括一个或多个干燥的棉签,和一个或多个浸湿的棉签。首先用干燥的棉签移除大部分样品,然后用浸湿的棉签移除残留的样品(即,残留的样品可能会继续递送药品进入皮肤)和/或清洗皮肤。 To support a demonstration of the sensitivity of the IVPT study, the permeation profile produced by the target dose duration for the IVPT study (e.g., 6 hours) should be compared with a shorter dose duration (e.g., 2 hours) that is expected to perceptibly decrease the drug delivery, and also be compared with a longer dose duration (e.g., 12 hours) that is expected to perceptibly increase the drug delivery. Thereby, the three dose durations compared in the IVPT sensitivity study are designed to produce perceptible changes in the cutaneous pharmacokinetics of the drug as a function of differences in drug delivery, and thereby support a demonstration of the sensitivity of the IVPT method.
为了证明IVPT研究的灵敏度,将IVPT研究中目标剂量持续时间(如,6小时)的渗透曲线分别与较短剂量维持时间(如,2小时)和较长剂量维持时间(如,12小时)的渗透曲线进行比较,较短和较长剂量维持时间应分别有明显较低和较高的剂量递送。因此,在IVPT灵敏度研究中,通过设计比较三种不同剂量维持时间,可产生明显不同的“能反映药物递送差异的”药物皮肤药代动力学,支持IVPT方法的灵敏度论证。 The specific dose durations may be selected based upon an initial exploratory IVPT study performed during IVPT method development that characterizes the permeation profile when the dose is left on the skin for a longer duration (e.g., 24 or 48 hours). An important feature of the results from such an IVPT study is the duration of the initial phase of the permeation profile, when the flux is increasing at a relatively rapid rate.
在IVPT方法开发期间,可以根据初始的探索性IVPT研究中,剂量在皮肤上保留较长时间(如,24或48小时)的渗透曲线,选择特定的剂量维持时间。这种研究结果的一个重要特征是,在渗透曲线的初始阶段,通量以一个相对较快的速率增加。 For example, if such an exploratory study indicates that the flux increases on a steep slope until approximately 12 hours, and then continues to deliver the drug at a gradually increasing rate thereafter, it may suggest that the permeation profile for a dose duration of longer than 12 hours (e.g., 24 hours) may not be perceptibly different from that of the 12 hour dose duration, especially when compared in a relatively small number of donors and replicates (e.g., four donors with four replicates each per dose duration). It may also suggest that a 12-hour dose duration may be a good choice for the longest of the three dose durations in the IVPT sensitivity study.
例如,如果探索性研究结果表明,在12小时前通量快速增加,之后随着剂量维持时间的增加,通量与12小时无明显的差异;这种结果表明,超过12小时(如24小时)的剂量维持时间,获得的通量分布曲线可能与12小时无明显差异,尤其是在供体和重复数量较少的情况下(如,每个剂量维持时间4组供体皮肤,每组供体皮肤4个重复皮肤切片)。这也可能表明,在IVPT灵敏度研究中,12小时的剂量持续时间可能是一个较好的选择,也是三个剂量维持时间中最长时间。 The target dose duration should be selected based upon considerations like the sensitivity of the sample analytical method, the ability to produce a permeation profile that can be perceptibly discriminated from that produced by the longer (12 hour) dose duration, and/or the labeled use of the topical product (which may indicate that the topical product should be reapplied every 4–6 hours).
目标剂量维持时间的选择应基于以下考虑因素,如:样品分析方法的灵敏度、产生能明显区别于最长(12小时)剂量维持时间所产生的渗透曲线的能力、和/或外用制剂的说明书(其中可能说明,每4~6小时需要重复进行给药)。 The shortest of the three dose durations in the IVPT sensitivity study should be selected based upon the sensitivity of the sample analytical method and its ability to produce a permeation profile that can be perceptibly discriminated from that produced by the target (6 hour) dose duration.
在IVPT灵敏度研究中,三个剂量维持时间中最短时间的选择应基于样品分析方法的灵敏度,以及其产生能明显区别于目标剂量维持时间(6小时)所产生的渗透曲线的能力。
Modulation of Product Strength: To validate the sensitivity, specificity, and selectivity of an in vitro release test (IVRT) method, altered strength formulations are routinely prepared. While it may seem convenient to use these altered strength formulations in an attempt to demonstrate the sensitivity and selectivity of an IVPT method, doing so may not produce the desired outcomes. There may be circumstances when this strategy may produce perceptibly different permeation profiles, however, in many instances, the resulting permeation profiles may not be perceptibly different when compared in a relatively small number of donors and replicates (e.g., four donors with four replicates each per topical product strength). In general, the modulation of topical product strength to support a demonstration of IVPT sensitivity is not recommended because it may not consistently produce the expected increase or decrease in drug delivery; however, in certain situations, higher and lower strength formulations (relative to the nominal strength of the RS) may suitably increase and decrease the drug delivery and cutaneous pharmacokinetics relative to that from the nominal strength topical product. 调整产品规格:对于IVRT方法的灵敏度、专属性和选择性验证而言,常见的方式是改变配方制剂的规格。虽然在IVPT方法的灵敏度和选择性验证中,采用改变配方制剂规格的方式似乎也比较方便,但这种方式可能不会产生预期的结果。在某些情况下,这种策略可能会产生明显不同的渗透曲线;然而,在很多情况下,由于在对比研究中采用的供体组和重复数较少(如,每种外用制剂规格采用4个供体组,每组供体4个重复),并不能产生具有明显不同的渗透曲线。通常,不建议通过调整外用制剂规格的方式去论证IVPT的灵敏度,因为它可能不会持续产生预期的药物递送增加或降低;然而,在某些情况下,相对于外用制剂的目标规格,较高和较低规格的配方制剂(相对于对照制剂的规格)可以适当的增加和降低药物递送和皮肤药代动力学。
IVPT选择性是IVPT方法区分“对照制剂(RS)”和“与RS在药物递送方面存在差异的外用制剂或配方”在药物皮肤药代动力学差异的能力。在IVPT初步研究中,通过将RS、自研外用制剂和“已知或设计不同于RS”的第三种外用制剂或配方进行平行评估,提供支持性证据,说明IVPT方法对药物递送的差异具有选择性。如适用,应在研究报告中递交,IVPT方法开发、验证和初步研究中用到的所有外用制剂的相关批信息,包括但不限于:批配方、生产日期、批量、变更的生产工艺(如适用),以及效价和含量均匀度(如有)。可基于渗透曲线和/或IVPT终点的定性或定量比较进行不等效性评估。
J. Robustness 耐用性
A primary assumption related to robustness testing is that the test system performs consistently when all system variables (e.g., temperature, stirring rate) are at nominal settings. A value of robustness testing is that it can verify whether the system continues to provide a consistent output when specific variables are slightly altered, thereby qualifying operational ranges for those variables. However, the variability inherent in the permeability of human skin, whether in vitro or in vivo, may not be compatible with the primary assumption related to the consistency of the test system.
与耐用性测试相关的一个主要假设是,当所有系统变量(如,温度、搅拌速率)为标准设置时,测试系统的性能一致。耐用性测试的意义在于,它可以确认当特定变量稍微改变时,系统是否可以提供一致的输出结果,从而确定这些变量的操作范围。然而,无论是在体外还是在体内,人体皮肤渗透性的固有可变性可能与测试系统一致性的初始假设不相容。
Nonetheless, results from studies during IVPT method development that appear to support the robustness of the IVPT method or system should be reported, if relevant. For example, an IVPT method may be robust to substantial variations in the stirring rate of the receptor compartment. Similarly, the permeation profile of a drug into and through human skin may appear to be robust to certain differences in the topical product strength. Ultimately, because it may not always be feasible to validate the robustness of IVPT method parameters, IVPT study procedures should be controlled as precisely as possible.
尽管如此,如果相关,应报告在IVPT方法开发期间获得的可以支持IVPT方法或系统耐用性的研究结果。例如,IVPT方法对接收室中搅拌速率的显著变化具有耐用性。类似地,药物进入并通过人体皮肤的渗透曲线可能对外用制剂规格的改变具有耐用性。因此,对IVPT方法参数的耐用性验证并不总是可行的,在IVPT研究中应尽可能精准的控制IVPT研究程序。
V. Sample analytical method validation 样品分析方法验证
虽然在IVPT方法开发的探索性研究中,可以采用未验证的样品分析方法,但作为IVPT方法验证的一部分,在IVPT方法验证时,必须采用已验证的样品分析方法。已验证的IVPT方法应当使用已验证的样品分析方法(如,HPLC/MS或UPLC/MS)。因此,该部分讨论用于IVPT方法的样品分析方法。
然而,与IVPT方法相关的研究方案和报告与用于IVPT接收液中样品定量的分析方法不同。样品分析方法验证,就其本身而言,并不能证明IVPT方法的有效性。因此,应分别递交样品分析方法(如,HPLC/MS或UPLC/MS)和IVPT方法的验证报告。
如果,在方法开发期间使用的样品分析方法与最终验证的样品分析方法不同,与其相关的IVPT方法研究结果不能用于支持论证IVPT方法的有效性。在IVPT方法验证报告中,应提供参考的样品分析方法验证信息,并明确表明IVPT方法验证报告中的所有相关结果均是采用经验证的样品分析方法(而不是与经验证的分析方法具有不同参数的样品分析方法)获得的。
接收液中样品的分析方法(如,通常为HPLC/MS或UPLC/MS系统)应使用具有审计追踪的色谱软件(如,色谱数据系统),并应包括具有适当质量控制样品的多点(6~8个)校准曲线,同时,应符合FDA生物分析方法验证行业指南要求。
如适用,接收液中样品分析方法的验证应包括相关的稀释完整性确认,以及样品在最高相关温度的接收液中放置最长相关时间的稳定性评估;最高相关温度可以略高于32℃,因为接收液的温度通常高于皮肤表面温度。对于在每个取样时间点替换整个接收液的情况,最长相关时间为各相邻取样时间点中,间隔最长时间;但对于接收液部分取样的情况,时间可能更长(如,34℃放置48h)。
如果在测定前,需要用特定的方式对样品进行处理(如:将样品干燥后重新用小体积溶剂配制以提高分析灵敏度;或通过稀释接收液样品,使其浓度到已验证的样品分析方法曲线范围内),应对该处理方法进行确认(如,在样品分析方法验证期间确认稀释完整性)。药物在接收液中的稳定性,应在IVPT正式研究相关的条件下,与扩散池中皮肤下侧接触的接受液基质中进行。
Refer to 21 CFR 320.38, 320.63 and the FDA guidances for industry Handling and Retention of BA and BE Testing Samples (May 2004) and Compliance Policy for the Quantity of Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Samples Retained Under 21 CFR 320.38(c) (August 2020), as applicable, regarding considerations for retention of study drug samples and to 21 CFR 320.36 for requirements for maintenance of records of BE testing. Retention samples should be randomly selected from the drug supplies received before allocating topical product units for use in an IVPT study in which the test topical product and RS are compared.
B. Control of Study Procedures 研究程序的控制
Study procedures that have the potential to influence the results of the study should be appropriately controlled. Also, experimental observations that may have the potential to influence the interpretation of the study results, as well as any protocol or standard operating procedure (SOP) deviations, should be reported.
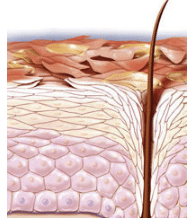
Control of procedures related to the skin include the consistent control across the study of the skin preparation (e.g., dermatoming of skin sections) and the thickness of skin sections mounted on diffusion cells, as well as the skin storage conditions, including the duration for which the skin was frozen and the number of freeze-thaw cycles to which the skin was exposed. Skin from the same anatomical location should be used from all donors, and the demographics (age, race, sex) should be reported for all donors. Also, the IVPT sensitivity, pilot, and pivotal studies should use skin from the same anatomical site; otherwise, if skin from different anatomical sites is used across the different study phases, it may not be possible for the results of the IVPT sensitivity and pilot studies to support a demonstration of the discrimination ability of the IVPT method used for the pivotal study because the method parameters would not be aligned across the respective studies. Similarly, if a non-rate-limiting support membrane is used beneath the skin section (e.g., a filter membrane used in a validated IVRT method for the same topical product) then it should be used in a consistent manner for the IVPT sensitivity, pilot, and pivotal studies.
与剂量或上样相关的控制程序,包括:对上样面积、上样量、上样技术、剂量维持时间的控制,以及在研究中每个扩散池采用的盲法和随机化方法的一致性。不同的上样技术可能改变上样到皮肤上剂型的形态,扩散池孔口扩散面积的不一致可能会显著影响上样面积,进而导致通量计算的偏差。
与取样相关的控制程序,包括:取样时间精准度、取样技术、取样和替代接收液的时间间隔、取样体积或流速,以及样品的处理和储存。
在正式研究期间的相关控制程序,包括:对每组皮肤供体的非剂量控制皮肤切片,按照与上样皮肤切片一致的方式将其安装到扩散池中并进行后续处理,在所有时间点对接收液进行取样,以确保IVPT正式中,在接收液中检测到的药物为实际渗透进入的量,而不是研究期间由于皮肤的药物污染渗透进入。建议从每个扩散池中采集“零”浓度样品,用于识别每个皮肤切片和/或每个扩散池的潜在污染。
Study personnel identification, training, qualification, and responsibilities 研究人员的识别、培训、资质和职责 Study management and study management personnel responsibilities 研究管理和研究管理人员职责 Quality control (QC) and QC personnel responsibilities 质量控制(QC)和QC人员职责 Quality assurance (QA) and QA personnel responsibilities 质量保证(QA)和QA人员职责 Use of SOPs 操作规程(SOP)的制定 Use of study protocols 研究方案的制定 Use of study reports 研究报告的制定 Maintenance and control of the study facility environment and systems 研究设施环境和系统的维护和控制 Qualification and calibration of instruments and computerized systems 仪器和计算机系统的确认和校准 Good documentation practices including, but not limited to, contemporaneous documentation of study procedures and recording of experimental observations or deviations from procedures specified in the study protocol or in relevant SOPs 良好的文件规范,包括但不限于:及时记录研究过程、试验观察、以及与研究方案及相关SOPs中规格程序的偏离 Maintenance of suitable records that facilitate the reconstruction of study events and procedures, including study sample handling and storage records (e.g., sample tracking logs), audit trails for sample analysis procedures, control of study materials and reagents, and electronic data control 对记录进行适当的维护,以便研究过程可以重现,包括:研究样品的处理和保存记录(如,样品跟踪日志)、样品分析过程的审计跟踪、研究物料和试剂的控制以及电子数据控制 Archival of study records 研究记录归档
C. Blinding Procedure 盲法程序
A detailed description of the blinding procedure should be provided in the study protocol and final report. The packaging of the test topical product and RS should be similar in appearance to maintain adequate blinding of the investigator and any experimental operators.
D. Randomization 随机化
The method of randomization should be described in the protocol of the IVPT study and the randomization schedule provided, preferably in a SAS data set in .xpt format (created using the SAS XPORT procedure). It is recommended that an independent third party generate and hold the randomization code throughout the conduct of the study to minimize bias. The applicant may generate the randomization code if not involved in the packaging and labeling of the test topical product and RS dosed in the study. A sealed copy of the randomization scheme should be retained at the study site and should be available to FDA investigators at the time of site inspection to allow for verification of the treatment identity of each skin section.
应在IVPT研究方案中描述随机化方法,并推荐以.xpt格式的SAS数据集形式(使用SAS XPORT程序创建)提供随机化计划表。在整个研究过程中,建议由独立的第三方生成并保存随机化代码,以减少偏差。如果不参与自研外用制剂和RS的包装和标签,申请人可以自行生成随机化代码。随机化方案的密封副本应保留在研究现场,以便在现场核查期间可随时提供给FDA审评员,用于确认每个皮肤切片的具体信息。
E. Dosing 上样
In the IVPT pivotal study, the test topical product and RS should be dosed in an alternating pattern on successive diffusion cells (skin sections) from each donor. One of two dosing sequences (illustrated below) may be randomly assigned for each donor:
a. ABABAB…
b. BABABA…
b. BABABA…
F. Study Design 研究设计
The IVPT pivotal study should compare the cutaneous pharmacokinetics of the drug from the test topical product versus that from the RS using excised human skin with a competent skin barrier mounted on a qualified diffusion cell system. The IVPT pivotal study should use a design that directly compares the test topical product and RS on skin from the same set of donors, each with the same number of replicate skin sections per donor per treatment group (dosed with either test topical product or RS topical), using the same IVPT method parameters.
The IVPT pivotal study design, methodology, and diffusion cell equipment considerations relating to sampling precision should be controlled as precisely as possible. For example, it may be appropriate to stagger the dose application on successive diffusion cells and to synchronize the sampling time points with the dosing time for that diffusion cell, to ensure consistent durations between dosing and sampling of all diffusion cells.
应尽可能精准的控制IVPT正式研究的设计、方法和扩散池设备的取样精密度。例如,对于连续的扩散池,可以错开上样时间,根据上样时间的差异同步取样时间,以确保所有扩散池的上样和取样时间的间隔一致。
G. Inclusion Criteria 纳入标准
In general, the following inclusion criteria should apply: healthy, normal, barrier-competent skin from male and/or female donors of at least 18 years of age. Inclusion criteria related to donor demographics (e.g., age, race, sex) should be specified in the study protocol and demographic information should be reported for each donor. Additional criteria may be added by the applicant.
通常,应采用以下纳入标准:至少18周岁的健康、正常、具有屏障完整性的雄性和/或雌性供体。应在研究方案中规定符合纳入标准的人口统计信息(如,年龄、种族、性别),并报告每个供体的个人信息。申请人可以增加其它纳入标准。
The skin may be harvested following excision from patients undergoing a surgical procedure or excised from cadavers. A consistent source is recommended for all the skin used. The anatomical region specified in the study protocol (e.g., posterior torso) should be consistent for all donors whose skin is included in the study.
建议使用人体离体皮肤,可以从接受外科手术的病人或尸体获取。所用的所有皮肤应有一致的来源,且所有的供体应为相同的解剖区域(如,背部躯干),并在研究方案中进行明确规定。
The study protocol should specify the inclusion (acceptance) criteria for skin sections based upon the barrier integrity test result, which should be reported for each skin section. The study protocol should specify inclusion criteria related to the temperature and duration of skin storage as well as the number of freeze-thaw cycles, all of which should be reported for each donor’s skin. The study protocol should specify the inclusion criteria related to the skin harvesting/processing procedures and skin thickness (e.g., dermatomed skin of 500 μm ± 250 μm thickness) used in the IVPT study.
研究方案中应规定皮肤切片的屏障完整性测试纳入(接受)标准;并规定每组供体皮肤的储存温度和时间,以及冻融循环次数;同时规定IVPT研究中所用皮肤的获取/处理方法和厚度(如,厚度为500 μm ± 250 μm)。
H. Exclusion Criteria 排除标准
In general, the following exclusion criteria should apply. Skin from subjects with a known (history of) dermatological disease should be excluded from the study. Skin with tattoos, stretch marks, or any visible sign of abnormality should be excluded from the study. Skin exhibiting a significant density of terminal hair is not recommended and should be excluded from the study. Additional criteria may be added by the applicant.
通常,应采用以下排除标准。包括:患有已知皮肤疾病(病史)的供体皮肤;带有纹身、妊娠纹或任何异常迹象的皮肤;表现出明显浓密的末端毛发的皮肤等。申请人可以增加其它排除标准。
While gentle washing or rinsing of the skin surface is appropriate, submerging the skin in an aqueous solution for more than a few minutes may damage the skin barrier and should be avoided; such skin sections should be excluded from the study. Also, skin that has been subjected to shaving with a blade; abrasive polishing; tape-stripping; or cleansing with alcohols, solvents, or other strong solutions that could damage the skin barrier should be excluded from the study.
虽然可以采用温和的清洗或冲洗方式处理皮肤表面,但是,如果将皮肤浸泡在水溶液中几分钟,就有可能破坏皮肤屏障,应避免该处理方式。此外,也不建议采用刀片剃须、研磨抛光、胶带剥离,或采用乙醇或其它强极性溶剂处理皮肤,因为这些处理方式可能破坏皮肤屏障。
Skin from donors with significant background levels of the drug or other compounds that may interfere with the quantification of the drug in receptor solution samples should be excluded from the study. Skin from donors exhibiting a high barrier integrity test failure rate among replicate skin sections may be excluded from the study, and skin from an alternative donor may be used instead.
含有显著的药物背景水平或含有的其他化合物可能干扰接收液中药物定量测定的皮肤供体,应排除在研究之外。重复皮肤切片中屏障完整性测试失败率高的供体皮肤应排除在研究之外,采用其他的供体皮肤进行替代。
I. IVPT Endpoints IVPT终点
The endpoints for the IVPT pivotal study are based upon parameters that characterize the rate and extent to which the drug permeates into and through the skin and becomes available in the receptor solution. Specifically, the rate of drug permeation is characterized by the flux (J) and the extent of drug permeation is characterized by the total cumulative amount (AMT) of drug permeated into the receptor solution across the study duration.
IVPT关键研究的皮肤药代动力学终点是基于表征药物渗透和通过皮肤进入接收液的速率和程度的参数。具体来说,药物的渗透速率采用通量(J)进行表征,而药物的渗透程度采用整个研究期间渗透到接收液的累积总量进行表征。
以通量(药物渗透速率)为纵坐标Y-轴,时间为横坐标X-轴作图;其中Y-轴用“J”标识,以质量/面积/时间(如,纳克/平方厘米/小时)为单位。通量分布模型通常类似于血浆药代动力学分布模型,尽管通量是一个速率单位,并不代表浓度。也应对药物的渗透程度作图,以药物累积渗透量(单位为质量/面积,如纳克/平方厘米)为纵坐标Y-轴,时间为横坐标X-轴。
应计算并报告各扩散池的所有相邻采样点之间的通量,并为整个研究期间的所有扩散池绘制通量曲线。上述计算的速率可以对应于2小时的实际时间点进行绘制,也可以采用0和2小时之间的中间点(即,1小时)。
b. 自然对数换算后的总累积渗透量(AUC)
It is the responsibility of the applicant to determine the number of donors required to adequately power the IVPT pivotal study, however, a minimum of four dosed replicates per donor per treatment group (test product or RS) is recommended.
At the completion of the study, if the number of skin replicates is the same for all donors in the test topical product and RS treatment groups in the IVPT study, a statistical analysis for a balanced design is recommended. If skin sections or diffusion cells are excluded from the final statistical analysis because of experimental loss/issues, and the resulting data set is unbalanced, a statistical analysis for an unbalanced design is recommended.
申请人有责任确定足以支持IVPT关键研究所需的供体数量,然而,建议每个试验组(自研制剂或RS)每个供体至少4个重复剂量。
在本指南的第VIII部分,对正式研究的统计分析方法进行了描述。附录I提供了用于测定平衡数据集和非平衡数据集BE的SAS代码示例。附录II提供了模拟数据集的具体示例。附录III提供了测定BE的R代码示例。
VII. Submitting information on IVPT studies in an ANDA ANDA中递交的IVPT研究信息
对于支持外用制剂产品BE论证的IVPT研究,在ANDA申请中应递交IVPT方法验证(包括IVPT初步研究)和IVPT正式研究的详细研究方案、相关SOPs和报告。此外,应递交描述IVPT方法开发的详细报告。这些方案、SOPs和报告应在电子通用技术文件(eCTD)的模块5.3.1.2中递交,并对相关的试验方法、研究控制、质量管理程序和数据分析进行描述。
注意:用于IVPT接收液中样品浓度的定量分析方法(如,HPLC/MS或UPLC/MS方法)与IVPT方法相关的研究方案、SOPs和报告不同。应单独递交样品分析方法验证的方案和SOPs。样品分析方法开发和验证报告、初步和正式IVPT研究样品分析报告,以及与采用人体皮肤进行IVPT研究相关的样品分析SOPs和方案,应在eCTD的模块5.3.1.4中递交。
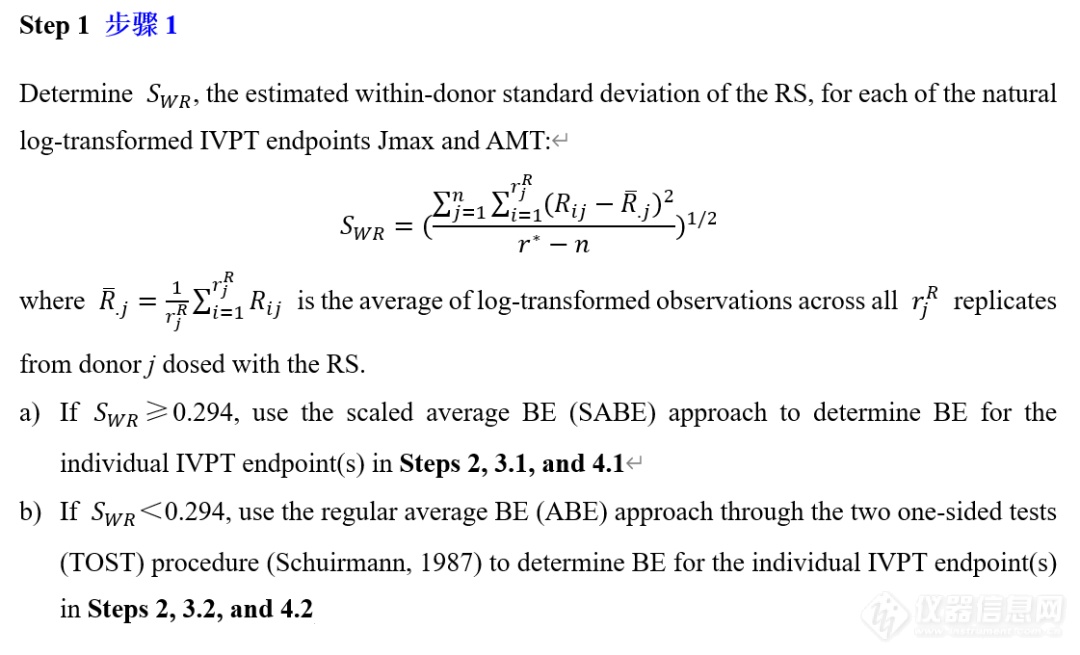
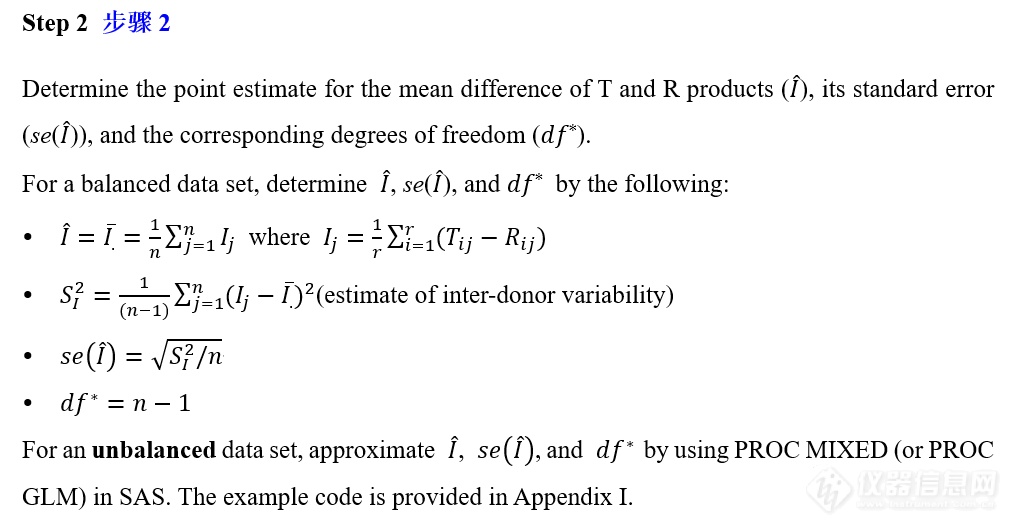
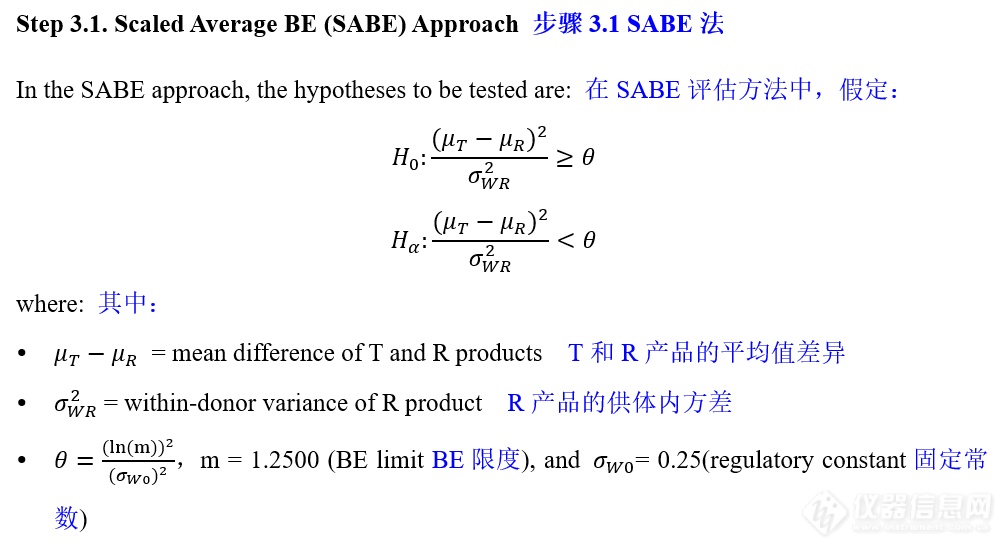
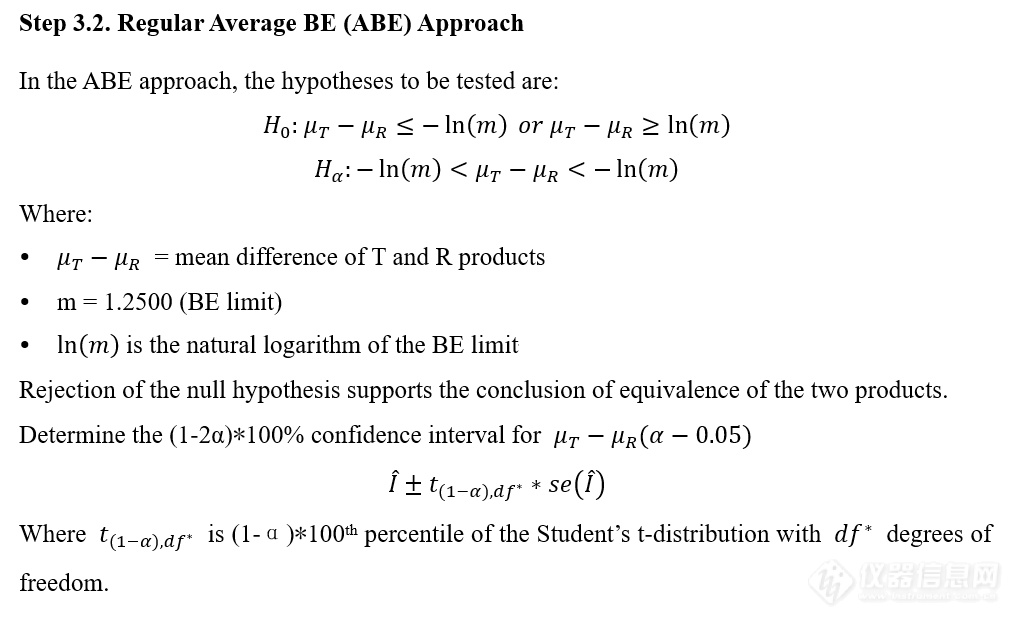
VIII. IVPT pivotal study statistical analysis IVPT正式研究统计分析










更多![]()
离体猪皮肤完整性随IVPT试验时间的动态变化探究
厂商
2024.07.15
透皮研究中离体猪皮活性的保存与挑战
厂商
2024.07.08
USP<1724>半固体药品性能试验 | 生物膜的关键质量要求
厂商
2024.06.28
FDA IVPT资料 | 透皮外用制剂(IVPT)研究参考案例
厂商
2024.06.24