Plant Soil:澳洲学者 | 植物-土壤界面的Cl-迁移调节大麦耐Cd
期刊:Plant Soil
主题:植物-土壤界面的Cl-迁移调节大麦耐Cd
标题:Chloride transport at plant-soil Interface modulates barley cd tolerance
影响因子:3.306
检测指标:Cd2+
通讯作者:澳大利亚西悉尼大学陈仲华
英文摘要
Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic metal in soilsand its accumulation in plants poses severe problems to agri-culturalproduction and human health. Most of research has focused on the Cd toxicity toplants, but reports on Cd co-transport and regulation by the major counter ionChloride (Cl) is limited. This study aims to understand the mechanisms of theinteraction between soil Cl and phytol-toxicity of Cd.
We utilised soil chemical, plantphysiological, biophysical, and molecular approaches to test the hy-pothesisthat Cl transport increases the mobility and phytol-toxicity of Cd to barley.
Cd-sensitive Gairdner utilised highamount of Cl? from soil for optimal growth and yield in the control, ut thisalso caused higher tissue Cd uptake and signif-icantly affected photosynthesisin treatments of Cd-Cl combinations. Net ion fluxes from the root mature zonein Cd treatments and relative expression of transporter genes exhibitedstriking difference between two geno-types. Our results also highlightedevidence that Cd sensitivity is related to higher Cl? and Cd2+ uptake and lowercapacity to regulate root ion homeostasis and gene expression.
We present a new finding thatsoil Cl? and Cd availability and Cd uptake and its interaction with other ionsplay a major role in barley Cd tolerance. These findings will guide futurebreeding for low Cl? uptake genotypes to reduce Cd accumulation for barleygrown in Cd contaminated soils and for the economi-cally sound and cleaner productionof barley for the global feed, food and brewery industry.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
镉(Cd)是土壤中的有毒金属,其在植物中的积累对农业生产和人类健康造成严重问题。大多数研究都集中在Cd对植物的毒性,但是关于Cd共转运和由主要抗衡离子氯(Cl)调节的报道是有限的。本研究旨在了解土壤Cl与植物醇对Cd的毒性相互作用的机制。
我们利用土壤化学,植物生理,生物物理和分子方法来检验Cl运输增加Cd对大麦的迁移率和植物毒性的假设。
Cd敏感的Gairdner利用土壤中大量的Cl-在对照中获得最佳生长和产量,但这也导致更高的组织Cd摄取并显着影响Cd-Cl组合处理中的光合作用。来自Cd处理的根成熟区的净离子通量和转运蛋白基因的相对表达在两种基因型之间表现出显着差异。我们的研究结果还强调了Cd的敏感性与较高的Cl-和Cd2+摄取以及较低的调节根离子稳态和基因表达的能力有关的证据。
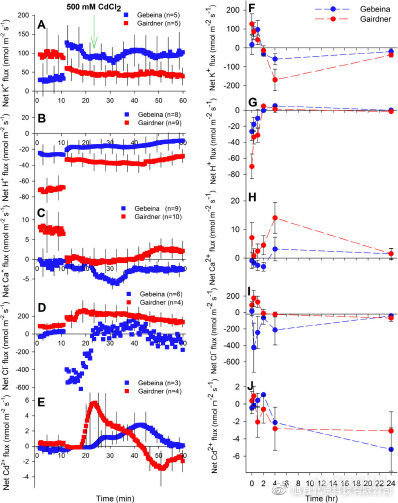
Fig. 3Transient and time-dependent Cd-induced ion flux from barley roots. Net K+ (a,f), H+ (b, g), Ca2+ (c, h), Cl? (d, i), and Cd2+ (e, j) fluxes at transient(a-e) and steady-state (f-j) were determined from mature root zone of 3-day-oldbarley seedlings of Gebeina and Gairdner at 0, 0.33, 1, 2, 4 and 24 h. Data aremean±standard error (n =4–10 seedlings)
我们提出了一个新发现,即土壤Cl-和Cd的有效性和Cd吸收及其与其他离子的相互作用在大麦Cd耐受性中起主要作用。这些研究结果将指导未来的低Cl-摄取基因型育种,以减少Cd污染土壤中生长的大麦的Cd积累,以及为全球饲料,食品和啤酒行业提供经济合理和清洁的大麦生产。
即日起,中关村NMT联盟统筹安排全国NMT测试服务,如需开展NMT相关实验,请联系联盟.
更多![]()
新产品发布及研讨会
新品
2002.09.09
新品上市_X'TRA Companion 高阶常规分析型台式XRD
新品
2023.08.23
重磅!赛默飞化学品全新官网发来袭,新注册送定制冰箱贴!
厂商
2024.05.27
半导体行业解决方案之热分析应用
厂商
2024.07.26