产地类别: 进口
为您推荐相似的脑立体定位仪
玉研仪器自主研发脑立体定位仪十四年,适用于大鼠、小鼠等实验动物,经典十字操作臂实现精准定位,精度可达10微米,特制螺纹精密螺杆,稳固不晃动实现对特定脑区的精确定位,是神经环路研究、神经系统性疾病、神经药理等领域内的重要研究设备,广泛面向全国各大科研院校,医院,高新企业,药企,医疗机构等科研单位。新一代电脑控制自动化立体定位仪,集成脑图谱,快速定位,实现实验动物脑部精确钻孔与微量注射等操作。
全自动脑立体定位仪是结合了stoelting公司经典的U型框设计,定制马达和创新性软件,是一款全新的划时代产品。通过StereoDrive软件,全自动脑立体定位仪能够通过马达和电脑控制三个轴方向上的位移 。另外软件中整合了 Paxinos 和 Watson 的《大鼠脑定位图谱》,能够更方便和更直观的进行脑立体定位。
产品特点:
|
|
操作方便、精准
· 脑立体定位仪,对于小动物的脑部手术来说,是一种可靠的,多功能的设备。
· 通过仪器的精确定位,可以确保电极、微管以及其它设备在实验过程中的精确定位。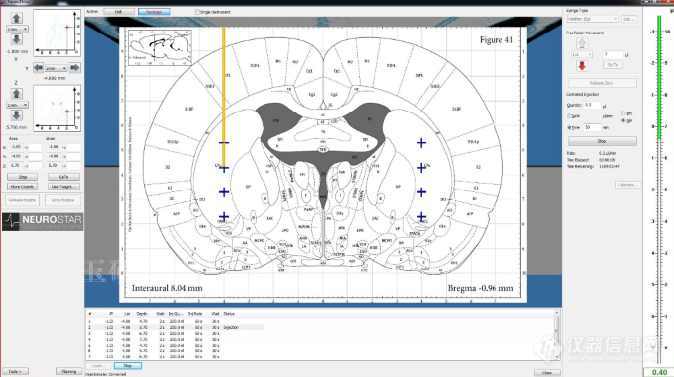
微量注射泵模块(可选):
· 由微型电动机来准确地控制推进和停止hamilton注射器,注射器可以方便地固定在脑立体定位仪上。
· 菜单操作简单,可以通过平台选择注射器的型号,设定注射容量、注射速度。
· 流速范围:0.01 µl/min到200 µl/min
颅骨钻模块(可选):
· 集成式电动机和低震动的柔韧性轴,噪音低,性能可靠;
· 电动机集成化固定在支撑架上;
· 可选用手动或脚踏开关控制,颅钻最大转速每分钟10000转。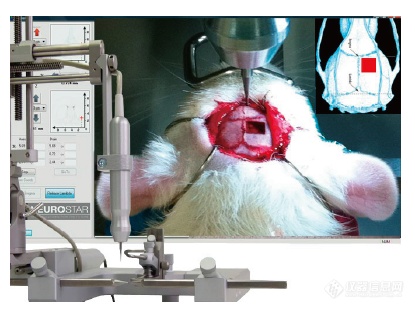
前囟监测观察器(可选):
· 实时精确观察定位情况;
· 减少人为失误,确保手术精度;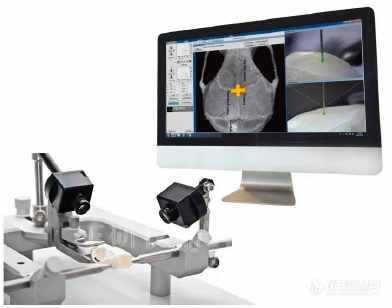
motorized rat stereotaxic instruments
The Motorized Rat Stereotaxics combines the classic stereotaxic design with customized motors and state-of-the-art software. Integrated with popular stereotaxic atlases the StereoDrive software allows motorized, computer controlled stereotaxic positioning in all 3 orthogonal axes. The intuitive movement control enables unprecedented accuracy and higher throughput in all stereotaxic applications.
The Motorized Lab Standard Stereotaxic combines the classic design of our time-proven ‘U’-Frame with customized motors and state-of-the-art software.
Designed to adapt conventional stereotaxic systems, the StereoDrive software allows motorized, computer controlled stereotaxic positioning in all 3 orthogonal axes.
Integrated with Paxinos and Watson’s Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, for either rat or mouse, the intuitive movement control enables unprecedented accuracy and higher throughput in all stereotaxic applications.
Features:
Digital Atlas integration
Frame representation
Calibration of frame coordinates
Setting of logical coordinate system (Bregma)
Coordinates and Atlas visualization of the probe
Advanced 3D visualization options
Spatial Atlas representation
Intuitive probe control
Intuitive navigation
Axial View Coronal View Sagittal View Working View
Motorized UpgradeYour choice of two service options:
Option 1: New Motorized Manipulator Arm and Axis StereoDrive Software
Keep your existing arm. We'll ship you a new one.
Option 2: Conversion to Motorized Manipulator Arm and Axis StereoDrive Software
Send us your existing arm. We will convert it to motorized for you.
Motorized Lab Standard Stereotaxic Software SamplerThe StereoDrive software display is divided into the navigation section on the left and the 3D atlas view on the right side of the window.
1. Atlas View
2. Actual position of the probe (logical or physical)
3. Axial view thumbnail — indicating the movement in anterior-posterior (X-axis) or medio-lateral (Y Axis) direction
4. Coronal view thumbnail — indicating the movement in medio-lateral (Y-axis) or inferior-superior (Z Axis) direction
5. Anterior-posterior (X) drive control region
6. Medio-lateral (Y) drive control region
7. Inferior-superior (Z) drive control region
8. Actual coordinates of the probes tip
9. Editable target coordinates of the probes tip
10. Stop button
11. GoTo button
12. Set Lambda button — setup of the logical coordinate system
13. Set Bregma button — setup of the logical coordinate system
14. Tools — access to the microdrive calibration (frame coordinate system)
Motorized StereoDrive Software
Included with Motorized Lab Standard? Stereotaxic
Axis StereoDrive Software integrates seamlessly with the precision controlled motors. Motor movement can be executed by using the keyboard arrow keys or clicking on the screen with the mouse.
The software coordinates motor movement of all 3 axes (anterior-posterior, medial-lateral, and dorsal-ventral) probe placement in relation to 3-dimensional visual representation of a rat (Paxinos & Watson, 6th Edition) or mouse (Watson, 3rd edition) Brain Atlas.
Features
Easy calibration
Software-driven control of stereotaxic movement
Virtual visualization of probe location
One micron resolution
Download coordinates to computer for recall and/or archiving
Angle adjustments
Variable speed on 2-axis (dorsal-ventral)
The Motorized Lab Standard Stereotaxic combines the classic design of our time-proven ”U”-Frame with customized motors and state-of-the-art software.Designed to adapt conventional stereotaxic systems, the StereoDrive software allows motorized, computer controlled stereotaxic positioning in all 3 orthogonal axes.
Integrated with Paxinos and Watson’s Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, the intuitive movement control enables unprecedented accuracy and higher throughput in all stereotaxic applications
Image manipulations include:
Spatial Rotation
Fixed Rotation
Zooming
Panning
参考文献:
1. Albéri, L., Lintas, A., Kretz, R., Schwaller, B., & Villa, A. E. (2013). The calcium-binding protein parvalbumin modulates the firing 1 properties of the reticular thalamic nucleus bursting neurons. Journal of neurophysiology, 109(11), 2827-2841.
2. Sonati, T., Reimann, R. R., Falsig, J., Baral, P. K., O’Connor, T., Hornemann, S., Aguzzi, A. (2013). The toxicity of antiprion antibodies is mediated by the flexible tail of the prion protein. Nature, 501(7465), 102-106.
3. Ali, I., O’Brien, P., Kumar, G., Zheng, T., Jones, N. C., Pinault, D., O’Brien, T. J. (2013). Enduring Effects of Early Life Stress on Firing Patterns of Hippocampal and Thalamocortical Neurons in Rats: Implications for Limbic Epilepsy. PLOS ONE, 8(6), e66962.
4. Bell, L. A., Bell, K. A., & McQuiston, A. R. (2013). Synaptic Muscarinic Response Types in Hippocampal CA1 Interneurons Depend on Different Levels of Presynaptic Activity and Different Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes. Neuropharmacology.
5. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
6. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
7. Babaei, P., Tehrani, B. S., & Alizadeh, A. (2013). Effect of BDNF and adipose derived stem cells transplantation on cognitive deficit in Alzheimer model of rats. Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science, 3, 156-161.
8. Gilmartin, M. R., Miyawaki, H., Helmstetter, F. J., & Diba, K. (2013). Prefrontal Activity Links Nonoverlapping Events in Memory. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(26), 10910-10914.
9. Feng, L., Sametsky, E. A., Gusev, A. G., & Uteshev, V. V. (2012). Responsiveness to nicotine of neurons of the caudal nucleus of the solitary tract correlates with the neuronal projection target. Journal of Neurophysiology, 108(7), 1884-1894.
10. Clarner, T., Diederichs, F., Berger, K., Denecke, B., Gan, L., Van der Valk, P., Kipp, M. (2012). Myelin debris regulates inflammatory responses in an experimental demyelination animal model and multiple sclerosis lesions. Glia, 60(10), 1468-1480.
11. Girardet, C., Bonnet, M. S., Jdir, R., Sadoud, M., Thirion, S., Tardivel, C., Troadec, J. D. (2011). Central inflammation and sickness-like behavior induced by the food contaminant deoxynivalenol: A PGE2-independent mechanism.Toxicological Sciences, 124(1), 179-191.
12. Hruška-Plocháň, M., Juhas, S., Juhasova, J., Galik, J., Miyanohara, A., Marsala, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A27 Expression of the human mutant huntingtin in minipig striatum induced formation of EM48+ inclusions in the neuronal nuclei, cytoplasm and processes. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
13. Brooks, S., Jones, L., & Dunnett, S. B. (2010). A29 Frontostriatal pathology in the (C57BL/6J) YAC128 mouse uncovered by the operant delayed alternation task. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A10.
14. Yu, L., Metzger, S., Clemens, L. E., Ehrismann, J., Ott, T., Gu, X., Nguyen, H. P. (2010). A28 Accumulation and aggregation of human mutant huntingtin and neuron atrophy in BAC-HD transgenic rat. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
15. Baxa, M., Juhas, S., Pavlok, A., Vodicka, P., Juhasova, J., Hruška-Plocháň, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A26 Transgenic miniature pig as an animal model for Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A8-A9.
请关注玉研仪器的更多相关产品。
如对产品细节和价格感兴趣,敬请来电咨询!
保修期: 1年
是否可延长保修期: 否
现场技术咨询: 无
免费培训: 1次电话视频指导或者上门安装服务
免费仪器保养: 12个月
保内维修承诺: 免费维修,免费更换问题配件
报修承诺: 2小时电话相应解决客户的问题
stoelting脑立体定位仪Stoelting ?51700的工作原理介绍
脑立体定位仪Stoelting ?51700的使用方法?
stoeltingStoelting ?51700多少钱一台?
脑立体定位仪Stoelting ?51700可以检测什么?
脑立体定位仪Stoelting ?51700使用的注意事项?
stoeltingStoelting ?51700的说明书有吗?
stoelting脑立体定位仪Stoelting ?51700的操作规程有吗?
stoelting脑立体定位仪Stoelting ?51700报价含票含运吗?
stoeltingStoelting ?51700有现货吗?
最多添加5台
