Chemosphere :南华大学丨黑曲霉缓解铀毒促芋属植物生长的机制(钙信号,附NMT实验体系)
期刊:Chemosphere主题:黑曲霉缓解铀毒促芋属植物生长的机制(钙信号)标题:Aspergillus niger changes the chemical form of uranium to decrease its biotoxicity, restricts its movement in plant and increase the growth of Syngonium podophyllum影响因子:4.427监测指标:Ca2+流速检测部位:合果芋(白蝴蝶)根部成熟区、黑曲霉菌丝Ca2+流速流实验处理方法:3.0 mg·L-1铀处理5min/24h Ca2+流速流实验测试液成份:0.1mM CaCl2,pH 6.0作者:南华大学王永东、邹超英文摘要Aspergillus niger (A. niger) and Syngonium podophyllum (S. podophyllum) have been used for wastewater treatment, and have exhibited a promising application in recent years.To determine the effects of A. niger on uranium enrichment and uranium stress antagonism of S. podophyllum, the S. podophyllum-A. niger combined system was established, and hydroponic remediation experiments were carried out with uranium-containing wastewater.The results revealed that the bioaugmentation of A. niger could increase the biomass of S. podophyllum by 5–7%, reverse the process of U(VI) reduction induced by S. podophyllum, and increase the bioconcentration factor (BCF) and translocation factor (TF) of S. podophyllum to uranium by 35–41 and 0.01–0.06, respectively, thereby improving the reduction of uranium in wastewater.Moreover, A. niger could promote the cell wall immobilization and the subcellular compartmentalization of uranium in the root of S. podophyllum, reduce the phytotoxicity of uranium entering root cells, and inhibit the calcium efflux from root cells, thereby withdrawing the stress of uranium on S. podophyllum. 中文摘要黑曲霉(A.niger)和Syngonium podophyllum(S.potophyllum)已经用于废水处理,并且近年来已经展现出有希望的应用。为了确定黑曲霉对S. podophyllum,S。podophyllum-A的铀浓缩和铀胁迫拮抗作用。建立了尼日尔联合系统,并对含铀废水进行了水培修复试验。结果表明,黑曲霉的生物强化可以使S. podophyllum的生物量增加5-7%,逆转S. podophyllum诱导的U(VI)还原过程,提高生物富集因子(BCF)和转运因子。 (TF)S. podophyllum分别为35-41和0.01-0.06的铀,从而改善了废水中铀的还原。此外,黑曲霉可促进S. podophyllum根部细胞壁的固定化和铀的亚细胞区室化,降低铀进入根细胞的植物毒性,抑制根细胞的钙外流,从而消除铀的压力。 S. podophyllum。结果表明:在图中,黑曲霉的钙离子流速维持在约0pmol·cm-2·s-1,这表明在3.0mg·L-1铀胁迫下,Ca2+浓度梯度在黑曲霉细胞保持平衡,其正常生长不受抑制。加入3.0mg·L-1的铀溶液5min后(图A),对照组的白蝴蝶根细胞的钙离子外排约为300pmol·cm-2·s-1。这表明在铀胁迫下,白蝴蝶根细胞中Ca2+浓度梯度被破坏,其正常生长受到抑制。钙离子的外排也发生在治疗组中。然而,与对照组相比,外排率显着下降,达到42pmol·cm-2·s-1以下,且持续下降。然后,最终稳定在约20pmol·cm-2·s-1。这表明黑曲霉可以抑制白蝴蝶根细胞的钙外流,从而减弱白蝴蝶生长中铀的毒性。用3.0mg·L-1的铀胁迫处理24h后(图B),对照组根系的钙外排速率降至76 pmol·cm-2·s-1以下,并呈现持续下降趋势。保持在约30pmol·cm-2·s-1。这可能是因为白蝴蝶的自我调节以减弱铀的植物毒性。处理组根细胞的钙离子外排速率维持在20pmol·cm-2·s-1。这反映出黑曲霉抑制白蝴蝶根细胞钙外排的作用可持续很长时间。
厂商
2019.09.12
SCI REP-UK :山东农大丨磁处理对盐胁迫下杨树氮吸收与分布的影响(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:Scientific Reports主题:磁处理对盐胁迫下杨树氮吸收与分布的影响标题:The effects of magnetic treatment on nitrogen absorption and distribution in seedlings of Populus?×?euramericana ‘Neva’ under NaCl stress影响因子:4.011检测指标:NH4+、NO3-流速检测部位:杨树根部(伸长区距离根尖15mm)叶肉细胞NH4+、NO3-流速流实验处理方法:杨树幼苗,在0g/L NaCl+磁化(M0),0g/L NaCl+非磁化(NM0),4g/L NaCl+磁化(M4),4g/L NaCl+非磁化(NM4)中处理 NH4+、NO3-流速流实验测试液成份:NH4+: 0.1 mM NH4NO3, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.3 mM MES, pH 5.5NO3-: 0.1 mM NH4NO3, 1.0 mM KCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.3 mM MES, pH 5.5作者:山东农业大学林学院马风云、刘秀梅英文摘要A potted experiment with Populus?×?euramericana ‘Neva’ was carried out to assess whether there are positive effects of magnetic treatment of saline water (MTSW) on nitrogen metabolism under controlled conditions in a greenhouse.Growth properties, nitrogen contents, enzyme activities and metabolite concentrations were determined based on field experiments and laboratory analysis after a 30-day treatment.The results were as follows: (1) Biomass accumulation, root morphological properties and total nitrogen content were improved by MTSW. (2) Magnetization led to a greater increase in nitrate-nitrogen (NO3?-N) content in roots than in leaves, accompanied by greater NO3? efflux and activated nitrate reductase. (3) MTSW led to a higher ammonium-nitrogen (NH4+-N) content and greater uptake of net NH4+ in the leaves than that in the roots. (4) Magnetization stimulated glutamine synthase, glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamate synthase activities, whereas the concentrations of glutathione and oxidized glutathione were increased in leaves but decreased in roots, and the total glutathione content was increased.Overall, these results indicated some beneficial impacts of MTSW on nitrogen translocation under field conditions, especially for equilibrating the distribution of NO3?-N and NH4+-N. Moreover, these findings confirmed the potential of using low-quality water for agriculture. 中文摘要进行了欧洲杨(Populus×euramericana'Neva')的盆栽试验,以评估在温室中受控条件下盐水(MTSW)磁处理对氮代谢的积极影响。在30天处理后,基于田间实验和实验室分析确定生长特性,氮含量,酶活性和代谢物浓度。结果如下:(1)MTSW提高了生物量积累,根系形态特征和总氮含量。(2)磁化导致根中硝态氮(NO3-N)含量比叶片更大,伴随着更多的NO3-外排和活化的硝酸还原酶。(3)MTSW导致叶片中铵态氮(NH4+-N)含量较高,净NH4+吸收量高于根系。 (4)磁化刺激谷氨酰胺合成酶,谷氨酸脱氢酶和谷氨酸合酶活性,而谷胱甘肽和氧化型谷胱甘肽的浓度在叶片中增加但在根中减少,总谷胱甘肽含量增加。总体而言,这些结果表明MTSW对田间条件下氮转运的一些有益影响,特别是对于平衡NO3- N和NH4+-N的分布。此外,这些发现证实了使用劣质水进行农业的潜力。结果表明:使用NMT技术监测叶肉细胞中和距离根尖15mm的伸长区NO3-净流速,两者均显示外排。在测量的溶液中,叶肉细胞的NO3-外排从235.09增加到290.23 pmol cm-2 s-1(图A),暴露于NaCl溶液中,细根中从123.53到157.51 pmol cm-2 s-1显着增加(p NO3-流速增加,并且叶肉细胞中的外排量大于根伸长区域中的外排量。与非磁处理组中的流速相比,NO3-流速在暴露于磁场条件下的叶肉细胞中显示出显着更高的速率。吸收的为M4(290.23 pmol cm-2 s-1),吸收量为NM0(181.42 pmol cm-2 s-1)。然而,NO3-流速在根中表现出相反的模式,在伸长区域中的外排显着降低;NO3-外排为NM4(157.51 pmol cm-2 s-1),外排量为M0(38.05 pmol cm-2 s-1)结果表明:NH4+的净流速不同于NO3-;叶肉细胞为吸收趋势(图A),根部为外排趋势(图B)。叶中NH4+的吸收显示出较低的值。暴露于NaCl溶液(M4,NM4)的样品和暴露于对照处理(M0,NM0)的样品相比,M0显示出的流入量(-2518.85pmol cm-2 s-1),M4显示出第二大流出量(1164.15pmol cm-2 s-1),他们有着显着不同(p 此外,NM4中NH4+通量的值与NM0非常接近,并且它们彼此没有差异。相反,盐胁迫下新生长的细根中NH4+的外排高于对照中观察到的,并且M4显示出的外排量(186.83 pmolcm-2 s-1),与M0相比显着不同(p如在叶中观察到的,NM4中的NH4+外排与根中的NM0相似,并且数值没有差异。与盐水处理的效果不同,磁处理诱导NH4+的外排比非磁处理更大,并且M4和M0都显示出比NM4和NM0更高的值。这两个因素之间也存在显着的相互作用(p
厂商
2019.09.09
AQUAT TOXICOL :台湾师大联盟专家 | 银铜纳米颗粒对斑马鱼胚胎侧线毛细胞的毒性作用(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:Aquatic Toxicology主题:银铜纳米颗粒对斑马鱼胚胎侧线毛细胞的毒性作用标题:Toxic e?ects of silver and copper nanoparticles on lateral-line hair cells ofzebra?sh embryos影响因子:3.794检测指标:Ca2+流速检测部位:斑马鱼胚胎侧线毛细胞Ca2+流速流实验处理方法:斑马鱼胚胎在受精后0-96 h(hpf),0, 0.9, 9.3, 27.8 μM的AgNPs,和0,0.16,1.6,15.8μM的CuNP分别进行处理Ca2+流速流实验测试液成份:0.5mM NaCl, 0.2mM CaSO4, 0.2mM MgSO4, 0.16mM KH2PO4, and 0.16mM K2HPO4 (pH 7.0),300μM MOPS,0.1 mg/l tricaine作者:台湾师范大学林豊益、Hsiu-Ju Yen英文摘要The potential toxicity of nanoparticles (NPs) to the early stages of fish is still unclear. In this study, we investigated the toxic effects of silver (AgNPs) and copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) on lateral-line hair cells of zebrafish embryos. Zebrafish embryos were incubated in different concentrations of AgNPs and CuNPs at 0?96?h post-fertilization (hpf). Both AgNPs and CuNPs were found to cause toxic effects in zebrafish embryos in a dose-dependent manner. Values of the 96-h 50% lethal concentration (LC50) of AgNPs and CuNPs were 6.1?ppm (56.5?μM) and 2.61?ppm (41.1?μM), respectively.The number of FM1-43-labeled hair cells and the microstructure of hair bundles were significantly impaired by AgNPs [≥1?ppm (9.3?μM)] and CuNPs [≥0.01?ppm (0.16?μM)]. Ca2+ influxes at hair bundles of hair cells were measured with a scanning ion-selective microelectrode technique to evaluate the function of hair cells.AgNPs [≥0.1?ppm (0.9?μM)] and CuNPs [≥0.01?ppm (0.16?μM)] were both found to significantly reduce Ca2+ influxes. Similar toxic effects were also found in hatched embryos subjected to 4?h of exposure (96?100?hpf) to AgNPs and CuNPs. This study revealed that lateral-line hair cells of zebrafish are susceptible to AgNPs and CuNPs, and these contaminants in aquatic environments could pose a threat to fish survival. 中文摘要(谷歌机翻)纳米粒子(NPs)对鱼类早期的潜在毒性尚不清楚。在这项研究中,我们研究了银(AgNPs)和铜纳米颗粒(CuNPs)对斑马鱼胚胎侧线毛细胞的毒性作用。 在受精后0~96h(hpf),将斑马鱼胚胎在不同浓度的AgNPs和CuNPs中孵育。发现AgNPs和CuNPs都以剂量依赖的方式对斑马鱼胚胎产生毒性作用。 AgNPs和CuNPs的96小时50%致死浓度(LC50)的值分别为6.1ppm(56.5μM)和2.61ppm(41.1μM)。AgNPs [≥1ppm(9.3μM)]和CuNPs [≥0.01ppm(0.16μM)]显着损害了FM1-43标记的毛细胞数量和发束的微观结构。用扫描离子选择性微电极技术测量毛细胞发束处的Ca2+流入,以评估毛细胞的功能。发现AgNPs [≥0.1ppm(0.9μM)]和CuNPs [≥0.01ppm(0.16μM)]均可显着降低Ca2+流入量。在孵化4h(96?100hpf)的AgNPs和CuNPs孵化的胚胎中也发现了类似的毒性效应。这项研究表明,斑马鱼的侧线毛细胞对AgNPs和CuNPs敏感,这些污染物在水生环境中可能对鱼类的存活构成威胁。结果表明:在经历96小时AgNP或CuNP处理的胚胎中也发现了毛细胞的功能损伤。使用NM测量L1神经瘤的毛细胞的Ca2+流入量(图A),在0.1,1和3ppm(0.9,9.3和27.8μM)的AgNP组中,Ca2+流入量显着减少26%,46%和91%(图B)。在0.01 ppm(0.16μM)CuNP组中,Ca2+流入量减少了38%,而在0.1和1 ppm(1.6和15.8μM)CuNP组中,Ca2+流入几乎检测不到(图C)联盟专家暨本文作者介绍林豊益,博士,教授。台湾师范大学生命科学学院生理组,主要从事鱼类环境生理、水生环境毒理、机械性感觉生理、斑马鱼疾病模式与药物筛选研究。近期代表性成果Lin, L. Y., Y. H. Yeh, G.Y. Hung, C. H. Lin, P. P. Hwang, J. L. Horng. 2018. Role of calcium-sensingreceptor in mechanotransducer-channel-mediated Ca2+ influx in hair cells ofzebrafish larvae. Front. Physiol. 649:9.L. Horng, L. L. Yu, S. T. Liu, P. Y. Chen, L. Y. Lin. 2017. Potassiumregulation in medaka (Oryzias latipes) larvae acclimated to fresh water:passive uptake and active secretion by the skin cells. Sci. Rep. 7, 16215.Liu, S. T., J. L. Horng, P. Y. Chen, P. P. Hwang, L.Y. Lin. 2016. Saltsecretion is linked to acid-base regulation of ionocytes in seawater-acclimatedmedaka: new insights into the salt-secreting mechanism. Sci. Rep. 6, 31433.Horng, J. L., P. L. Chao, P. Y. Chen, T. H. Shih, L.Y. Lin. 2015.Aquaporin 1 is involved in acid secretion by ionocytes of zebrafish embryosthrough facilitating CO2 transport. Plos One 10(8):e0136440.Lin, Y. H., G. Y. Hung, L. C. Wu, S. W. Chen, L. Y. Lin. J. L. Horng.2015. Anion exchanger 1b in sereocilia is required for the functioning ofmechanotransducer channels in lateral-line hair cells of zebrafish. Plos One10(2): e0117041.洪君琳,博士,副教授。台北医学大学医学院医学科学研究所,斑马鱼模式核心服务实验室主任,主要从事以斑马鱼为模式研究毛细胞功能及药物影响的研究。近期代表性成果Lin LY, et al,. Role of Calcium-Sensing Receptor in Mechanotransducer Channel Mediated Ca2+ Influx in Hair Cells of Zebrafish Larvae . frontiers in physiology .2018 ;(9):649Hung Giun Yi, et al,. Incidence of immune thrombocytopenia in Taiwan: a nationwide population-based study . Transfusion .2018 ;(58):2712-2719Horng JL, et al,. Potassium Regulation in Medaka (Oryzias latipes) Larvae Acclimated to Fresh Water: Passive Uptake and Active Secretion by the Skin Cells. . Sci Rep. .2017 ;(7):16215Hung GY, et al,. Cancer in adolescents: Incidences and trends during 1995-2009 in Taiwan. . Cancer Lett .2016 ;(372):110-117Hung GY, et al,. Changing incidence patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma among age groups in Taiwan . J Hepatol .2015 ;(63):1390-1396
厂商
2019.09.04
PROTOPLASMA :河南农大丨高温干旱胁迫致ABA和ROS积累影响水稻萌发(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:PROTOPLASMA主题:高温和干旱胁迫导致水稻脱落酸和活性氧的积累,抑制种子萌发生长标题:High temperature and drought stress cause abscisic acid and reactive oxygen species accumulation and suppress seed germination growth in rice.影响因子:2.633检测指标:Ca2+、H2O2流速检测部位:水稻胚芽鞘出苗位点Ca2+、H2O2流速流实验处理方法:种子分别在高温38摄氏度,20%PEG-6000处理5天Ca2+、H2O2流速流实验测试液成份:0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.1 mM KCl,0.3mM MES, pH 6.0作者:河南农业大学赵全志、刘娟英文摘要Seed germination is one of the most important biological processes in the life cycle of plants, and temperature and water are the two most critical environmental factors that influence seed germination.In the present study, we investigated the roles of the plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in high temperature (HT) and drought-induced inhibition of rice seed germination. HT and drought stress caused ABA accumulation in seeds and inhibited seed germination and seedling establishment. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed that HT and drought stress induced the expression of OsNCED3, a key gene in ABA synthesis in rice seeds.In addition, ROS (O2•- and H2O2) and malondialdehyde contents were increased in germinating seeds under HT and drought stress. Moreover, we adopted the non-invasive micro-test technique to detect H2O2 and Ca2+ fluxes at the site of coleoptile emergence. HT and drought stress resulted in a H2O2 efflux, but only drought stress significantly induced Ca2+ influx. Antioxidant enzyme assays revealed that superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase, catalase (CAT), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) activity were reduced by HT and drought stress, consistent with the expression of OsCu/ZnSOD, OsCATc, and OsAPX2 during seed germination.Altogether, these results suggest that ABA and ROS accumulation under HT and drought conditions can inhibit rice seed germination and growth. 中文摘要种子萌发是植物生命周期中最重要的生物过程之一,温度和水是影响种子萌发的两个最关键的环境因素。在本研究中,我们研究了植物激素脱落酸(ABA)和活性氧(ROS)在高温(HT)和干旱诱导的水稻种子萌发抑制中的作用。 HT和干旱胁迫导致种子中ABA积累,抑制种子萌发和幼苗建立。定量实时聚合酶链反应分析表明,HT和干旱胁迫诱导水稻种子ABA合成中关键基因OsNCED3的表达。此外,在HT和干旱胁迫下,萌发种子中ROS(O2• - 和H2O2)和丙二醛含量增加。此外,我们采用非侵入性微测试技术检测胚芽鞘出现部位的H2O2和Ca2+通量。 HT和干旱胁迫导致H2O2流出,但只有干旱胁迫才能显着诱导Ca2 +流入。抗氧化酶测定表明,HT和干旱胁迫使超氧化物歧化酶(SOD),过氧化物酶,过氧化氢酶(CAT)和抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)活性降低,与种子萌发过程中OsCu / ZnSOD,OsCATc和OsAPX2的表达一致。总之,这些结果表明,在HT和干旱条件下ABA和ROS的积累可以抑制水稻种子的萌发和生长。 结果表明:干旱胁迫显着加剧了发芽种子中胚芽鞘出苗位点的Ca2+净吸收(图b),Ca2+净吸收量比对照种子高61.2%。同时,HT对Ca2+净流入没有显着影响,尽管与对照相比略有下降。 H2O2流速在对照组和治疗组之间的方向和大小上显示出显着差异(图c)。对照种子表现出H2O2的吸收。然而,在HT和干旱胁迫下,H2O2从种子外排到测试溶液中,分别达到1.20和0.44pmol cm-2 s -1。这些结果可能表明H2O2外排进一步意味着在HT和干旱胁迫下发芽种子中积累更多的H2O含量。
厂商
2019.09.02
NMT历史上的今天丨Int J Mol Sci 低温胁迫Ca信号文章发表
NMT历史上的今天2018年8月30日,东北农业大学王金刚、周爱民利用NMT在International Journal ofMolecular Sciences上发表了标题为PsCor413pm2, a Plasma Membrane-Localized, Cold-Regulated Protein from Phlox subulata, Confers Low Temperature Tolerance in Arabidopsis的研究成果。期刊:International Journal of Molecular Sciences主题:PsCor413pm2,来自福禄考的等离子膜定位,冷调节蛋白,在拟南芥中具有低温耐受性标题:PsCor413pm2, a Plasma Membrane-Localized, Cold-Regulated Protein from Phlox subulata, Confers Low Temperature Tolerance in Arabidopsis影响因子:3.687检测指标:Ca2+流速检测部位:拟南芥根部伸长区Ca2+流实验处理方法:7日龄拟南芥,低温(4摄氏度)瞬时胁迫Ca2+流实验测试液成份:0.1 mM KCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.1 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM NaCl, 0.3 mM MES, and 0.2 mM Na2SO4, pH 6作者:东北农业大学周爱民、王金刚英文摘要Low temperature stress adversely affects plant growth and development. Isolation and characterization of cold response genes from cold-tolerant plants help to understand the mechanism underlying low temperature tolerance.In this study, PsCor413pm2, a cold-regulated (COR) gene isolated from Phlox subulata, was transferred to Arabidopsis plants to investigate its function. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis revealed that PsCor413pm2 expression was induced by cold. Subcellular localization revealed that the PsCor413pm2-green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion protein localized to the plasma membrane in tobacco and Arabidopsis plants.Furthermore, overexpression of PsCor413pm2 in Arabidopsis plants enhanced tolerance to low temperature stress. Transgenic Arabidopsis roots had more influx of Ca2+ after a cold shock than wild-type plants, as shown using non-invasive micro-test technology (NMT). Moreover, the transcription abundance of five COR and two C-repeat (CRT) binding factor (CBF) genes in transgenic Arabidopsis plants was higher than that in the wild-type plants under cold stress.Taken together, our results suggest that overexpression of PsCor413pm2 enhances low temperature tolerance in Arabidopsis plants by affecting Ca2+ flux and the expression of stress-related COR and CBF genes. 中文摘要(谷歌机翻)低温胁迫对植物生长和发育产生不利影响。来自耐寒植物的冷响应基因的分离和表征有助于理解低温耐受性的机制。在这项研究中,从福禄考(Phlox subulata)分离的冷调节(COR)基因PsCor413pm2被转移到拟南芥植物中以研究其功能。实时定量PCR分析显示PsCor413pm2表达是由冷诱导的。亚细胞定位揭示了PsCor413pm2-绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)融合蛋白定位于烟草和拟南芥植物中的质膜。此外,拟南芥植物中PsCor413pm2的过表达增强了对低温胁迫的耐受性。如使用非侵入性微测试技术(NMT)所示,转基因拟南芥根在冷休克后比野生型植物具有更多的Ca2+流入。此外,转基因拟南芥植物中5个COR和2个C重复(CRT)结合因子(CBF)基因的转录丰度高于野生型植物在冷胁迫下的转录丰度。总之,我们的结果表明PsCor413pm2的过表达通过影响Ca2+通量和应激相关的COR和CBF基因的表达来增强拟南芥植物的低温耐受性。Effect of cold shock on net Ca2+ flux in the root elongation zone of transgenic Arabidopsis and wild type (WT) seedlings. (A) The root zones of Arabidopsis seedlings as measured using non-invasive micro-test technology (NMT). (B) Ca2+ kinetics recorded after a cold (4 °C) solution was added (at red arrow) to the chamber are shown. Prior to the cold shock, Ca2+ fluxes in roots were examined for approximately 5 min at room temperature (22 °C). (C) The mean Ca2+ flux rate in the root elongation zone of transgenic Arabidopsis plants (#10) overexpressing PsCor413pm2, as well as WT plants during the period of cold shock is shown. Error bars show the SE of the values from six replicates.
厂商
2019.08.30
PP :林金星IAA流成果丨NRT1.1磷酸化调节侧根发育的机制
期刊:Plant Physiology主题:NRT1.1磷酸化调节侧根发育的机制标题:Phosphorylation-mediated dynamics of nitrate transceptor NRT1.1 regulate auxin flux and nitrate signaling in lateral root growth影响因子:6.305检测指标:IAA流速检测部位:酵母细胞IAA流速流实验处理方法:转化酵母细胞在SD-URA培养基长到对数期,转至SG-URA培养基[SD-URA培养基中的dextrose替换为2%(m/v)galactose]上,培养24-48小时,诱导NRT1.1,T101A,T101D,mRuby表达。离心收集并制成SG-URA悬液。IAA流速流实验测试液成份:0.5 μM IAA, 2% (m/v) galactose, 0.3 mM MES, pH 5.8作者:北京林业大学单晓昳、林金星、张曦英文摘要The dual-affinity nitrate transceptor NITRATE TRANSPORTER 1.1 (NRT1.1) has two modes of transport and signaling, governed by threonine101 (T101) phosphorylation. NRT1.1 regulates lateral root (LR) development by modulating nitrate-dependent basipetal auxin export and nitrate-mediated signal transduction.Here, using the Arabidopsis thaliana NRT1.1T101D phosphomimetic and NRT1.1T101A non-phosphorylatable mutants, we found that the phosphorylation state of NRT1.1 plays a key role in NRT1.1 function during LR development. Single-particle tracking revealed that phosphorylation affected NRT1.1 spatiotemporal dynamics. The phosphomimetic NRT1.1T101D form showed fast lateral mobility and membrane partitioning that facilitated auxin flux under low-nitrate conditions.By contrast, non-phosphorylatable NRT1.1T101A showed low lateral mobility and oligomerized at the plasma membrane (PM), where it induced endocytosis via the clathrin-mediated endocytosis and microdomain-mediated endocytosis pathways under high-nitrate conditions. These behaviors promoted LR development by suppressing NRT1.1-controlled auxin transport on the PM and stimulating Ca2+-ARABIDOPSIS NITRATE REGULATED 1 (ANR1) signaling from the endosome. 中文摘要(谷歌机翻)双亲和硝酸盐转运蛋白NITRATE TRANSPORTER 1.1(NRT1.1)具有两种运输和信号传导模式,由苏氨酸101(T101)磷酸化控制。 NRT1.1通过调节硝酸盐依赖性碱基生长素输出和硝酸盐介导的信号转导来调节侧根(LR)发育。在这里,使用拟南芥NRT1.1T101D磷酸化和NRT1.1T101A非磷酸化突变体,我们发现NRT1.1的磷酸化状态在LR发育期间在NRT1.1功能中起关键作用。单粒子追踪显示磷酸化影响NRT1.1时空动态。磷酸化模拟NRT1.1T101D形式显示出快速的侧向移动性和膜分配,其促进了在低硝酸盐条件下的生长素通量。相比之下,不可磷酸化的NRT1.1T101A显示出低的侧向迁移率并且在质膜(PM)处寡聚化,其在高硝酸盐条件下通过网格蛋白介导的内吞作用和微区介导的胞吞作用途径诱导内吞作用。 这些行为通过抑制PM上的NRT1.1控制的生长素转运并刺激来自内体的Ca2 + -ARABIDOPSIS硝酸盐调节1(ANR1)信号传导来促进LR发展。 酵母细胞IAA流检测对照、NRT1.1、T101A、T101D转化酵母菌的IAA流(外排)结果。
厂商
2019.08.30
CELL RES :万建民院士丨钙离子启动免疫系统的分子机制(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:cell research主题:钙离子启动免疫系统的分子机制标题:A cyclic nucleotide-gated channel mediates cytoplasmic calcium elevation and disease resistance in rice影响因子:17.848检测指标:Ca2+流速检测部位:水稻叶肉细胞Ca2+流速流实验处理方法:水稻幼苗,10uM chitin或10uM flg22肽瞬时胁迫Ca2+流速流实验测试液成份:0.2mM CaCl2, 0.1mM NaCl, 0.1mM MgCl2 and 0.1mM KCl,pH 5.2作者:中国农科院万建民、王家昌英文摘要The transient elevation of cytoplasmic calcium is essential for pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-triggered immunity (PTI). However, the calcium channels responsible for this process have remained unknown.Here, we show that rice CDS1 (CELL DEATH and SUSCEPTIBLE to BLAST 1) encoding OsCNGC9, a cyclic nucleotide-gated channel protein, positively regulates the resistance to rice blast disease. We show that OsCNGC9 mediates PAMP-induced Ca2+ influx and that this event is critical for PAMPs-triggered ROS burst and induction of PTI-related defense gene expression. We further show that a PTI-related receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase OsRLCK185 physically interacts with and phosphorylates OsCNGC9 to activate its channel activity.Our results suggest a signaling cascade linking pattern recognition to calcium channel activation, which is required for initiation of PTI and disease resistance in rice. 中文摘要(谷歌机翻)细胞质钙的瞬时升高对病原体相关分子模式(PAMP)- 触发免疫(PTI)至关重要。然而,负责该过程的钙通道仍然未知。在这里,我们显示编码OsCNGC9(环核苷酸门控通道蛋白)的水稻CDS1(CELL DEATH和SUSCEPTIBLE to BLAST 1)正向调节对稻瘟病的抗性。我们显示OsCNGC9介导PAMP诱导的Ca2+内流,并且该事件对于PAMPs触发的ROS爆发和诱导PTI相关的防御基因表达是至关重要的。我们进一步显示PTI相关受体样细胞质激酶OsRLCK185与OsCNGC9物理相互作用并使其磷酸化以激活其通道活性。我们的研究结果表明信号级联将模式识别与钙通道激活联系起来,这是启动水稻PTI和抗病性所必需的。结果表明:响应于几丁质或flg22刺激,WT叶肉细胞比cds1叶肉细胞表现出强烈且快速的Ca2+流入(图3a,b和补充信息,图S6)。这些结果表明OsCNGC9可以介导水稻PTI中的Ca2+流入,并且这种能力在cds1突变体中受损。结果表明:响应几丁质刺激,Nipponbare叶肉细胞比Osrlck185/ 55双突变体叶肉细胞,表现出快速的Ca2+内流(图e)。此外,在几丁质处理Oscerk1敲除突变体后未观察到显着的Ca2+流入(图f)。这些结果共同表明OsRLCK185及其紧密同源物OsRLCK55参与水稻抗稻瘟病和PAMP诱导的Ca2+内流的调节。结果表明:在PAMPs刺激后,与Kitaake植物相比,OsCNGC9-OE转基因植物的叶肉细胞显示出更强的Ca2+流入。结合其他实验表明,OsCNGC9是水稻PTI的限速正调控因子。
厂商
2019.08.27
兰州丨第五届陆地生态系统青年学者会丨特邀中科院专家NMT报告+两天现场答疑
转自“中关村NMT联盟”2019年8月25日至8月27日,由青年生态学者联盟发起,兰州大学生命科学学院承办,兰州大学草地农业生态系统国家重点实验室和生态学创新研究院协助承办的“第五届陆地生态系统青年学者学术研讨会”在甘肃兰州举行。中关村NMT联盟受邀作技术报告。此次,联盟邀请了中科院西北生态环境资源研究所石玉兰博士作《ω-3脂肪酸去饱和酶在植物耐受非生物胁迫中的功能》的报告。会议现场技术人员全程为您答疑解惑。第五届陆地生态系统青年学者学术研讨会会场地点:甘肃省兰州市兰州大学盘旋路校区(天水南路校区)逸夫生物楼会议室305 报告时间:2019年8月27日 10:20报告题目:ω-3脂肪酸去饱和酶在植物耐受非生物胁迫中的功能报告人介绍 石玉兰 博士中科院西北生态环境资源研究院助理研究员,甘肃省寒区旱区逆境生理与生态重点实验室成员,中科院“西部之光”入选者。主要从事植物逆境分子生态学研究。 石玉兰博士利用非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology)发现了转CbFAD3基因烟草在逆境胁迫下Ca2+流的变化,为该基因激发的整合调控提供了有力证据。相关研究工作已经在Journalof Experimental Botany等期刊上发表,并获得一项专利发明。
厂商
2019.08.23
FOOD CHEM:南京农大丨钙参与盐胁迫下作物酚类积累的GABA信号转导(钙信号,附NMT实验体系)
稍后还会为大家带来一作视频讲解期刊:Food Chemistry主题:钙参与盐胁迫下作物酚类积累的GABA信号转导(钙信号)标题:Ca2+ involved in GABA signal transduction for phenolics accumulation in germinated hulless barley under NaCl stress影响因子:5.399检测指标:Ca2+流速检测部位:根尖细胞Ca2+流实验处理方法:三日龄的大麦幼苗,60mM NaCl、60mM NaCl + 0.5mM GABA、60mM NaCl + 0.1mM 3-MP分别处理四天和六天Ca2+流实验测试液成份:0.1mM KCl, 0.1mM CaCl2, 0.1mM MgCl2, 0.5mM NaCl, 0.3mM MES, 0.2mM Na2SO4,ph 6.0通讯作者:南京农业大学杨润强、马燕英文摘要In this study, in order to investigate the role of Ca2+ in GABA signal transduction involved in phenolics accumulation in barley seedlings under NaCl stress, the seedlings were treated with exogenous GABA and its synthesis inhibitor, 3-mercaplopropionic acid (3-MP), as well as Ca2+ channel blockers La3+, Ca2+ chelator EGTA, and Ca2+ release channel inhibitor 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB).The results showed that GABA significantly enhanced phenolics, calcium and calmodulin content. It also induced Ca2+ influx in barley root tips cells, and altered the distribution of Ca2+, making calcium precipitates more uniform and intensive. While, 3-MP treatment led to opposite changes, which suggested that GABA was essential for calcium content increase. In addition, accumulation of phenolics was inhibited by LaCl3, EGTA and 2-APB treatments, and this inhibition could be alleviated partly by exogenous GABA.Taken together, Ca2+ was involved in GABA signal transduction for phenolics accumulation in barley seedlings under NaCl stress. 中文摘要(谷歌机翻)在本研究中,为了研究Ca2+在NaCl胁迫下大麦幼苗中酚类物质积累的GABA信号转导中的作用,用外源GABA及其合成抑制剂3-巯基丙酸(3-MP)处理幼苗。以及Ca2+通道阻滞剂La3+,Ca2+螯合剂EGTA和Ca2+释放通道抑制剂2-氨基乙氧基二苯基硼酸盐(2-APB)。结果表明,GABA显着增强了酚类,钙和钙调蛋白的含量。它还诱导大麦根尖细胞内的Ca2+流入,并改变Ca2+的分布,使钙沉淀更均匀和密集。然而,3-MP处理导致相反的变化,这表明GABA对钙含量的增加至关重要。此外,LaCl3,EGTA和2-APB处理抑制了酚类物质的积累,这种抑制作用可以通过外源性GABA部分缓解。总之,Ca2+参与了NaCl胁迫下大麦幼苗中酚类物质积累的GABA信号转导。结果表明,对照大麦幼苗根尖Ca2+外排,与对照相比,NaCl处理引起的Ca2+由外排向吸收转变。GABA处理得到稳定的Ca2+吸收,其中处理6天的吸收明显高于处理4天吸收。GAD抑制剂(3-MP)在不同处理时期产生了不同的趋势,与单独使用NaCl处理相比,第4天Ca2+的外排速率显着增加,但第6天Ca2+流入量较弱。注:CK表示大麦用蒸馏水喷洒; N表示60mM NaCl处理; NG表示60mM NaCl + 0.5mM GABA处理; NM表示60mM NaCl + 0.1mM 3-MP处理。
厂商
2019.08.08
NMT历史上的今天丨Int J Mol Sci 氮营养、Physiol Plantarum 光合文章发表
NMT历史上的今天2018年8月6日,北京林业大学尹伟伦、孟森利用NMT技术在International journal of molecular sciences 上发表了标题为Distinct Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism of Two Contrasting Poplar Species in Response to Different N Supply Levels的文章。影响因子为3.687。2012年8月6日,中科院海洋所王广策、林阿朋利用NMT技术在Physiologia Plantarum上发表了标题为Simultaneous measurements of H+and O2 fluxes in Zostera marina and its physiological implications 的文章。影响因子为3.067.期刊:International journal of molecular sciences主题:两种杨树对不同氮素供应水平的碳氮代谢差异标题:Distinct Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism of Two Contrasting Poplar Species in Response to Different N Supply Levels影响因子:3.687检测指标:NH4+、NO3-、H+流速流速检测部位:杨树根部NH4+、NO3-、H+流实验处理方法:杨树在低中高(0.01,1或10 mM的NH4NO3)的氮浓度下处理4周NH4+、NO3-、H+流实验测试液成份:0.01mM/1mM/10mM NH4NO3,0.1mM KCl,0.1mM CaCl 2,pH 5.5通讯作者:北京林业大学尹伟伦、孟森英文摘要Poplars have evolved various strategies to optimize acclimation responses to environmental conditions. However, how poplars balance growth and nitrogen deficiency remains to be elucidated.In the present study, changes in root development, carbon and nitrogen physiology, and the transcript abundance of associated genes were investigated in slow-growing Populus simonii (Ps) and fast-growing Populus euramericana (Pe) saplings treated with low, medium, and high nitrogen supply. The slow-growing Ps showed a flourishing system, higher δ15N, accelerated C export, lower N uptake and assimilation, and less sensitive transcriptional regulation in response to low N supply.The slow-growing Ps also had greater resistance to N deficiency due to the transport of photosynthate to the roots and the stimulation of root development, which allows survival. To support its rapid metabolism and growth, compared with the slow-growing Ps, the fast-growing Pe showed greater root development, C/N uptake and assimilation capacity, and more responsive transcriptional regulation with greater N supply. These data suggest that poplars can differentially manage C/N metabolism and photosynthate allocation under different N supply conditions.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)杨树已经发展出各种策略来优化对环境条件的适应性反应。然而,杨树如何平衡生长和氮缺乏仍有待阐明。在本研究中,在慢生长的小叶杨(Pops simonii)(Ps)和快速生长的欧洲杨(Populus euramericana(Pe)幼树)中研究了根系发育,碳和氮生理学以及相关基因的转录本丰度的变化。高氮供应。缓慢生长的Ps显示出繁殖系统,更高的δ15N,加速的C输出,更低的N吸收和同化,以及响应于低N供应的较不敏感的转录调节。由于光合产物向根部的转运和根系发育的刺激,缓慢生长的Ps对N缺乏具有更大的抗性,这允许存活。为了支持其快速代谢和生长,与生长缓慢的Ps相比,快速生长的Pe显示出更大的根发育,C / N吸收和同化能力,以及具有更大N供应的更具响应性的转录调节。这些数据表明,杨树可以在不同的氮供应条件下差异化地控制C / N代谢和光合产物分配。Figure 4. Net NH4+ (A), NO3? (B) and H+ (C) fluxes of P. simonii (Ps) and Populus euramericana (Pe) under 0.01, 1 and 10 mM NH4NO3. Bars labelled with different letters indicate significant difference between the treatments. p-Values of the ANOVAs of species, N treatment, and their interaction are indicated. ** p .期刊:Physiologia Plantarum主题:同时测量H+和O2流速及其生理意义标题:Simultaneous measurements of H+ and O2 fluxes in Zostera marina and its physiological implications影响因子:3.067检测指标:H+、O2流速检测部位:大叶藻叶片H+、O2流实验处理方法:大叶藻叶片瞬时由暗至光(300μmolm-2s-1)处理H+、O2流实验测试液成份:天然海水(NSW)盐浓度30–32‰通讯作者:中科院海洋所王广策、林阿朋英文摘要Zostera marina (eelgrass) is an important ecological component of many shallow, temperate lagoons. Evidence suggests that Z. marina has a high bicarbonate utilization capability, which could be promoted by possible proton extrusion and the consequent formation of an ‘acid zone’ in the apoplastic space (unstirred layer) of its leaves.It has been found that 50?mM of the buffer Tris significantly inhibited the photosynthetic O2 evolution of Z. marina and it was proposed that this was because of Tris's ability to bond with protons outside the cell wall. To investigate if H+ played an important role in the photosynthetic carbon utilization of Z. marina, it is very important to simultaneously monitor the photosynthesis status and possible H+ fluxes. However, probably because of the lack of suitable techniques, this has never been attempted.In this study, experiments were undertaken on Z. marina by monitoring H+ and O2 fluxes and the relative electron transport rates during light–dark transition. During stable photosynthesis, in addition to an obvious O2 outflow, there was a significant net H+ influx connected to Z. marina photosynthesis. The inhibitory effects of both Tris and respiration inhibitors on apparent O2 evolution of Z. marina were confirmed. However, evidence did not support the proposed Tris inhibition mechanism.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)Zostera marina(eelgrass)是许多浅水温带泻湖的重要生态组成部分。有证据表明,Z。marina具有较高的碳酸氢盐利用能力,可以通过可能的质子挤出促进,并因此在其叶片的非质外体空间(未搅拌层)中形成“酸性区域”。已经发现50mM的缓冲液Tris显着抑制了Z.marina的光合作用O2进化,并且提出这是因为Tris能够与细胞壁外的质子结合。为了研究H +是否在Z. marina的光合碳利用中起重要作用,同时监测光合作用状态和可能的H +通量是非常重要的。然而,可能由于缺乏合适的技术,这从未尝试过。在这项研究中,通过监测H +和O2通量以及在明暗过渡期间的相对电子传输速率对Z.marina进行了实验。在稳定的光合作用期间,除了明显的O2流出外,还有显着的净H +流入与Z. marina光合作用相关。证实了Tris和呼吸抑制剂对Z. marina的表观O2进化的抑制作用。然而,证据不支持所提出的Tris抑制机制。Fig. 1. Typical transient changes in H+ ?ux near Zostera marina leaf segments in response to bright white light. The result of a single measurement is used in this ?gure as multiple results in one graph would result in large ?uctuations and mask the transient responses. The sample was dark adapted for >1 h. After 25 min of measurement, leaf segments were exposed to bright white light (300 μmol m?2 s?1)for 15 min. Measurements were made at intervals of 6.4 s. Each point on the graph represents average data over an interval of three measurements.
厂商
2019.08.07
周日烟台丨山东植物科学学术论坛丨特邀中科院专家NMT报告+全天现场答疑
2019年8月4日,由山东植物生理学会主办、鲁东大学协办的“2019山东省植物科学学术论坛”在山东烟台举行。中关村NMT联盟受邀作技术报告。 此次,联盟邀请了中科院烟台海岸带研究所李连祯副研究员作《非损伤微测技术及其在重金属生态毒理效应研究中的应用》的报告。会议现场8:00-17:00,联盟技术人员将为您答疑解惑。2019 山东省植物科学学术论坛会场地点:山东省烟台市大马路118号虹口大酒店 报告时间:2019年8月4日 11:10报告题目:非损伤微测技术及其在重金属生态毒理效应研究中的应用联系人:程老师,18515811370报告人介绍李连祯 副研究员中科院烟台海岸带研究所副研究员,中科院海岸带环境过程与生态修复重点实验室成员。主要从事盐碱地植物的重金属生态毒理效应研究。 李连祯副研究员在基于非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology)的重金属离子流活体检测传感器研发上取得过重要成果。其在国际上首次实现了植物根际微区Pb2+、Cu2+流的实时、动态、活体检测,目前相关研究工作已经在Plant and Soil和Environmental Pollution等期刊上发表,获得两项发明专利。
厂商
2019.08.02
JIPB:山东农大、枣庄学院丨TaPUB1提升小麦耐盐性机制(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:J Integr Plant Biol主题:TaPUB1提升小麦耐盐性机制标题:The involvement of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase TaPUB1 in salt stress tolerance影响因子:3.129检测指标:Na+、K+、H+流速检测部位:根部分生区Na+、K+、H+流实验处理方法:7日龄小麦,200mM NaCl瞬时胁迫处理/200uM NaC处理7天Na+、K+、H+流实验测试液成份:文献无推荐测试液成份:Na+/H+:0.5mM NaCl ,0.3mM MES,pH6.0K+/H+:0.1mM KCl ,0.3mM MES,pH6.0通讯作者:山东农业大学王玮、枣庄学院王文强英文摘要U‐box E3 ubiquitin ligases play important roles in the ubiquitin/26S proteasome machinery and in abiotic stress responses. TaPUB1‐overexpressing wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) were generated to evaluate its function in salt tolerance. These plants were more salt stress tolerance during seedling and flowering stages, whereas the TaPUB1‐RNAi‐mediated knock‐down transgenic wheat showed more salt stress sensitivity than the wild type (WT).TaPUB1 overexpression up‐regulated the expression of genes related to ion channels and increased the net root Na+ efflux, but decreased the net K+ efflux and H+ influx, thereby maintaining a low cytosolic Na+/K+ ratio, compared with the WT. However, RNAi‐mediated knock‐down plants showed the opposite response to salt stress. TaPUB1 could induce the expression of some genes that improved the antioxidant capacity of plants under salt stress. TaPUB1 also interacted with TaMP (Triticum aestivum.α‐mannosidase protein), a regulator playing an important role in salt response in yeast and in plants.Thus, low cytosolic Na+/K+ ratios and better antioxidant enzyme activities could be maintained in wheat with overexpression of TaPUB1 under salt stress. Therefore, we conclude that the U‐box E3 ubiquitin ligase TaPUB1 positively regulates salt stress tolerance in wheat. 中文摘要(谷歌机翻)U-box E3泛素连接酶在泛素/ 26S蛋白酶体机制和非生物应激反应中起重要作用。产生TaPUB1-过表达的小麦(Triticum aestivum L.)以评估其在耐盐性中的功能。这些植物在幼苗和开花期间具有更多的盐胁迫耐受性,而TaPUB1-RNAi介导的敲低转基因小麦显示出比野生型(WT)更多的盐胁迫敏感性。与WT相比,TaPUB1过表达上调与离子通道相关的基因的表达并增加净根Na +流出,但降低净K +流出和H +流入,从而维持低细胞溶质Na + / K +比率。然而,RNAi介导的敲低植物显示出对盐胁迫的相反反应。TaPUB1可诱导某些基因的表达,从而提高盐胁迫下植物的抗氧化能力。TaPUB1还与TaMP(Triticumaestivum.α-甘露糖苷酶蛋白)相互作用,TaMPUB是一种在酵母和植物中的盐响应中起重要作用的调节剂。因此,在盐胁迫下过表达TaPUB1的小麦中可以维持较低的细胞溶质Na + / K +比率和较好的抗氧化酶活性。因此,我们得出结论,U-box E3泛素连接酶TaPUB1正调节小麦的盐胁迫耐受性。Figure 6. The fluxes of Na+, K+ and H+ in response to 200 mM NaCl shock(A, C and E) The transient kinetics of Na+, K+ and H+ fluxes in roots of transgenic and WT plants before and after salt shock (Before salt shock, steady fluxes for 2 minutes). (B, D, and F) The mean net Na+, K+, and H+ fluxes in roots of transgenic and WT plants during a short period of salt shock. The data were presented as the mean ±SD of three independent experiments. Asterisks above each column indicate statistical differences to the WT plants (*P
厂商
2019.07.31
BMC Plant Biol:国科大丨BjHMA4R通过结合胞质Cd2+促植物耐镉(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:BMC Plant Biology主题:BjHMA4R通过结合胞质Cd2+促植物耐镉标题:A repeat region from the Brassica juncea HMA4 gene BjHMA4R is specifically involved in Cd2+ binding in the cytosol under low heavy metal concentrations影响因子:3.930检测指标: Cd2+流速检测部位:大肠杆菌细胞,酵母细胞Cd2+流实验处理方法:大肠杆菌,酵母细胞,30μMCdCl2胁迫Cd2+流实验测试液成份:文献无推荐测试液成份:0.03 mM CdCl2, 0.3 mM MES, 10 mM glucose, pH 6.0通讯作者:中国科学院大学生命科学学院柴团耀、梁爽英文摘要HMA4 transporters are involved in the transport and binding of divalent heavy metals (Cd, Zn, Pb [lead] and Co [cobalt]). In general, as efflux pumps, HMA4 transporters can increase the heavy metal tolerance of yeast and Escherichia coli. Additional research has shown that the C-terminus of HMA4 contains a heavy metal-binding domain and that heterologous expression of a portion of peptides from this C-terminal domain in yeast provides a high level of Cd tolerance and Cd hyperaccumulation.We cloned BjHMA4 from Brassica juncea, and quantitative real-time PCR analysis revealed that BjHMA4 was upregulated by Zn and Cd in the roots, stems and leaves. Overexpression of BjHMA4 dramatically affects Zn/Cd distribution in rice and wheat seedlings. Interestingly, BjHMA4 contains a repeat region named BjHMA4R within the C-terminal region; this repeat region is not far from the last transmembrane domain. We further characterized the detailed function of BjHMA4R via yeast and E. coli experiments. Notably, BjHMA4R greatly and specifically improved Cd tolerance, and BjHMA4R transformants both grew on solid media that contained 500?μM CdCl2 and presented improved Cd accumulation (approximately twice that of wild-type [WT] strains). Additionally, visualization via fluorescence microscopy indicated that BjHMA4R clearly localizes in the cytosol of yeast. Overall, these findings suggest that BjHMA4R specifically improves Cd tolerance and Cd accumulation in yeast by specifically binding Cd2+ in the cytosol under low heavy metal concentrations. Moreover, similar results in E. coli experiments corroborate this postulation.BjHMA4R can specifically bind Cd2+ in the cytosol, thereby substantially and specifically improving Cd tolerance and accumulation under low heavy metal concentrations.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)HMA4转运蛋白参与二价重金属(Cd,Zn,Pb [铅]和Co [钴])的转运和结合。通常,作为外排泵,HMA4转运蛋白可以增加酵母和大肠杆菌的重金属耐受性。另外的研究表明,HMA4的C末端含有重金属结合结构域,并且酵母中来自该C末端结构域的一部分肽的异源表达提供了高水平的Cd耐受性和Cd超积累。我们从芥菜中克隆了BjHMA4,定量实时PCR分析表明BjHMA4在根,茎和叶中被Zn和Cd上调。BjHMA4的过表达显着影响水稻和小麦幼苗的Zn / Cd分布。有趣的是,BjHMA4在C末端区域内含有一个名为BjHMA4R的重复区域;这个重复区域距离最。后一个跨膜结构域不远。我们通过酵母和大肠杆菌实验进一步表征了BjHMA4R的详细功能。值得注意的是,BjHMA4R极大地且特异性地改善了Cd耐受性,并且BjHMA4R转化体均在含有500μMCdCl2的固体培养基上生长并且呈现出改善的Cd积累(大约是野生型[WT]菌株的两倍)。另外,通过荧光显微镜观察表明BjHMA4R清楚地定位于酵母的胞质溶胶中。总体而言,这些发现表明BjHMA4R通过在低重金属浓度下特异性结合胞质溶胶中的Cd2+,特异性地改善了酵母中的Cd耐受性和Cd积累。此外,大肠杆菌实验中的类似结果证实了这种假设。BjHMA4R可特异性结合胞质溶胶中的Cd2+,从而在低重金属浓度下基本上和特异性地改善Cd耐受性和积累。Fig. 12. Detection of BjHMA4R activity by Cd2+ flux measurements. Transgenic BjHMA4R and control cells were exposed to 30?μM Cd2+ and measurements were taken for 600?s, using a vibrating probe, after the flux became ready. a yeast cells, b E. coli cells. The data are expressed as the mean?±?SE of three replicates; * and ** indicate significant levels at 5 and 1% (evaluated by Student’s t test), respectively
厂商
2019.07.26
EEB:西北农林科技大学丨MsPIP2; 2提升转基因拟南芥耐盐性(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:Environmental and Experimental Botany(EEB)主题:MsPIP2; 2提升转基因拟南芥耐盐性标题:MsPIP2; 2, a novel aquaporin gene from Medicago sativa, confers salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis影响因子:3.712检测指标: Na+、K+流速检测部位:伸长区,距离根尖550-600μmNa+、K+流实验处理方法:7日龄拟南芥,150mM NaCl处理24小时Na+、K+流实验测试液成份:文献无推荐测试液成份:Na+:0.5mMNaCl ,0.3mM MES,pH6.0K+:0.1mMKCl ,0.3mM MES,pH6.0通讯作者:西北农林科技大学杨培志英文摘要Aquaporins (AQPs) are channel proteins that facilitate water transport across cell membranes and play important roles in many biological processes. However, most AQP functions are still poorly understood in the plant kingdom. Here, MsPIP2;2 was isolated and identified from alfalfa (Medicago sativa). MsPIP2;2 was localized to the plasma membrane, and its expression was induced by salt and abscisic acid (ABA) treatment. Overexpression of MsPIP2;2 in Arabidopsis increased the seed germination rate, seedling root length, survival rate, proline content and antioxidant defence activity and decreased cell membrane damage and reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation compared to those in WT under salt stress.The salt tolerance of MsPIP2;2 was affected by Ca2+ and pH in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. MsPIP2;2-overexpressing plants maintained a better K+/Na+ ratio and higher Ca2+ content under salt stress. The higher K+/Na+ maintenance in transgenic plants was mainly achieved by increasing Na+ efflux and K+ retention in roots via regulating the expression of the related ion channel genes. Stress-responsive genes, including P5CS1, RD29A, DREB2 and KIN2, were upregulated in transgenic plants under salt stress.These results suggest that MsPIP2;2 confers salt tolerance by regulating antioxidant defence system-mediated ROS scavenging, K/Na ion homeostasis and stress-responsive gene expression in plants.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)水通道蛋白(AQPs)是促进水跨细胞膜转运的通道蛋白,在许多生物过程中起重要作用。然而,大多数AQP功能在植物界仍然知之甚少。在此,从紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa)中分离并鉴定了MsPIP2; 2。MsPIP2; 2定位于质膜,其表达由盐和脱落酸(ABA)处理诱导。与盐胁迫下WT相比,拟南芥中MsPIP2; 2的过量表达提高了种子萌发率,幼苗根长,存活率,脯氨酸含量和抗氧化防御活性,降低了细胞膜损伤和活性氧(ROS)积累。MsPIP2; 2的耐盐性受转基因拟南芥植物中Ca2+和pH的影响。MsPIP2; 2过表达植物在盐胁迫下保持更好的K+ / Na+比率和更高的Ca2+含量。转基因植物中较高的K+ / Na+维持率主要通过调节相关离子通道基因的表达来增加根中的Na+流出和K+保留来实现。应激反应基因,包括P5CS1,RD29A,DREB2和KIN2,在盐胁迫下在转基因植物中上调。这些结果表明,MsPIP2; 2通过调节抗氧化防御系统介导的ROS清除,K / Na离子稳态和植物中的应激反应基因表达来赋予耐盐性。Fig. 9. The net ?ux of Na+ and K+ at the root tip elongation zones of 7-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings. (A) The net Na+ ?ux under normal conditions (0 mM NaCl). (B) The net Na+ ?ux after 150 mM NaCl stress. (C) The mean Na+ ?ux. (D) The net K+ ?ux under normal conditions (0 mM NaCl). (E) The net K+ ?ux after 150 mM NaCl stress. (F) The mean K+ ?ux. Bars represent the mean ± SE (n = 3). Asterisks and double asterisks above the bars indicate signi?cant di?erences between the transgenic lines and the WT under the same growth conditions: *, P 文章链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0098847219300036
厂商
2019.07.23
台州学院丨活体植物逆境功能基因研究应用培训
转自“中关村NMT联盟”2019年7月24日,由中关村NMT联盟组织的非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)活体植物逆境功能基因研究应用培训,将在台州学院举行。台州学院主讲内容非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)是研究功能基因的一种技术,通过检测活体植物根茎叶与内/外环境间Ca/Cd/Na/K/N/O2...交换量的实时变化,揭示:丙酮酸载体调控植物耐镉的机理AHA2促初生根伸长适应低磷的信号机制CBL激酶提升植物抗盐耐寒能力的生理证据COLD1等位基因和特异SNP赋予水稻的耐寒新机制......时间:2019年7月24日 星期三地点:台州学院生命科学学院570会议室卓仁英 研究员中国林科院亚热带林业研究所研究员,从事林木抗逆育种研究,利用非损伤微测技术在Environ Exp Bot、Sci Rep、Front Plant Sci上发表多篇植物重金属、耐盐研究成果。阮丽 副研究员中国农业科学院茶叶研究所副研究员,从事茶树抗性遗传育种研究,利用非损伤微测技术在Front Plant Sci、Sci Rep-UK上发表多篇植物氮营养研究成果。刘蕴琦 NMT高级顾问中关村非损伤微测技术产业联盟秘书长,《NMT 101问》、《NMT论文集》副主编。协助中国农大武维华院士、中科院植物所种康院士等课题组,设计了Cell、Plant Cell等研究成果中的非损伤离子流实验部分。近5年,直接协助国内学者发表的SCI文章共67篇,累计影响因子308.64。巨肖宇 中关村NMT联盟认证高级售后工程师美国扬格(旭月北京)售后部负责人,拥有5年以上非损伤微测系统操作应用、售后经验,累计售后服务经验3000+小时。Cu、Pb流速传感器商业化研发团队骨干成员。非损伤微测技术目前可检测的指标有:H+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、Mg2+、Cd2+、Cu2+、Pb2+、NH4+、NO3-、O2、H2O2、IAA。
厂商
2019.07.22
Plant Sci:湖南农大丨氮素利用效率与镉耐受性的平衡-附NMT实验体系
期刊:plant science主题:氮素利用效率与镉耐受性的平衡标题:Balance between nitrogen use efficiency and cadmium tolerance in Brassica napus and Arabidopsis thaliana影响因子:3.785检测指标: H+、Cd2+、NO3-流速检测部位:根部液泡H+、Cd2+、NO3-流实验处理方法:4周龄拟南芥,20 μM CdCl2处理3天21日龄油菜,100 μM CdCl2处理7天H+、Cd2+、NO3-流实验测试液成份:文献无推荐测试液成份:拟南芥根部液泡:0.002mM CdCl2,0.1 mM KNO3 , 600 mM mannitol, 0.05mM MES, pH 7.2油菜根部液泡:0.01mM CdCl2,0.1 mM KNO3 , 600 mM mannitol, 0.05mM MES, pH 7.2作者:湖南农业大学张振华、廖琼英文摘要The transmembrane transport of NO3? andCd2+ into plant cell vacuoles relies on the energy from their tonoplast protonpumps, V-ATPase and V-PPase. If the activity of these pumps is reduced, itresults in less NO3? and Cd2+ being transported into the vacuoles, whichcontributes to better nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and lower Cd2+ tolerance inplants.The physiological mechanisms that regulatethe balance between NUE and Cd2+ tolerance remain unknown. In our study, twoBrassica napus genotypes with differential NUEs, xiangyou 15 and 814, andAtclca-2 mutant and AtCAX4 over-expression line (AtCAX4-OE) of Arabidopsisthaliana, were used to investigate Cd2+ stress responses.We found that the Brassica napus genotype,with higher NUE, was more sensitive to Cd2+ stress. The AtCAX4-OE mutant, withhigher Cd2+ vacuolar sequestration capacity (VSC), limited NO3? sequestrationinto root vacuoles and promoted NUE. Atclca-2 mutants, with decreased NO3? VSC,enhanced Cd2+ sequestration into root vacuoles and conferred greater Cd2+tolerance than the WT. This may be due to the competition between Cd2+ andNO3?in the vacuoles for the energy provided by V-ATPase and V-PPase. Regulating thebalance between Cd2+ and NO3? vacuolar accumulation by inhibiting the activityof CLCa transporter and increasing the activity of CAX4 transporter willsimultaneously enhance both the NUE and Cd2+ tolerance of Brassica napus,essential for improving its Cd2+ phytoremediation potential.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)NO3-和Cd2+跨膜转运到植物细胞液泡中依赖于其液泡膜质子泵,V-ATP酶和V-PPase的能量。如果这些泵的活性降低,则导致较少的NO3-和Cd2+被输送到液泡中,这有助于提高植物的氮利用效率(NUE)和降低Cd2+耐受性。调节NUE和Cd2+耐受性之间平衡的生理机制尚不清楚。在我们的研究中,使用具有差异NUE,香优15和814的两种甘蓝型油菜基因型和拟南芥的Atclca-2突变体和AtCAX4过表达系(AtCAX4-OE)来研究Cd2+应激反应。我们发现甘蓝型油菜基因型具有较高的NUE,对Cd2+胁迫更敏感。具有较高Cd2+液泡隔离能力(VSC)的AtCAX4-OE突变体限制NO3-隔离到根空泡中并促进NUE。具有降低的NO3-VSC的Atclca-2突变体增强了Cd2+隔离到根空泡中并且赋予比WT更大的Cd2+耐受性。这可能是由于V-ATP酶和V-PPase提供的能量在液泡中Cd2+和NO3-之间的竞争。通过抑制CLCa转运蛋白的活性和增加CAX4转运蛋白的活性来调节Cd2+和NO3-液泡积累之间的平衡将同时增强甘蓝型油菜的NUE和Cd2+耐受性,这对于改善其Cd2+植物修复潜力是必需的。Fig. 2. The Arabidopsis thaliana vha-a2, vha-a3, and avp1 mutants were more sensitive to Cd2+ stress than the wild-type Col-0. (A) The phenotype and (B) the chlorophyll loss, in relation to the controls, of Col-0 and the vha-a2, vha-a3, and avp1 mutants grown for 4 weeks and then exposed to 20 μM CdCl2 for 3 days. Mean rates of (C) H+ ?uxes and (D) Cd2+ ?uxes during the ?rst 160 s of measurements within the root vacuoles.
厂商
2019.07.18
东农学者视频课:NMT捕捉实时低温胁迫钙流信号丨第10期中关村NMT联盟活体研究大家谈
点击查看视频提示:内容纯干货!不看可惜,不要错过!观看视频即可参与实验内容制定,期待您的关注。【栏目介绍】 本节目为中关村旭月非损伤微测技术产业联盟指定的一个网络视频窗口,在这里您不仅可以获取到新的NMT科研信息,同时还可以掌握联盟的新动态,希望您多多关注。不仅如此,如果您观看了节目后,将节目建议或想看内容详细发送到公众号中,可参与实验内容制定。中关村NMT联盟统筹安排全国NMT测试服务,如需开展NMT相关实验,请联系联盟。联盟介绍《中关村旭月非损伤微测技术产业联盟》(简称“中关村NMT联盟”),创始于2015年9月,是由北京中关村示范区内国家高新技术企业和知名高等院校科研院所自愿联合发起成立的,北京市社会团体登记管理机关核准登记并监督运行的非营利性社会团体。 中关村NMT联盟的宗旨是配合国家科技创新发展战略,应对日益激烈的国际科技竞争,发挥制度优势、先发优势、区域优势,打造具有世界影响力的,先进NMT技术产业集群。联盟将利用过去十几年来,中国在NMT技术创新、产品研发、科研应用及产业化方面所积累的优势,搭建中国NMT 技术的公共服务平台,一方面通过拓展NMT科研应用领域,进一步确立中国在NMT领域的地位,努力扩大在全球的影响力;另一方面通过鼓励产学研合作,加速NMT的科技成果转化和产业化进程。 联盟主要发起单位为:旭月(北京)科技有限公司,其他有代表性的会员单位有:北京医院、中科院烟台海岸带研究所、中国农业大学、北京农业信息技术研究中心、山东显微科学仪器有限公司、北京师范大学等单位会员36家,其中高校15家;科研院所13家;企业8家。
厂商
2019.07.17
JXB:华中农大丨南瓜和黄瓜耐盐性差异的分子机制(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:Journal of Experimental Botany主题:南瓜和黄瓜耐盐性差异的分子机制标题:Tissue-specific respiratory burst oxidase homologue -dependent H2O2 signaling to the plasma membrane H+-ATPase confers potassium uptake and salinity tolerance in Cucurbitaceae影响因子:5.360检测指标: K+流速检测部位:距离根尖1mmK+流实验处理方法:5日龄黄瓜幼苗,75mM NaCl处理24小时K+流实验测试液成分:0.5mM KCl,0.1mM CaCl2,pH 5.7作者:华中农业大学别之龙、黄远英文摘要Potassium (K+) is a critical determinant ofsalinity tolerance, and H2O2 has been recognised as an important signalingmolecule that mediates many physiological responses. However, the details onhow H2O2 signaling regulates potassium uptake in the root under salt stressremain elusive. In this study, the salt sensitive cucumber and salt tolerantpumpkin which belong to the same family cucurbitaceae were used to answer theabove question.Weshow that higher salt tolerance in pumpkin was related to its superior abilityfor K+ uptake and higher H2O2 accumulation in the root apex. Transcriptomeanalysis showed that salinity induced 5886 (3005 up and 2811 down) and 4679(3965 up and 714 down) differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in cucumber andpumpkin, respectively. DEGs encoding NADPH oxidase (RBOHD), 14-3-3 protein(GRF12), plasma membrane H+- ATPase (AHA1) and potassium transporter (HAK5)showed higher expression in pumpkin than cucumber under salinity stress.Treatment with a NADPH oxidase inhibitor diphenylene iodonium resulted in alower RBOHD, GRF12, AHA1 and HAK5 expression, reduced plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity, and smaller K+ uptake, resulting in a loss of salinitytolerance trait in pumpkin. The opposite results were obtained when the plantswere pre-treated with exogenous H2O2. Knocking out of RBOHD in pumpkin byCRISPR-Cas9 editing of coding sequences resulted in lower root apex H2O2 and K+content and GRF12, AHA1 and HAK5 expression, ultimately resulting in asalt-sensitive phenotype. However, ectopic expression of pumpkin RBOHD inArabidopsis led to the opposite effect.Taken together, this study shows that RBOHD-dependent H2O2 signaling in the root apex is important for the pumpkin salttolerance and suggests a novel mechanism that confers this trait, namelyRBOHD-mediated transcriptional and post-translational activation of plasmamembrane H+-ATPase operating upstream of HAK5 K+ uptake transporters.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)钾(K+)是耐盐性的关键决定因素,H2O2已被认为是介导许多生理反应的重要信号分子。然而,关于H2O2信号如何在盐胁迫下调节根中钾吸收的细节仍然难以捉摸。在这项研究中,使用属于同一科葫芦科的盐敏感黄瓜和耐盐南瓜来回答上述问题。 我们表明,南瓜中较高的耐盐性与其对根尖的K +吸收能力和较高的H2O2积累有关。转录组分析显示盐度分别诱导黄瓜和南瓜中5886(3005上和下2811下)和4679(3965上和下714)差异表达基因(DEG)。在盐胁迫下,编码NADPH氧化酶(RBOHD),14-3-3蛋白(GRF12),质膜H+- ATP酶(AHA1)和钾转运蛋白(HAK5)的DEGs在南瓜中的表达高于黄瓜。用NADPH氧化酶抑制剂二亚苯基碘处理导致较低的RBOHD,GRF12,AHA1和HAK5表达,降低的质膜H+- ATP酶活性和较小的K+摄取,导致南瓜中盐度耐受性状的丧失。当用外源H2O2预处理植物时获得相反的结果。通过编码序列的CRISPR-Cas9编辑敲除南瓜中的RBOHD导致较低的根尖H2O2和K+含量以及GRF12,AHA1和HAK5表达,最终导致盐敏感表型。然而,拟南芥中南瓜RBOHD的异位表达导致相反的效果。 总之,本研究表明,根尖中依赖RBOHD的H2O2信号传导对南瓜耐盐性具有重要意义,并提示了一种赋予这种特性的新机制,即RBOHD介导的质膜H+-ATPase的转录和翻译后激活。 HAK5 K+摄取转运蛋白的上游。Figure 7. Relative expression of GRF (14-3-3 protein), AHA (plasma membrane H+-ATPase) and HAK5 (high affinity K+ transporter) in the root apex of cucumber (A, C, E) and pumpkin (B, D, F) exposed to 75 mM NaCl for 24 h. (G) to (J): plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity and net K+ flux measured after 24 h of exposure to 75 mM NaCl stress from the root apex pre-treated for 1 h in solutions containing specific chemicals (DPI, an NADPH oxidase inhibitor, H2O2) in cucumber (G, I) and pumpkin (H, J). Values are the mean ± SE (n=4). Different letters indicate significant difference (P
厂商
2019.07.15
Rice:浙江理工丨通气促进水稻根部Cd滞留
期刊:Rice 主题:通气促进水稻根部Cd滞留标题:Aeration Increases Cadmium (Cd) Retention by Enhancing Iron Plaque Formation and Regulating Pectin Synthesis in the Roots of Rice (Oryza sativa) Seedlings影响因子:3.513检测指标:O2、Cd2+流速检测部位:距离根尖200微米、500微米,木质部O2、Cd2+流实验处理方法:3周龄水稻幼苗,50uM CdCl2及充空气(每小时30分钟)处理14天O2、Cd2+流实验测试液成份:0.01mM CdCl2,0.1mM KCl, 0.1mM CaCl2 and 0.3mM MES , pH 5.4作者:浙江理工大学熊杰、李沪波英文摘要Aeration and water management increasingrhizosphere oxygen amount significantly promote rice (Oryza sativa) growth andyield, but the effect of root aeration on cadmium (Cd) toxicity andaccumulation in rice seedlings under hydroponic culture remains unclear. Results showed that aeration promoted riceseedling growth and alleviated Cd toxicity. Transverse section discovered thatCd accelerated root mature and senescence while aeration delayed the mature andsenescence of roots. Non-invasive Micro-test Technology (NMT) showed thataeration increased net O2 and Cd2+ influxes on the surface of roots whiledecreased net Cd2+ influx in xylem. Perls blue staining showed that aerationand Cd treatments increased iron plaque formation on the surface of roots.Results of metal concentration analysis showed that besides increasing Cdretention in iron plaque, aeration also increasing Cd retention in the cellwall of rice roots. Cell wall component analysis showed that aeration not onlyincreased pectin content but also decreased pectin methylesterification degree(PMD) by increasing pectin methylesterase (PME) activity.Conclusions All of these results indicate that aerationnot only delays root mature and senescence but also increases Cd retention in rootsby enhancing iron plaque formation and regulating pectin synthesis in the rootsof rice seedlings.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)曝气和水分管理增加根际氧气量显着促进了水稻(Oryza sativa)的生长和产量,但根系曝气对水培过程中水稻幼苗镉(Cd)毒性和积累的影响仍不清楚。结果表明,曝气促进了水稻幼苗生长,减轻了Cd的毒性。横切面发现Cd加速根成熟和衰老,而通气延迟了根的成熟和衰老。非损伤微测技术(NMT)显示,通气增加了根表面的净O2和Cd2+流入,同时降低了木质部中的净Cd2+流入。Perls蓝染色显示通气和Cd处理增加了根表面的铁斑块形成。金属浓度分析结果表明,除了增加铁斑块中Cd的保留外,还可以增加水稻根细胞壁中Cd的保留。细胞壁成分分析表明,通气不仅可以增加果胶含量,还可以通过增加果胶甲酯酶(PME)活性来降低果胶甲酯化程度(PMD)。所有这些结果表明,通气不仅可以延缓根系成熟和衰老,还可以通过增强水稻幼苗根系中铁斑块形成和调节果胶合成来增加根中Cd的保留。Fig. 3 Effects of aeration or/and 50 μM CdCl2 treatments on net O2 and Cd2+ fluxes in the roots of rice seedling. a Time-course of Net O2 flux on the surface of root at 500?μm from root apex (elongation zone); b Time-course of Net Cd2+ flux on the surface of root at 500?μm from apex (elongation zone); c Statistical results of steady-state net O2 and Cd2+ fluxes on the surface of root at 500?μm from apex (elongation zone); d Time-course of Net O2 flux on the surface of root at 200?μm from root apex (meristematic zone); e Time-course of Net Cd2+ flux on the surface of root at 200?μm from apex (meristematic zone); f Statistical results of steady-state net O2 and Cd2+ fluxes on the surface of root at 200?μm from apex (meristematic zone); g Time-course of Net O2 flux in the xylem of root at 500?μm from root apex (elongation zone); h Time-course of Net Cd2+ flux in the xylem of root at 500?μm from apex (elongation zone); i Statistical results of steady-state net O2 and Cd2+ fluxes in the xylem of root at 500?μm from apex (elongation zone). The 3-week-old rice seedlings under hydroponic culture were aerated with air pump (30?min per hour) in the absence or presence of 50 μM CdCl2 for 14 d. The values are means ± SE (n?=?100). Different letters on bar indicate significant differences at P
厂商
2019.07.10
Chemosphere:福建农林丨生物炭中的盐分影响水稻对土壤镉的吸收累积
期刊:Chemosphere主题:生物炭中的盐分影响水稻对土壤镉的吸收累积标题:Chlorine weaken the immobilization of Cd in soil-rice systems by biochar影响因子:5.108检测指标:Cd2+流速Cd2+流实验处理方法:5天的水稻幼苗,6mM NaCl瞬时处理Cd2+流实验测试液成份:0.1mM KCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.01mM CdCl2, pH= 5.8作者:福建农林大学王果、李荭荭英文摘要Rice (Oryza sativa L.) was cultivated in a Cd-contaminated soilswith rice straw biochar (BC) and water-washed rice straw biochar (W-BC) wereapplied to investigate the underlying mechanisms and possible reasons for biochar'sweakening effects on the immobilization of Cd in soil-rice system. The results indicated that W-BC reduced the Cd concentration inpore water as well as in the roots and shoots of rice by 26.24%, 53.23% and62.47% respectively. On the contrary, there was an increase in Cd contents by50.27% in pore water, 2.32% in the roots, and 12.80% in the shoots of riceunder BC treatment. Furthermore, Cd content in rice shoot was significantly andpositively correlated with Cl? addition to the soil (P This phenomenon could be attributed to several combined effects:(1) the increase of Cl? in the soil decreased the soil pH, enhanced thedissolved organic carbon in soil pore water and increased the complexes of Cd2+and Cl?, resulting in the release of Cd from solid phase into solution phase,(2) the chloride in the soil increased the uptake of CdCl+ instead of Cd2+ bythe roots, thereby causing an increase of Cd in rice tissues. These resultsdemonstrate for the first time that biochar with high chloride content couldweaken its immobilization effects on soil Cd and even enhance Cd uptake byrice.中文摘要水稻(Oryza sativa L.)在镉污染土壤中种植稻草生物炭(BC)和水洗稻草生物炭(W-BC),以研究生物炭对生物炭减弱作用的潜在机制和可能的原因。土壤 - 水稻体系中Cd的固定化。结果表明,W-BC使孔隙水以及水稻根冠中Cd含量分别降低26.24%,53.23%和62.47%。相反,在BC处理下,孔隙水中Cd含量增加50.27%,根中Cd含量增加2.32%,水稻枝条中Cd含量增加12.80%。水稻中Cd含量与土壤中Cl-的含量呈显着正相关(P 这种现象可归因于以下几种综合效应:(1)土壤中Cl-的增加降低了土壤pH值,增加了土壤孔隙水中溶解的有机碳,增加了Cd2+和Cl-的络合物,导致了土壤的释放。 Cd从固相进入溶液相,(2)土壤中的氯化物增加了CdCl+对Cd2+的吸收,从而导致水稻组织中Cd的增加。这些结果首次表明,氯含量高的生物炭可以减弱其对土壤Cd的固定化效应,甚至可以提高水稻对Cd的吸收。氯添加对水稻根表镉离子流的影响
厂商
2019.07.09
New Phytol:中农丨PTP3ases调节棉花耐盐新机制(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:New Phytologist主题:PTP3ases调节棉花耐盐新机制标题:Phosphatase GhDsPTP3a interacts with annexin protein GhANN8b to reversely regulate salt tolerance in cotton (Gossypium spp.)影响因子:7.299检测指标:Ca2+、Na+、K+流速Ca2+流实验方法:7d拟南芥,100 mM NaCl瞬时盐胁迫处理,检测距根尖1000微米的点Ca2+流实验测试液成份:0.1 mM KCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.1 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM NaCl, 0.3 mM MES, 0.2 mM Na2SO4, 0.1 % sucrose, pH 6.0K+、Na+流实验方法:· 5d拟南芥,0、100 mM NaCl处理24h,检测距根尖200微米的点· 6d拟南芥,50 uM LaCl3+100 mM NaCl处理24h,检测距根尖200微米的点K+、Na+流实验测试液成份:0.5 mM KCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.1 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM NaCl,0.3 mM MES, pH 6.0作者:中国农业大学李芳军、穆春、得州农工大学单丽波英文摘要Salinity is among the major factorslimiting crop production worldwide. Despite having moderate salt‐tolerance,cotton (Gossypium spp.) suffers severe yield losses to salinity stresses,largely due to being grown on saline‐alkali and drylands.To identify genetic determinants conferringsalinity tolerance in cotton, we deployed a functional genomic screen using acotton cDNA library in a virus‐induced gene silencing (VIGS) vector. We have revealed thatsilencing of GhDsPTP3a, which encodes a protein phosphatase, increases cottontolerance to salt stress.Yeast two‐hybrid screensindicated that GhDsPTP3a interacts with GhANN8b, an annexin protein, whichplays a positive role in regulating cotton response to salinity stress. Saltstress induces GhANN8b phosphorylation, which is subsequently dephosphorylated byGhDsPTP3a. Ectopic expression of GhDsPTP3a and GhANN8b oppositely regulatesplant salt tolerance and calcium influx. In addition, we have revealed thatsilencing of GhDsPTP3a or GhANN8b exerts opposing roles in regulating GhSOS1transcript levels, and ectopic expression of GhANN8b elevates Na+ efflux inArabidopsis under salinity stress.Our study demonstrates that a cottonphosphatase GhDsPTP3a and an annexin protein GhANN8b interact and reverselymodulate Ca2+ and Na+ fluxes in cotton salinity responses.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)盐度是限制全球作物生产的主要因素之一。尽管具有适度的耐盐性,但棉花(Gossypium spp。)遭受盐度胁迫的严重产量损失,主要是由于在盐碱地和干旱地区生长。为了鉴定赋予棉花耐盐性的遗传决定因子,我们在病毒诱导的基因沉默(VIGS)载体中使用棉花cDNA文库部署了功能基因组筛选。我们已经发现,编码蛋白磷酸酶的GhDsPTP3a的沉默会增加棉花对盐胁迫的耐受性。酵母双杂交筛选表明GhDsPTP3a与膜联蛋白GhANN8b相互作用,后者在调节棉花对盐胁迫的反应中起着积极作用。盐胁迫诱导GhANN8b磷酸化,其随后被GhDsPTP3a去磷酸化。GhDsPTP3a和GhANN8b的异位表达相反地调节植物盐耐受性和钙内流。此外,我们发现GhDsPTP3a或GhANN8b的沉默在调节GhSOS1转录水平中发挥相反的作用,并且GhANN8b的异位表达在盐胁迫下提高拟南芥中的Na+流出。我们的研究表明棉花磷酸酶GhDsPTP3a和膜联蛋白GhANN8b在棉花盐度反应中相互作用并反向调节Ca2+和Na+通量。(b) Ectopic-expression of GhDsPTP3a or GhANN8b alters extracellular Na+ efflux upon salt stress in live roots via NMT assay. (c) LaCl3 blocks GhANN8b-induced Na+ efflux upon salt stress in live roots via NMT assay.
厂商
2019.07.05
内蒙古大学生环院丨活体植物功能基因研究应用培训
2019年7月10日,由中关村NMT联盟组织的非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)活体植物功能基因研究应用培训,将在内蒙古大学举行。主讲内容非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)是研究功能基因的一种技术,通过检测活体植物根茎叶与内/外环境间Ca/Cd/Na/K/N/O2...交换量的实时变化,揭示:CBL激酶提升植物抗盐耐寒能力的胜利证据AHA2促初生根伸长适应低磷的信号机干旱胁迫如何促进植物的氮吸收......时间:2019年7月10日 星期三 9:00~11:30 地点:内蒙古大学北校区生物楼226会议室刘蕴琦 NMT高级顾问中关村非损伤微测技术产业联盟秘书长,《NMT 101问》、《NMT论文集》副主编。协助中国农大武维华院士、中科院植物所种康院士等课题组,设计了Cell、Plant Cell等研究成果中的非损伤离子流实验部分。近5年,直接协助国内学者发表的SCI文章共67篇,累计影响因子308.64。非损伤微测技术目前可检测的指标有:H+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、Mg2+、Cd2+、Cu2+、Pb2+、NH4+、NO3-、O2、H2O2、IAA。
厂商
2019.07.03
PP:南农资环院丨MADS-box转录因子促低氮时根系吸硝(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:Plant Physiology主题:MADS-box转录因子促低氮时根系吸硝标题:A Transcription Factor, OsMADS57, Regulates Long-distance Nitrate Transport and Root Elongation影响因子:6.305检测指标:NO3-流速NO3-流实验处理方法:0.2 mM NO3-培养2周后,N饥饿处理3天NO3-流实验测试液成份:0.2 mM KNO3, 0.2 mM CaCl2, 0.1 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM MgSO4, 0.3 mM MES, pH 6.0作者:南京农业大学张亚丽、黄双杰英文摘要Root nitrate uptake adjusts tothe plant’s nitrogen demand for growth. Here, we report that OsMADS57, aMADS-box transcription factor, modulates nitrate translocation from rice (Oryzasativa) roots to shoots under low-nitrate conditions. OsMADS57 is abundantlyexpressed in xylem parenchyma cells of root stele and is induced by nitrate.Compared with wild-type rice plants supplied with 0.2 mM nitrate, osmads57mutants had 31% less xylem loading of nitrate, while overexpression lines had2-fold higher levels. Shoot-root 15N content ratios were 40% lower in themutants and 76% higher in the overexpression lines. Rapid NO3? root influxexperiments showed that mutation of OsMADS57 did not affect root nitrateuptake. Reverse transcriptionquantitative PCR analysis of OsNRT2 nitrate transporter genes showed that after5 min in 0.2 mM nitrate, only OsNRT2.3a (a vascular-specific high-affinitynitrate transporter) had reduced (by two-thirds) expression levels. At 60 minof nitrate treatment, lower expression levels were also observed for threeadditional NRT2 genes (OsNRT2.1/2.2/2.4). Conversely, in the overexpressionlines, four NRT2 genes had much higher expression profiles at all time pointstested. As previously reported, OsNRT2.3afunctions in nitrate translocation, indicating the possible interaction betweenOsMADS57 and OsNRT2.3a. Yeast one-hybrid and transient expression assaysdemonstrated that OsMADS57 binds to the CArG motif (CATTTTATAG) within theOsNRT2.3a promoter. Moreover, seminal root elongation was inhibited in osmads57mutants, which may be associated with higher auxin levels in and auxin polartransport to root tips of mutant plants. Taken together, these results suggestthat OsMADS57 has a role in regulating nitrate translocation from root to shootvia OsNRT2.3a.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)根硝酸盐吸收可调节植物对氮的生长需求。在这里,我们报告OsMADS57,一种MADS-box转录因子,在低硝酸盐条件下调节从水稻(Oryza sativa)根到芽的硝酸盐易位。OsMADS57在根茎的木质部薄壁细胞中大量表达,并由硝酸盐诱导。与提供0.2mM硝酸盐的野生型水稻植物相比,osmads57突变体的硝酸盐木质部负载量减少31%,而过表达株系的水平增加2倍。芽根15N含量比率在突变体中低40%,在过表达株系中高76%。快速NO3-根流入实验表明,OsMADS57的突变不影响硝酸根的吸收。OsNRT2硝酸盐转运蛋白基因的逆转录定量PCR分析显示,在0.2mM硝酸盐中5分钟后,仅OsNRT2.3a(血管特异性高亲和力硝酸盐转运蛋白)表达水平降低(三分之二)。在硝酸盐处理60分钟时,还观察到另外三种NRT2基因(OsNRT2.1 / 2.2 / 2.4)的较低表达水平。相反,在过表达株系中,四个NRT2基因在所有测试时间点具有高得多的表达谱。如先前报道,OsNRT2.3a在硝酸盐易位中起作用,表明OsMADS57和OsNRT2.3a之间可能的相互作用。酵母单杂交和瞬时表达测定证明OsMADS57与OsNRT2.3a启动子内的CArG基序(CATTTTATAG)结合。此外,osmads57突变体中的精液根伸长受到抑制,这可能与突变植物根尖中的生长素水平和生长素极性转运相关。总之,这些结果表明OsMADS57通过OsNRT2.3a调节从根到茎的硝酸盐易位。Figure 3. NO3- acquisition in wild-type (WT), mutants (m1-2) and overexpression lines (Ox1-3). Rice seedlings were grown in IRRI nutrient solution containing 0.2 mM NO3- for 2 weeks and then deprived of N for 3 d. The plants were transferred to IRRI nutrient solution containing 0.2 mM 15 NO3- for 5 min. (B) Net NO3- fluxes in the seminal root meristem of rice plants supplied with 0.2 mM NO3- for 11 min. (C) Mean rate of NO3- fluxes during the entire 11 min. Data are means of five replications ± SE. *, P 文章链接:http://www.plantphysiol.org/content/180/2/882
厂商
2019.07.02
非损伤微测技术用户风险提醒 | 中关村NMT联盟发布
通 知鉴于中美贸易争端已经蔓延至科技领域,并有持久趋势。中关村NMT联盟提醒中国大陆的大专院校、科研院所等企事业单位,在采购非损伤微测技术设备时,充分考虑风险,建议优先选择已在中国大陆设立研发机构和售后服务机构,且产品已经完成国产化的国外厂商,或者拥有自主知识产权的国内厂商所生产的设备。避免因为零部件的断供,导致科学研究、产品研发受阻等重大损失。
厂商
2019.06.28
BMC Plant Biol:中国农科院丨油菜素内酯促黄瓜根系铵硝吸收机制
转自“中关村NMT联盟”期刊:BMC Plant Biology主题:油菜素内酯促黄瓜根系铵硝吸收机制标题:24-Epibrassinolide promotes NO3- andNH4+ ion flux rate and NRT1 gene expression in cucumber under suboptimal root zone temperature影响因子:3.930检测指标:NO3-、NH4+流速检测部位:根毛区作者:中国农业科学院蔬菜与花卉研究所Ali Anwar、李衍素、于贤昌英文摘要Suboptimal root zone temperature (RZT) causes a remarkable reduction in growth of horticultural crops during winter cultivation under greenhouse production. However, limited information is available on the effects of suboptimal RZT on nitrogen (N) metabolism in cucumber seedlings. The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of 24-Epibrassinolide (EBR) on nitrate and ammonium flux rate, N metabolism, and transcript levels of NRT1 family genes under suboptimal RZT in cucumber seedlings.Suboptimal RZT (LT) negatively affected on cucumber growth and proportionately decreased EBR contents, bleeding rate, root activity, enzyme activities of nitrate reductase (NR), nitrite reductase (NiR), glutamine synthetase (GS), and glutamate synthase (GOGAT), nitrate (NO3?) influx rate, ammonium (NH4+) efflux rate, and transcript levels of nitrate transporter (NRT1) encoding genes. However, exogenous EBR reduced the harmful effects of suboptimal RZT and increased endogenous EBR contents, bleeding rate, root activity, enzyme activities of NR, NiR, GS, and GOGAT, NH4+ and NO3? flux rates and contents, and N accumulation. EBR-treated seedlings also upregulated the transcript levels of nitrate transporters CsNRT1.1, CsNRT1.2A, CsNRT1.2B, CsNRT1.2C, CsNRT1.3, CsNRT1.4A, CsNRT1.5B, CsNRT1.5C, CsNRT1.9, and CsNRT1.10, and downregulated CsNRT1.5A and CsNRT1.8. LT treatment upregulated the expression level of CsNRT1.5A, while exogenous BZR application downregulated the expression level of NRT1 genes.These results indicate that exogenous application of EBR alleviated the harmful effects of suboptimal RZT through changes in N metabolism, NH4+ and NO3? flux rates, and NRT1 gene expression, leading to improved cucumber seedlings growth. Our study provides the first evidence of the role of EBR in the response to suboptimal RZT in cucumber, and can be used to improve vegetable production.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)次优根区温度(RZT)导致在温室生产期间冬季栽培期间园艺作物的生长显着减少。然而,关于次优RZT对黄瓜幼苗中氮(N)代谢的影响的信息有限。本研究的目的是研究24-表油菜素内酯(EBR)对黄瓜幼苗次优RZT下NRT1家族基因的**盐和铵通量,N代谢和转录水平的影响。次优RZT(LT)对黄瓜生长有负面影响,并且比例降低EBR含量,出血率,根系活力,**还原酶(NR),亚**还原酶(NiR),谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)和谷氨酸合成酶(GOGAT)的酶活性,**盐(NO3-)流入速率,铵(NH4 +)流出速率和**盐转运蛋白(NRT1)编码基因的转录水平。然而,外源EBR降低了次优RZT的有害作用,增加了内源EBR含量,出血率,根系活力,NR,NiR,GS和GOGAT的酶活性,NH4 +和NO3-通量率和含量以及N积累。 EBR处理的幼苗也上调了**盐转运蛋白CsNRT1.1,CsNRT1.2A,CsNRT1.2B,CsNRT1.2C,CsNRT1.3,CsNRT1.4A,CsNRT1.5B,CsNRT1.5C,CsNRT1.9和CsNRT1的转录水平。 .10,并下调CsNRT1.5A和CsNRT1.8。 LT处理上调CsNRT1.5A的表达水平,而外源BZR应用下调NRT1基因的表达水平。这些结果表明,外源施用EBR通过改变N代谢,NH4 +和NO3-通量率以及NRT1基因表达减轻了次优RZT的有害作用,从而改善了黄瓜幼苗的生长。我们的研究首次证明了EBR在黄瓜中对次优RZT的反应中的作用,并可用于改善蔬菜生产。Fig. 4 Effects of suboptimal RZT and EBR on NO3- (A; scatter NO3- flux rate, B; average NO3- flux rate) flux rate in roots of cucumber seedlings under suboptimal RZT treatment. Flux rate was recorded for 10?min in roots seven days after treatment. Each point is the mean of nine individual seedlings and bars indicate standard deviations. Treatments with the same letters are not significantly different by the least significant difference (LSD) test at P?=?0.05
厂商
2019.06.27
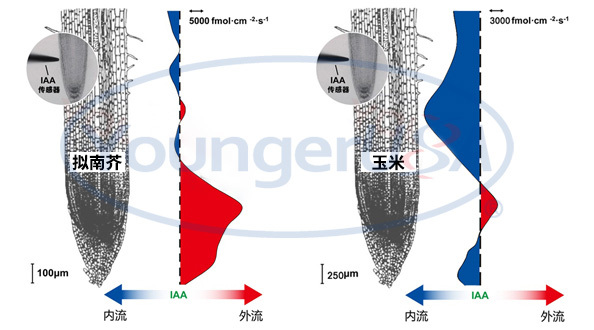
前沿技术观摩邀请:兰大草科院丨活体根系IAA流检测演示
受兰州大学生科院邀请,中关村NMT联盟委托美国扬格/旭月工程师,于2019年6月27日在兰州大学草地农业科技学院,公开演示IAA、H2O2、O2三种分子的流速检测实验。美国扬格公司不仅提供自动化的现代NMT设备,而且与旭月公司等中国合作伙伴共同开发了商业化的IAA、Cu2+、Pb2+等流速传感器。演示地点:兰州大学天水南路校区逸夫生物二楼424房间演示时间:2019年06月27日 上午10:00-12:00,下午2:30-6:00左图:拟南芥根,右图:玉米根1、分子流的科研空白与先机目前,IAA、H2O2、O2这三种分子的流速数据,鲜见于文献成果,存在巨大的科研空白。尤其是IAA,美国扬格/旭月IAA流速传感器是世界上一款商业化的、可检测活体植物IAA生长素的流速传感器。点击查看视频2、IAA传感器研发团队骨干现场答疑解惑现场工程师的NMT实验经验均在1500小时以上,其中,IAA传感器研发团队骨干将到场,答疑解惑。
厂商
2019.06.27
EEB:广东农科院丨提升铵营养有助于抑制水稻镉积累?
期刊:Environmental and Experimental Botany(EEB)主题:提升铵营养有助于抑制水稻镉积累标题:Increasing ammonium nutrition as a strategy for inhibition of cadmium uptake and xylem transport in rice (Oryza sativa L.) exposed to cadmium stress影响因子:3.666检测指标:Cd2+流速检测部位:距根尖700μm作者:广东农科院王旭、王富华、吴志超英文摘要Nitrogen (N) speciation could in?uence the e?ciency of Cd accumulation by plants grown in Cd-contaminated areas. However, limited information has been reported on how the application of N speciation to rice a?ects the Cd accumulation. Here, we investigated the physiological and genetic mechanisms involved in Cd uptake by roots, xylem translocation and subsequent Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) a?ected by di?erent NO3?/ NH4+ ratios under low-and-high Cd stress. Results showed that both N speciation and Cd stress a?ected plant growth, with high NH4+-N ratios treatments having higher tissue biomass, and high Cd treatment reducing tissue biomass. The Cd concentrations in shoots and roots were reduced with the increasing NH4+-N ratios (except for the full NO3?-N treatment), but did not a?ect the Cd translocation factor (TF). The total Cd accumulation of the whole plant were also reduced with the high NH4+-N ratios (NO3?/NH4+, 1:2 and 0:1) on the low Cd treatment due to the decline both in the Cd accumulation of shoots and roots. A Non-invasive Micro-test Technology (NMT) showed that the net Cd2+ in?uxes at the root hair zone were inhibited with the increasing NH4+-N ratios in absence or pretreatment with di?erent NO3?/NH4+ ratios. Additionally, the Cd concentrations in xylem sap were also displayed a decline trend with the increasing NH4+-N ratios under two dose Cd treatments.Furthermore, the gene expression related to Cd uptake (OsIRT1 and OsNRAPM5) and transport (OsHMA2) in roots showed the familiar tendencies with those of Cd uptake and transport at the physiological level treated with di?erent NO3?/NH4+ ratios under two dose Cd treatments.It is concluded that increasing ammonium nutrition contributes to the inhibition of Cd uptake, xylem transport and subsequent accumulation in rice.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)氮(N)物种形成可能影响镉污染地区生长的植物对Cd积累的影响。然而,关于如何将N形态应用于水稻以影响Cd积累的报道有限。在这里,我们研究了在低和高Cd胁迫下由不同NO3-/NH4+比例影响的水稻(Oryza sativa L.)根系吸收Cd,木质部易位和随后Cd积累所涉及的生理和遗传机制。 结果表明,N形态和Cd胁迫均影响植物生长,高NH4+-N比处理具有较高的组织生物量,高Cd处理降低组织生物量。随着NH4+-N比值的增加,芽和根中的Cd浓度降低(除了完全的NO3-N处理),但不影响Cd转运因子(TF)。由于芽和根中Cd积累量的下降,低Cd处理的NH4+-N比值(NO3-/NH4+,1:2和0:1)也降低了整株植物的总Cd积累量。 非损伤微测技术(NMT)显示,在不存在或预处理不同的NO3-/NH4+比率时,NH4+ -N比率增加时,根毛区的流体中的净Cd2+受到抑制。此外,在两剂Cd处理下,随着NH4+-N比值的增加,木质部汁液中的Cd浓度也呈下降趋势。此外,与Cd吸收(OsIRT1和OsNRAPM5)和转运(OsHMA2)相关的基因表达显示了在两种剂量Cd处理下用不同的NO3-/NH4+比率处理的生理水平的Cd摄取和转运的熟悉趋势。 结论是,增加铵营养有助于抑制水稻的Cd吸收,木质部运输和随后的积累。Fig. 1. E?ect of di?erent NO3-/NH4+ ratios (A and B) or pretreatment with di?erent ratios of NO3-/NH4+ (C and D) on net Cd2+ in?ux at root hair zone by Non-invasive Micro-test Technology(NMT). Each point represents the mean values of Cd2+ in?ux of six roots from six individual plants during the time of 6th-10th minutes. Bars with di?erent letters mean signi?cantly statistical di?erences followed by one-way ANOVA analysis (LSD test, P
厂商
2019.06.26
JIPB:种康院士 | OsCIPK7改变激酶活性调控水稻耐寒机制(钙信号)
种康院士2015年Cell文章Ca2+流实验介绍期刊:Journalof integrative plant biology(JIPB)主题:OsCIPK7改变激酶活性调控水稻耐寒机制(钙信号)标题:OsCIPK7point-mutation leads to conformation and kinase-activity change for sensingcold response影响因子:3.129检测指标:Ca2+作者:中科院植物所 种康英文摘要Calcineurin B-like interacting proteinkinases (CIPKs) play important roles via environmental stress. However, less isknown how to sense the stress in molecular structure conformation level. Here, an OsCIPK7 mutant via TILLINGprocedure with a point mutation in the kinase domain showed increased chillingtolerance, which could be potentially used in the molecular breeding. We found that this point mutation ofOsCIPK7 led to a conformational change in the activation loop of the kinasedomain, subsequently with an increase of protein kinase activity, thusconferred an increased tolerance to chilling stress.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)钙调神经磷酸酶B样相互作用蛋白激酶(CIPKs)通过环境压力发挥重要作用。 然而,人们对如何感知分子结构构象水平的应力知之甚少。在此,通过TILLING程序在激酶结构域中具有点突变的OsCIPK7突变体显示出增加的耐寒性,其可能潜在地用于分子育种。我们发现OsCIPK7的这一点突变导致激酶结构域的激活环的构象变化,随后随着蛋白激酶活性的增加,因此赋予对低温胁迫的增加的耐受性。NMT measurements show dynamic change of extracellular Ca2+ in?ux in live roots of various genetic backgrounds responding to cold shock. The blue background represents the duration of cold treatment. The number was the cold treatment time on the abscissa. The minus numbers were the time before the treatment.NMT瞬时处理实验流速数据分析思路文章链接:http://www.jipb.net/EN/10.1111/jipb.12800即日起,中关村NMT联盟统筹安排全国NMT测试服务,如需开展NMT相关实验,请联系联盟.
厂商
2019.06.25
中关村NMT联盟测试类基金获批简报(2019.05.20-06.20)
转自“中关村NMT联盟”为贯彻国家创新战略和应对国际科技竞争的新形势,新挑战,联盟受国家委托,向中国非损伤微测技术使用者提供设备、测试、耗材、研发、技术报告等各类基金资助,延续并扩大中国学者在NMT技术创新、产品研发、科研应用及产业化方面所积累的优势,确保中国科研人员及时抢占以非损伤微测技术为代表的,活体基因功能研究领域制高点。NMT创新实验资助项目项目针对计划利用NMT从事具有创新性实验的科研工作者。创新性既包含广义的科研创新,也包含在非损伤微测技术领域的创新,尤其是非损伤微测技术的空白领域,例如新方向、新方法、新样品等。NMT实验方案优化资助项目项目针对利用NMT从事科学研究过程中,流速结果与现有研究成果、理论不相符,并且计划利用NMT进一步探究原因的科研工作者。 2019.05.20-06.20简报姓名:田连福单位:湖南师范大学研究方向:植物分子与遗传基金类型:NMT实验方案优化基金获批额度:5000-10000元 姓名:何佳丽单位:沈阳农业大学研究方向:果树栽培与生理生态基金类型:NMT创新实验基金获批额度:1000-5000元姓名:孙毓单位:东北师范大学研究方向:污废水处理-微生物溶藻基金类型:NMT创新实验基金获批额度:500-1000元姓名:段文学单位:山东省农业科学院作物研究所研究方向:甘薯栽培生理基金类型:NMT创新实验基金获批额度:1000-5000元
厂商
2019.06.21