NMT历史上的今天丨Plant Soil 植物Pb、Cu重金属胁迫 文章发表
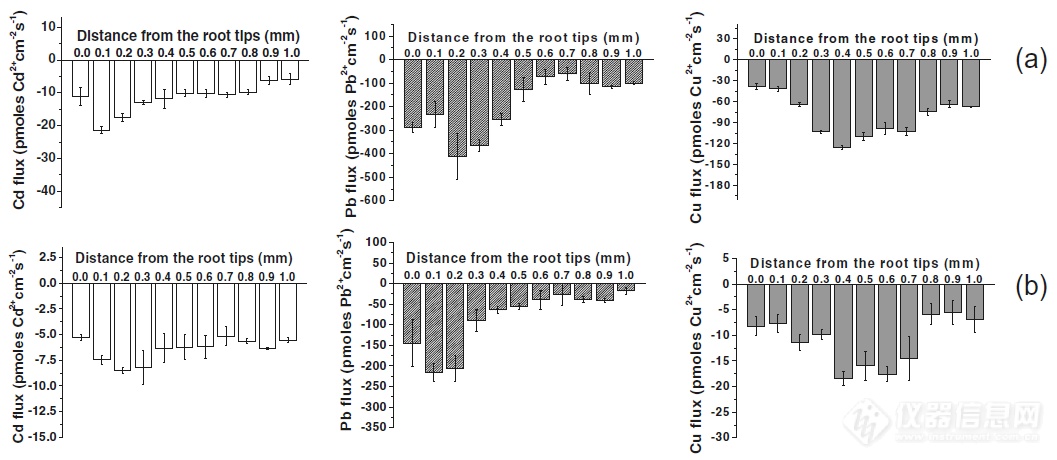
NMT是基因功能的活体检测技术,已被31位诺贝尔奖得主所在单位,及北大、清华、中科院使用。NMT历史上的今天2016年11月13日,中科院烟台海岸带研究所骆永明、李连祯利用NMT在Plant and Soil 上发表了标题为Determining the fluxes of ions (Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+) at the root surface of wetland plants using the scanning ion-selective electrode technique的研究成果。期刊:Plant and Soil主题:使用扫描离子选择电极技术确定湿地植物根表面离子(Pb2+,Cu2+和Cd2+)的通量标题:Determining the fluxes of ions (Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+) at the root surface of wetland plants using the scanning ion-selective electrode technique影响因子:3.410检测指标:Pb2+、Cu2+、Cd2+流速作者:中科院烟台海岸带研究所骆永明、李连祯英文摘要Measuring specific ion fluxes from different regions of the root under practical physiological conditions is crucial for understanding metal uptake mechanisms by plants.We developed and tested a neutral carrier-based liquid-membrane Pb2+ and Cu2+ ion selective microelectrode (ISME) to investigate ion-transport processes along the roots of three common wetland plant species.The Pb2+ and Cu2+ ISME exhibited a Nernstian response with Pb2+ and Cu2+ activities as low as 1.0 nM and 1.0 μM in deionized water and simulated soil solution, respectively. Phragmites australis had a region of Cu2+ release for approximately the first 200 μm, while it exhibited Pb2+ and Cd2+ outward net flux up to the first 500 μm. Although in older sections of the root of Phragmites australis there were areas of influx of Cu2+, Pb2+ and Cd2+, the overall influx was much smaller than that of Typha latifolia or Canna indica. Such a reduced uptake and/or an increased efflux of metal ions across the root-cell plasma-membrane might explain the higher resistance of Phragmites australis to metals, at least in part.The Pb2+ and Cu2+ ISMEs are shown to permit detailed investigation of heavy-metal ion transport in plant roots, especially for plants used for phytoremediation.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)在实际的生理条件下,测量来自根不同区域的比离子通量对于理解植物对金属的吸收机理至关重要。我们开发并测试了基于中性载体的液膜Pb2+和Cu2+离子选择性微电极(ISME),以研究沿三种常见湿地植物物种根部的离子迁移过程。在去离子水和模拟土壤溶液中,Pb2+和Cu2+的ISME表现出Nernstian响应,Pb2+和Cu2+的活性分别低至1.0 nM和1.0μM。芦苇在大约最初的200μm处具有Cu2+释放区域,而在最初的500μm处表现出Pb2+和Cd2+向外净通量。尽管在芦苇根部的较老部分中有Cu2+,Pb2+和Cd2+的流入区域,但总流入量比香蒲或印度香豆小得多。穿过根细胞质膜的这种减少的金属离子吸收和/或增加的金属离子外流可能至少部分解释了芦苇对金属的更高抗性。研究表明,Pb2+和Cu2+ ISME可以详细研究植物根特别是用于植物修复的植物中重金属离子的转运。Fig. 3 Measurement of fluxes (outward positive) of Cd2+,Pb2+ and Cu2+ (mean ± standard error) across the root tips of three common wetland plant species, Typha latifolia (a) Canna indic (b) and Phragmites australis (c), using Cd2+,Pb2+ and Cu2+ ion selective microelectrodes and the scanning ion-selective electrode higher metal influx in the root regions, especially in the meristematic and elongation zone (Fig. 3).
厂商
2019.11.14
Tree Physiol :中科院南土所丨红柳和棉花在干旱胁迫下对硝吸收的差异?(附NMT实验体系)
NMT是基因功能的活体检测技术,已被31位诺贝尔奖得主所在单位,及北大、清华、中科院使用。期刊:Tree Physiology主题:红柳和棉花在干旱胁迫下对硝吸收的差异标题:Characterization and comparison of nitrate fluxes in Tamarix ramosissima and cotton roots under simulated drought conditions影响因子:3.389检测指标:NO3-流速检测样品:红柳、棉花根部(距离根尖5mm,20mm)NO3-流速流实验处理方法:15% PEG瞬时处理NO3-流速流实验测试液成份:0.1 mM KNO3, 0.1 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2 and 0.3 mM 2-(N-morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid hydrate (MES), pH 6.2作者:中科院南京土壤所施卫明、李光杰、张琳英文摘要Tamarix ramosissima Ledeb., a major host plant for the parasitic angiosperm Cistanche tubulosa, and known for its unique drought tolerance, has significant ecological and economic benefits. However, the mechanisms of nitrogen acquisition by the T. ramosissima root system under drought have remained uncharacterized.Here, uptake of nitrate (NO3?) in various regions of the root system was measured in T. ramosissima using Non-invasive Micro-test Technology at the cellular level, and using a 15NO3–-enrichment technique at the whole-root level. These results were compared with responses in the model system cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Tamarix ramosissima had lower net NO3– influx and a significantly lower Km (the apparent Michalis–Menten constant; 8.5 μM) for NO3– uptake than cotton under normal conditions.Upon simulated drought conditions, using polyethylene glycol (PEG), NO3– flux in cotton switched from net influx to net efflux, with a substantive peak in the white zone (WZ) of the root. There were no significant NO3– influx signals observed in the WZ of T. ramosissima under control conditions, whereas PEG treatment significantly enhanced NO3– influx in the WZ of T. ramosissima. The effect of PEG application on NO3– fluxes was highly localized, and the increase in net NO3– influx in response to PEG stimulation was also found in C. tubulosa-inoculated T. ramosissima. Consistently, root nitrogen (N) content and root biomass were higher in T. ramosissima than in cotton under PEG treatment.Our study provides insights into NO3– uptake and the influence of C. tubulosa inoculation in T. ramosissima roots during acclimation to PEG-induced drought stress and provides guidelines for silvicultural practice and for breeding of T. ramosissima under coupled conditions of soil drought and N deficiency.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)Tamarix ramosissima Ledeb。是寄生被子植物肉stan蓉的主要寄主植物,以其独特的耐旱性而闻名,具有显着的生态和经济效益。然而,在干旱条件下,T。ramosissima根系对氮素的吸收机制尚未阐明。在这里,使用非侵入性微测试技术在细胞水平上使用毛细线虫,并在全根水平上使用15NO3-富集技术测量了毛滴虫在根系各个区域中**盐(NO3-)的吸收。将这些结果与模型系统棉(Gossypium hirsutum L.)中的响应进行比较。在正常条件下,柳的净NO3-流入量较低,而NO3-吸收量的Km(表观Michalis-Menten常数; 8.5μM)则显着低于棉花。在模拟干旱条件下,使用聚乙二醇(PEG),棉花中的NO3-通量从净流入量转换为净流出量,在根部的白色区域(WZ)出现一个实质性的峰值。在控制条件下,没有观察到明显的NO3-流入信号,而PEG处理显着增强了T. ramosissima的W3区NO3-流入。 PEG施用对NO3-通量的影响高度局限,并且在接种C.tubulosa的T. ramosissima中还发现了响应PEG刺激的NO3-净流入量的增加。一致地,在PEG处理下,T.ramosissima的根氮(N)含量和根生物量均高于棉花。我们的研究为适应PEG诱导的干旱胁迫提供了NO3的吸收以及在T. ramosissima根中接种C.tubulosa的影响,并为土壤干旱和N耦合条件下的营林实践和T. ramosissima育种提供了指导。不足。结果表明:使用PEG进行瞬时处理后,棉花根系的NO3-由吸收转为外排,最高值可达400 pmol·m-2·s-1,由此降低根系的N含量;而红柳根系经PEG瞬时处理后吸收明显增加,最高可达300 pmol·m-2·s-1,提高了根系的N含量。
厂商
2019.11.14
NMT历史上的今天丨J Biol Chem、J Exp Bot 盐胁迫、重金属胁迫 文章发表
NMT是基因功能的活体检测技术,已被31位诺贝尔奖得主所在单位,及北大、清华、中科院使用。11月8日下午,中关村NMT联盟受山东当地会员单位邀请,在山东农业大学开展了非损伤微测技术理论应用培训。生科院赵翔宇副院长,园艺学院史庆华教授、姚玉新教授、马方放教授出席了培训会,农学院、园艺学院、生科院、资环院等老师同学参加了培训。此外,联盟还邀请了生科院杨兴洪教授的博士生李大兴,做题为《非损伤微测技术在低磷、盐胁迫研究上的应用》的报告。
厂商
2019.11.13
New Phytol :中科院南土所丨根系铁毒敏感机制同一氧化氮调控的根尖区钾离子稳态平衡密切相关(附NMT实验体系)
NMT是基因功能的活体检测技术,已被31位诺贝尔奖得主所在单位,及北大、清华、中科院使用。期刊:New Phytologist主题:根系铁毒敏感机制同一氧化氮调控的根尖区钾离子稳态平衡密切相关标题:Excess iron stress reduces root tip zone growth through nitric oxide-mediated repression of potassium homeostasis in Arabidopsis影响因子:7.433检测指标:K+流速检测样品:拟南芥K+流速流实验处理方法:4°C下冷处理48小时K+流速流实验测试液成份:2 mM KH2PO4、5mM NaNO3、2 mM MgSO4、1 mM CaCl2、50lM Fe-EDTA,50 lMH3BO3、12lM MnSO4、1lM ZnCl2 ,1lM CuSO4、0.2lMNa2MoO4、1%蔗糖,0.5 g / l MES和0.8%琼脂 pH 5.7作者:中国科学院土壤研究所土壤与可持续农业国家重点实验室施卫明、李光杰、张琳文章简介铁毒是热带和淹水土壤常见的障碍因子。植物发生铁毒害时,根系生长受阻,严重时根系腐坏死亡。然而,人们对铁毒抑制植物根系发育的生物学机制的认识还很初步,也不利于对土壤铁毒逆境下保根壮苗等农艺技术的研发。中科院南京土壤所施卫明研究员课题组长期关注根系铁毒害分子响应机制,分别在铁毒抑制植物的根系伸长、侧根形成的分子生理机制等方面取得一系列进展。相关结果陆续发表在Plant Physiology, Journal of Experimental Botany(Li Guangjie et al., 2015a,b)上。相关成果得到了国内外同行的广泛关注,受Frontiers in Plant Science和Plant Signal and Behavior期刊邀请撰写发表了相关综述和评论(Li Guangjie et al., 2016a,b)。文章中用到的新型分根研究方法,也受到国际知名的方法学期刊Bio-Protocol的邀请撰写了详细的介绍文章(Li Guangjie et al., 2017)。上述系列研究证实根尖区是根系生长响应铁毒胁迫的关键位点,而且比根系其它区段对铁毒胁迫更加敏感。但是为何根尖区会对铁毒胁迫更加敏感,仍未探究清楚。围绕该科学问题,该团队进行了更深入研究。利用非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)测定不同根系区段的钾离子流,并配合离子通道抑制剂和相关突变体进行了研究。研究发现铁毒胁迫引发根尖区细胞一氧化氮(NO)上升后诱导了SNO1 (sensitive to nitric oxide 1)//SOS4活性增强。进而加剧非选择性离子通道(NSCC)介导的钾离子外流,造成根尖细胞钾离子稳态失衡,从而导致了根尖区对铁毒胁迫非常敏感。有意思的是,补充供钾可以一定程度上缓解铁毒胁迫,但是因为没有清除铁毒胁迫诱导的NO信号和SNO1/SOS4活性,因此,并不能彻底解除铁毒对根系的伤害。研究结果也说明了,抑制NO信号和SNO1/SOS4活性以及补施钾肥都对提升植物抵御土壤铁毒逆境有重要作用,但在源头上抑制铁毒诱导的NO信号和SNO1/SOS4活性更为重要和有效。相关结果已在New Phytologist(Zhang Lin and Li Guangjie et al., 2018)发表。张琳博士为第一作者,施卫明研究员和李光杰副研究员为文章通讯作者。实时加入Fe试剂后,拟南芥根尖K+吸收速率变化情况英文摘要The root tip zone is regarded as the principal action site for iron (Fe) toxicity and is more sensitive than other root zones, but the mechanism underpinning this remains largely unknown.We explored the mechanism underpinning the higher sensitivity at the Arabidopsis root tip and elucidated the role of nitric oxide (NO) using NO‐related mutants and pharmacological methods.Higher Fe sensitivity of the root tip is associated with reduced potassium (K+) retention. NO in root tips is increased significantly above levels elsewhere in the root and is involved in the arrest of primary root tip zone growth under excess Fe, at least in part related to NO‐induced K+ loss via SNO1 (sensitive to nitric oxide 1)/SOS4 (salt overly sensitive 4) and reduced root tip zone cell viability. Moreover, ethylene can antagonize excess Fe‐inhibited root growth and K+ efflux, in part by the control of root tip NO levels.We conclude that excess Fe attenuates root growth by effecting an increase in root tip zone NO, and that this attenuation is related to NO‐mediated alterations in K+ homeostasis, partly via SNO1/SOS4.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)根尖区被认为是铁(Fe)毒性的主要作用部位,比其他根区更敏感,但其根源机理尚不清楚。我们探索了支持拟南芥根尖较高敏感性的机制,并使用NO相关突变体和药理方法阐明了一氧化氮(NO)的作用。根尖的高Fe敏感性与钾(K +)保留减少有关。根尖中的NO显着高于根中其他位置的水平,并且参与了过量Fe下主要根尖区的生长的抑制,至少部分与NO诱导的通过SNO1(对一氧化氮1敏感)导致的K +损失有关/ SOS4(盐过于敏感4)并降低了根尖区细胞的活力。此外,乙烯可以拮抗过量铁抑制的根生长和钾离子外排,部分原因是通过控制根尖NO含量。我们得出结论,过量的铁会通过增加根尖区NO的含量而减缓根的生长,并且这种衰减与NO介导的K +动态平衡的改变有关,部分是通过SNO1 / SOS4引起的。
厂商
2019.11.12
NMT历史上的今天丨Traffic 植物营养 文章发表
NMT历史上的今天2017年11月07日,首都师范大学印莉萍、谭松利用NMT在Traffic上发表了标题为TMD1 domain and CRAC motif determine the association and disassociation of MxIRT1 with detergent‐resistant membranes 的研究成果。期刊:Traffic主题:TMD1域和CRAC基序决定MxIRT1与耐去污剂膜的缔合和解离标题:TMD1 domain and CRAC motif determine the association and disassociation of MxIRT1 with detergent‐resistant membranes影响因子:4.133检测指标:Cd2+流速作者:首都师范大学印莉萍、谭松英文摘要Iron is essential for most living organisms. The iron‐regulated transporter1 (IRT1) plays a major role in iron uptake in roots, and its trafficking from endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to plasma membrane (PM) is tightly coordinated with changes in iron environment.However, studies on the IRT1 response are limited. Here, we report that Malus xiaojinesis IRT1 (MxIRT1) associates with detergent‐resistant membranes (DRMs, a biochemical counterpart of PM microdomains), whereas the PM microdomains are known platforms for signal transduction in the PM. Depending on the shift of MxIRT1 from microdomains to homogeneous regions in PM, MxIRT1‐mediated iron absorption is activated by the cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) motif of MxIRT1.MxIRT1 initially associates with DRMs in ER via its transmembrane domain 1 (TMD1), and thus begins DRMs‐dependent intracellular trafficking. Subsequently, MxIRT1 is sequestered in COPII vesicles via the ER export signal sequence in MxIRT1.These studies suggest that iron homeostasis is influenced by the CRAC motif and TMD1 domain due to their determination of MxIRT1‐DRMs association.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)铁对大多数生物都是必不可少的。铁调节转运蛋白1(IRT1)在根部吸收铁中起主要作用,其从内质网(ER)到质膜(PM)的运输与铁环境的变化紧密相关。但是,有关IRT1反应的研究有限。在这里,我们报告说,小金海棠IRT1(MxIRT1)与耐去污剂的膜(DRM,PM微域的生化对应物)相关,而PM微域是PM中信号转导的已知平台。取决于MxIRT1从PM的微区到均质区的转移,MxIRT1介导的铁吸收被MxIRT1的胆固醇识别/相互作用氨基酸共有(CRAC)基序激活。MxIRT1最初通过其跨膜结构域1(TMD1)与ER中的DRM结合,从而开始依赖DRM的细胞内运输。随后,通过MxIRT1中的ER出口信号序列将MxIRT1隔离在COPII囊泡中。这些研究表明,由于铁的动态平衡决定了MxIRT1-DRM的相关性,因此受CRAC基序和TMD1域的影响。G) Average Cd2+flux in the different transgenic Arabidopsis root hairs in 7-minute incubation with 0.05 mM CdCl2 measured by Non-invasion Micro-test Technology. The bars represent the means standard errors of 3 independent analyses (n = 3). Significant differences were determined byStudent’s t test. *P
厂商
2019.11.08
Chemosphere :深圳大学丨盐度调控的海洋硅藻细胞表面镉离子流
NMT是基因功能的活体检测技术,已被31位诺贝尔奖得主所在单位,及北大、清华、中科院使用。点击添加图片描述(最多60个字)期刊:Chemosphere主题:盐度调控的海洋硅藻细胞表面镉离子流标题:Salinity-dependent nanostructures and composition of cell surface and its relation to Cd toxicity in an estuarine diatom影响因子:4.427检测指标:Cd2+流速检测部位:硅藻藻细胞Cd2+流速流实验处理方法:不同盐度的硅藻细胞Cd2+流速流实验测试液成份:0.1mM KCl,0.1mM MgCl2, 0.5mM NaCl, 0.3mM 2-(N-morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid (MES), 0.2mM Na2SO4 and 0.1% sucrose, pH 8.0,8.9μM CdCl2作者:深圳大学潘科、马捷文章简介盐度是河口环境中变化较大的因子之一,会影响海洋主要初级生产力——硅藻与金属之间的相互作用,之前研究发现这一影响主要由环境水化学变化引起。但却忽略了盐度也可能通过改变硅藻本身的生理生化状态来影响其响应重金属的过程。此项研究模拟河口的盐度梯度,在18,25,和32 psu三个盐度下培养了新月菱形藻,在18 psu低盐度时,施加8.9 μM的Cd2+对细胞生长的抑制最强。但值得注意的是,Cd离子浓度的升高约一倍,引起的细胞生长抑制却是约四倍,说明Cd重金属毒性的增加可能存在着其它机制。从分布上看,大部分(>75%)Cd都吸附于细胞表面,表明新月菱形藻的细胞壁在最初的Cd累积过程中有着重要的作用。基于上述现象,研究利用非损伤微测技术测定不同盐度培养的硅藻单细胞表面的Cd2+离子流。结果发现,硅藻细胞在低盐度时细胞表面的Cd2+离子流速更快,而Cd2+吸收速率是影响其毒性最主要因素。进一步结合其它物理化学手段最终揭示了硅藻在不同盐度下通过改变细胞壁的功能基团种类和数量来影响其吸附Cd的细胞表面化学机制。此项研究为近海盐度强烈变化条件下防控重金属的污染和食物链传递提供了重要的理论依据。点击添加图片描述(最多60个字)不同盐度培养的新月菱形藻,细胞表面Cd2+离子流的差异性。负值表示吸收。英文摘要The interactions between metal and phytoplankton are affected by salinity in estuarine environments. While water chemistry is an important factor regulating the metal bioavailability in phytoplankton, the physiological adaptation of the algae cells may also change their intrinsic response to metals.In this work, we tried to interpret the salinity-dependent Cd toxicity in a pennate diatom Nitzchia closterium from a biological side. As with many studies, we observed Cd toxicity to the diatom increased with decreasing salinity. However, changing free Cd ion concentrations may be partly responsible for the enhanced Cd toxicity.Multiple evidences showed that diatom cells acclimated at low salinity had stronger intrinsic Cd adsorption capacity. Salinity significantly affected not only the nanostructures but also the biochemical composition in the cell surface of the diatom. Diatom cells grown at lower salinity had a lower surface potential, higher specific surface area, and more sulfur-containing groups in the cell wall, leading to stronger Cd binding capacity in the cells. Meanwhile, more Si was present as poly-silicic acid when the salinity decreased. The change of Si content and speciation in the cell wall are also considered a major reason for the variations of Cd surface binding.Our study provided new clues for the salinity-dependent metal toxicity in marine diatoms.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)在河口环境中,盐度影响金属和浮游植物之间的相互作用。尽管水化学是调节浮游植物中金属生物利用度的重要因素,但藻类细胞的生理适应性也可能改变其对金属的内在响应。在这项工作中,我们试图从生物学的角度来解释盐度依赖的Cd毒性在戊二烯硅藻Nitzchia closterium中。与许多研究一样,我们观察到Cd对硅藻的毒性随着盐度的降低而增加。但是,改变游离Cd离子浓度可能是造成Cd毒性增强的部分原因。多种证据表明,低盐度适应的硅藻细胞具有更强的固有Cd吸附能力。盐度不仅显着影响硅藻的纳米结构,而且显着影响硅藻细胞表面的生化组成。在较低盐度下生长的硅藻细胞具有较低的表面电势,较高的比表面积和细胞壁中更多的含硫基团,从而导致细胞中更强的Cd结合能力。同时,当盐度降低时,更多的Si作为聚硅酸存在。 Si含量的变化和细胞壁中的形态也被认为是Cd表面结合变化的主要原因。我们的研究为海洋硅藻的盐度依赖性金属毒性提供了新的线索。
厂商
2019.11.04
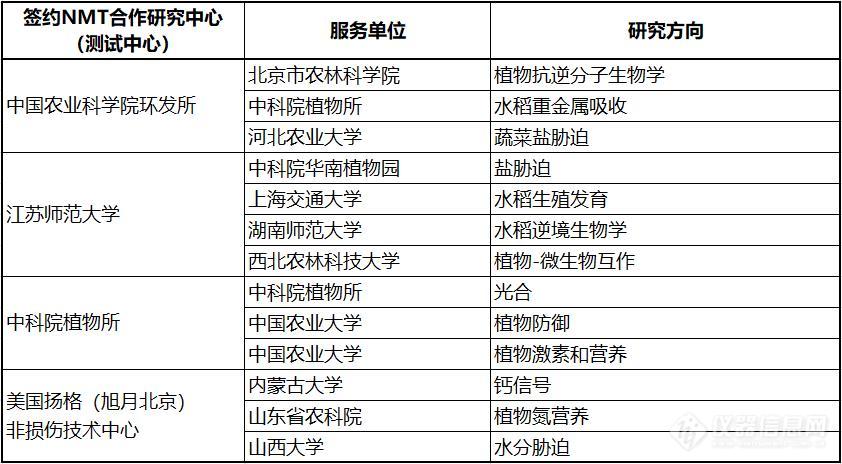
J Exp Bot :江苏师范大学丨多倍体维持钠钾稳态促耐盐能力的新机制
NMT是基因功能的活体检测技术,已被31位诺贝尔奖得主所在单位,及北大、清华、中科院使用。2019年10月江苏师大NMT合作研究中心(测试中心)服务信息期刊:Journal of Experimental botany主题:钾离子和钙离子可渗透通道对H2O2的根区特异性敏感性决定了盐碱化二倍体和六倍体三叉戟的离子xxxxx标题:Root-zone-specific sensitivity of K+-and Ca2+-permeable channels to H2O2 determines ion homeostasis in salinized diploid and hexaploid Ipomoea trifida影响因子:5.354检测指标:K+、H+、Ca2+、Na+流速检测部位:甘薯K+、H+、Ca2+瞬时:分生区(距离根尖500μm处),伸长(距尖端3毫米),成熟(尖端15毫米)K+、Na++:分生组织区(距离尖端300-600μm)测量间隔为100μm),伸长区(1-3 mm)测量间隔为500μm的尖端和成熟区(距尖端10-15毫米,测量间隔为1毫米)K+、H+、Ca2+、Na+流速流实验处理方法:甘薯幼苗,150mM NaCl处理7d/150mM NaCl瞬时处理K+、H+、Ca2+、Na+流速流实验测试液成份:H+/K+/Ca2+瞬时:0.1 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM MgCl2,0.1 mM CaCl2, and 0.5 mM KCl at pH 5.7K+:150 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM CaCl2, and 0.5 mM KCl, pH 5.7作者:江苏师范大学孙健、李宗芸英文摘要 Polyploids generally possess superior K+/Na+ homeostasis under saline conditions compared with their diploid progenitors.In this study, we identified the physiological mechanisms involved in the ploidy-related mediation of K+/Na+ homeostasis in the roots of diploid (2x) and hexaploid (6x; autohexaploid) Ipomoea trifida, which is the closest relative of cultivated sweet potato. Results showed that 6x I. trifida retained more K+ and accumulated less Na+ in the root and leaf tissues under salt stress than 2x I. trifida.Compared with its 2x ancestor, 6x I. trifida efficiently prevents K+ efflux from the meristem root zone under salt stress through its plasma membrane (PM) K+-permeable channels, which have low sensitivity to H2O2. Moreover, 6x I. trifida efficiently excludes Na+ from the elongation and mature root zones under salt stress because of the high sensitivity of PM Ca2+-permeable channels to H2O2.Our results suggest the root-zone-specific sensitivity to H2O2 of PM K+- and Ca2+-permeable channels in the co-ordinated control of K+/Na+ homeostasis in salinized 2x and 6x I. trifida. This work provides new insights into the improved maintenance of K+/Na+ homeostasis of polyploids under salt stress. 中文摘要(谷歌机翻)与二倍体祖细胞相比,多倍体在盐水条件下通常具有优越的K+ / Na+稳态。在这项研究中,我们确定了与二倍体(2x)和六倍体(6x;自六倍体)Tripoda的根的K+/ Na+稳态的倍性相关介导有关的生理机制,这是栽培红薯的近亲。结果表明,与2x I. trifida相比,在盐胁迫下6x I. trifida保留更多的K +并在根和叶组织中积累较少的Na+。与2x祖先相比,6x裂叶线虫通过其对H2O2敏感性低的质膜(PM)K+渗透通道有效地防止了盐胁迫下分生组织根区的K+流出。此外,由于PM Ca2+的可渗透通道对H2O2的敏感性高,因此6x I. trifida有效地将Na+从盐胁迫下的伸长和成熟根区中排除。我们的结果表明,在盐渍化2x和6x盐粉虱的K+ / Na+动态平衡控制中,PM K+-和Ca2+渗透通道对H2O2的根区特异性敏感性。这项工作为改善盐胁迫下多倍体K+ / Na+稳态的维持提供了新的见解。结果表明:在分生组织区中,观察到更高的K+流出量的是2x,在盐处理(约30分钟)期间,盐诱导的K+渗漏的平均速率高达4800 pmol cm-2 s-1(比6x高1.9倍)。但是,在伸长和成熟的根部区域观察到相反的趋势,其中6x比2x表现出更强烈的K+外排。
厂商
2019.11.04
8月-9月测试类基金获批简报
为贯彻国家创新战略和应对国际科技竞争的新形势,新挑战,联盟受国家委托,向中国非损伤微测技术使用者提供设备、测试、耗材、研发、技术报告等各类基金资助,延续并扩大中国学者在NMT技术创新、产品研发、科研应用及产业化方面所积累的领先优势,确保中国科研人员及时抢占以非损伤微测技术为代表的,活体基因功能研究领域制高点。NMT创新实验资助项目项目针对计划利用NMT从事具有创新性实验的科研工作者。创新性既包含广义的科研创新,也包含在非损伤微测技术领域的创新,尤其是非损伤微测技术的空白领域,例如新方向、新方法、新样品等。NMT实验方案优化资助项目项目针对利用NMT从事科学研究过程中,流速结果与现有研究成果、理论不相符,并且计划利用NMT进一步探究原因的科研工作者。2019.08-2019.09简报姓名:王忆-柴小粉单位:中国农业大学研究方向:果树逆境生理研究基金类型:NMT创新实验基金获批额度:1000-3000元姓名:张颖-孙瑞雪单位:东北农业大学研究方向:微生物(细菌)对有机污染物的降解基金类型:NMT创新实验基金获批额度:1000-3000元姓名:熊兴耀-李青单位:中国农科院蔬菜花卉研究所研究方向:马铃薯耐盐性机制研究基金类型:NMT创新实验基金获批额度:10000-15000元 姓名:李东屏-郝小花单位:湖南师范大学研究方向:植物离子运输与耐逆基金类型:NMT创新实验基金获批额度:3000-5000元姓名:曲乐庆-熊硕单位:中国科学院植物研究所研究方向:植物重金属吸收基金类型:NMT创新实验基金获批额度:1000-3000元
厂商
2019.11.01
上海交通大学丨非损伤设备操作培训顺利完成
据联盟会员单位旭月公司反馈,上海交通大学农生院非损伤设备操作培训,已于2019年10月30日完成。 联盟受上海交大邀请,将于下周三(11月6日)14:00在闵行校区农创楼201,开展非损伤微测技术理论应用培训,欢迎您来参加。
厂商
2019.11.01
哪个研究方向最火!?丨全国NMT测试服务网测试信息
2019年10月,中关村NMT联盟全国测试服务网信息中关村NMN联盟合作研究中心(测试中心)一览中科院植物所(北京)中国农科院环发所(北京)美国扬格(旭月北京)非损伤技术中心(北京)江苏师范大学(徐州)中国林科院亚热带林业研究所(杭州)东北农业大学(哈尔滨)河南农业大学(郑州)南京农业大学(南京)中科院成都生物所(成都,建设中)四川农业大学(成都,建设中)
厂商
2019.10.30
山东农业大学丨活体植物逆境功能基因研究应用培训
2019年11月08日,由中关村NMT联盟组织的非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)活体植物逆境功能基因研究应用培训,将在山东农业大学举行。主讲内容非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)是研究功能基因的一种技术,通过检测活体植物根茎叶与内/外环境间Ca/Cd/Na/K/N/O2...交换量的实时变化,揭示:AHA2促初生根伸长适应低磷的信号机制根瘤促进多氯联苯降解的直接证据CBL激酶提升植物抗盐耐寒能力的胜利证据胞外ATP诱导细胞程序性死亡的模型OsCBL10启动子自然变异影响水稻适应低氧胁迫的机制......培训内容:理论应用培训、专家分享、上机演示时间:2019年11月08日 星期五 14:00~16:30地点:山东农业大学国家重点实验室2楼学术交流厅NMT应用专家正在邀请中......刘蕴琦 NMT高级顾问中关村非损伤微测技术产业联盟秘书长,《NMT 101问》、《NMT论文集》副主编。协助中国农大武维华院士、中科院植物所种康院士等课题组,设计了Cell、Plant Cell等研究成果中的非损伤离子流实验部分。近5年,直接协助国内学者发表的SCI文章共67篇,累计影响因子308.64。叶 斌 NMT高级工程师中关村NMT联盟测试部部长,拥有10年非损伤微测系统操作应用经验,是全球一款商业化活体样品IAA流速检测传感器研发团队核心成员,重点参与了H2O2、O2等分子流速传感器的研发。非损伤微测技术目前可检测的指标有:H+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、Mg2+、Cd2+、Cu2+、Pb2+、NH4+、NO3-、O2、H2O2、IAA。
厂商
2019.10.30
上海交通大学丨活体植物逆境功能基因研究应用培训
2019年11月06日,由中关村NMT联盟组织的非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)活体植物逆境功能基因研究应用培训,将在上海交通大学闵行校区举行。主讲内容非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)是研究功能基因的一种技术,通过检测活体植物根茎叶与内/外环境间Ca/Cd/Na/K/N/O2...交换量的实时变化,揭示:稻瘟病菌利用K通道抑制先天免疫的机制COLD1等位基因赋予水稻的耐寒新机制丙酮酸载体调控植物耐镉的机理干旱胁迫如何促进植物的氮吸收......培训内容:理论应用培训、专家分享、上机演示时间:2019年11月06日 星期三 14:00~16:30地点:上海交通大学闵行校区 农创楼201联系人:程老师 18515811370NMT应用专家正在邀请中......刘蕴琦 NMT高级顾问中关村非损伤微测技术产业联盟秘书长,《NMT 101问》、《NMT论文集》副主编。协助中国农大武维华院士、中科院植物所种康院士等课题组,设计了Cell、Plant Cell等研究成果中的非损伤离子流实验部分。近5年,直接协助国内学者发表的SCI文章共67篇,累计影响因子308.64。叶 斌 NMT高级工程师中关村NMT联盟测试部部长,拥有10年非损伤微测系统操作应用经验,是全球唯一一款商业化活体样品IAA流速检测传感器研发团队核心成员,重点参与了H2O2、O2等分子流速传感器的研发。非损伤微测技术目前可检测的指标有:H+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、Mg2+、Cd2+、Cu2+、Pb2+、NH4+、NO3-、O2、H2O2、IAA。
厂商
2019.10.29
NMT设备操作视频上线啦!!
您还在苦恼于对NMT系统操作不熟练而导致实验效率偏低嘛?您还在纠结于系统操作培训完成后,由于长时间不练习而导致对操作流程有遗忘嘛?旭月公司售后客户们“日思夜想”的NMT系统操作视频终于上线了!通过此视频您可以完美地解决操作过程中遇到的各种问题,并且会大幅度提高您的实验效率。您还在等什么?!赶快登录一站式服务网站——流速云来查看NMT系统操作视频吧!!(温馨提示!本视频仅辅助NMT系统操作人员进一步学习和练习培训后的相关操作知识,非NMT系统操作人员请接受正规的操作培训。目前中关村NMT联盟设立了资质认证培训基金,您可以对系统操作培训服务进行基金申请,有兴趣的客户可联系中关村NMT联盟进行咨询一站式服务网站——流速云介绍旭月公司推出了一站式服务网站——流速云!!可以满足您接触NMT后的所有基础需求:安装培训耗材订购实验设计及前期准备设备操作方法及经验数据处理及分析作图文章撰写及发表其它资源等……
厂商
2019.10.25
中科院植物所-中关村NMT联盟 合作研究中心丨非损伤应用培训
今天上午,中关村NMT联盟受邀在中科院植物所光生物学重点实验室,开展了非损伤微测技术理论应用培训、上机演示操作培训,现场不仅有植物所的老师同学,还有来自林科院等其他院校的老师同学来到现场。目前,联盟与光生物学重点实验室已经成立“NMT合作研究中心”,光生物学重点实验室的NMT设备已经加入全国测试服务网,可提供对外服务。
厂商
2019.10.25
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces:中科院深圳先进院丨可降解生物材料微环境pH分布及其对破骨细胞活性的调节作用
期刊:ACS Appl Mater Interfaces主题:可降解生物材料周边微环境pH空间分布及其对破骨细胞活性的调节作用标题:Spatial Distribution of Biomaterial Microenvironment pH and Its Modulatory Effect on Osteoclasts at Early Stage of Bone Defect Regeneration影响因子:8.097监测指标:H+流速检测部位:生物材料玻璃材料H+流速流实验处理方法:不同配比的玻璃材料H+流速流实验测试液成份:模拟体液作者:中科院深圳先进技术研究院潘浩波、刘文龙文献简介2019年2月,中科院深圳先进技术研究院潘浩波研究员团队发表了题为 “Spatial Distribution of Biomaterial Microenvironment pH and Its Modulatory Effect on Osteoclasts at the Early Stage of Bone Defect Regeneration” 的文章,通过关联可降解生物材料周边微环境H+离子分布和破骨细胞活性,旨在描绘 “材料-机体” 交互作用之 “微环境” 分布范围。相关成果发表于ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces。近年来,由人工组织与机体微环境交互作用而引起的材料学及生物学效应受到越来越多的关注。团队早期研究发现pH值在调控骨修复过程中破骨与成骨间平衡具有重要作用,并采用微电极技术初步探明存在微碱性范围内的某一pH 阈值,使得成骨细胞、破骨细胞及骨髓基质干细胞在阈值两侧的活性产生明显变化(即“开/关”效应)(Liu WL et al., Osteoporosis International, 2016; Shen YH et al., Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012; Shen YH et al., Langmuir, 2011)。进而,本研究采用非损伤微测技术,考察了系列可降解材料近表面(50-3000μm)氢离子流速及空间分布的梯度效应。相对于表面pH微电极,NMT系统在检测信号种类,空间和时间的可控性等方面展现出了独到的优势。结果证明,破骨细胞在微碱性环境中(pH>7.8)的分化及侵蚀骨板能力基本丧失;基于此,团队制备了系列碱性可降解硅硼酸盐玻璃,并使用NMT系统描绘出与破骨细胞产生“开/关”效应相对应的材料表面微环境的影响范围(400 ± 50 μm)。为研究“材料-骨组织”早期的相互作用,团队使用最新建立的小鼠骨缺损动物模型(Liu WL et al., Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods, 2016),证明了材料周边碱性微环境能促进骨质疏松骨缺损的快速再生。本研究进而表明,对微环境离子浓度的精确调控将为未来新材料的设计提供指导意义。英文摘要It is generally accepted that biodegradable materials greatly influence the nearby microenvironment where cells reside; however, the range of interfacial properties has seldom been discussed due to technical bottlenecks.This study aims to depict biomaterial microenvironment boundaries by correlating interfacial H+ distribution with surrounding cell behaviors. Using a disuse-related osteoporotic mouse model, we confirmed that the abnormal activated osteoclasts could be suppressed under relatively alkaline conditions. The differentiation and apatite-resorption capability of osteoclasts were “switched off” when cultured in titrated material extracts with pH values higher than 7.8.To generate a localized alkaline microenvironment, a series of borosilicates were fabricated and their interfacial H+ distributions were monitored spatiotemporally by employing noninvasive microtest technology. By correlating interfacial H+ distribution with osteoclast “switch on/off” behavior, the microenvironment boundary of the tested material was found to be 400 ± 50 μm, which is broader than the generally accepted value, 300 μm.Furthermore, osteoporotic mice implanted with materials with higher interfacial pH values and boarder effective ranges had lower osteoclast activities and a thicker new bone.To conclude, effective proton microenvironment boundaries of degradable biomaterials were depicted and a weak alkaline microenvironment was shown to promote regeneration of osteoporotic bones possibly by suppressing abnormal activated osteoclasts.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)人们普遍认为,可生物降解的材料会极大地影响细胞所在的附近微环境。然而,由于技术瓶颈,很少讨论界面性质的范围。这项研究旨在通过将界面H+分布与周围细胞行为相关联来描绘生物材料微环境的边界。使用与废品相关的骨质疏松小鼠模型,我们确认了在相对碱性条件下可以抑制异常活化的破骨细胞。当在pH值高于7.8的滴定材料提取物中培养时,破骨细胞的分化和磷灰石吸收能力被“关闭”。为了产生局部的碱性微环境,制造了一系列的硼硅酸盐,并采用无创微测试技术对它们的界面H+分布进行了时空监测。通过将界面H+分布与破骨细胞的“开/关”行为相关联,发现被测材料的微环境边界为400±50μm,比公认的值300μm宽。此外,植入具有较高界面pH值和边界有效范围的材料的骨质疏松小鼠的破骨细胞活性较低,新骨较厚。总而言之,描绘了可降解生物材料的有效质子微环境边界,并显示了弱碱性微环境可能通过抑制异常活化的破骨细胞来促进骨质疏松骨骼的再生。
厂商
2019.10.25
NMT历史上的今天丨AGR ECOSYST ENVIRON、Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 文章发表
NMT历史上的今天2018年10月22日,福建农林大学林文雄、林生利用NMT在Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment上发表了标题为Rhizosphere responses to environmental conditions in Radix pseudostellariae under continuous monoculture regimes的研究成果。2018年10月22日,华中农业大学孙学成、史凯丽利用NMT在Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 上发表了标题为Non-invasive microelectrode cadmium flux measurements reveal the decrease of cadmium uptake by zinc supply in pakchoi root (Brassica chinensis L.)的研究成果。期刊:Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment主题:连续单培养条件下假星豆根际对环境条件的响应标题:Rhizosphere responses to environmental conditions in Radix pseudostellariae under continuous monoculture regimes影响因子:3.541检测指标:H+流速作者:福建农林大学林文雄、林生英文摘要The root exudates of Radix pseudostellariae, working as a rhizospheric intermediary between plants and microbes, can deteriorate the microbial community in the rhizosphere in a consecutive monoculture system.We assessed the e?ects of arti?cially applied R. pseudostellariae root exudates on R. pseudostellariae seedling growth, rhizo-sphere soil microbial communities, and soil physicochemical properties. We found that phenolic acids and or-ganic acids acted as a driver of changes in the microbial community. High-throughput sequencing and qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated that treatment with phenolic acids signi?cantly decreased the relative abundance of Trichoderma, Penicillium, Pseudomonadales, Xanthomonadales, and Streptomycetales.Organic acids had a sig-ni?cant negative e?ect on the relative abundance of Pseudomonadales and Streptomycetales and signi?cantly increased the abundance of Fusarium, Xanthomonadales, Micrococcales, and Gemmatimonadales. Analysis based on the noninvasive microtest technique indicated that root exudates increased H+ e?ux and plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity in the pathogenic fungi and decreased them in the bene?cial fungi.These phenomena created an acidic environment for the inhibition of bene?cial bacteria and accumulation of specialized plant pathogens. This study explains the mechanisms underlying the shift in micro?ora and structural disorder caused by root exudates in continuously monocultured R. pseudostellariae rhizosphere soil through responses to en-vironmental conditions.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)在植物和微生物之间作为根际中介体工作的伪星根的根系分泌物会在连续的单培养系统中破坏根际微生物群落。我们评估了人工施用的拟星果根分泌物对拟星果幼苗生长,根际土壤微生物群落和土壤理化特性的影响。我们发现酚酸和有机酸是微生物群落变化的驱动力。高通量测序和qRT-PCR分析表明,用酚酸处理可显着降低木霉菌,青霉菌,假单胞菌,黄单胞菌和链霉菌的相对丰度。有机酸对假单胞菌和链霉菌的相对丰度有明显的负面影响,并显着增加了镰刀菌,黄单胞菌,微球藻和Gemmatimonadales的丰度。基于非侵入性微测试技术的分析表明,根系分泌物增加了病原真菌中的H +流动和质膜H+ -ATPase活性,而减少了其有益真菌中的H+酶和质膜H+ -ATPase活性。这些现象为抑制有益细菌和特殊植物病原体的积累创造了酸性环境。这项研究解释了通过对环境条件的响应,在连续单培养的假星菌根际土壤中根系分泌物引起的微孔和结构紊乱转变的潜在机制。Fig. 7. E?ect of Fusarium oxysporum on steady H+ ?uxes in R. pseudostellariae roots. CK represents roots without F. oxysporum stimulation;F. oxysporum re-presents roots stimulated with F. oxysporum. 期刊:Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety主题:非侵入式微电极镉通量测量显示小菜根(甘蓝)中锌供应对镉吸收的减少标题:Non-invasive microelectrode cadmium flux measurements reveal the decrease of cadmium uptake by zinc supply in pakchoi root (Brassica chinensis L.)影响因子:3.974检测指标:Cd2+流速检测部位:小白菜根部(距离静止中心200um)作者:华中农业大学孙学成、史凯丽英文摘要Zinc (Zn) possesses similar properties to cadmium (Cd) and inhibits Cd uptake in plants. To get more detailed mechanisms of Zn-inhibited Cd uptake in pakchoi, a hydroponic experiment was conducted to investigate the e?ects of various Zn levels on Cd concentrations, real time ?ux of Cd, expressions of genes related to Cd uptake under Cd exposure.The results showed that the Cd concentrations and Cd accumulations in pakchoi root de-creased with increasing Zn levels, which were coincident with that real time Cd in?ux and net Cd in?ux of pakchoi root decreased with increasing Zn levels by non-invasive micro-test technology (NMT). Additionally, the expressions of Cd-related transporters including BcNRAMP5, BcIRT1 and BcMGT1 decreased with the increase of Zn levels under Cd exposure, especially BcIRT1 with the highest decreased rates. Furthermore, the expressions of these genes decreased gradually with the prolongation of Zn treated time under Cd toxicity.The results indicate that Zn inhibits Cd uptake by inhibition of the expressions of Cd-related transporters, especially BcIRT1 in pakchoi root.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)锌(Zn)具有与镉(Cd)相似的特性,并抑制植物中Cd的吸收。为了更详细地了解小白菜中Zn抑制Cd吸收的机理,进行了水培试验,研究了各种Zn水平对Cd浓度,Cd实时通量以及Cd暴露下与Cd吸收有关的基因表达的影响。结果表明,通过无创微试验技术,小白菜根中的Cd浓度和Cd积累量随Zn水平的升高而降低,这与小菜根的实时Cd输入量和Cd净含量随Zn含量的增加而降低。 (NMT)。另外,随着镉暴露下锌水平的升高,包括BcNRAMP5,BcIRT1和BcMGT1在内的Cd相关转运蛋白的表达下降,尤其是下降率最高的BcIRT1。此外,随着镉对镉的毒害作用时间的延长,这些基因的表达逐渐降低。结果表明,Zn通过抑制小白菜根中Cd相关转运蛋白特别是BcIRT1的表达来抑制Cd的吸收。Fig. 3. E?ects of Zn on net Cd2+ in?uxes in root of pak-choi by Non-invasive micro-test technology. The 10 d pakchoi seedlings treated with Zn de?ciency Hoagland solution were used to analyze the Cd in?ux. The Zn con-centrations of 0 (Zn 0), 1 (Zn 1), 5 (Zn 5) and 10 μM (Zn 10) represented that the concentrations of Zn were added the basic solution containing 9 μM Cd. (A) The steady-state Cd2+ in?ux before and after the Zn supply into the basic solution. (B) Mean rates of Cd2+ in?ux of the time in A. Each point represents the mean of six roots from six in-dividual plants. Data are the means of 6 replicates ± standard error. Di?erent lowercase represents signi?cant di?erences between treatments (p
厂商
2019.10.22
中国作物学会学术年会 | 2019版《NMT论文集》亮相大会手提袋
2019年10月27至10月30日,“中国作物学会第十一届会员代表大会暨2019年学术年会”将在浙江省杭州市举行。因主办方认为非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)与此次会议主题契合,为促进中国科研人员及时抢占以NMT为代表的,活体基因功能研究领域制高点,特邀请联盟为与会代表提供技术资料——2019年新版《NMT论文集》,届时会出现在参会代表的手提袋中。2019版《NMT论文集》除了收录了2018~2019期间,国内外学者利用NMT发表的近100篇SCI文献外,首页还有价值3000元NMT测试体验券、1000元NMT测试/耗材代金券、首次测试优惠券等。会议时间:2019年10月27日-10月30日 会议地点:浙江省杭州市宝盛水博园大酒店
厂商
2019.10.22
祝贺北京大学采购扬格/旭月第七代NMT系统
祝贺北京大学通过单一来源的方式,采购扬格/旭月的国产第七代自动化非损伤微测系统。第七代自动化NMT系统的优势备注:1.全能:指标配能够检测 IAA、O2、H2O2、Ca2+、H+、K+、Na+、Cd2+、Cl-、NH4+、NO3-、Mg2+,其余指标可升级。2. 个性化升级:指标配能够检测 IAA、O2、H2O2、Ca2+、H+、K+、Na+、Cd2+、Pb2+、Cu2+、Cl-、NH4+、NO3-、Mg2+种的2-3种指标,其余指标可升级。3. 新研发指标:IAA、Pb2+、Cu2+等。4. 高通量多传感器相关知识产权号:ZL200620132388.1。5. 自动化传感器制作相关知识产权号:ZL200620158604.X,201710116315.6,2016SRBJ0259。6. 第七代NMT系统所检测和输出的数据为流速和浓度,该数据可直接通过流速云平台绘图。其他代别的NMT系统所检测和输出的信号为电压或电流的信号,需要依据文献、公式进行额外的整理、换算,才能得到流速数据。7. 流速云知识产权号:2019SR0347969。8. imFluxes软件知识产权号:2016SRBJ020。9. 中关村NMT联盟:《中关村旭月非损伤微测技术产业联盟》(原简称“中关村NMT联盟”),创始于2015年9月,由北京中关村示范区内国家高新技术企业和知名高等院校科研院所自愿联合发起,并由北京市民政局正式批准成立的政府扶持、独立运营的非营利性社会团体。统一社会信用代码为51110000MJ012204XL。为鼓励和表彰理事单位旭月(北京)科技有限公司在非损伤微测技术产业发展中做出的杰出贡献及其技术先驱地位,由北京市政府相关部门于2018年8月特批,将“旭月”作为联盟冠名品牌。10. 中关村NMT联盟认证:扬格/旭月已取得联盟证书包括NMT管理体系认证证书(编号N1001180619A、N2001180619A)、NMT耗材认证证书(N1001180619B、N2001180619B)、NMT研发机构认证证书(N1001180619C)、NMT工程师认证证书(NMTSBCZ20180001、NMTSBCZ20190001、NMTSH20180001等)。11. ISO质量管理系统认证证书编号:1125672C。12. 目前,美国扬格公司及旭月公司所生产和销售的NMT系统,全部为中关村NMT联盟认证的第七代自动化NMT产品。
厂商
2019.10.22
中科院植物所丨活体植物逆境功能基因研究应用培训
2019年10月24日,由中关村NMT联盟组织的非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)活体植物逆境功能基因研究应用培训,将在中科院植物所举行。主讲内容非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)是研究功能基因的一种技术,通过检测活体植物根茎叶与内/外环境间Ca/Cd/Na/K/N/O2...交换量的实时变化,揭示:COLD1等位基因和特异SNP赋予水稻的耐寒新机制稻瘟病菌利用K通道抑制先天免疫的机制丙酮酸载体调控植物耐镉的机理干旱胁迫如何促进植物的氮吸收......培训内容:理论应用培训、上机演示时间:2019年10月24日 星期四 9:00~11:30地点:中科院植物所景天楼303室刘蕴琦 NMT高级顾问中关村非损伤微测技术产业联盟秘书长,《NMT 101问》、《NMT论文集》副主编。协助中国农大武维华院士、中科院植物所种康院士等课题组,设计了Cell、Plant Cell等研究成果中的非损伤离子流实验部分。近5年,直接协助国内学者发表的SCI文章共67篇,累计影响因子308.64。叶 斌 NMT高级工程师中关村NMT联盟测试部部长,拥有10年非损伤微测系统操作应用经验,是全球一款商业化活体样品IAA流速检测传感器研发团队核心成员,重点参与了H2O2、O2等分子流速传感器的研发。非损伤微测技术目前可检测的指标有:H+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、Mg2+、Cd2+、Cu2+、Pb2+、NH4+、NO3-、O2、H2O2、IAA。
厂商
2019.10.21
Sci Total Environ :湘潭大学丨城市污水中的季铵盐对绿藻NH4+吸收的影响(附NMT实验体系)
期刊:Science of The Total Environment主题:城市污水中的季铵盐对绿藻NH4+吸收的影响标题:Extracellular polymeric substrates of Chlorella vulgaris F1068 weaken stress of cetyltrimethyl ammonium chloride on ammonium uptake影响因子:4.610监测指标:NH4+流速检测部位:小球藻藻细胞NH4+流速流实验处理方法:小球藻,有无0.5 mg/L CTAC在光照/黑暗下处理6小时NH4+流速流实验测试液成份:NH4Cl 37.4 mg/L, NaH2PO42·7H2O 9.8 mg/L, CaCl2·2H2O 14.7 mg/L,MgSO4·7H2O 24.6 mg/L and NaHCO3 42mg/L,pH 7.5作者:湘潭大学葛飞、匡扬铎英文摘要This study investigated the influences of cetyltrimethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (CTAC), an emerging pollutant quaternary ammonium compound (QAC) in municipal effluents, on the transfer and uptake of NH4+ by Chlorella vulgaris F1068 cells removed EPS artificially (EPS-R) and coated EPS naturally (EPS-C) under different scenarios (e.g., the presence or absence of CTAC, different photoperiod sequences (light 12?h: dark 12?h or dark 12?h: light 12?h)).The results showed that the removal of EPS increased the transfer and uptake of NH4+ but the presence of EPS caged NH4+ and effectively weakened the stress of CTAC (Thereby, the findings of this study provided an insight into the role of algal EPS in transfer and uptake of nutrients under the coexisted toxics for the future algae-based sewage treatment application.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)这项研究调查了十六烷基三甲基三甲基氯化铵(CTAC)(一种新兴的污染物季铵化合物(QAC))在城市污水中对寻常绿藻F1068细胞人工去除EPS(EPS-R)和包被EPS的转移和吸收NH4+的影响。自然地(EPS-C)在不同情况下(例如,是否存在CTAC,不同的光周期序列(亮12 h:暗12 h或暗12 h:亮12 h))。结果表明,EPS的去除增加了NH4+的转移和吸收,但是EPS的存在笼罩了NH4+,有效地减弱了CTAC(因此,本研究的发现为藻类EPS在未来基于藻类的污水处理应用中在共存有毒物质的转移和吸收养分中的作用提供了见解。结果表明:在没有CTAC的6小时光照下,EPS-C细胞或EPS-R细胞的NH4+通量分别达到-1.87ng /(cm2·s)和-2.63ng /(cm2·s)。当添加0.5 mg / L的CTAC时,EPS-C或EPS-R细胞的NH4+通量急剧下降至-0.94 ng /(cm2·s)和-0.73 ng /(cm2·s)。相反,当EPS-R细胞和EPS-C细胞在黑暗中培养6小时无论CTAC存在与否,EPS-C细胞和EPS-R细胞的NH4+流速从负值转换为正值,表明NH4+从细胞内环境流出到培养基。
厂商
2019.10.18
NMT历史上的今天丨Sci Rep-UK 东南景天金属转运蛋白有助于转基因拟南芥中镉的积累 的文章发表
NMT历史上的今天2017年10月17日,中国林科院亚热带林业研究所卓仁英、陈双双利用NMT在Scientific Reports上发表了标题为Sedum alfredii SaNramp6 Metal Transporter Contributes to Cadmium Accumulation in Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana的研究成果。期刊:Scientific Reports主题:东南景天金属转运蛋白有助于转基因拟南芥中镉的积累标题:Sedum alfredii SaNramp6 Metal Transporter Contributes to Cadmium Accumulation in Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana影响因子:4.259检测指标:Cd2+流速检测部位:拟南芥根部(距离根尖120μm)Cd2+流实验处理方法:30日龄的拟南芥幼苗,在0/50μM CdCl2中处理24 hCd2+流实验测试液成份:0.05 mM CdCl2, 0.1 mM KCl, 0.02 mM CaCl2, 0.02 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM Na2SO4 and 0.3 mM MES, pH 5.7作者:中国林科院亚热带林业研究所卓仁英、陈双双英文摘要The plant natural resistance-associated macrophage protein (Nramp) family plays an important role in tolerance to heavy metal stress. However, few Nramps have been functionally characterized in the heavy metal-accumulating plant Sedum alfredii.Here, Nramp6 was cloned and identified from S. alfredii and its function analyzed in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. SaNramp6 cDNA contains an open reading frame of 1, 638?bp encoding 545 amino acids.SaNramp6′s expression can be induced by cadmium (Cd) stress, and, after treatment, it peaked at one week and 12?h in the roots and leaves, respectively. SaNramp6 localized to the plasma membrane in protoplasts isolated from A. thaliana, Nicotiana benthamiana lower leaf and onion (Allium cepa) epidermal cells. The heterologous expression of SaNramp6 in the Δycf1 yeast mutant increased the Cd content in yeast cells.SaNramp6 also rescued the low Cd accumulation of the A. thaliana nramp1 mutant. Transgenic A. thaliana expressing SaNramp6 exhibited high Cd accumulation levels, as determined by a statistical analysis of the Cd concentration, translocation factors and net Cd2+ fluxes under Cd stress.Thus, SaNramp6 may play a significant role in improving Cd accumulation, and the gene may be useful for the biotechnological development of transgenic plants for phytoremediation.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)植物天然抗性相关的巨噬细胞蛋白(Nramp)家族在重金属胁迫耐受性中起重要作用。然而,在重金属富集植物景天草中,很少有Nramps在功能上有特征。在此,从苜蓿链球菌克隆并鉴定了Nramp6,并在转基因拟南芥中分析了其功能。 SaNramp6 cDNA包含一个1,638 bp的开放阅读框,编码545个氨基酸。SaNramp6的表达可以通过镉(Cd)胁迫诱导,处理后,其在根和叶中分别在1周和12μh达到峰值。 SaNramp6定位于原生质体中的质膜,该原生质体是从拟南芥,本氏烟草下部叶片和洋葱(洋葱)表皮细胞中分离出来的。 SaNramp6在Δycf1酵母突变体中的异源表达增加了酵母细胞中Cd的含量。SaNramp6还挽救了拟南芥nramp1突变体的低Cd积累。表达SaNramp6的转基因拟南芥表现出高Cd积累水平,这是通过对Cd胁迫下Cd浓度,易位因子和Cd2 +净通量的统计分析确定的。因此,SaNramp6可能在改善Cd积累中起重要作用,该基因可能对转基因植物进行植物修复的生物技术开发有用。Figure 8. Comparison of Cd concentrations and net Cd2+ -influx rates in four lines - WT (wild type); OE 2 and OE 3 (overexpression lines); Atnr (mutant line); Atnr-N24 and Atnr-N28 (rescue lines). (a,c) Cd2+ flux rateswith Cd treatment for 24 h. (b,d) Mean flow rates of Cd2+. Bars indicate means ± standard deviations (SDs) of at least three independent biological experiments. One or two asterisks indicate a significant difference at P
厂商
2019.10.17
NMT历史上的今天丨Environ Exp Bot 水稻如何促进镉吸收的 文章发表
NMT历史上的今天2015年10月14日,浙江理工大学熊杰、中国水稻所陶龙兴利用NMT在Environmental and Experimental Botany上发表了标题为Excessive nitrate enhances cadmium (Cd) uptake by up-regulating the expression of OsIRT1 in rice (Oryza sativa)的研究成果。期刊:Environmental and Experimental Botany主题:过量的硝酸盐通过上调水稻(Oryza sativa)中OsIRT1的表达来提高镉(Cd)的吸收标题:Excessive nitrate enhances cadmium (Cd) uptake by up-regulating the expression of OsIRT1 in rice (Oryza sativa)影响因子:3.712检测指标:Cd2+流速检测部位:水稻根部Cd2+流实验处理方法:三周龄的水稻幼苗,在不同的NO3浓度(0mM、2.86mM、5.72mM)下培养7天,30 mM Cd2+处理30-60minCd2+流实验测试液成份:30 μM CdCl2, 0.1 mM KCl, 0.05 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM Na2SO4, 0.3 mM MES, pH 5.5作者:浙江理工大学熊杰、中国水稻所陶龙兴英文摘要In order to pursue higher yield of rice, higher amount of NO3? is often used in rice production, but limited information is available on cadmium (Cd) uptake promoted by nitrate (NO3?) in rice.Here, hydroponic experiments with integration of three NO3? levels (0 mM, 2.86 mM and 5.72 mM simplify as 0, NO3? and 2NO3?) and two Cd concentrations (0 and 100 μM) were conducted. Phenotypes and physiological indexes related to Cd uptake were measured; content changes of nitrogen, Cd and Fe also were measured. In addition, net Cd2+ flux was monitored and quantitative RT-PCR was applied to determine the expression of Fe/Cd transporters.The results showed that although excessive NO3? had no significant promoting effect on rice growth in absence or presence of Cd, it enhanced Cd influx in elongation zone of rice roots and increased Cd accumulation in rice plants and grains. Excessive NO3? also increased OsIRT1 expression and Fe accumulation in rice seedlings in the absence or presence of Cd.In conclusion, excessive NO3? increases OsIRT1 expression and Cd influx in elongation zone of rice roots, and then it increased Cd and Fe uptake and accumulation in rice plants and grains, which raises an increased-risk for human health. 中文摘要(谷歌机翻)为了追求更高的水稻产量,通常在水稻生产中使用大量的NO3-,但是关于水稻中硝酸盐(NO3-)促进镉(Cd)吸收的信息有限。在这里,进行了整合三个NO3-浓度(0 mM,2.86 mM和5.72 mM简化为0,NO3-和2NO3-)和两个Cd浓度(0和100μM)的水培实验。测量与镉吸收有关的表型和生理指标;还测量了氮,镉和铁的含量变化。此外,监测净Cd2 +通量并应用定量RT-PCR确定Fe / Cd转运蛋白的表达。结果表明,尽管过量的NO3-在没有或没有Cd的情况下对水稻的生长没有明显的促进作用,但是它增加了Cd在水稻根部伸长区的流入量,并增加了Cd在水稻和谷物中的积累。在没有或没有镉的情况下,过量的NO3-也会增加水稻幼苗中OsIRT1的表达和铁的积累。总之,过量的NO3-会增加稻根伸长区OsIRT1的表达和Cd的流入,然后增加稻米和谷物中Cd和Fe的吸收和积累,从而增加人体健康的风险。Effects of different concentrations of nitrate (NO3??) on root net Cd2+ in?ux in rice seedlings. Root net Cd2+ in?ux of 3-week-old rice seedlings cultivated in 0, 2.86 and 5.72 mM NO3?? conditions for 7 days. Then, 30 mM Cd2+ were added into the solution for 30–60 min. Net Cd ?ux of meristematic zone (B and D) and elongation zone (A and C) of the main root were monitored and steady-state Cd ?ux was recorded for 10 min. Bar indicates 50 mm in (A and B), the values are means ?? SE (n = 107), different letters on the bar indicate signi?cant differences at P = 0.05.
厂商
2019.10.15
NMT历史上的今天丨Plant Soil 刺曲霉可降低水稻的Cd浓度的文章发表
NMT历史上的今天2017年10月11日,鲁东大学资源与环境工程学院傅金民利用NMT在Plant and soil上发表了标题为Application of Aspergillus aculeatus to rice roots reduces Cd concentration in grain的研究成果。期刊:Plant and soil主题:在水稻根部施用刺曲霉可降低谷物中的Cd浓度标题:Application of Aspergillus aculeatus to rice roots reduces Cd concentration in grain影响因子:3.306检测指标:Cd2+流速检测部位:水稻根部(距离根尖500μm)Cd2+流实验处理方法:三周龄的水稻幼苗,50uM镉处理、50uM镉+ A. aculeatus处理7/14天Cd2+流实验测试液成份:50 μMCdCl2, 0.5 mMKCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.1mMNaCl, 0.1mMMgCl2 and 0.3mM2-(Nmorpholino)ethane sulfonic acid (MES)作者:鲁东大学资源与环境工程学院傅金民英文摘要‘Cd toxicity in rice’ events have resulted in vast public concern and uncertainty. Effective bioremediation could be accomplished via applying microbes that are capable of alleviating Cd content in rice grains.Here, we investigated the effect of inoculating Aspergillus aculeatus on tolerance, uptake and transportation of Cd in rice cultivated in Cd contaminated growth medium.A. aculeatus facilitated rice growth in Cd polluted growth medium and alleviated Cd toxic effects according to our observations on biomass, leaf and root length and grain yield. Cd accumulation analysis indicated that the plants which were inoculated with A. aculeatus exhibited minimum Cd level in all organs. Particularly in grain we observed a 40.5% reduction compared to the Cd only treated plants. Differences in Cd accumulation in rice inoculated with A. aculeatus might be attributed to the enhancement of cell wall-bound Cd, decreasing the Cd inorganic forms in roots, and inhibiting the expression of OsNRAMP5 and OsNRAMP1. A. aculeatus inoculation also led to minimum growth medium DTPA-Cd concentration, which possibly reduced the availability of the metals for plant uptake.These results suggested that A. aculeatus might potentially be applicable to improve Cd tolerance and reduce Cd transportation in grains of rice.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)大米事件中的镉毒性已引起公众的广泛关注和不确定性。通过应用能够减轻稻米中Cd含量的微生物,可以实现有效的生物修复。在这里,我们研究了接种刺曲霉对Cd污染的生长培养基中种植的水稻对Cd的耐受性,吸收和运输的影响。根据我们对生物量,叶片和根长以及籽粒产量的观察,A。aculeatus促进了水稻在Cd污染的生长培养基中的生长,并减轻了Cd的毒性作用。镉的积累分析表明,接种了棘孢曲霉的植物在所有器官中都表现出较低的镉水平。与仅使用镉处理的植物相比,特别是在谷物中我们观察到减少了40.5%。接种A. aculeatus的水稻中Cd积累的差异可能归因于细胞壁结合的Cd的增强,根部中Cd无机形式的减少以及抑制OsNRAMP5和OsNRAMP1的表达。刺果曲霉的接种还导致生长培养基中DTPA-Cd的浓度降至低,这可能会降低植物吸收金属的有效性。这些结果表明,刺果曲霉具有提高Cd耐性和减少Cd在水稻籽粒中运输的潜力。Supplementary Fig. 1 Effects of the Cd- resistant strain A. aculeatus on the net fluxes (a, c) and the mean fluxes (b, d) of Cd2+ in rice roots. Values are means ± SD. The different letters indicate the values that were significantly different at P
厂商
2019.10.12
NMT历史上的今天丨ENVIRON EXP BOT 铵营养与Cd胁迫关系 文章发表
NMT历史上的今天2017年10月10日,扬州大学王赪胤利用NMT在Sensors and Actuators B上发表了标题为Voltammetric simultaneous ion flux measurements platform for Cu2+, Pb2+ and Hg2+ near rice root surface: Utilizing carbon nitride heterojunction film modified carbon fiber microelectrode的研究成果。英文摘要Developing an available analysis platform for simultaneous heavy metal ion flux measurement at trace level is urgent for understanding the mechanisms of phytoremediation.Herein, oxygenous functionalized carbon nitride nanosheets assembled porous films on multi-walled carbon nanotube formed nano frameworks was firstly prepared on a carbon fiber disk microelectrode by an advanced drop-casting method. The as-prepared electrode shows low detection limit (The 1.0 × 10?13 mol L?1 for Cu2+, 1.8 × 10?11 mol L?1 for Pb2+ and 8.0 × 10?12 mol L?1 for Hg2+), acceptable linear range (6.6 × 10?12 ~ 8.5 × 10?6 mol L?1 for Cu2+, 8.1 × 10?10 ~ 8.5 × 10?6 mol L?1 for Pb2+ and 2.2 × 10?11 ~ 8.5 × 10?6 mol L?1 for Hg2+) and fine selectivity in simultaneous determination. The improved accumulation ability of modifier is attributed to improved conductivity and the porous morphology of the film, which may improve useful rate of the chelation groups.Based on the as-prepared electrode and a stepper motor, the voltammetric platform for simultaneous heavy metal ion flux measurement at trace level is fabricated for the first time. This platform can be utilized for mechanism investigation of simultaneous metal uptake on the surface of rice roots at trace level.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)为了了解植物修复的机理,迫切需要开发一种可用于同时进行痕量重金属离子通量测量的分析平台。在此,首先通过先进的滴铸法在碳纤维盘微电极上制备了在多壁碳纳米管形成的纳米框架上组装多孔膜的含氧官能化的氮化碳纳米片。所制备的电极显示出较低的检测限(对于Cu2+为1.0×10-13 mol L-1,对于Pb2+为1.8×10-11 mol L-1,对于Hg2+为8.0×10-12 mol L-1),可以接受线性范围(Cu2+为6.6×10-12?8.5×10-6 mol L-1,Pb2+为8.1×10-10?8.5×10-6 mol L-1和2.2×10-11?8.5×10-6 mol Hg2+的L-1)和同时测定的优良选择性。改性剂积累能力的提高归因于膜的导电性和多孔形态的改善,这可以提高螯合基团的有用率。基于准备好的电极和步进电机,首次制造了用于痕量水平同时重金属离子通量测量的伏安平台。该平台可用于研究水稻根部表面微量金属同时摄取的机理。Figure 4. (A) Photograph of the VPSIFM in determination of heavy metal ions near root surface of rice. (B) Testing positions of the voltammetric ion fluxes measurements near the root surface of the rice. Measurement of fluxes (outward positive) of Cu2+, Pb2+ and Hg2+ (error bars mean the standard error of 5 duplicate tests) across the root tips of rice, utilizing the voltammetric platform for simultaneous heavy metal ion flux measurements P-CN_T60/MWCNT/CFE. Ion flux measurement of (C) Cu2+, (D) Pb2+ and (E) Hg2+ in extracted solution at high concentration level. Ion flux measurements of (F) Cu2+,(G) Pb2+ and (H) Hg2+ in extracted solution at low concentration level. (Black and white)
厂商
2019.10.11
桂林理工大学丨植物重金属转运及胁迫信号研究应用培训
2019年10月16日,由中关村NMT联盟组织的非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)植物重金属转运及胁迫信号研究应用培训,将在桂林理工大学举行。桂林理工大学主讲内容非损伤微测技术(Non-invasive Micro-test Technology, NMT)是研究功能基因的一种技术,通过检测活体植物根茎叶与内/外环境间Ca/Cd/Na/K/N/O2...交换量的实时变化,揭示: 丙酮酸载体调控植物耐Cd的机制 硅酸化纳米壳增强水稻拒Cd能力 根瘤促进多氯联苯降解的直接证据 γ-谷氨酰半胱氨酸合成酶调控Cd解毒的机制 ......时间:2019年10月16日 星期三 8:30~12:00地点:桂林理工大学12栋12405会议室联系人:程老师 18515811370刘蕴琦 NMT高级顾问中关村非损伤微测技术产业联盟秘书长,《NMT 101问》、《NMT论文集》副主编。协助中国农大武维华院士、中科院植物所种康院士等课题组,设计了Cell、Plant Cell等研究成果中的非损伤离子流实验部分。近5年,直接协助国内学者发表的SCI文章共67篇,累计影响因子308.64。吴景涛 中关村NMT联盟认证高级售后工程师美国扬格(旭月北京)中国北区及西南区售后负责人,高级培训工程师,拥有近3年的售后服务经验。非损伤微测技术目前可检测的指标有:H+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、Mg2+、Cd2+、Cu2+、Pb2+、NH4+、NO3-、O2、H2O2、IAA。
厂商
2019.10.10
NMT活体基因功能研究专项基金 | 2019全国植物生物学大会
中关村NMT联盟将参加2019年10月11日~14日在四川成都召开的“2019全国植物生物学大会”。 为贯彻国家创新战略和应对国际科技竞争的新形势,新挑战,中关村NMT联盟受国家委托,向中国非损伤微测技术使用者提供设备、测试等各类基金资助,延续并扩大中国学者在NMT技术创新、产品研发、科研应用及产业化方面所积累的优势,确保中国科研人员及时抢占以非损伤微测技术为代表的,活体基因功能研究领域制高点。经相关申请审批流程,面向此次大会的“NMT活体基因功能研究专项基金”于9月底正式获批,相关情况如下:设备采购基金只面向2019全国植物生物学大会参会者,凡计划购置经中关村NMT联盟认证的非损伤微测设备,将提供¥100,000~1,000,000元的采购经费资助,资助力度为普通申请者的200%申请办法:联盟展位处(A25)登记备案,并于2020年3月31日前完成网络申请。实验测试基金只面向2019全国植物生物学大会参会者,提供非损伤微测技术实验总费用20%~50%的资助,资助力度为普通申请者的200%,资助上限为¥200,000元;申请办法:联盟展位处(A25)登记备案,并于2019年12月31日前完成网络申请。 联盟展位:A25 联系人:程老师,18515811370
厂商
2019.10.08
2019年旭月公司国庆放假安排
旭月公司2019年国庆放假安排如下:10月1日(周二)至10月7日(周一)放假7天。9月29日(周日)、10月12日(周六)公司正常上班。请广大客户提前安排好实验,放假期间如有问题咨询,可以拨打我公司电话400-06-98983转23进行留言,或点击公司主页在线客服进行留言,我们会在上班后第一时间回复您。
厂商
2019.09.27
NMT历史上的今天丨Front Plant Sci 硫化氢介导盐胁迫下耐盐和盐敏感杨树离子动态平衡成果发表
NMT历史上的今天2018年9月19日,北京林业大学陈少良、林善枝、赵楠、孙健利用NMT在Frontiers in Plant Science上发表了标题为Hydrogen Sulfide Mediates K+ and Na+ Homeostasis in the Roots of Salt-Resistant and Salt-Sensitive Poplar Species Subjected to NaCl Stress的研究成果。期刊:Frontiers in Plant Science主题:硫化氢介导盐胁迫和盐敏感杨树种根系中的K+和Na+稳态标题:Hydrogen Sulfide Mediates K+ and Na+ Homeostasis in the Roots of Salt-Resistant and Salt-Sensitive Poplar Species Subjected to NaCl Stress.影响因子:3.678检测指标:K+、Na+、H+流速检测部位:杨树根部(距离根尖300um)K+、Na+、H+流实验处理方法: 一年生的胡杨幼苗,在对照,对照加NaHS(50mM),NaCl(50mM)和NaCl(50mM)加上NaHS(50mM)这四种处理分别处理24小时和5天K+、Na+、H+流实验测试液成份:0.1 mM KCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.1 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM NaCl, 0.2 mM Na2SO4, and 0.3 mM MES, pH 4.0作者:北京林业大学陈少良、林善枝、赵楠、孙健英文摘要Non-invasive micro-test techniques (NMT) were used to analyze NaCl-altered flux profiles of K+, Na+, and H+ in roots and effects of NaHS (a H2S donor) on root ion fluxes in two contrasting poplar species, Populus euphratica (salt-resistant) and Populus popularis (salt-sensitive).Both poplar species displayed a net K+ efflux after exposure to salt shock (100 mM NaCl), as well as after short-term (24 h), and long-term (LT) (5 days) saline treatment (50 mM NaCl, referred to as salt stress). NaHS (50 μM) restricted NaCl-induced K+ efflux in roots irrespective of the duration of salt exposure, but K+ efflux was not pronounced in data collected from the LT salt stress treatment of P. euphratica.The NaCl-induced K+ efflux was inhibited by a K+ channel blocker, tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA) in P. popularis root samples, but K+ loss increased with a specific inhibitor of plasma membrane (PM) H+-ATPase, sodium orthovanadate, in both poplar species under LT salt stress and NaHS treatment. This indicates that NaCl-induced K+ loss was through depolarization-activated K+ channels. NaHS caused increased Na+ efflux and a corresponding increase in H+ influx for poplar roots subjected to both the short- and LT salt stress.The NaHS-enhanced H+ influx was not significant in P. euphratica samples subjected to short term salt stress. Both sodium orthovanadate and amiloride (a Na+/H+ antiporter inhibitor) effectively inhibited the NaHS-augmented Na+ efflux, indicating that the H2S-enhanced Na+ efflux was due to active Na+ exclusion across the PM. We therefore conclude that the beneficial effects of H2S probably arise from upward regulation of the Na+/H+ antiport system (H+ pumps and Na+/H+ antiporters), which promote exchange of Na+ with H+ across the PM and simultaneously restricted the channel-mediated K+ loss that activated by membrane depolarization. 中文摘要非侵入性微测试技术(NMT)用于分析NaCl中改变的根中K+,Na+和H+的通量分布以及NaHS(H2S供体)对两种对比杨树胡杨(Populus euphratica)根系离子通量的影响(耐盐)和Populus popularis(盐敏感)。在暴露于盐休克(100mM NaCl)之后,以及在短期(24小时)和长期(LT)(5天)盐水处理(50mM NaCl,参考)之后,两种杨树物种都表现出净K+外排。作为盐胁迫)。无论盐暴露的持续时间如何,NaHS(50μM)都限制了NaCl诱导的根中的K+流出,但是从胡杨的LT盐胁迫处理收集的数据中K+流出不明显。NaCl诱导的K+流出受到K+通道阻滞剂,四乙基氯化铵(TEA)在P.pularis根样品中的抑制,但K+损失随着特异性质膜抑制剂(PM)H+ -ATPase,原钒酸钠在杨树中的增加而增加。 LT盐胁迫和NaHS处理下的物种。这表明NaCl诱导的K+损失是通过去极化激活的K+通道。 NaHS导致Na+流出增加,并且受到短盐和LT盐胁迫的杨树根的H+流入相应增加。经受短期盐胁迫的胡杨(P. euphratica)样品中NaHS增强的H+流入量不显着。原钒酸钠和阿米洛利(Na+ / H+逆向转运蛋白抑制剂)均有效抑制NaHS增强的Na+流出,表明H2S增强的Na+流出是由于PM中的活性Na+排斥。因此,我们得出结论,H2S的有益作用可能源于Na+ / H+反向运输系统(H+泵和Na+ / H+反向运输)的向上调节,其促进Na+与H+在PM上的交换并同时限制通道介导的K+损失。通过膜去极化激活。FIGURE 1丨Effects of NaHS on NaCl shock-altered transient K+ kinetics within P. euphratica and P. popularis root samples. Young root samples of P. euphratica and P. popularis were equilibrated for 30 min in a basic solution [NaCl (0.1 mM), MgCl2 (0.1 mM), CaCl2 (0.1 mM), and KCl (0.5 mM)] supplemented with or without 25, 50, and 200 μM NaHS. Thereafter, K+ kinetics were recorded at meristems (300 μm from the root tip) for ca. 40 min after NaCl shock. The salt shock (100 mM NaCl) was given by adding acquired amount of NaCl stock (0.2 M, pH 6.0 adjusted with NaOH and HCl) to the measuring solution. Before the NaCl shock, steady-state K+ fluxes were recorded for 10 min. Each point is the mean of five individual plants and bars represent the standard error of the mean.
厂商
2019.09.19
Plant Physiol :山东大学、山东省农科院丨线粒体丙酮酸载体调控植物耐镉的机理
期刊:Plant Physiology主题:线粒体丙酮酸载体调控植物耐镉的机理标题:Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carriers Prevent Cadmium Toxicity by Sustaining the TCA Cycle and Glutathione Synthesis影响因子:5.949监测指标:Cd2+流速检测部位:拟南芥根(距离根尖400μm)Cd2+流速流实验处理方法:拟南芥种子萌发3天后,50μMCdCl2处理7天Cd2+流速流实验测试液成份:0.1 mM KCl, 0.05 mM CdCl2, 0.3 mM MES, pH 5.8作者:山东大学、山东省农科院张伟、高建伟、贺立龙英文摘要Cadmium (Cd) is a major heavy metal pollutant, and Cd toxicity is a serious cause of abiotic stress in the environment. Plants protect themselves against Cd stress through a variety of pathways.In a recent study, we found that mitochondrial pyruvate carriers (MPCs) are involved in Cd tolerance in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). Following the identification of MPCs in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) in 2012, most studies have focused on the function of MPCs in animals, as a possible approach to reduce the risk of cancer developing.The results of this study show that AtMPC protein complexes are required for Cd tolerance and prevention of Cd accumulation in Arabidopsis. AtMPC complexes are composed of two elements, AtMPC1 and AtMPC2 (AtNRGA1 or AtMPC3). When the formation of AtMPCs was interrupted by the loss of AtMPC1, glutamate could supplement the synthesis of acetyl-coenzyme A and sustain the TCA cycle. With the up-regulation of glutathione synthesis following exposure to Cd stress, the supplementary pathway could not efficiently drive the tricarboxylic acid cycle without AtMPC. The ATP content decreased concomitantly with the deletion of tricarboxylic acid activity, which led to Cd accumulation in Arabidopsis.More importantly, ScMPCs were also required for Cd tolerance in yeast. Our results suggest that the mechanism of Cd tolerance may be similar in other species.中文摘要(谷歌机翻)镉(Cd)是一种主要的重金属污染物,Cd毒性是环境中非生物胁迫的严重原因。植物通过各种途径保护自己免受Cd胁迫。在最近的一项研究中,我们发现线粒体丙酮酸载体(MPCs)参与拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)的Cd耐受。继2012年在酵母(酿酒酵母)中鉴定MPC后,大多数研究都集中在MPCs在动物体内的功能,作为降低癌症发展风险的可能方法。该研究的结果表明,AtMPC蛋白复合物是拟南芥中Cd耐受和预防Cd积累所必需的。AtMPC复合物由两种元素组成,AtMPC1和AtMPC2(AtNRGA1或AtMPC3)。当AtMPC的形成中断AtMPC的形成时,谷氨酸可以补充乙酰辅酶A的合成并维持TCA循环。随着暴露于Cd胁迫后谷胱甘肽合成的上调,补充途径不能在没有AtMPC的情况下有效地驱动三羧酸循环。随着三羧酸活性的缺失,ATP含量同时下降,导致拟南芥中Cd的积累。更重要的是,ScMPCs也是酵母中Cd耐受性所必需的。我们的研究结果表明,其他物种的镉耐受机制可能相似。结果表明:结果表明:在50μMCdCl2处理下,mpc1-1根系中的Cd2+吸收远高于野生型和互补株系(图C和D))。结果表明:通过在野生型和mpc1-1的根中添加1mM ATP,Cd2+吸收受到显着影响并变为外排。此外,野生型的Cd2+流速变化比mpc1-1更明显。野生型Cd2+流速从大约-10pmolcm-2s-1变为70pmol cm-2s-1,而mpc1-1从大约-20pmolcm-2s-1变为20pmol cm-2s-1(图b和c)。在MPC存在下,ATP有助于Cd2+的外排。
厂商
2019.09.18
NMT历史上的今天丨New Phytol ABA促进拟南芥/水稻适应水胁迫文章发表
NMT历史上的今天2012年9月16日,中科院南京土壤研究所施卫明、张建华、许卫锋利用NMT在New Phytologist上发表了标题为Abscisic acid accumulation modulates auxin transport in the root tip to enhance proton secretion for maintaining root growth under moderate water stress的研究成果。期刊:New Phytologist主题:脱落酸积累调节根尖中的生长素运输以增强质子分泌以在中度水胁迫下维持根生长标题:Abscisic acid accumulation modulates auxin transport in the root tip to enhance proton secretion for maintaining root growth under moderate water stress影响因子:6.645检测指标:H+流速检测部位:拟南芥、水稻根尖(从根冠分界处50、100、200、300、400、500、600、700、800、900、1000、1200、1500、1800、2000、2500、3000、3500、4000和5000μm)H+流实验处理方法:15日龄水稻幼苗,5%PEG 8000或0.1 μM ABA处理24小时H+流实验测试液成份:文献无推荐测试液:0.1mM CaCl20.3mM MES,pH6.0作者:中科院南京土壤研究所施卫明、张建华、许卫锋英文摘要Maintenance of root growth is essential for plant adaptation to soil drying. Here, we tested the hypothesis that auxin transport is involved in mediating ABA's modulation by activating proton secretion in the root tip to maintain root growth under moderate water stress.Rice and Arabidopsis plants were raised under a hydroponic system and subjected to moderate water stress (?0.47 MPa) with polyethylene glycol (PEG). ABA accumulation, auxin transport and plasma membrane H+‐ATPase activity at the root tip were monitored in addition to the primary root elongation and root hair density.We found that moderate water stress increases ABA accumulation and auxin transport in the root apex. Additionally, ABA modulation is involved in the regulation of auxin transport in the root tip. The transported auxin activates the plasma membrane H+‐ATPase to release more protons along the root tip in its adaption to moderate water stress. The proton secretion in the root tip is essential in maintaining or promoting primary root elongation and root hair development under moderate water stress.These results suggest that ABA accumulation modulates auxin transport in the root tip, which enhances proton secretion for maintaining root growth under moderate water stress. 中文摘要保持根系生长对植物适应土壤干燥至关重要。在这里,我们测试了生长素转运通过激活根尖中的质子分泌来介导ABA调节以在中等水分胁迫下维持根生长的假设。在水培系统下培养水稻和拟南芥植物,并用聚乙二醇(PEG)进行适度的水分胁迫(-0.47MPa)。除了初生根伸长和根毛密度之外,还监测根尖处的ABA积累,生长素转运和质膜H+-ATP酶活性。我们发现,适度的水分胁迫会增加根尖中ABA的积累和生长素的转运。另外,ABA调节涉及根尖中生长素运输的调节。运输的生长素激活质膜H+-ATPase以沿着根尖释放更多的质子,以适应中度水分胁迫。根尖中的质子分泌对于在中度水分胁迫下维持或促进初生根伸长和根毛发育是必不可少的。这些结果表明,ABA积累调节根尖中的生长素运输,这增强了质子分泌,从而在中度水分胁迫下维持根生长。Fig. 1 Effects of moderate water stress or exogenous ABA treatment on H+ ?ux along the root tip of rice or Arabidopsis plants (0–5000 lm from the root cap junction). Fifteen-day-old rice or Arabidopsis plants were exposed to control conditions (●, control), moderate water stress (○,5%PEG 8000) or exogenous ABA (▼, 0.1 lM) for 24 h in hydroponics. The values are the means and SD of six replicates from two independent experiments.
厂商
2019.09.17