样品为复方维生素,其中一项是核黄素磷酸钠,没找到核黄素磷酸钠的对照品,故用的核黄素对照品样品制备:先用水溶,然后用流动相稀释,流动相弱酸性做出的结果比标示量低了很多啊用核黄素对照品代替核黄素磷酸钠对照品,请问结果可信吗?
因为刚接触药品检验,在做核黄素磷酸钠的游离磷酸的测定的时候,做了几次都不合格。 按照标准要求进行对照及样品配制,对照品为蓝色的澄清液体,但是样品很浑浊,土黄色。在730nm处进行测定,结果不符合规定。 因为样品很浑浊,所以吸收值很大(2.0),大过了对照品; 我们把样品用0.45的滤膜过滤,吸收值(0.35)低于对照,但是我们怀疑过滤的影响太大,我们就再次过滤样品,吸收值又降低了一半(0.13). 请各位大侠帮帮忙啊!!!
[size=5]GB 14752-1993 食品添加剂 核黄素(维生素B2)[/size]
何莉萍CNS_08.148_核黄素[align=center][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]目录[/color][/size][/font][/align][font='等线'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]核黄素的物理性质[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]1[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]2[/size][/font][/url][font='等线'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]核黄素的光物理和光化学性质[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]第二章核黄素的生理功能[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]2[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]1[/size][/font][/url][font='等线'][size=14px]4[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]核黄素与铁代谢[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]2[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][/url][font='等线'][size=14px]5[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]核黄素与心血管疾病[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]第三章 核黄素的应用[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]1[/size][/font][/url][font='等线'][size=14px]5[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]6[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px]7[/size][/font][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px].[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]微生物法[/size][/font][/url][url=#][font='等线'][size=14px]参考文献[/size][/font][/url] [font='等线'][size=14px]9[/size][/font][align=center][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]第一章 核黄素的理化性质[/color][/size][/font][/align][size=16px]核黄素是一种水溶性[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B[/size][/font][size=16px]族维生素[/size][size=16px]。[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]920[/size][/font][size=16px]年第[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][size=16px]次发现[/size][size=16px],[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]933[/size][/font][size=16px]年第[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][size=16px]次从卵蛋白中分离出来[/size][size=16px],[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]935[/size][/font][size=16px]年核黄素的化学结构被鉴定[/size][size=16px]。[/size][size=16px]核黄素是人体新陈代谢酶系统的一个组成部分[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]也是生物生命活动中不可缺少的维生素之一[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]与人体内碳水化合物[/size][size=16px]、[/size][size=16px]脂肪及氨基酸代谢有着密切的关系[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]核黄素缺乏可以引起体内多种代谢障碍。[/size][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素的物理性质[/color][/size][/font][size=16px]水溶性维生素,但微溶于水,在[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]27.5℃[/size][/font][size=16px]下,溶解度为[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]12mg/100mL[/size][/font][size=16px]。可溶于氯化钠溶液,易溶于稀的氢氧化钠溶液,在碱性溶液中容易[/size][size=16px]分[/size][size=16px]解,在强酸溶液中稳定。耐热、耐氧化。光照及紫外照射引起不可逆的分解。[/size][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素的化学性质[/color][/size][/font][size=16px]分子式为[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]C[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]17[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]H[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]N[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]O[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][size=16px],化学结构式见图[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],具有一个核糖醇侧链的异咯嗪的衍生物。橙黄色晶体,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]280℃即熔化分解。在平常的湿度下稳定,而且不受空气中氧的影响。微溶于水,溶液呈现出强的黄绿色荧光。不溶于有机溶剂,在强酸溶液中稳定;在碱性条件下或者暴露于可见光或紫外线中时不稳定。食物中的核黄素很容易吸收,但单独服用,则只有15%的吸收率。核黄素在生物体储存量不多,多余的在尿液中排出,使尿液呈鲜黄色。核黄素在生物界分布极广,各种组织中均含有核黄素,广泛地分布在所有的叶菜,温血动物和鱼的肉中,但各种食物的含量相差很大,每[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]一[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]百[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]克[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]食物含量低的只有0.01mg,高的可[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]达[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3.5mg,以肝脏含量最高,浅色蔬菜和薯类含量最低。[/size][/font][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2021/07/202107251438050080_5202_1608728_3.png[/img][/align][align=center][size=13px]图[/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px]1[/size][/font][size=13px]核黄素的化学结构[/size][/align][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素的光物理和光化学性质[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在生物学上,核黄素具有重要作用,如:向光性,趋光性和光治疗,其本身又是一类重要的光敏化剂[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],研究表明这些重要的光生物学过程大多与核黄素的激发态有关。由于核黄素的吸收波段很宽(从紫外到可见光)且系间窜越的量子产额较高([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Φ[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]ISC[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]=[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]67[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],故无论在生物体内还是体外的组织和器官,只要能透过光,就能激发产生激发态,并与细胞内的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]或其他组分发生反应,导致细胞死亡或加速衰老[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]研究发现,核黄素在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]337nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]激光作用下,可产生激发三重态;而在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]248nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]激光作用下,既可产生激发三重态,又可生成氧化性自由基,核黄素氧化性自由基比激发三重态具有更强的氧化性[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]第二章核黄素的生理功能[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与生长发育[/color][/size][/font][size=16px]核黄素为机体健康和正常生长所必需,其形成的辅酶是许多氧化酶系统不可缺少的组成部分,在生物氧化过程中参与氢的传递,促进碳水化合物,蛋白质,脂肪,核酸的代谢。其缺乏可产生一些重要的影响,其中最主要的是生长障碍。杨焕民等人以[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][size=16px]日龄大鼠作实验时发现,低温下补充适量核黄素有利于生长激素和胰岛素的分泌,从而有利于生长;且通过增加肾上腺皮质束状带宽度及束状带和髓质细胞数,降低血清[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]T3[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]T4[/size][/font][size=16px]皮质醇水平,促进机体冷适应[/size][size=16px],[/size][font='arial'][size=16px]提高机体耐寒力。因此耐寒环境下适量补加核黄素有利于动物的生长[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。人体研究也得出相应的结论[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]7[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]:孕期核黄素摄入量与新生儿出生体重呈正相关,强化核黄素的食品能有效地改善小学生营养状况和促进其生长发育。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与铁代谢[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素的缺乏将导致人和动物铁吸收、储存、利用降低,其机制可能通过影响体内[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]NAD[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]FMN[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]氧化还原酶而起作用,核黄素缺乏时引起人和动物生长停滞,因而铁缺乏的同时,核黄素的严重缺乏将抑制儿童和幼龄动物对铁的需求,从而掩盖肌体铁的缺乏。因此,无论治疗核黄素缺乏病还是缺铁性贫血,同时补充铁和核黄素都是有益的[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]国内外大量的动物实验表明,核黄素缺乏可能通过影响小肠中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]NADH[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]FMN[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]氧化还原酶(即铁蛋白还原酶)活力而参与铁代谢[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][6][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],即核黄素缺乏可能影响到体内铁的吸收,从而导致缺铁性贫血[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](IDA)[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]发生率的增多。人群调查证实,核黄素缺乏者的平均血红蛋白量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](Hb)[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]与血清铁蛋白([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]SF[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])浓度均低于正常者,且其贫血率及缺铁率高于核黄素营养状况正常者,全血谷胱甘肽还原酶活性系数与[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Hb[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]SF[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]均呈负相关[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][9][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在核黄素与铁同时缺乏的研究中,动物实验表明,核黄素缺乏对缺铁大鼠的铁状况不但不进一步协同加速恶化,相反起一定程度的缓解作用[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]其[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]原因可能是核黄素与铁同时缺乏时,核黄素缺乏因明显地抑制了大鼠的生长,使体重增长缓慢、血容量扩充不明显,使机体对铁的需求相对降低,即核黄素缺乏对铁状况有“节约效应”。而单纯缺铁时,体重增长抑制远不如核黄素和铁同时缺乏时明显,血容量仍大量扩充,机体对铁的需求大,饲料又缺铁,就易出现铁营养状况的恶化。因此,二者同时缺乏时,核黄素缺乏通过其对生长的抑制作用而掩盖铁状况的恶化。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与癌[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]大量的流行病学和动物实验资料表明,核黄素等微量营养素具有防癌和抗癌作用。据调查发现[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]:[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]伊朗[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]中国等地居民因核黄素缺乏或严重摄入不足导致慢性食道炎普遍存在或食管癌区域高发[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][10][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。林英等研究也证实:补充核黄素组的食管癌前病人的食管上皮细胞增生转换的好转率和稳定率明显高于安慰剂组。可见核黄素可抑制食管上皮增生或促进其向正常转化[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]11[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。除影响上皮组织完整性外,核黄素还有抗突变作用,经[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Ames[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]试验检测,核黄素是黄曲霉毒素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]突变剂的很有效的拮抗物[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]12[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] 周纯先[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]13[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]指出:小鼠腹腔注射核黄素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]kg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]以上及饮水含核黄素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]时,可显著降低[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]HgCl2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]致小鼠微核作用 随后李建端等以大鼠作实验时发现,在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]RPMI1640[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]培养基中添加核黄素([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]26[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]130μmol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])可显著抑制甲基苄基亚硝胺([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]MBNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])的致细胞突变作用[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]14[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]4[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与心血管疾病[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素通过黄素辅酶参与机体的生物氧化还原反应,抑制脂质过氧化,减少自由基的生成,保护心血管系统免受氧化损伤。而核黄素缺乏会激发细胞凋亡,造成正常细胞损伤,削弱了机体的抗氧化能力。研究表明,氧化应激的过度和机体抗氧化能力的不足是心血管疾病和其他疾病的发病机制之一[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]15[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。单细胞凝胶电泳实验显示,冠状动脉疾病患者与正常健康者对照比较[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]损伤程度显著升高,而且损伤程度与总抗氧化能力呈负相关。冠心病患者总抗氧化能力下降,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]损伤增加,而且[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]损伤增加与年龄相关的抗氧化酶减少和修复能力的下降有关。核黄素作为抗氧化剂,可能有助于保护[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]免于受损。刘秀玲等[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][16][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]报道,适宜浓度的核黄素能降低过氧化氢诱导的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DNA[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]氧化损伤。殷慧群[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]等[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][17][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]研究证明,[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]通过核黄素干预后[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],有助于保护冠状动脉血管内皮,维持内皮功能的完整性[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]综上所述,核黄素是机体必需微量营养素之一,具有广泛的生理功能,世界卫生组织([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]WTO[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])将其列为评价人体生长发育和营养状况六大指标之一。但我国人均每日摄取入核黄素([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]VB2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])不足[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]尤见于儿童、青少年、孕妇,。因此,正确引导儿童的食物消费,优化膳食模式,增加富含核黄素等一些微量营养素食物的摄入,如:动物内脏,奶类,蛋类,豆制品及蔬菜,并对缺乏者采用适宜的干预措施和核黄素药物治疗,仍是当前营养工作中的一个重要环节。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]第三章 核黄素的应用[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]1[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6] 核黄素与放射性黏膜炎[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6] [/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]肿瘤患者在放疗、化疗过程中容易出现口腔黏膜炎、肠黏膜炎、胃溃疡等,严重时可导致全身性感染,危及生命。对于中晚期鼻咽癌,同期放化疗已经成为标准的治疗模式。然而同期放化疗在杀伤肿瘤细胞的同时也造成对正常组织的损伤,尤其是黏膜炎加重,降低了部分患者的耐受性,增加了患者的痛苦。在实际临床工作中也可能因为耐受性的问题而调整治疗强度,中断、甚至停止治疗。因此在治疗期间防治黏膜炎已成为鼻咽癌同期放化疗过程中面临的主要问题之一。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]素类药物对治疗黏膜炎和口腔溃疡有较好的疗效[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]18[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]9[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。蒋秀美等[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]报道,核黄素可用于预防造血干细胞移植后口腔黏膜炎,使黏膜炎损伤程度减轻,恢复时间比较快。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素缺乏间接地削弱了机体的抗氧化功能,而补充核黄素则可能增加机体的抗氧化功能,从而可以很好地预防黏膜炎和口腔溃疡,提高了放疗、化疗患者的耐受力[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][21][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3.2 核黄素与秋季腹泻[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]秋季腹泻是儿科最常见的疾病之一,估计我国[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]岁以下小儿中腹泻病平均 每年[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]次/人,而秋季腹泻占[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]87%[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]主要病原是轮状病毒。临床应用核黄素治疗小儿腹泻,增加了机体的抗氧化功能,使肠黏膜细胞得到快速修复,从而使其吸收和分泌功能恢复正常[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][21][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3.3 核黄素与烧伤[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素是一种可用于中小面积烧伤创面的安全、有效的外用药。大面积烧伤的患者长时间大剂量应用抗生素[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px], 可诱发核黄素缺乏, 最终导致真菌感染加重, 辅以核黄素治疗有利于防止真菌感染[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。其机制可能是核黄素参与了生物氧化作用和机体三大代谢过程[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px], 足量的核黄素使体内酸性物质减少, 不利于真菌生长, 从而使患者不易发生真菌感染[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][21][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3.4 [/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]核黄素与心血管疾病[/color][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=18px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=18px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]核黄素类药物对患者心脏功能有一定的改善作用[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px], 核黄素通过黄素辅酶参与机体的生物氧化还原反应, 抑制脂质过氧化, 减少自由基的生成, 保护心血管系统免受氧化损伤。[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]而核黄素缺乏会激发细胞凋亡[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px], 造成正常细胞损伤, 削弱了机体的抗氧化能力[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][21][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][align=center][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]第四章核黄素的检测[/color][/size][/font][/align][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]4[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].1.[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]高效液相色谱法[/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]原理[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]试样在稀盐酸环境中恒温水解,调[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]pH[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],用木瓜蛋白酶和高峰淀粉酶酶解,定容过滤后,滤液经反相色谱柱分离,高效液相色谱荧光检测器检测,外标法定量。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][size=16px].[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][size=16px].[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][size=16px]分析步骤[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].试样制备[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]取样品约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]500g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],用组织捣碎机充分打匀均质,分装入洁净棕色磨口瓶中,密封,并做好标记,避光存放备用。称取[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px](精确至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]01g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])均质后的试样(试样中维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的含量大于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]具塞锥形瓶中,加入[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]60mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]盐酸溶液,充分摇匀,塞好瓶塞。将锥形瓶放入高压灭菌锅内,在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]121[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]下保持[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]30min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],冷却至室温后取出。用[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]氢氧化钠溶液调[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]pH[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],加入[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]混合酶溶液,摇匀后,置于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]37[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]培养箱或恒温水浴锅中过夜酶解。将酶解液转移至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]容量瓶中,加水定容至刻度,用滤纸过滤或离心,取滤液或上清液,过[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]45μm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]水相滤膜作为待测液。(注:操作过程应避免强光照射)[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]不加试样,按同一操作方法做空白试验。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].仪器条件[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]a[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])色谱柱:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]C18[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]柱,柱长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]150mm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],内径[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6mm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],填料粒径[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5μm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],或相当者[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]b[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])流动相:乙酸钠溶液([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]05mol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])-甲醇([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]65[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]∶[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]35[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]) [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]c[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])流速:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]d[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])柱温:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]30[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]e[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])检测波长:激发波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]462nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],发射波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]522nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]f[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])进样体积:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20μL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].标准曲线的制作[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]将标准系列工作液分别注入高效液相色谱仪中,测定相应的峰面积,以标准工作液的浓度为横坐标,以峰面积为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].试样溶液的测定[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]将试样溶液注入高效液相色谱仪中,得到相应的峰面积,根据标准曲线得到待测液中维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的浓度。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].空白试验[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]要求空白试验溶液色谱图中应不含待测组分峰或其他干扰峰。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]精密度[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在重复性条件下获得的两次独立测定结果的绝对差值不得超过算术平均值的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]%。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]7[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].其他[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]当取样量为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]00g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]时,方法检出限为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]02mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],定量限为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]05mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]4[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].2[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]荧光分光光度法[/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]原理[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]440nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]500nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]波长光照射下发生黄绿色荧光。在稀溶液中其荧光强度与维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的浓度成正比。在波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]525nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]下测定其荧光强度。试液再加入连二亚硫酸钠,将维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]还原为无荧光的物质,然后再测定试液中残余荧光杂质的荧光强度,两者之差即为试样中维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]所产生的荧光强度。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]分析步骤[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].试样制备[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]试样的水解取样品约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]500g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],用组织捣碎机充分打匀均质,分装入洁净棕色磨口瓶中,密封,并做好标记,避光存放备用。称取[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px](精确至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]01g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],约含[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]200μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])均质后的试样于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]具塞锥形瓶中,加入[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]60mL0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mol[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的盐酸溶液,充分摇匀,塞好瓶塞。将锥形瓶放入高压灭菌锅内,在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]121[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]下保持[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]30min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],冷却至室温后取出。用氢氧化钠溶液调[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]pH[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]试样的酶解加入[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]混合酶溶液,摇匀后,置于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]37[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]培养箱或恒温水浴锅中过夜酶解。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]过滤将上述酶解液转移至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]容量瓶中,加水定容至刻度,用干滤纸过滤备用。此提取液在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]冰箱中可保存一周。注:操作过程应避免强光照射。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].氧化去杂质[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]视试样中核黄素的含量取一定体积的试样提取液(约含[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])及维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]标准使用溶液分别置于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的带盖刻度试管中,加水至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]15mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。各管加[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]冰乙酸,混匀。加[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL30g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]L[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]高锰酸钾溶液,摇匀,放置[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],使氧化去杂质。滴加[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]%过氧化氢溶液数滴,直至高锰酸钾的颜色褪去。剧烈振摇试管,使多余的氧气逸出。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]的吸附和洗脱[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]吸附柱硅镁吸附剂约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]用湿法装入柱,占柱长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px](约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5cm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])为宜(吸附柱下端用一小团脱脂棉垫上),勿使柱内产生气泡,调节流速约为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]60[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]滴/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]min[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。(注:可使用等效商品柱)[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]过柱与洗脱将全部氧化后的样液及标准液通过吸附柱后,用约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]热水淋洗样液中的杂质。然后用[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]洗脱液将试样中维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]洗脱至[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]容量瓶中,再用[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]水洗吸附柱,洗出液合并至容量瓶中,并用水定容至刻度,混匀后待测定。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].标准曲线的制备[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]分别精确吸取维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]标准使用液[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]9mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]25mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px](相当于[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]9μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]25μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0μg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])或取与试样含量相近的单点标准按[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]和[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]操作。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].试样溶液的测定[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]于激发光波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]440nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],发射光波长[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]525nm[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],测量试样管及标准管的荧光值。待试样管及标准管的荧光值测量后,在各管的剩余液(约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]~[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]7mL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px])中加[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1mL20[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]%连二亚硫酸钠溶液,立即混匀,在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20s[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]内测出各管的荧光值,作各自的空白值。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].精密度[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]在重复性条件下获得的两次独立测定结果的绝对差值不得超过算术平均值的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]%。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]7[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].其他[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]当取样量为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]00g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]时,方法检出限[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]006mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px],定量限:[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]02mg[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]/[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100g[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]4[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6].[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]3[/color][/size][/font][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]微生物法[/color][/size][/font][size=16px]某一种微生物的生长繁殖必需某一种维生素,;例如干酪乳酸杆菌的生长需要核黄素,培养基中若缺乏这种维生素该细菌则不能生长。在一定条件下,该细菌生长情况,以及它的代谢物乳酸的浓度与培养基中该维生素含量成正比,因此可以用浑浊度的测定法来测试试样中核黄素的含量。[/size][size=16px]微生物法测定食物中核黄[/size][size=16px]素[/size][size=16px]是经典方[/size][size=16px]法,[/size][size=16px]特异性和灵敏度均高[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]但方法费时[/size][size=16px],[/size][size=16px]周期较长[/size][size=16px],已从国家标准中删除。[/size][font='等线'][size=14px][color=#2e75b6]参考文献[/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][1]Bensasson R V,Land E J,Truscott T G.Flash Photolysis and Pulse Radiolysis in Biologyand Medicine [J],Oxford:Pergamon Press,1993:140-147[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][2]Ito K,Inous Yamamoto K,etal.8-Hydroxyguanosine formation at the5-GG3 sequences in double-stranded DNA by UV radiation with riboflavin[J].Journal Biological Chemistry.1993:268:13220-13227[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][3]Frier C Fontecave M,Mouscadet J,et al. Flavin-oligonucleotide conjugates sequence specific photocleavage of DNA [J].Chemical Communication,1998:2457-2458[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]4[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]]陆长元,韩镇辉,蔡喜臣,陈雨玲,姚思德.核黄素(维生素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]B2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px])的光物理和光化学性质[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].中国科学([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]B[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]辑化学),[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2000[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]05[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]428[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]435[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][5]Delane AA,Powers HJ.The influence of riboflavin deficiency on absorption and liver storage of iron in the growth rat[J].Br J Nutr,1986,8(1):41.[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][6]Delane AA,Powers HJ.Efeccts of combined riboflavin and iron deficicncy on the hematological status and iron concert ration of the rat[J].JNutr,1986,116:1257.[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]7[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]]柳启沛,陈文根,张琪,翁聪颖,朱朝勇,邓春勤,朱元桢,张亚非,沈镇平,徐达道.铁、核黄素与贫血关系研究及其防治应用[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].医学研究通讯,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]1994[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]29[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]30[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]8[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]]项昭保,戴传云,朱蠡庆.核黄素生理生化特征及其功能[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].食品研究与开发,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2004[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]06[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]90[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]92[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]+[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]95[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]9[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]][/size][/font][size=12px]陈文[/size][size=12px]根.核黄素缺乏对铁代谢的影响[/size][size=12px][[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][size=12px]]国外医学+卫生学分册[/size][size=12px],[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]1990[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]5[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]) [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]283[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][10][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff]Mu?ozN.,GrassiA.,QiongShen,etal.PRECURSORLESIONSOFOESOPHAGEALCANCERINHIGH-RISKPOPULATIONSINIRANANDCHINA[J].TheLancet,1982,319(8277):876-879.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff][11]林英,王旗,朱明君,陈萍萍.核黄素营养水平对食管上皮增生转化的影响[J].河南预防医学杂志,1995(04):192-193.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff][12]郭志成.维生素对突变的抑制作用[J].解放军预防医学杂志,1993(05):396-400.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff][13]周纯先,肖棣,王帮霞,王允滋.维生素B2拮抗HgCl2致小鼠微核作用的研究[J].癌变.畸变.突变,1995(04):220-221.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][back=#ffffff][14]李建端,赵勤,李红娅,苗健,关链,陈本懋.核黄素等抗甲基苄基亚硝胺的致细胞突变作用[J].河南医科大学学报,1995(03):227-230.[/back][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]15[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]DemirhagR,YilmazR,KocyigitA.RelationshipbetweenDNAdamage,totalantioxidantcapacityandcoronaryarterydisease[J].MutatRes,2005,570(2):197-20[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]16]刘秀玲,王俐,姜春花,等.硫胺素和核黄素对H2O2诱导的DNA氧化损伤的影响[J[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]上海交通大学学报:医学版[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2009[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]29(9):1049-1052.[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]17[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]殷慧群,陈冬云,周云泳[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]核黄素对心肌缺血再灌注损伤时一氧化氮及其合酶的影响[J[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px].皖南医学院学报[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2005[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]24(3):179-181.[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]18[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]符起亚,邓芳成,张治汉.长效核黄素治疗复发性口腔溃疡患者疗效观察及对血清[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]IL[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]水平的影响[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].海南医学院学报,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2009[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]15[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]10[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]1303[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]1304[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]19[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]史建国.核黄素磷酸钠防治放射性口腔咽炎的临床研究[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].中国肿瘤临床与康复,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2007[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]14[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]3[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]272[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]273[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]20[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]蒋秀美,芮雪芹,濮益琴,等.长效核黄素预防血液病造血干细胞移植后口腔黏膜炎[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].江苏医药,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2009[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]35[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]6[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]727[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]728[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px][21][/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]李娜,杨建云,肖炳坤,黄荣清.核黄素临床应用研究进展[[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]J[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]].解放军医药杂志,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2012[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]24[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]04[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]):[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]52[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]54[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px].[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px][[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]22[/size][/font][font='arial'][size=12px]] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=12px]GB5009[/size][/font][size=12px].[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]85[/size][/font][size=12px]—[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]2016[/size][/font][size=12px]食品安全国家标准 食品中维生素[/size][font='times new roman'][size=12px]B2[/size][/font][size=12px]的测定[/size]
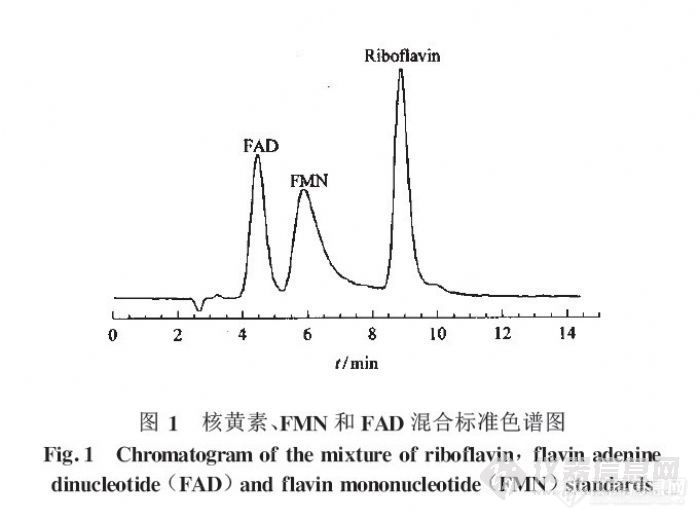
高效液相色谱法测定大鼠血浆和全血中核黄素的含量韦京豫, 郭长江, 杨继军, 蒋与刚, 李云峰, 徐琪寿(军事医学科学院卫生学环境医学研究所,天津)摘要:为了直接反映核黄素营养状况对血中核黄素水平的影响,建立了高效液相色谱测定大鼠血浆及全血中核黄素含量的方法。采用Diamonsil C18色谱柱250mmx4.6mm i.d.5um)分离,以甲醇5mol/l乙酸铵(体积比为1.2ml/min)为流动相,流速1.2ml/min,荧光检测器检测(激发波长450nm,发射波长:520nm)。样品经乙腈、三氯甲烷处理后进样分析。核黄素测定的线性范围5-200nmol/l,最低检测限为2.5nmol/l(s/n=2),日内测定的峰面积的相对标准偏差(RSD)为1.2%,日间测定的RSD=4.3%。核黄素在血浆样品中的加标回收率为97.0%-104%,在全血样品中的加标回收率为97.4%-104.4%.关键词:高效液相色谱法;核黄素;血浆;全血;大鼠http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2012/07/201207241234_379356_2355529_3.jpg
求USP36中核黄素的测定相关章节,急需要用到谢谢支持。
维生素B2又称核黄素,如果缺乏容易导致疲劳、乏力、喉咙痛、眼睛红痒、紫红色舌头、肌肤红疹、口腔生殖系统综合征,其对光比较敏感,容易被光所破坏。主要来源于猪肝、麸皮、鸡蛋、黄豆、核桃、牛肉、牛奶、花生仁、菠菜、油菜、瘦猪肉、鲫鱼、粳米、小麦、豆角等。
[color=red]荧光[/color]法测定面粉中的核黄素
[size=5]GBT 7297-2006 饲料添加剂 维生素B2(核黄素)[/size]
[color=#444444]用高效液相色谱测定核黄素的时候 前期应该用什么溶液洗柱子,AB流动相用 甲醇:乙酸铵 是否35:65 可行?谢谢大神[/color]
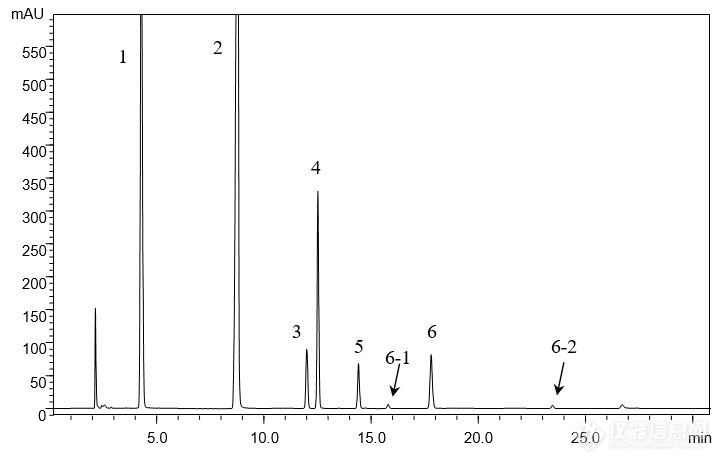
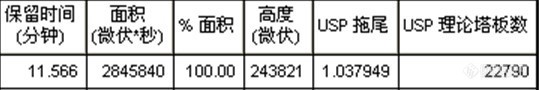
[align=center][b]注射用水溶性维生素的分析(1)[/b][/align][align=center][b]——维生素C钠、烟酰胺、泛酸钠、盐酸吡哆辛、硝酸硫胺、核黄素磷酸钠[/b][/align][align=center][b][/b][/align][align=left]客户提供了注射用水溶性维生素粉针剂及对照品(维生素C钠、烟酰胺、泛酸钠、盐酸吡哆辛、硝酸硫胺、核黄素磷酸钠),要求本实验室依据客户所提供方法筛选合适色谱柱,实现粉针剂中各组分物质的良好分离,同时满足方法中对分离度及理论塔板数的要求。[/align][align=left][/align][align=left]首先,依据客户提供的色谱条件,对对照品溶液进行分析。尝试使用不同填料类型的色谱柱,包括CAPCELL PAK C[sub]18[/sub] MGII,AQ S5,AQ S3,SUPERIOREX ODS,CAPCELL PAK ADME及PFP色谱柱。[/align][align=left][/align][align=left]由于不同色谱柱的分离选择性不同,最终发现CAPCELL PAK C[sub]18 [/sub]MGII色谱柱在完全按照客户提供方法的前提下能够得到最佳分离结果,对照品溶液中各组分均能够得到良好分离(如图1),分离度均在3.0以上,满足客户1.5要求;理论塔板数按核黄素计为103983,满足客户大于15000的要求(见表1)。[/align][align=left][/align][align=center][img=,690,443]http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2018/01/201801041022_5661_2222981_3.jpg!w690x443.jpg[/img][/align][align=center]图1 CAPCELL PAK C[sub]18[/sub] MGII分析对照品溶液结果[/align][align=center] 1. 维生素C钠 2. 烟酰胺 3. 泛酸钠 4. 盐酸吡哆辛 5. 硝酸硫胺 6, 6-1, 6-2 核黄素磷酸钠[/align][align=left][img=,690,270]http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2018/01/201801041022_1444_2222981_3.jpg!w690x270.jpg[/img][/align][align=left][/align][align=left][/align][align=center]表1 CAPCELL PAK C[sub]18 [/sub]MGII分析对照品溶液结果详表[/align][align=center][img=,458,316]http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2018/01/201801041022_2894_2222981_3.jpg!w458x316.jpg[/img][/align][align=center][/align][align=center]在上述色谱条件下,继续使用CAPCELL PAK C[sub]18[/sub] MGII色谱柱对粉针剂供试品溶液进行分析,各待测组分及相邻杂质均能够得到良好分离,结果见图2、图3及表2。[/align][align=center][/align][align=center][img=,682,427]http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2018/01/201801041023_7282_2222981_3.jpg!w682x427.jpg[/img][/align][align=center]图2 CAPCELL PAK C[sub]18[/sub] MGII分析供试品及空白溶液结果[/align][align=center]1. 维生素C钠 2. 烟酰胺 3. 泛酸钠 4. 盐酸吡哆辛 5. 硝酸硫胺 6, 6-1, 6-2 核黄素磷酸钠[/align][align=center][/align][align=left][img=,690,200]http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2018/01/201801041023_5300_2222981_3.jpg!w690x200.jpg[/img][/align][align=left][/align][align=center][img=,690,455]http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2018/01/201801041024_9636_2222981_3.jpg!w690x455.jpg[/img][/align][align=center]图3 CAPCELL PAK C[sub]18[/sub] MGII分析供试品溶液结果放大图[/align][align=center] [/align][align=center]表2 MGII分析供试品溶液结果详表[/align][align=center][img=,487,538]http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2018/01/201801041024_7687_2222981_3.jpg!w487x538.jpg[/img][/align][align=center][/align]
食品安全国家标准 食品添加剂 姜黄素
专家老师:您好!我想请问您——荧光素钠的激发波长和发射波长分别在多少nm处?核黄素的激发波长和发射波长的位置?多谢您!
急用!一直没找到,实验室又没有大黄素的标准品。请问谁有大黄素的标准光谱图,给我发一张吧!我的邮箱:HCM2100amy@hsbiotech.com谢谢了![em0808]
关于发布《食品添加剂核黄素5'-磷酸钠》(GB28301-2012)等71项食品安全国家标准的公告(卫生部公告2012年第7号) 2012年 第7号 根据《中华人民共和国食品安全法》和《食品安全国家标准管理办法》的规定,经食品安全国家标准审评委员会审查通过,现发布《食品添加剂核黄素5'-磷酸钠》(GB28301-2012)等71项食品安全国家标准。其编号和名称如下:GB 28301-2012食品添加剂 核黄素5'—磷酸钠GB 28302-2012食品添加剂 辛,癸酸甘油酯GB 28303-2012食品添加剂 辛烯基琥珀酸淀粉钠GB 28304-2012食品添加剂 可得然胶GB 28305-2012食品添加剂 乳酸钾GB 28306-2012食品添加剂 L-精氨酸GB 28307-2012食品添加剂 麦芽糖醇和麦芽糖醇液GB 28308-2012食品添加剂 植物炭黑GB 28309-2012食品添加剂 酸性红(偶氮玉红)GB 28310-2012食品添加剂 β-胡萝卜素(发酵法)GB 28311-2012食品添加剂 栀子蓝GB 28312-2012食品添加剂 玫瑰茄红GB 28313-2012食品添加剂 葡萄皮红GB 28314-2012食品添加剂 辣椒油树脂GB 28315-2012食品添加剂 紫草红GB 28316-2012食品添加剂 番茄红[/t
GB 26405-2011 食品安全国家标准 食品添加剂 叶黄素
最近,要开展食品中叶黄素的检测,存在叶黄素的标准品很贵,也很难购买在这里,也很想请高人们指点一下,检测过程中应注意哪些注意事项?
各位大叔大婶,谁有茶黄素的标准曲线图,万分火级!感谢!!
GB 317-2006白砂糖.pdfGB 2717-2003 酱油卫生标准.pdfGB 2718-2003 酱卫生标准 .pdfGB 2719-2003 食醋卫生标准.pdfGB 2720-2003 味精卫生标准.pdfGB 2721-2003 食用盐卫生标准.pdfGB 5461-2000 食用盐.pdfGB 18186-2000 酿造酱油.pdfGB 18187-2000 酿造食醋.pdfGBT 8967-2000谷氨酸钠(99味精).pdfGBT 19828-2005 食盐定点生产企业质量管理技术规范.pdfGBT 20293-2006 油辣椒.pdfNYT 857-2006 番茄粉 .pdfNYT 1053-2006 绿色食品 味精.pdfNYT 422-2006 绿色食品 食用糖.pdfQB 2238.1-2005 强化营养盐 钙强化营养盐.pdfQB 2238.2-2005 强化营养盐 锌强化营养盐.pdfQB 2238.3-2005 强化营养盐 硒强化营养盐.pdfQB 2238.4-2005 强化营养盐 铁强化营养盐.pdfQB 2238.5-2005 强化营养盐 核黄素强化营养盐.pdfQBT 2343.2—1997 赤砂糖试验方法.pdfQBT 2743-2005 泡菜盐.pdf
现发布《食品添加剂核黄素5'-磷酸钠》(GB28301-2012)等71项食品安全国家标准。 2012年 第7号 根据《中华人民共和国食品安全法》和《食品安全国家标准管理办法》的规定,经食品安全国家标准审评委员会审查通过,现发布《食品添加剂核黄素5'-磷酸钠》(GB28301-2012)等71项食品安全国家标准。其编号和名称如下:GB 28301-2012食品添加剂 核黄素5'—磷酸钠GB 28302-2012食品添加剂 辛,癸酸甘油酯GB 28303-2012食品添加剂 辛烯基琥珀酸淀粉钠GB 28304-2012食品添加剂 可得然胶GB 28305-2012食品添加剂 乳酸钾GB 28306-2012食品添加剂 L-精氨酸GB 28307-2012食品添加剂 麦芽糖醇和麦芽糖醇液GB 28308-2012食品添加剂 植物炭黑GB 28309-2012食品添加剂 酸性红(偶氮玉红)GB 28310-2012食品添加剂 β-胡萝卜素(发酵法)GB 28311-2012食品添加剂 栀子蓝GB 28312-2012食品添加剂 玫瑰茄红GB 28313-2012食品添加剂 葡萄皮红GB 28314-2012食品添加剂 辣椒油树脂GB 28315-2012食品添加剂 紫草红GB 28316-2012食品添加剂 番茄红GB 28317-2012食品添加剂 靛蓝GB 28318-2012食品添加剂 靛蓝铝色淀GB 28319-2012食品添加剂 庚酸烯丙酯GB 28320-2012食品添加剂 苯甲醛GB 28321-2012食品添加剂 十二酸乙酯(月桂酸乙酯)GB 28322-2012食品添加剂 十四酸乙酯(肉豆蔻酸乙酯)GB 28323-2012食品添加剂 乙酸香茅酯GB 28324-2012食品添加剂 丁酸香叶酯GB 28325-2012食品添加剂 乙酸丁酯GB 28326-2012食品添加剂 乙酸己酯GB 28327-2012食品添加剂 乙酸辛酯GB 28328-2012食品添加剂 乙酸癸酯GB 28329-2012食品添加剂 顺式-3-己烯醇乙酸酯(乙酸叶醇酯)GB 28330-2012食品添加剂 乙酸异丁酯GB 28331-2012食品添加剂 丁酸戊酯GB 28332-2012食品添加剂 丁酸己酯GB 28333-2012食品添加剂 顺式-3-己烯醇丁酸酯(丁酸叶醇酯)GB 28334-2012食品添加剂 顺式-3-己烯醇己酸酯(己酸叶醇酯)[
众位亲,求助一篇文献,叶黄素Lutein,FCC10中的质量标准。谢谢
《SN/T 3866-2014 出口保健食品中酚酞和大黄素的测定 液相色谱-质谱/质谱法》这个标准中要求过0.22微米孔径的有机相滤膜,可是过完滤膜后损失很大,换成0.45微米滤膜后还是损失很大,100ppb的标准溶液过完滤膜后就剩4ppb了。这个问题要怎么解决?
姜黄素是从姜科、天南星科中的一些植物的根茎中提取的一种化学成分,其中,姜黄约含3%~6%,是植物界很稀少的具有二酮的色素,为二酮类化合物。姜黄素为橙黄色结晶粉末,味稍苦。不溶于水。在食品生产中主要用于肠类制品、罐头、酱卤制品等产品的着色。医学研究表明,姜黄素具有降血脂、抗肿瘤、抗炎、利胆、抗氧化等作用。 姜黄素 Curcumin Turmeric yellow, Diferuloylmethane 1,6-Heptadiene-3,5-dione,1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)- C21H20O6; 368.37 橙黄色结晶性粉末, 熔点183°。不溶于水及乙醚, 溶于乙醇及冰醋酸。 有机酸及酚类。
12月1日起,多项与食品质量直接相关的国家标准将正式实施,其中既有《运动饮料》等涉及具体食品的产品标准,也有《婴幼儿配方粉企业良好生产规范》等涉及企业质量安全管理的生产标准,更有《保健食品中大豆异黄酮的测定方法 高效液相色谱法》等与食品安全相关的检测标准,还有《食品用塑料自粘保鲜膜》这样的包装标准和《塑料一次性餐饮具通用技术要求》这样的通用标准,它们将一起进入我国食品安全规范的大家庭,为食品安全保驾护航。 标准对兴奋剂等方面要求更严,运动饮料严禁添加世界反兴奋剂机构最新版规定的禁用物质。更新后的《运动饮料》将运动饮料定义为:“营养素及其含量能适应运动或体力活动人群的生理特点,能为机体补充水分、电解质和能量,可被迅速吸收的饮料”,首次强调运动饮料被机体迅速吸收的特点。 同时,新国标还取消了产品分类、对净含量的要求和“国际奥委会禁用物质”的附录。在理化指标上,放宽了钠和钾含量的范围,删除了抗坏血酸、硫胺素及其衍生物、核黄素及其衍生物、钙、镁等指标。同时,细化了卫生指标,要求铅含量≤0.3毫克/升;砷≤0.2毫克/升;每毫升样品中含有的菌落总数≤30000;不得检出致病菌。此前,我国尚未有一次性塑料餐具的国家标准,而是由每个企业制定企业标准,一次性塑料饭盒等不可降解餐具长期无标准可依,虽未明文禁止,却始终没有合法身份。12月1日起施行的国标《塑料一次性餐饮具通用技术要求》将彻底结束这一现状,长期不被认可的一次性塑料饭盒等不可降解餐具将有合法地位。 除此之外,标准还对一次性餐饮具的范围进行了明确的界定:是指预期用餐或类似用途的器具,包括一次性使用的餐盒、盘、碟、刀、叉、勺、筷子、碗、杯、罐、壶、吸管等,但不包括无预期用餐目的或类似用途的食品包装物,如生鲜食品托盘、酸奶杯、果冻杯等。同时,对餐饮具的耐热水性能、耐热油性能、漏水性能、负重性能以及微波炉耐温性能等,都作了具体的规定。 从12月1日起正式实施的国标《食品用塑料自粘保鲜膜》增加了对原料的技术要求,对于使用的树脂要求必须为“食品级”原料。而且,可用于包装食品的保鲜膜将标示“食品用”字样,并将标示出“不能接触带油脂食品”、“不得微波炉加热”、“不得高温使用”等警示性语言。 对于我国的广大婴幼儿配方企业来说,从12月1日起开始实施的国家标准《婴幼儿配方粉企业良好生产规范》,为其如何生产质量安全可靠的婴幼儿配方奶粉设定了“规矩”。该标准规定了婴幼儿配方生产企业在原材料采购、产品加工、包装及贮运等过程中,有关人员、建筑、设施、设备的设置,以及卫生、生产过程、产品品质等管理应达到的条件和要求,以确保提供安全、可靠、健康的产品。 以原材料为例,标准从原材料的采购与处理、原材料的卫生与质量管理等方面都进行了严格的规定,如标准规定,原料购进后对来源、规格、包装情况进行初步检查,按验收制度的规定填写入库账、卡,入库后应向质检部门申请取样检验。外包装有破损的原料应单独存放并有标示,在检验合格后方可使用。
紫外分光光度法测定盐酸麻黄素注射液含量关键词: 麻黄素;可见和紫外分光光度法[摘要] 目的:探讨盐酸麻黄素注射液含量测定的新方法,以求更快速、准确地适应临床用药需要。方法:用不同厂家不同批号的盐酸麻黄素注射液做供试品,用标准麻黄素做对照品,用紫外分光光度计测出标准品的最大吸收度,求出浓度与吸收度关系,得其回归方程,测其回收率。求出含量与药典法进行比较。结果:在256±1 nm处有最大吸收,以256 nm为测定波长,盐酸麻黄素浓度与吸收度呈标准曲线线性范围0.2~1.2 mg/ml(r=0.999 9),平均回收率为(100.31±1.02)%,两种方法测定结果差异无显著性(P>0.05)。结论:紫外分光光度法,可以做为盐酸麻黄素注射液含量测定的新方法。[中国图书资料分类法分类号] R 974.3;O 657.32 [文献标识码] A[文章编号] 1000-2200(2000)05-0380-02 盐酸麻黄素是拟肾上腺素药,目前对该病及其制剂的含量测定方法有非水滴定法[1]、银量法[1]及中和法[2]。本文采用紫外分光光度法[1],测定盐酸麻黄素注射液的含量[3],并与1995年版药典的非水滴定法进行比较,兹作报道。1 材料与方法1.1 仪器 Du-640型紫外分光光度计(美国贝克曼公司)。1.2 试药 盐酸麻黄素对照品,盐酸麻黄素注射液(上海信谊制药厂,批号951201-1,951201-2;无锡市第七制药厂,批号960117-1,960117-2,960610;规格均为1 ml∶50 mg)。1.3 测定方法 (1)盐酸麻黄素紫外吸收光谱:取盐酸麻黄素对照品适量,用蒸馏水溶解并配制成0.6 mg/ml的溶液,以蒸馏水为空白,在230~300 nm波长之间扫描,在256±1 nm波长处有最大吸收,故采用256 nm为测定波长。(2)标准曲线的绘制:精密称取经105℃干燥至恒重的盐酸麻黄素对照品50 mg,置25 ml量瓶中,加水溶解并稀释至刻度,摇匀。精密量取该药液1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0、5.0、6.0 ml分别置10 ml量瓶中,加水稀释至刻度,摇匀,以水为空白,在256 nm处分别测定吸收度。结果表明,在0.2~1.2 mg/ml浓度范围内,浓度与吸收度呈良好的线性关系。得其回归方程为:A=0.8256 C+0.012 0(r=0.999 9,n=6)。(3)稳定性实验:取(2)项下的各溶液于配制后0、1、2、3、4、8、16、24 h分别测吸收度,结果几无变化。(4)回收率试验:精密称取经105℃干燥至恒重的盐酸麻黄素对照品约25 mg,置50 ml量瓶中,加水溶解并稀释至刻度,以水为空白,在256 nm波长处依法测定吸收度,求出回收率。(5)样品测定:取不同批号的盐酸麻黄素注射液,精密量取1 ml,分别置于100 ml量瓶中,加水稀释至刻度,摇匀,以水为空白,在256 nm处测吸收度,计算其含量,并将本法测定的结果与中国药典1995年版收载的非水滴定法测定的结果进行比较。1.4 统计学方法 采用配对t检验。2 结果 紫外分光光度法回收率试验结果见表1;与药典法测定样品中盐酸麻黄素注射液的含量结果比较见表2。表1 回收率试验结果(n=5) 编号 加入量(mg) 测得量(mg) 回收率(%) ±s(%) 1 26.40 26.42 100.08 2 24.80 25.20 101.61 3 25.20 25.08 99.52 100.31±1.02 4 24.30 24.57 101.11 5 25.00 24.81 99.24 表2 两种方法测定结果比较(ni=15;±s) 测定方法 标示量(%) ±sd td P 紫外分光光度法药典法 100.17±1.07100.18±0.48 0.01±0.80 0.02 >0.05 3 讨论 盐酸麻黄素注射液是卫生部规定的控制药品。为保证患者用药的准确有效,防止在生产这类药品过程中盐酸麻黄素原料的流失,对其含有盐酸麻黄素的药品进行快速、简便、准确的含量测定显得尤为重要。传统的本品测定方法,不但操作过程繁琐,消耗试药量大,且非水滴定法中的醋酸汞试剂对人体有害,污染环境。 麻黄素属β肾上腺素受体激动剂,可直接或间接激动肾上腺素受体。对心血管系统、支气管平滑肌、中枢神经系统都有较强的作用。在临床上应用较为广泛且剂量要求十分准确,所以对其含量的准确、快速测定更为重要。特别是临床上经常使用“盐酸麻黄素滴鼻剂”是医院自配药品,效期短,配制频繁,在其准确的基础上,快速测定及时保证药品的临床供应,并指导临床用药有一定的意义。 两种方法测定结果差异无显著性(P>0.05),表明紫外分光光度法可以做为盐酸麻黄素注射液的含量测定新方法。且本法操作简便、快速、准确,重复性好。作者简介:郗 颖(1967-),女,安徽灵璧县人,药剂师.[参考文献][1]中华人民共和国卫生部药典委员会.中国药典二部[M].广州:广东科学技术出版社,1995.18,693~694.[2]中华人民共和国卫生部药政局.中国医药制剂规范*西药制剂[M].北京:中国医药科学技术出版社,1996.166~167.[3]熊凤英,简 洁,周淑群.紫外分光光度法测定米非司酮血药浓度[J].中国医院药学杂志,1998,18(6)∶262.
大黄素是从大黄的干燥根及根茎提取而得,味苦,具有泻热通肠,凉血解毒,逐瘀通经等功效。2010年药典中大黄中的大黄素就是用HPLC法检测,而大黄素在减肥、降脂、排毒、抗衰老等方面有很大的作用,保健食品也开始加入大黄素,下面我就简单说说说。1 仪器与试剂仪器:Waters2695型高效液相色谱仪,配2996型二极管检测器,,大黄素对照品(由中国药品生物制品检定所提供),乙腈(色谱纯),乙醚、甲醇、磷酸、硫酸、无水硫酸钠均为分析纯,二次蒸馏水。2 色谱条件 色谱柱:Topsil C18柱; 流动相:A泵乙腈,B泵0.1%磷酸水溶液(A:B=60:40); 流速:1.0mL/min; 柱温:室温; 检测波长:288nm; 进样量:20μL。3 标准 称取10mg对照品于50mL容量瓶中,用甲醇稀释溶解定容,再分取一定体积于50mL容量瓶中,用甲醇稀释溶解定容,分别配制成含大黄素4、20、40、80、100μg/mL的标准使用液,上机测定。4 样品预处理4.1 液体样品 量取一定体积样品,加入2.5mol·L-1硫酸20mL,置沸水浴上加热回流30分钟,放冷,用乙醚提取5次,每次5mL,合并乙醚液,用水洗至中性,过无水硫酸钠后旋转蒸发挥至近干,再用氮气吹干,残渣加甲醇适量溶解,移至50mL容量瓶中,加甲醇稀释于刻度。经0.45μm滤膜过滤,作为上机待测液。4.2 固体样品称取1g置索氏提取器中,加甲醇50mL,置于80℃水浴上加热回流至无色,提取液置水浴上蒸干,蒸干的残渣用2.5mol·L-1硫酸20ml溶解,按2.4.1处理。测试结果见下图,为了方便大家看拖尾因子和理论塔板数,特意把数字放大,供参考:图1 标准色谱图http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2011/05/201105171335_294598_1608710_3.jpghttp://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2011/05/201105171335_294599_1608710_3.jpg图2 样品色谱图http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2011/05/201105171336_294600_1608710_3.jpghttp://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2011/05/201105171336_294601_1608710_3.jpg
水质 硼的测定 姜黄素的方法中曲线绘制好像没有空白,但是标准里面有空白试验的方法,那做曲线和样品的时候要做空白吗
[align=center][font=DengXian]维生素[/font]B2[/align][font=DengXian]维生素[/font]B2[font=DengXian]又称核黄素,是具有糖醇结构的异咯嗪衍生物[/font][font=DengXian]。在自然状态下它常常是磷酸化的,而且起着辅酶的作用。它的一种形式为黄素单核苷酸[/font](FMN)[font=DengXian],另一种形式为黄素腺苷酰二核苷酸[/font](FAD)[font=DengXian],它们是某些酶如细胞色素[/font]C[font=DengXian]还原酶、黄素蛋白等的组成部分,后者起着电子载体的作用,在葡萄糖、脂肪酸、氨基酸和嘌呤的氧化中起作用。[/font][font=DengXian][font=DengXian]它是由核酸和[/font]6[font=DengXian],[/font]7[font=DengXian]—二甲基异咯嗪组成,呈黄色且分子中有核酸故又称核黄素。[/font][font=DengXian]食品中核黄素与硫酸和蛋白质结合形成复合物。动物性食品富含核黄素,尤其是肝、肾和心脏;奶类和蛋类中含量较丰富;豆类和绿色蔬菜中也有一定量的核黄素。[/font][font=DengXian]核黄素参与机体内许多氧化还原反应,一旦缺乏将影响机体呼吸和代谢,出现溢出性皮脂炎、口角炎和角膜炎等病症。[/font][/font][font=DengXian][/font]
参照标准 水质 硼的测定 姜黄素分光光光度法(HJ/T 49-1999)有用过这个标准的老师吗?在做硼的时候,水浴不显色。试剂都是按照标准上面配的,姜黄素溶解不完全,过滤了用。
http://simg.instrument.com.cn/bbs/images/brow/emyc1009.gifhttp://simg.instrument.com.cn/bbs/images/brow/emyc1009.gifhttp://simg.instrument.com.cn/bbs/images/brow/emyc1009.gif婴幼儿食品和乳品中维生素B2的测定;http://simg.instrument.com.cn/bbs/images/brow/emyc1003.gifhttp://simg.instrument.com.cn/bbs/images/brow/emyc1003.gifhttp://simg.instrument.com.cn/bbs/images/brow/emyc1003.gif维生素B2(核黄素)http://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2011/12/201112042054_335483_2206832_3.jpg中文名称:维生素B2,核黄素英文名称:Vitamin B2,riboflavin其它名称:乳黄素;卵黄素;7,8-二甲基-10-(1'-D-核糖基)-异咯嗪定义: 在自然界分布广泛的一种维生素。是哺乳动物必需的营养物,其辅酶形式是黄素单核苷酸和黄素腺嘌呤二核苷酸。维生素B2是机体中许多酶系统的重要辅基的组成成分,参与物质和能量代谢。物理性质 熔点: 290℃ 溶解性: 微溶于水,在乙醇中的溶解性比在水中差。不溶于乙醚和三氯甲烷,可溶于氯化钠溶液,易溶于稀的氢氧化钠溶液。 比旋光度: -135°(c=5, 0.05 M NaOH)化学性质 CAS号: 83-88-5 分子式: C17H20N4O6 分子量: 376.37核黄素水溶性较低,但在碱性溶液中容易溶解,在强酸溶液中稳定,光照及紫外照射引起不可逆的分解。核黄素在机体中有递氢的作用,并是机体中一些重要的氧化还原酶的辅酶。肝脏是最丰富的来源之一,肾脏、心脏亦含有相当可观的含量。样品前处理1、称取5g~10g(精确至0.01g)试样于150mL三角瓶中,加入60mL 0.1mol/L盐酸,充分摇匀;2、用棉塞和牛皮纸封口,放入高压灭菌锅内,在121℃下保持30min,待冷却至40℃下取出,轻摇数次;3、用2.0mol/L乙酸钠溶液调PH值至4.0左右,加入2.0ml混合酶溶液,摇匀后,置于37℃培养箱中过夜;